diagnostic tests
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
what is a diagnostic test
A diagnostic test is to test for the presence of a disease, condition or substance.
Patient presents with symptoms.
Diagnostic testing provides a collection of information which will clarify a patient’s clinical condition and help to determine prognosis.
This information can include: Patient characteristics, signs and symptoms, History, Physical examination, Tests using laboratory or other technical facilities.
The clinician does the test, receives the results and finds out whether the patient has the condition or not.
No diagnostic test is perfect. They might show a disease is not present, when infact it is.
whats the difference between a diagnostic and a screening test?

what is screening

what are the advantages of screening
Detects unrecognized disease early, where the prognosis can be improved
Detects those individuals at high risk of developing a certain disease, where the individual or clinician can take measures to delay (or even prevent) the development of the disease by reducing the risk
Identifies people with infectious disease, where an intervention can treat the infection and prevent transmission of the disease to others;
•A false sense of security if cases are missed (i.e., a false-negative screening result), which may delay the final diagnosis.
•Those tested negative may feel they have avoided the disease and therefore continue with their risk behaviour; for example, an individual who eats more than his recommended daily allowance of saturated fat may continue to do so if his cholesterol is within the normal range when tested by his general practitioner. Looking at the bigger picture, this may undermine primary prevention programmes;
•For cases that are true positives, treatment of early disease may be associated with potential side effects, even though the disease may not have actually progressed.
•Involves using medical resources and substantial amounts of money that could be used elsewhere, especially as the majority of people screened do not need treatment.
Stress and anxiety caused by false alarms (i.e., a false-positive screening result). The stress may be related to unnecessary investigations, especially if it involves an invasive procedure
whats the difference between screening and diagnostic
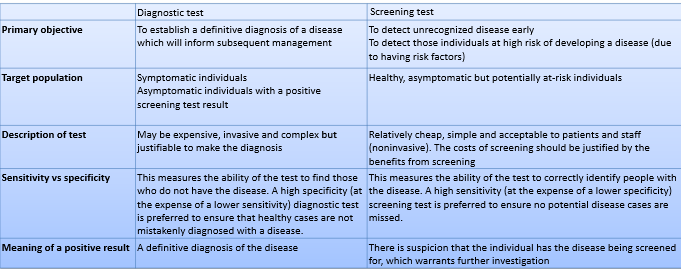
how are diagnostic test results presented

whats the likelihood ratio

how do you evaluate diagnostic technologies
Will a new technology result in improvements in the prognosis or physical health of a patient?
A hierarchy can be used to assess the effectiveness of technologies.
Technical performance Is the image quality sufficient to make diagnostic or therapeutic decisions?
Diagnostic Performance Is concerned with whether imaging can correctly or incorrectly assess the presence or absence of disease. Confirmed with a ‘gold standard’ test.
The following three levels need to be assessed using observational research designs
•Diagnostic impact Can the imaging technology replace other investigations?
•Therapeutic impact Is concerned with whether imaging can contribute to planning and delivery of therapy. A study could compare pre-imaging therapy plans with post imaging therapy plans.
•Patient outcome Does imaging improve patient outcomes?
Societal - Moves beyond the clinical effects of a technology to determine whether the cost of the technology is acceptable to society. Resources are limited and policy makers need to make decisions about how they are allocated.
what are type 1 and 2 errors

what are the measures used for diagnostic performance

what is sensitivity and specificity

mnemonics

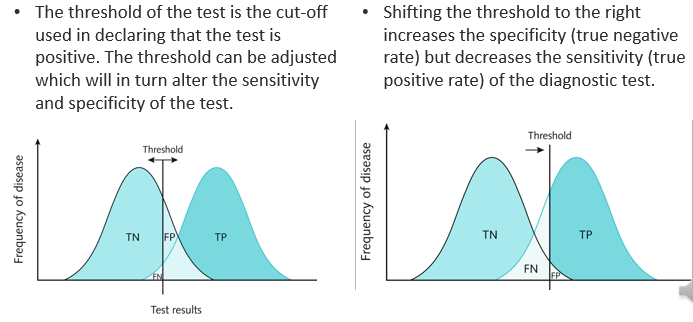
trade off sensitivity and specificity
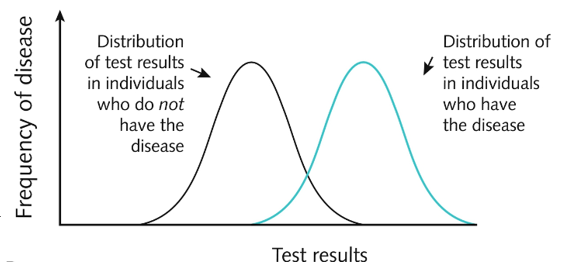
whats the threshold
what are positive and negative predictive values

whats the likelihood ratio

example: prostate cancer screening test
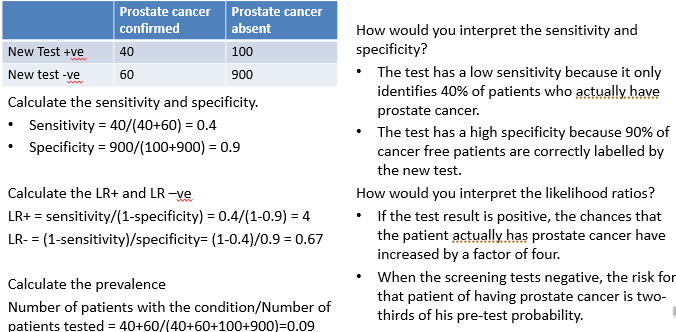
when is a high sensitivity or high specificity test preferred

what is interobserver reliiability

whats the kappa statistic

summary
