Topic 4.1 Linear Momentum
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
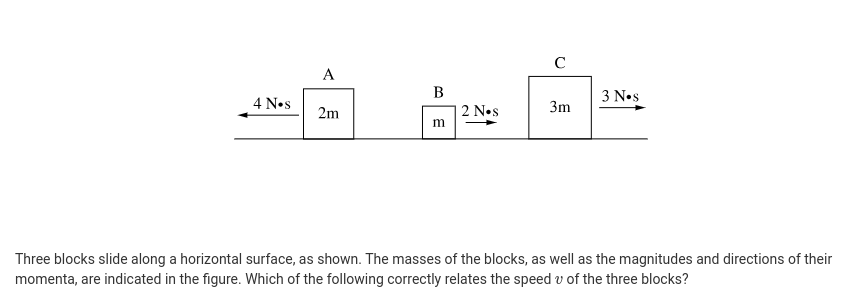

A cart carrying sand has a hole in the bottom that allows sand to spill out. At time t1, the cart has speed 1.5 m/s. A short time later at time t2, the cart still has speed 1.5m/s but 0.02kg of sand has fallen out of the hole in the cart between t1 and t2. What is the magnitude of the change in momentum of the cart and its contents between t1 and t2?
0
0.02N·s
0.03N·s
It cannot be determined without knowing the initial mass of the cart and sand.
Answer: 0.03 kgm/s


B

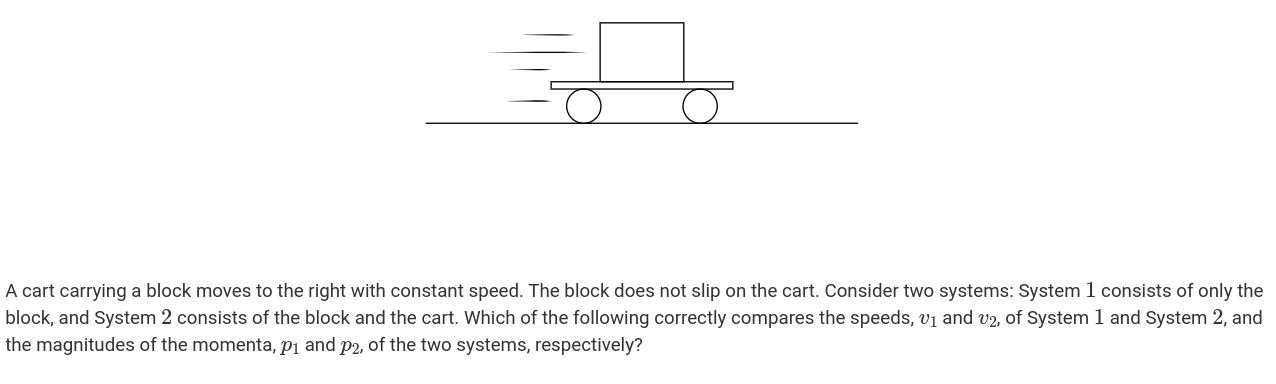
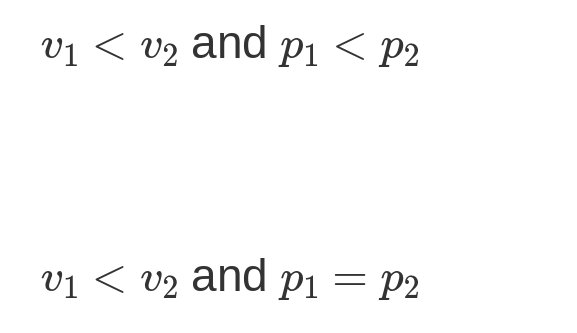
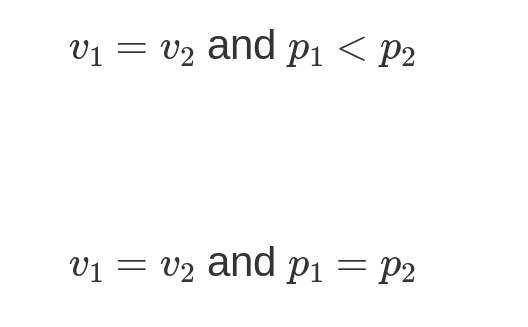
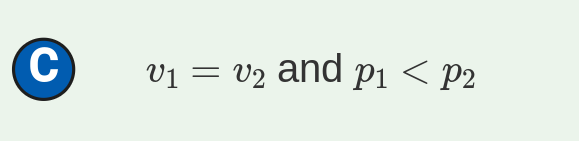
Correct. Because the block is moving with the cart, they have the same speed. System 1 has a smaller momentum because momentum is also proportional to mass, and the mass of System 1 is less than that of System 2.
In a controlled experiment, a small explosive device is placed inside of a cart that is designed to break apart easily. The device is activated and the cart splits evenly into two pieces of equal mass that move away from each other at equal constant speeds. Which of the following correctly indicates a model that could be used to describe the interactions involved in this scenario?
The device is external to the system and exerts a constant force on the two pieces as they move away from each other.
The pieces of the cart are exerting constant repulsive forces on each other as they move away.
The device is internal to the system and exerts a very brief force of equal magnitude but opposite direction on each piece of the cart.
The device is internal to the system and therefore does not exert any forces on the pieces of the cart.
3: An explosion is modeled as an internal force that moves parts of a system apart. The force on each part is equal and opposite because of Newton's third law.
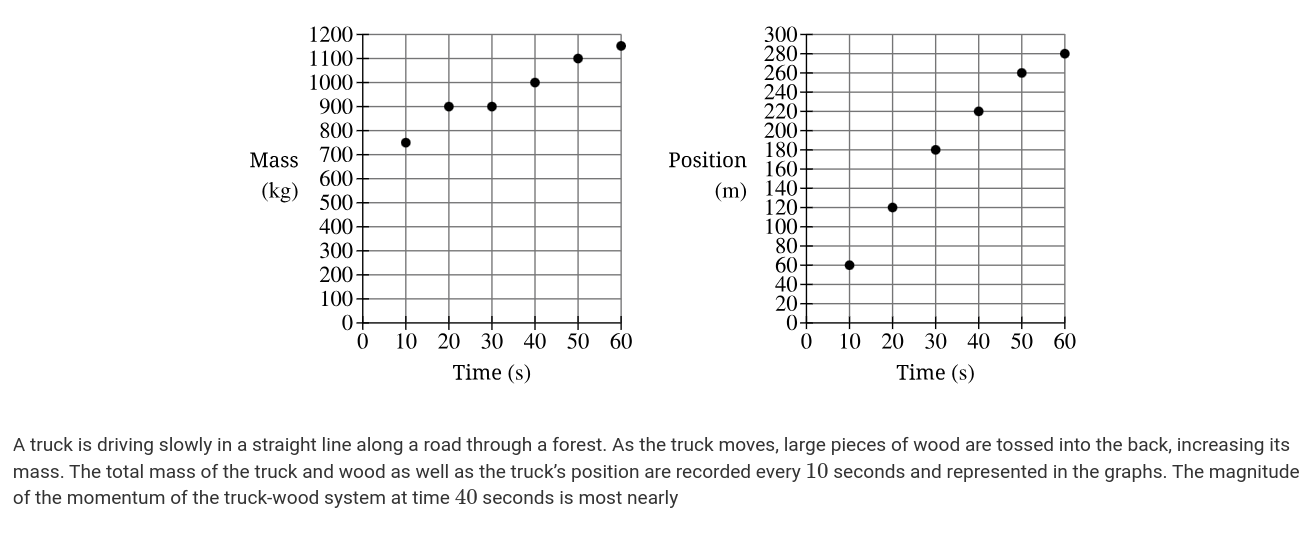
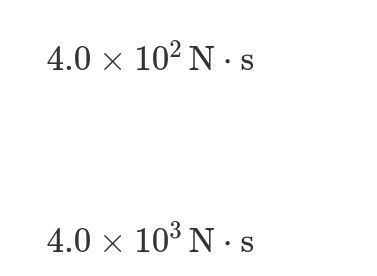
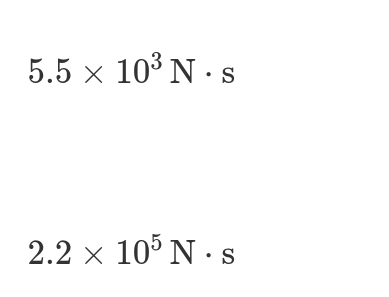
2: Correct. At 40 seconds, the slope of the position-time graph is approximately 4m/s. To calculate momentum, this velocity is multiplied by the mass at 40 seconds p=(1000kg)(4m/s)=4000N·s.
At time t1, a rocket in outer space has mass m, speed v, and the magnitude of the rocket’s momentum is p1. The rocket’s engines eject fuel, and the mass of the rocket decreases. At a later time t2, the rocket has mass m/2, speed 2v, and the magnitude of the rocket’s momentum is p2. Which of the following correctly relates p2 and p1?
p2=p1/2
p2=p1
p2=2p1
p2 = 4p1
B: The magnitude of the momentum is the product of the mass and the speed. At both times, this product is equal to mv.

B: Momentum is a vector quantity that is in the same direction as velocity. The velocity of an object in uniform circular motion has a constant magnitude but its direction is tangential to the circular path and therefore is changing.
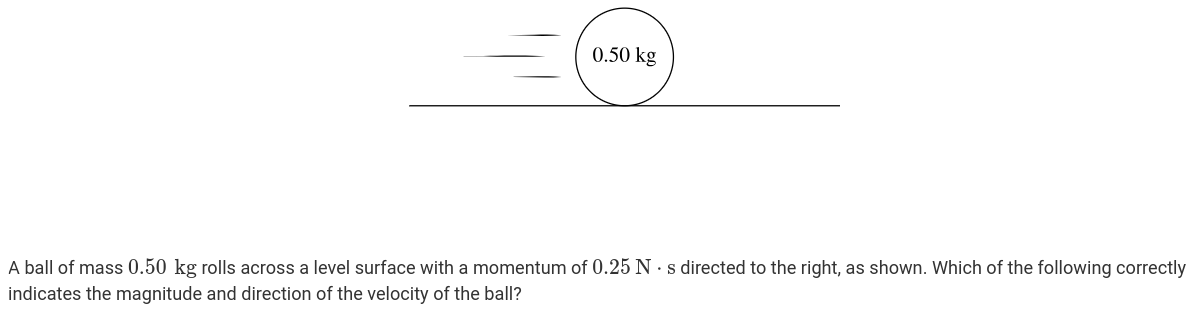
0.25m/s to the right
0.25m/s to the left
0.50m/s to the right
0.50m/s to the left
3: 0.5 m/s to the right
