PHS 3105 - Ch 15
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 15 - Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Sensory pathways
A series of neurons that relay sensory information from sensory receptors to the CNS
Sensory receptors
Specialized cells or neuron processes that monitor specific conditions inside or outside the body
Stimulated: generates action potential that are sent along sensory pathway
Afferent division (of NS)
Somatic and visceral sensory pathways
Somatic sensory: Information to the cerebral cortex
Visceral sensory: Information to the brainstem and diencephalon
Efferent division (of the NS)
Somatic motor pathways (control peripheral effectors)
Motor commands: From motor in brain along somatic motor pathway
Modified by higher-order function in brain
Effectors are skeletal muscles
What is… Sensation
Sesnroy information arriving in the CNS
What is… Perception
Conscious awareness of a sensation
What is… Transduction
Conversion of an arriving stimulus into an action potential by a sensory receptor
What are… General senses
Temperature
Pain
Touch
Pressure
Vibration
Proprioception (body position)
What are… Special senses
Olfaction (smell)
Gustation (taste)
Vision (sight)
Equilibrium (balnace)
Hearing
Special sensory receptors
Provide sensations of the special senses.
Location: Sense organs such as the eye or ear
Detection of stimuli
Receptor specifitiy
Receptive field
Receptor specificity
Each receptor has a characteristic sensitivity
Receptive field
The area monitored by a single receptor cell
The larger the field, the more difficult it is to localize a stimulus
Ex/ Backside v. tip of finger
Receptor potential (Detection of stimuli)
The stimulus changes the receptor membran potential
Depolarizing: Generator potential, brings membrane closer to threshold
Hyperholarizing: Brings membrane further away from threshold
Size of receptor potential depends on strength of stimulus
Tonic receptors (Sensory receptors)
Always active
Increase or decrease in stimulation causes increase or decrease in frequency of action potentials
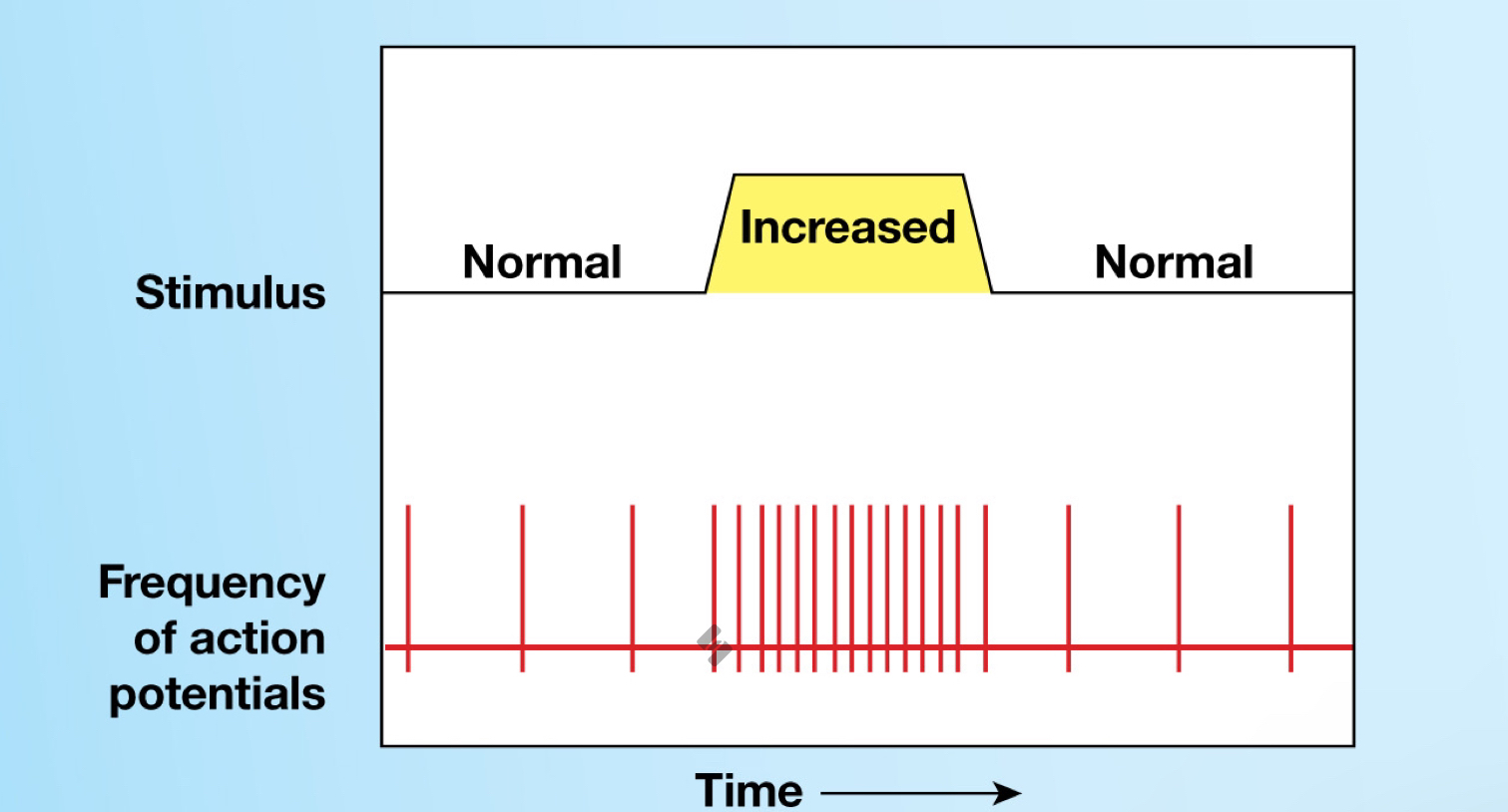
Phasic receptors (Sensory receptors)
Normally inactive, only get activated by stimulus
Provide information on intensity and rate of change of stimulus
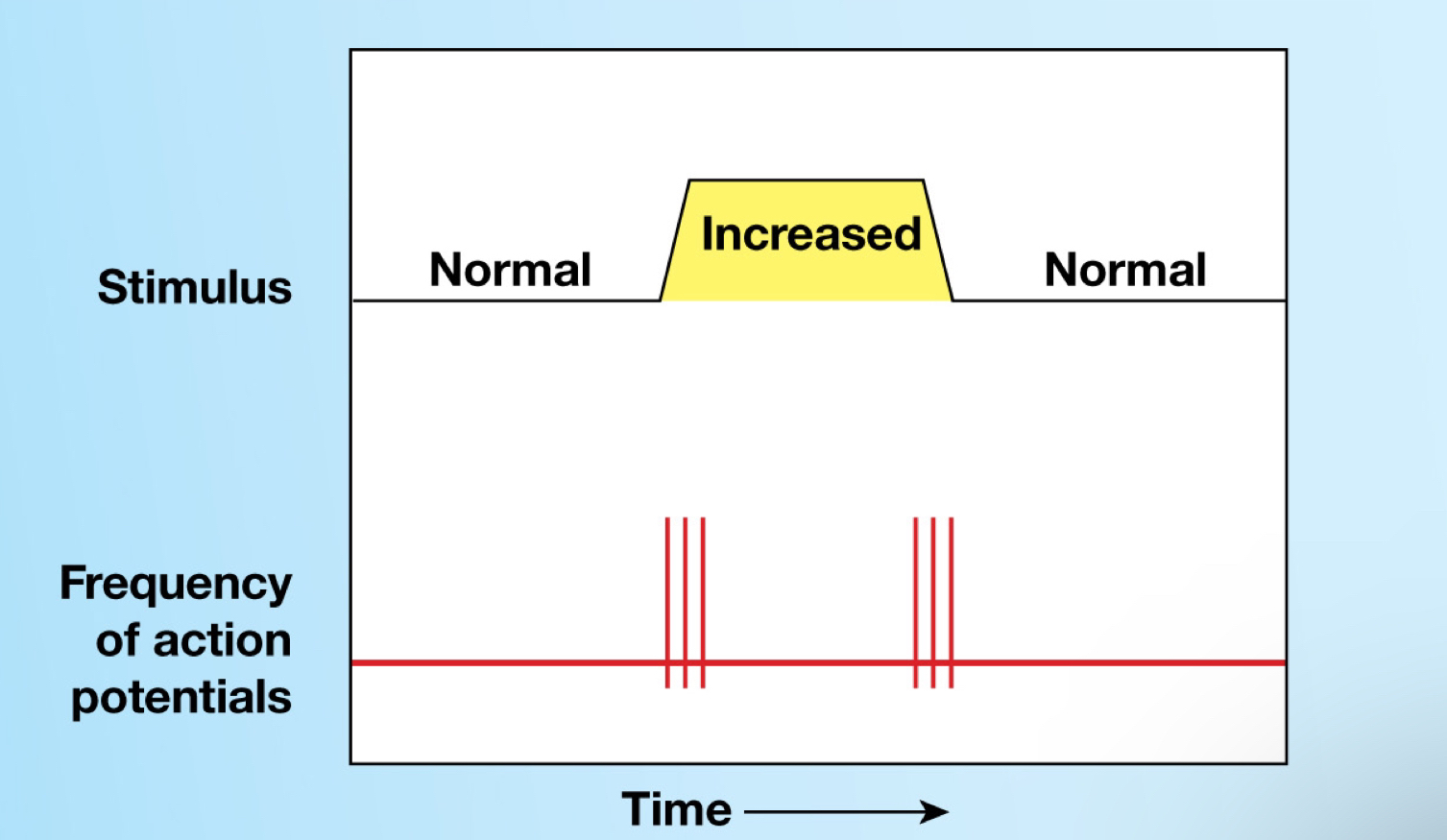
What is… Adaptation
(+ 2 types of adaptation)
Reduction of receptor sensitivity in the presence of a constant stimulus.
NS quickly adapts to painless, constant stimuli
Most incoming sensory information is processed in centers along the spinal cord, brain stem, or thalamus before it reaches the cerebral cortex
Conscious and subconscious
Ex/ Tuning out background noise/listening carefully
Fast-adapting receptors
Slow-adapting receptors
Fast-adapting receptors (Adaptation)
Respond strongly (intense) at first but then activity decreases (phasic receptors)
Ex/ Temperature
Needs strong stimulus, responds and decreases very quick
Slow-adapting receptors (Adaptation)
Show little peripheral adaptation (tonic receptors)
Ex/ Pain
Identify the types of sensory receptors
Exteroreceptors
Proprioreceptors
Interoreceptors
Nociceptors
Termoreceptors
Mecanoreceptors
Chemoreceptors
Exoreceptors
Provide information about the external environment
Proprioceptors (Mechanoreceptors)
Provide information about the position of skeletal muscles and joints
Only a somatic sensation, NONE in visceral organs
Types of proprioceptors:
Muscle spindles: Monitor skeletal muscle length and trigger stretch reflexes
Golgi tendon organs: At the junction between skeletal muscle and its tendon and monitor tension during muscle contraction
Receptors in joint capsules: Free nerve endings that detect pressure, tension, and movement at the joint
Ex/ What butt-cheek you’re sitting on has more weight put on it.😁
Interoreceptors
Provide information about visceral organs and functions
Ex/ Knowing when you need pee
Nociceptors
Detect pain
Free nerve endings w/ large receptive fields
Tonic receptors
Location: Superficial skin, joint capsules, periosteum of bones, around walls of blood vessels
Ex/ Temperature extremes (burning/freezing), mechanical damage, or dissolved chemicals (released by injured cells)
Endorphins and enkephalins inhibit pain pathways in the CNS
Thermoreceptors
Detect temperature
Phasic receptor
Location: Dermis, skeletal muscles, liver, and hypothalamus
Mechanoreceptors ★
(+ 3 classes)
Detect physical stimuli that distortion their plasma membranes
Contain mechanically-gated ion channels
Classes
Tactile receptors
Baroreceptors
Proprioceptors
Ex/ Touch, stretching, compression, twisting
Chemoreceptors
Detect chemical concentration. Respond to water-soluble and lipid-soluble substances that are dissolved in body fluids
Fast peripheral adaptation
Monitor pH, carbon dioxide, and oxygen levels in arterial blood inside body
Carotid bodies: Near the origin of the internal carotid arteries (CN, IX)
Aortic bodies: Between the major branches of the aortic arch (CN, X)
Medulla oblongata: Sensitive to changes in pH, O2 and CO2 in CSF
Ex/ Oxygen in body
Tactile receptors (Mechanoreceptors) ★
(+ 6 types of tactile receptors in skin)
Detect touch (shape or texture), pressure (degree of mechanical distortion), and vibration (pulsing pressure)
Fine touch and pressure receptors provide detailed information about: source, location, shape, size, and direction
Extremely sensitive
Narrow receptive fields
Crude touch and pressure receptors provide poor localization, little information about stimulus
Large receptive fields
Ex/ Backside
Types of tactile receptors
Free nerve endings
Root hair plexus
Tactile discs
Bulbous corpuscles
Lamellar corpuscles
Tactile corpuscles
Baroreceptors (Mechanoreceptors)
Detect pressure changes in blood vessels and in portions of the digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts
Free nerve endings branch with elastic tissue in wall of distensible organ
Ex/ Blood vessel
Respond immediately to change in pressure, adapt rapidly
Baroreceptors in the body:
Carotid sinuses and aortic arch
Lung
Digestive tract
Colon
Bladder wall
Types of pain (2)
Fast pain: Prickling pain
Carried by myelinated Type A fibers
Ex/ Injection or deep cut
Slow pain: Burning and aching pain
Carried by unmyelinated Type C fibers
Become aware of pain only with a general idea of area affected
Ex/ Soreness
Sensory neurons (3)
First-order neuron
Delivers sensations from the periphery (receptors) to the CNS
Cell body located in a spinal or cranial nerve ganglion
Second-order neuron
Interneuron in the spinal cord or brainstem
Crosses to the opposite side of the CNS (decussation)
Third-order neuron
Neuron in the thalamus
Somatic sensory pathways
(+ 3 pathways)
Carry sensory information from the skin and muscles of the body wall, head, neck, and limbs to the CNS
Spinothalamic pathway
Posterior column pathway
Spinocerebellar pathway
Made up of symmetrical pairs of spinal tracts. All axons in tract share common origin and destination
☆: Like different highways. Right goes to left, left goes to right.
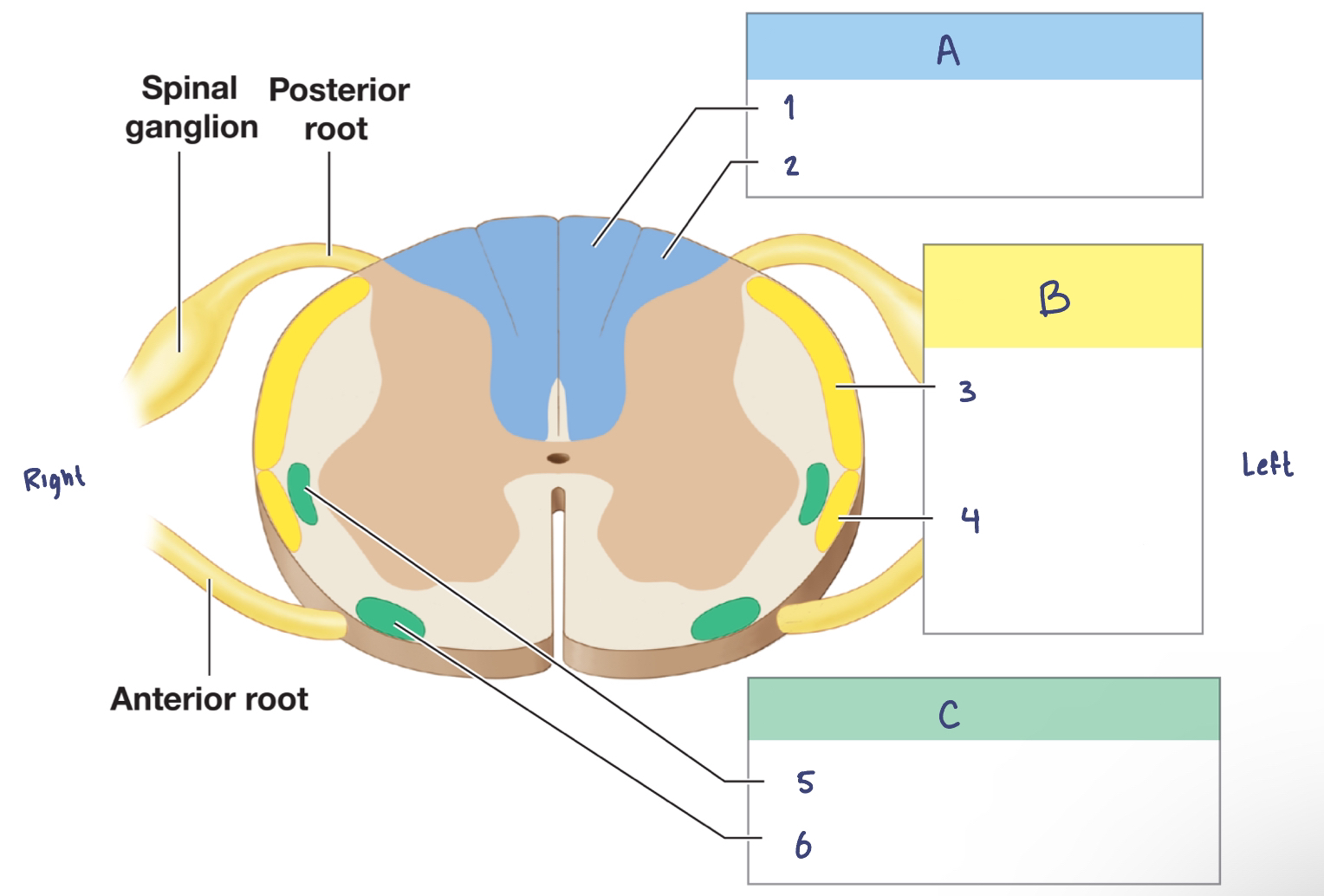
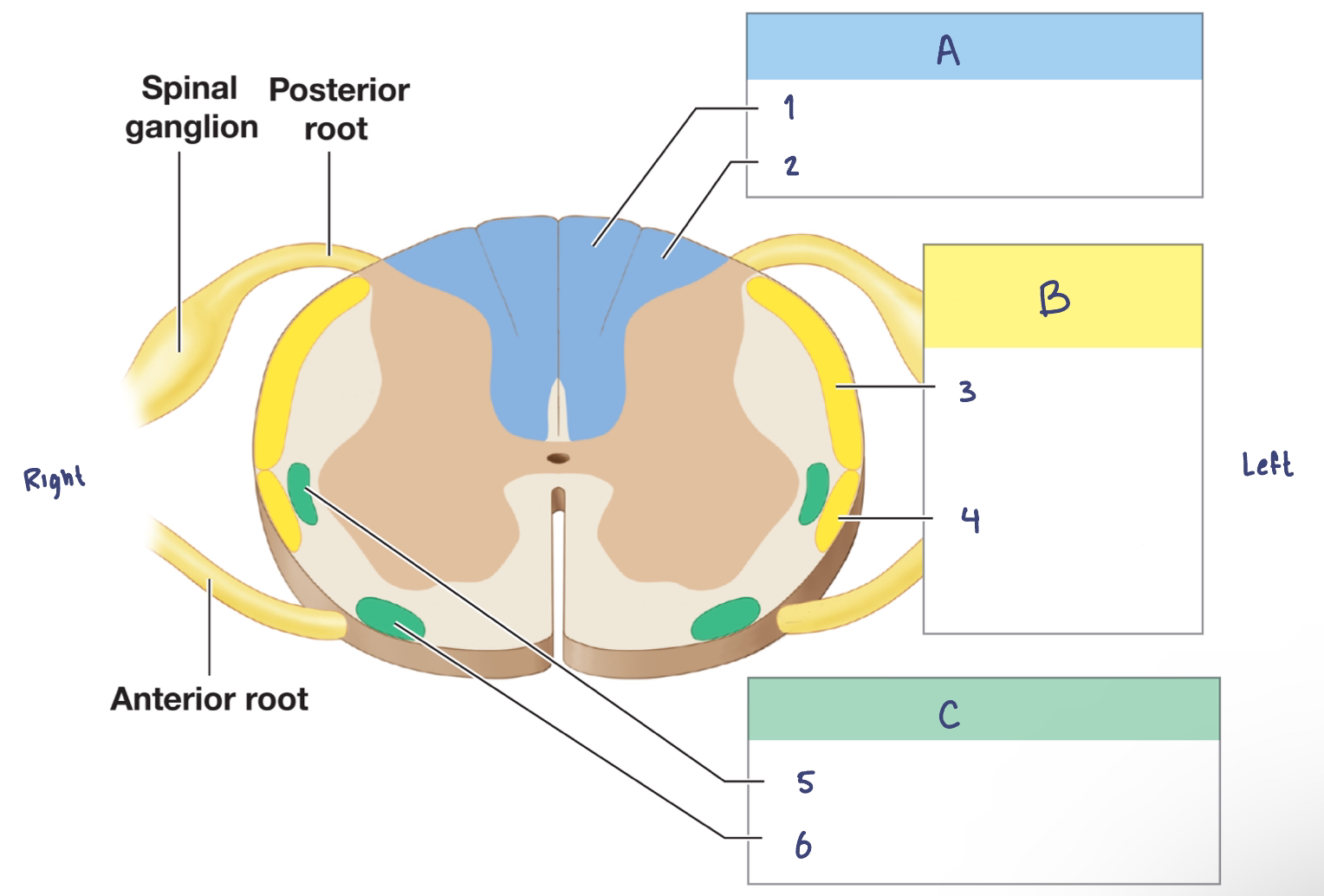
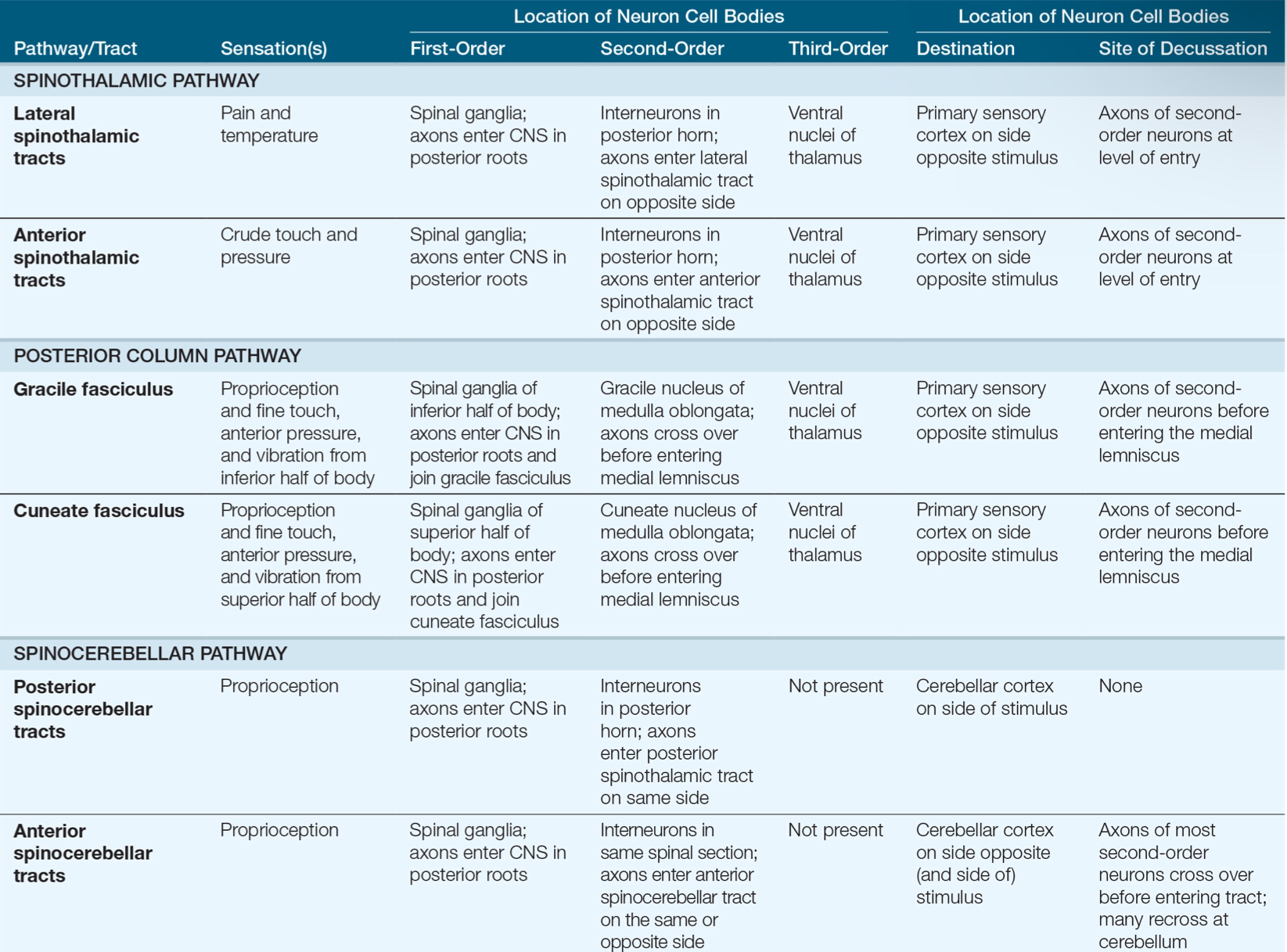
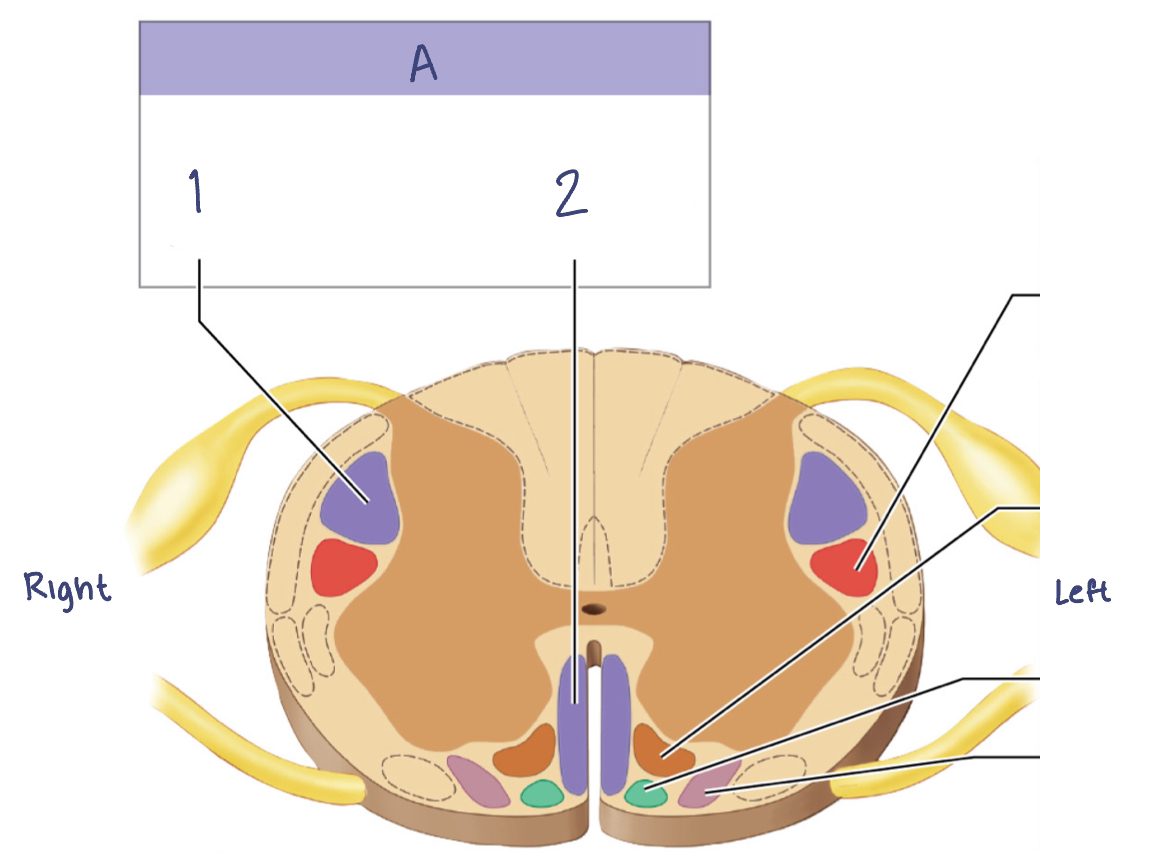
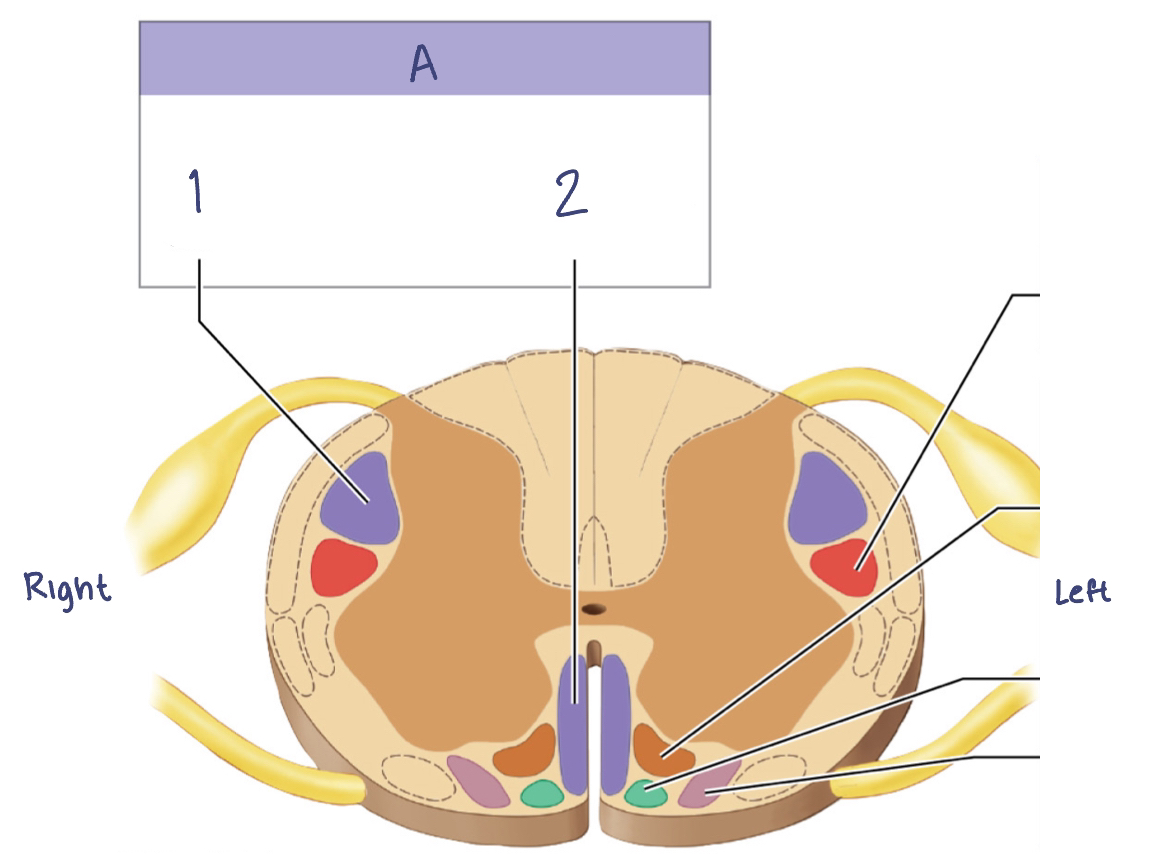
Sensory Pathways and Ascending Tracts in the Spinal Cord
A. —
—
—
B. —
—
—
C. —
—
—
A. Posterior Column Pathway
Gracile fasciculus
Cuneate fasciculus
B. Spinocerebellar Pathway
Posterior spinocerebellar tract
Anterior spinocerebllar tract
C. Spinothalamic Pathway
Lateral spinothalamic tract
Anterior spinothalamic tract
Spinothalamic pathway (Sensory pathway)
Carries sensations of crude touch, pressure, pain, and temperature
Ability to detect location of stimulus depends on the thalamus sending information to appropriate area of somatosensory cortex
Painful sensations that are not produced where they are not perceived to originate, may be felt
Ex/ Phantom limb syndrome
Referred pain
Tracts:
Anterior spinothalamic tract: Crude touch and pressure
Lateral spinothalamic tract: Pain and temperature
Ex/ Post-menopause hot flashes
☆: #-o.n. = #-order neuron
3-order neurons in the spinothalamic pathway
First-order neurons
Enter spinal cord and synapse with 2nd-o.n. with posterior horns
Second-order neurons
Cross to opposite side of the spinal cord and then ascend to synapse with 3rd-o.n.
Third-order neurons
In the ventral nuclei of the thalamus
Sort and process sensations and then carry information to neurons in primary somatosensory cortex
Referred pain (Spinothalamic pathway)
Visceral pain can manifest as body surface pain
Ex/ Heart attack frequently felt as pain in the left arm
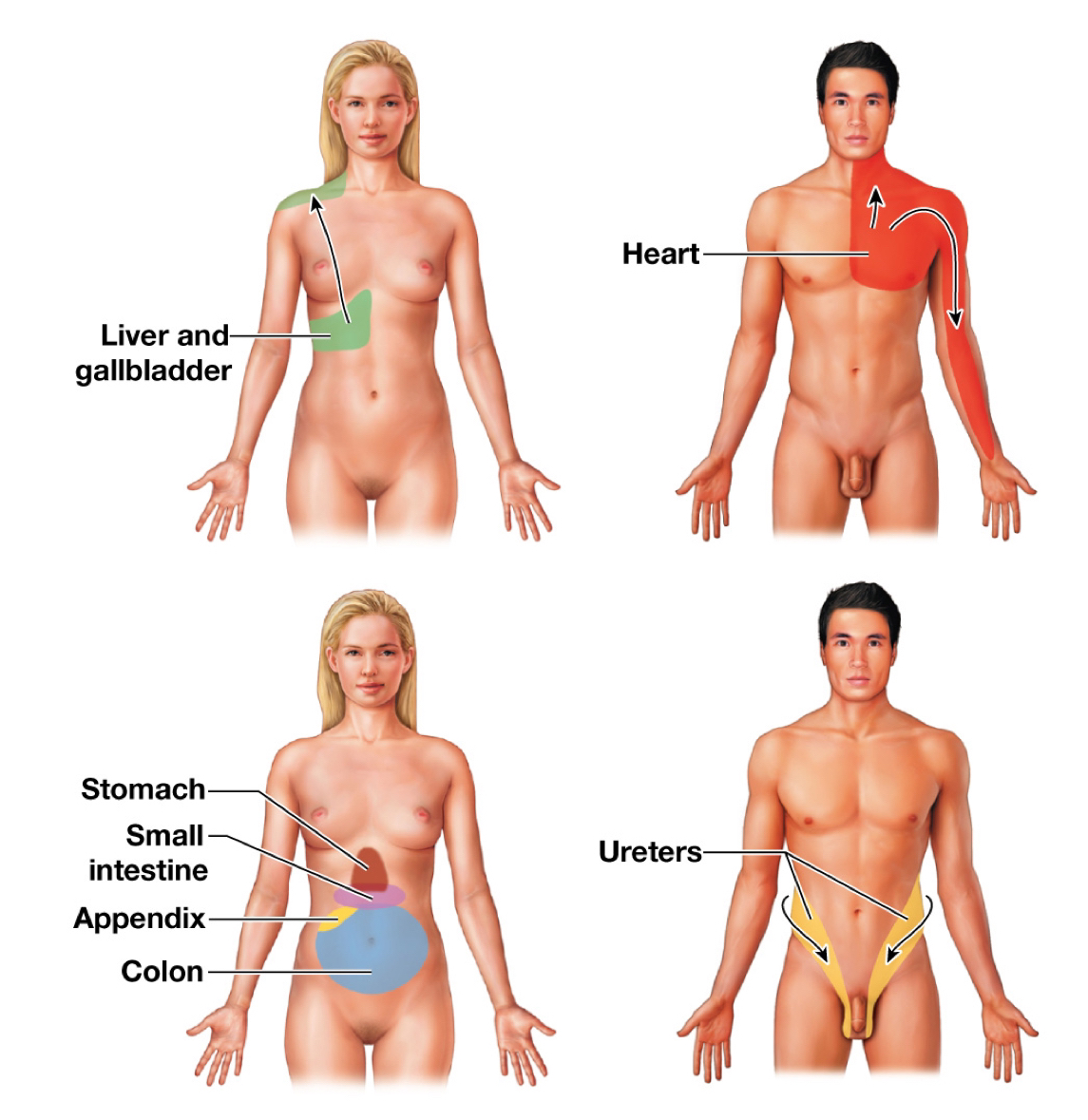
Anterior Spinothalamic Tract
☆: INFORMATIONAL DIAGRAM FLASHCARD
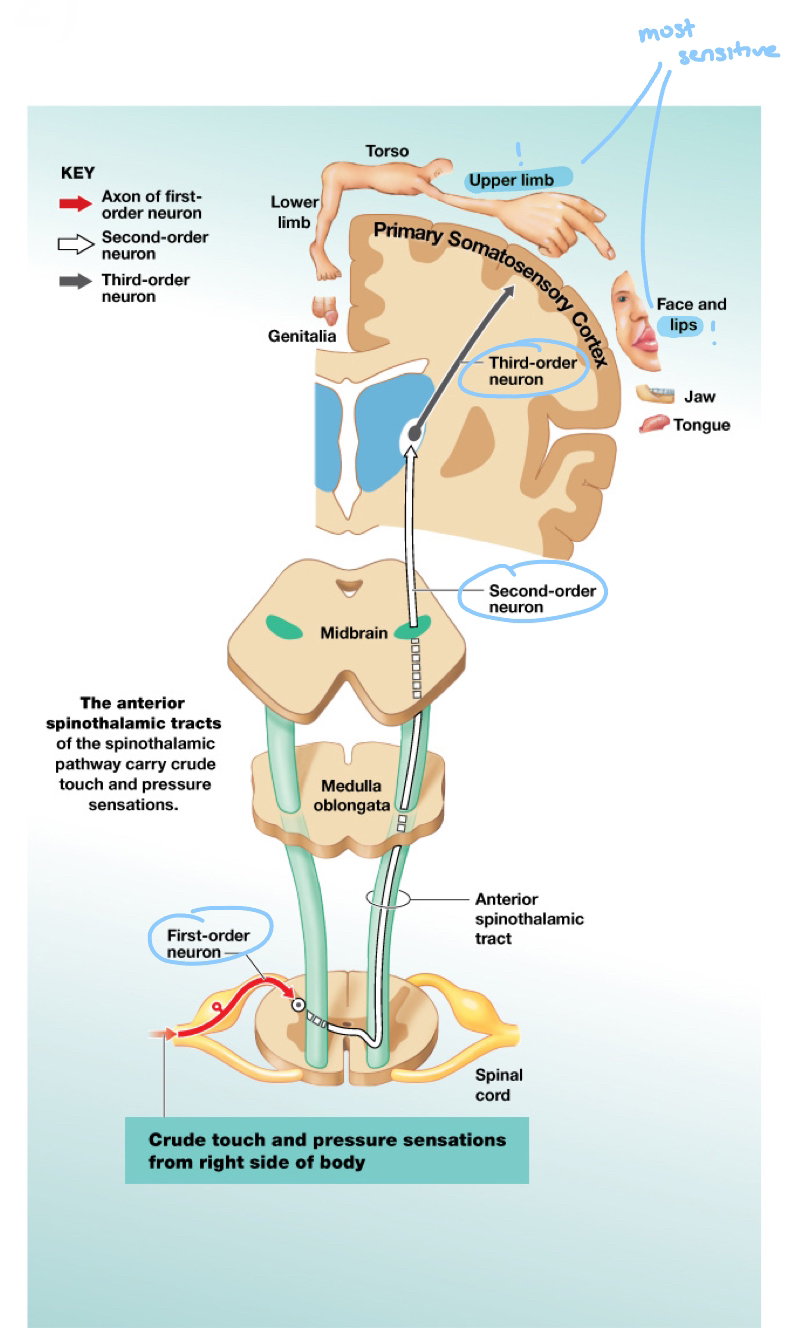
Lateral Spinothalamic Tract
☆: INFORMATIONAL DIAGRAM FLASHCARD
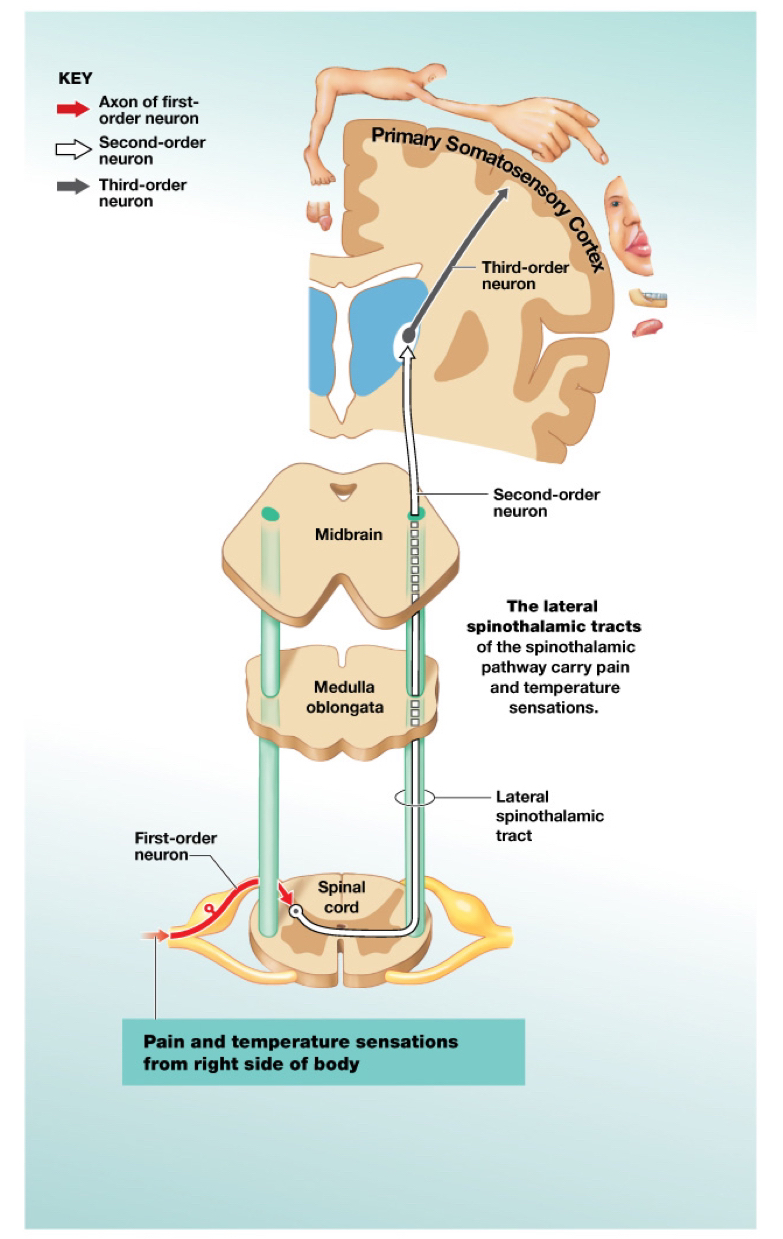
Posterior column pathway (Sensory pathways)
Carries sensations of fine touch, vibration, pressure, and proprioception (body positioning)
Tract:
Left and right gracile fasciculus: Axons that carry sensation from the inferior half of the body and synapse in gracile nucleus of the medulla oblongata
Left and right cuneate fasciculus: Axons that carry sensation from the superior half of the body and synapse in cuneate nucleus of the medulla oblongata
Medial lemniscus: Axons of 2nd-o.n. after they decussate
☆: Drugs and alcohol numb this pathway
3-order neurons in the posterior column pathway
First-order neuron
Reach the CNS and ascend grouped according to the region they innervate—synapse with 2nd-o.n. in the medulla oblongata
Second-order neuron
Decussate in the brain stem and ascend to the thalamus to synapse with 3rd-o.n.
Third-order neuron
In ventral nuclei of the thalamus
Sort and process sensations, then carry information to neurons in the primary somatosensory cortex
☆: #-o.n. = #-order neuron
Posterior Column Pathway
☆: INFORMATIONAL DIAGRAM FLASHCARD
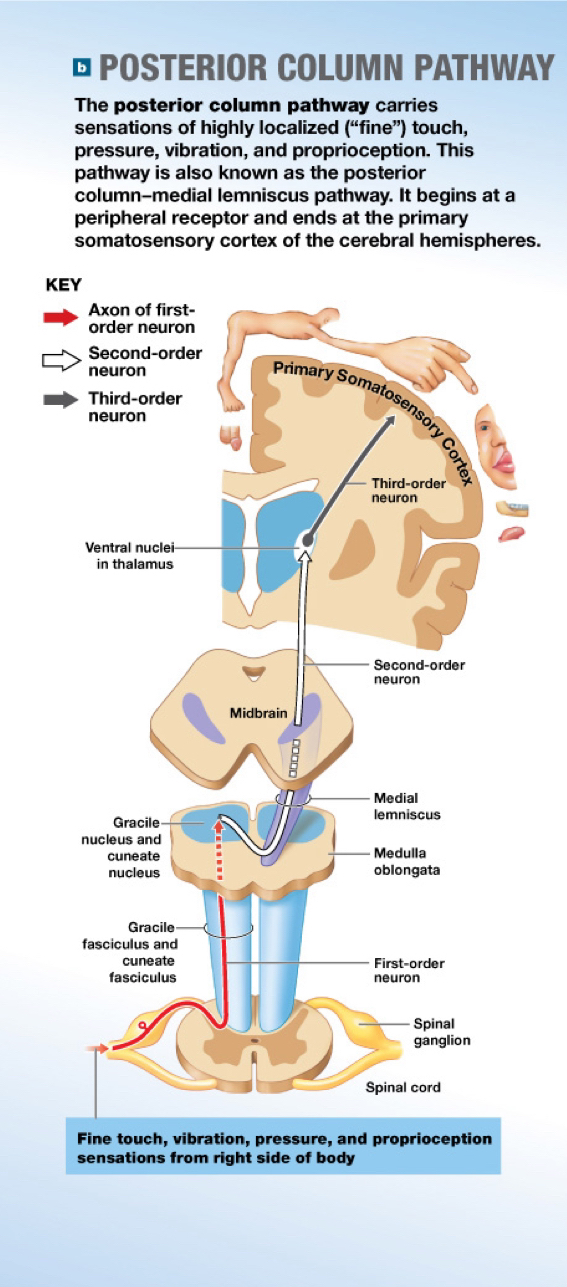
Sensory homunculus (Sensory pathway)
Functional map of the primary somatosensory cortex (cerebrum)
Corresponds with specific regions of the body
Area devoted to a particular body region is proportional to the density of sensory neurons in that region, not to region’s size
Ex/ Larger areas fro lips and tongue; smaller area for backside
Spinocerebellar pathway (Sensory pathway)★
Carries information about the position of muscles, tendons, and joints; coordination
Tracts:
Posterior spinocerebellar tracts: Travel through inferior cerebellar peduncle
Anterior spinocerebellar tracts: Travel via superior cerebellar peduncle
3-order neurons in the spinocerebellar pathway
First-order neurons
Reach the CNS and synapse with 2nd-o.n. in the posterior horn of the spinal cord
Second-order neurons
Ascend to the cerebellum and often decussate twice (in spinal cord and cerebellum)
Information arrives in cerebellum; coordination (Purkinje cells or the cerebellar cortex) and does not reach our awareness
☆: #-o.n. = #-order neuron
Spinocerebellar Pathway
☆: INFORMATIONAL DIAGRAM FLASHCARD
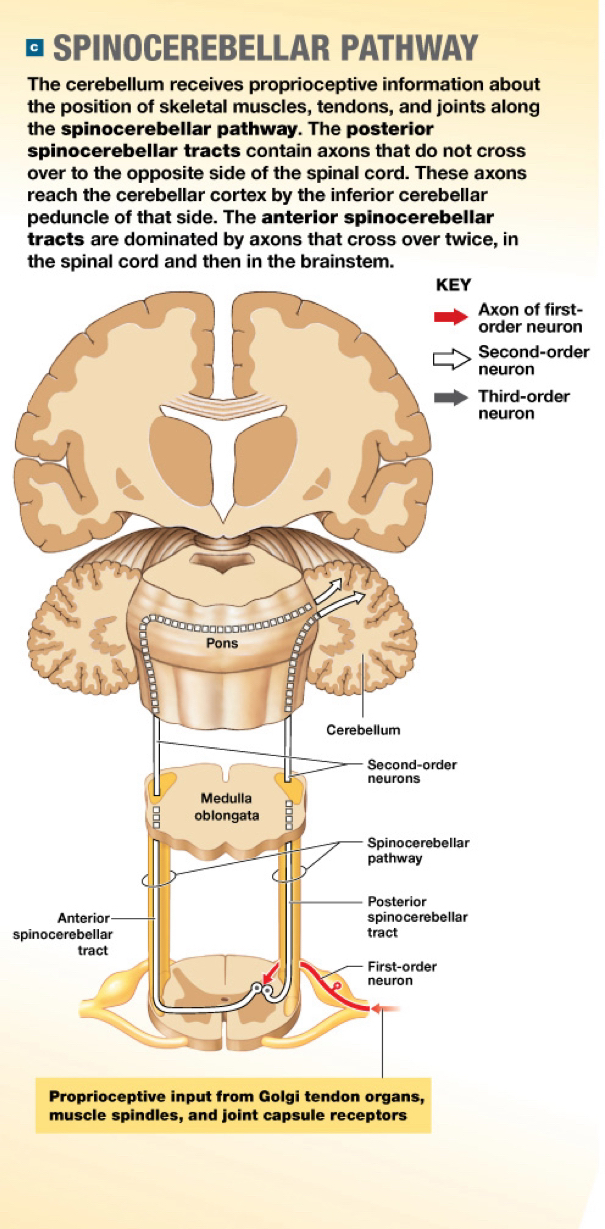
Visceral sensory pathways (Sensory pathway)★
Information collected by interoceptors monitoring the visceral tissues and organs within the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
★ Interoceptors include…
Nociceptors
Baroreceptors
Thermoreceptors
Tacticle receptors
Chemoreceptors
3-order neurons in the visceral sensory pathways
FIrst-order neurons
From the sensory portion of cranial nerves, V, VII, IX, and X and the posterior roots of spinal nerves T1-L2 and S2-S4
Secon-order interneurons
Ascend within the spinothalamic pathway and deliver the information to the solitary nuclei of the medulla oblongata
Solitary nuclei: Extensive connections with cardiovascular and respiratory centers and the reticular formation
Ascending (Sensory) Pathways
★: KNOW THIS CHART FOR THE EXAM
Somatic nervous system (SNS)
Controls skeletal muscles
Somatic motor pathways
Upper motor neuron
Lower motor neuron
Upper motor neuron (SNS)
Cell body lies in a CNS processing center
Primary motor cortex or premotor cortex and axon synapses on lower motor neuron
Lower motor neuron (SNS)
Cell body lies in a nucleus of the brain stem or spinal cord
Axon extends outside of the CNS to innervate a single motor unit in a skeletal muscle
Somatic motor pathways
—
—
—
Carry conscious and subconscious motor commands
The basal nuclei and the cerebellum monitor and adjust these pathways
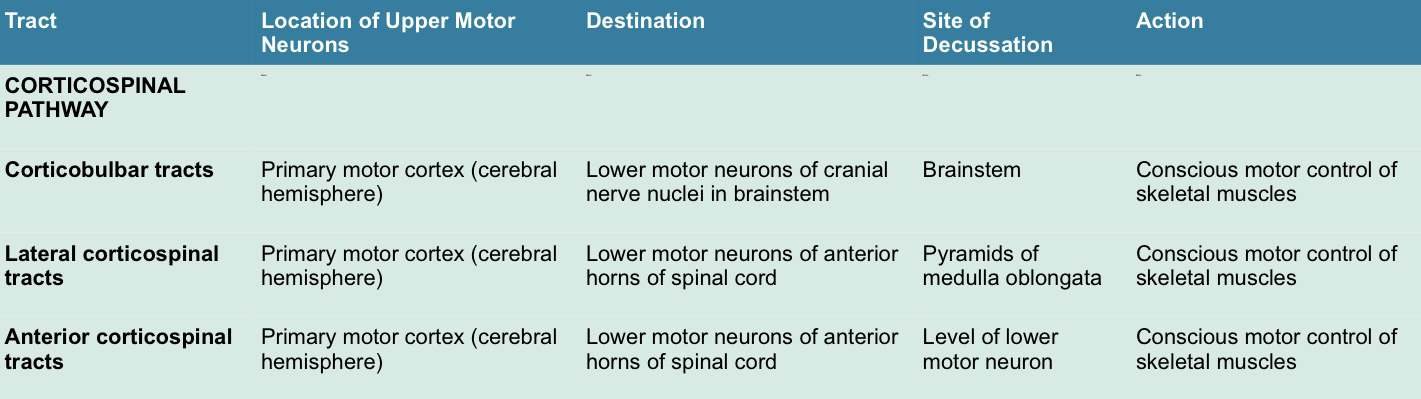
Corticospinal pathway
Medial pathway
Lateral pathway
Descending (Motor) Tracts in the Spinal Cord
A. —
—
—
A. Corticospinal pathway
Lateral corticospinal tract
Anterior corticospinal tract
Corticospinal pathway (Somatic motor pathways)
(Pyramidal system)
Upper motor neurons are the pyramidal cells of the primary motor cortex
Axons descend into brainstem and spinal cord and synapse on lower motor neurons that control skeletal muscles
Tracts:
Corticobulbar tracts
Lateral corticospinal tracts
Anterior corticospinal tracts
Corticobulbar tracts (Corticospinal pathway)
Axons of this tract synapse with lower motor neurons in the motor nuclei and cranial nervs III→VII, IX and XII
Provide conscious control of movement of the eyes, jaw, face, and some muscles of neck and pharynx
Innervate the motor centers of the medial and lateral pathways
Corticospinal Pathway
Sensory: Ascending
Premotor: From brain; down and out
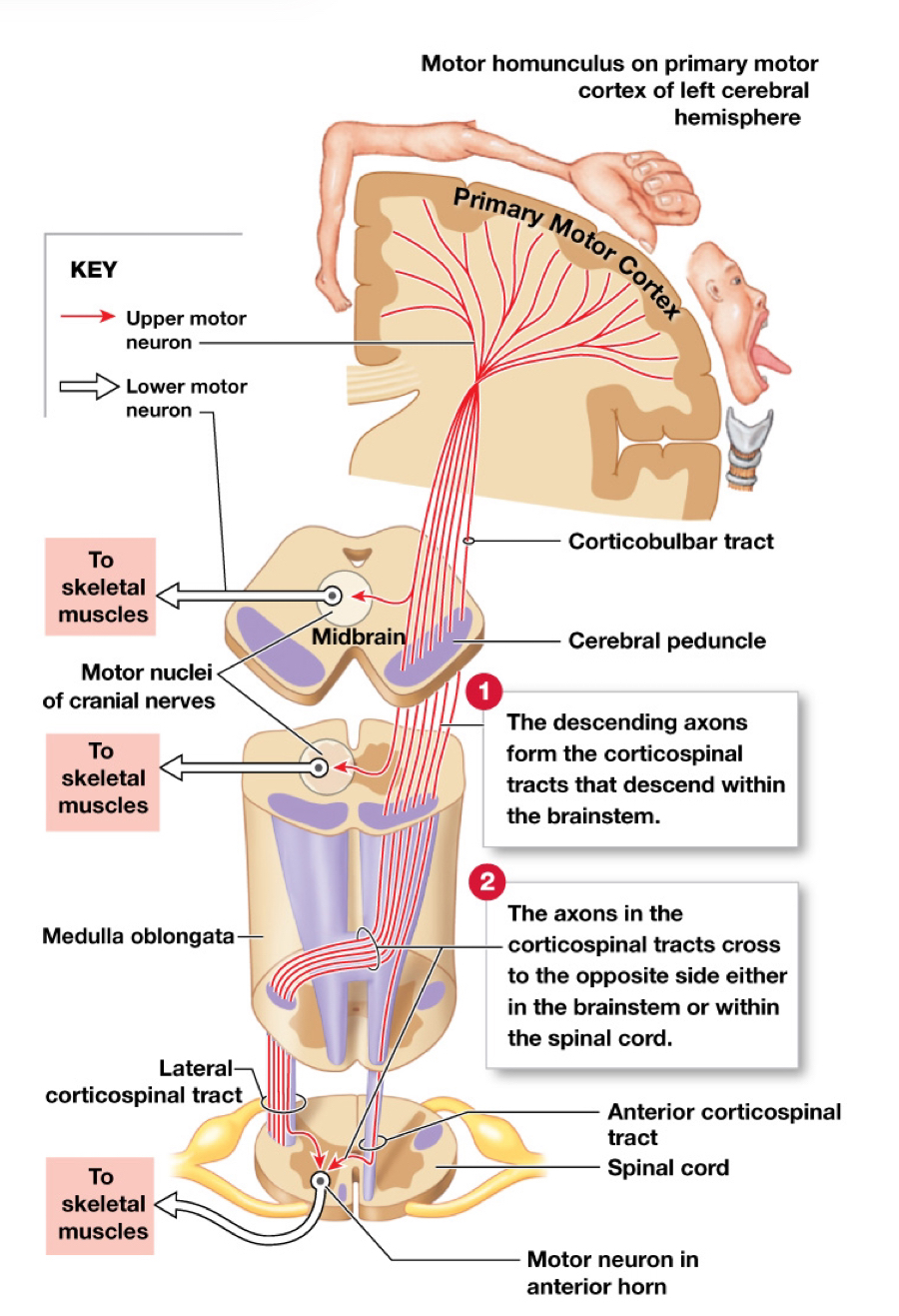
Motor homunculus (Somatic motor pathways)
Functional map of the primary motor cortex
Corresponds with specific regions of the body
Proportions similar to those of sensory homunculus
Medial pathway
Controls muscle tone and gross movements of the trunk and proximal limb muscles
Lateral pathway
Control muscle tone and movements of the distal limb muscles that perform precise movements
Descending (Motor) Pathways
☆: INFORMATIONAL DIAGRAM FLASHCARD
Basal nuclei and the cerebellum (Somatic motor pathway)
Responsible for conscious or subconscious coordination and feedback control over muscle contractions
Basal nuclei
Provide the background patterns of movement involved in voluntary motor activities
Cerebellum
Monitors proprioceptive (body positioning) sensations, visual information from eyes and vestibular (balance) sensations from internal ear to adjust movement accordingly
☆ Damage to these = no voluntary motor activity/coordination