nucleic acids
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
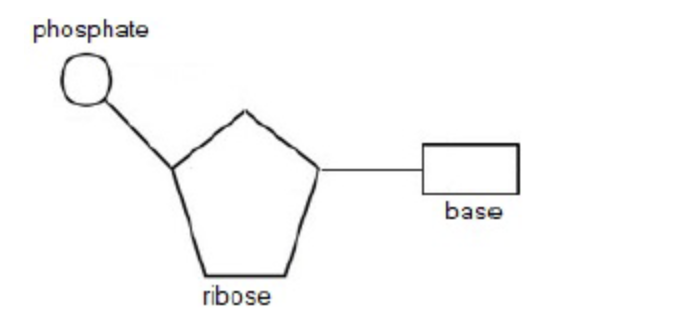
Draw labelled diagrams to show the structure of RNA nucleotides and how they are linked together to form a molecule of RNA (4)
a. ribose drawn as pentagon and labelled sugar/ribose;
b. base drawn with correct link to (C1 of) ribose and labelled base/nitrogenous base;
c. phosphate drawn with correct link to (C5 of) ribose and labelled P/phosphate;
d. two (or more) ribonucleotides drawn with correct link (C3 to C5)
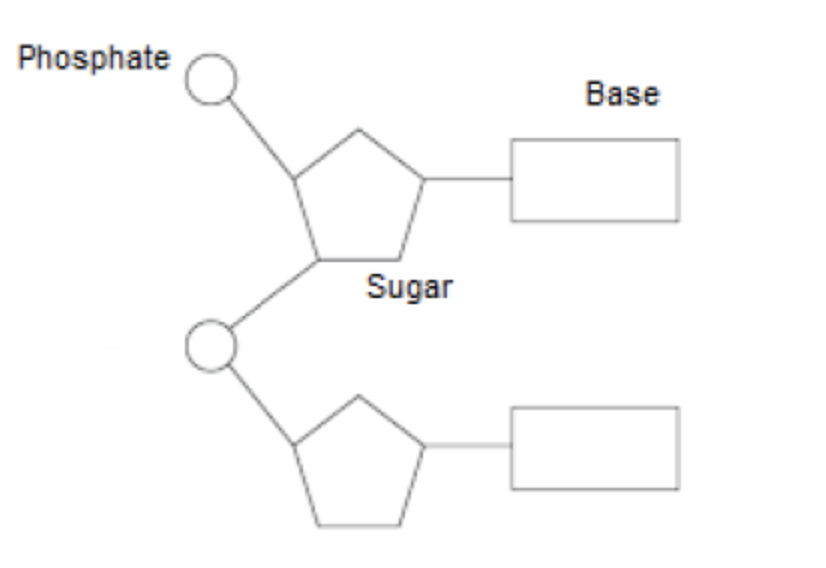
Explain how the two strands of the DNA double helix are held together (2)
hydrogen bonding between nucleotides / bases;
complementary base pairs;
adenine-thymine and cytosine-guanine form base pairs (between the two strands with H-bonding);
2 bonds between A and T, while 3 bonds between C and G
Describe the structure of the DNA molecule (5)
a. two stranded/double helix ✔
b. antiparallel / strands running in opposite directions
OR
one strand organized 5’ to 3’ and the other 3’ to 5’ ✔
c. sugar-phosphate backbone ✔
d. each strand formed by chains of nucleotides ✔
e. each nucleotide is formed by a phosphate, a deoxyribose and a base / annotated diagram of a nucleotide clearly indicated as a nucleotide ✔
f. the bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine ✔
g. strands held together by hydrogen bonds (between complementary base pairs)
OR
A pairs with T and C pairs with G ✔
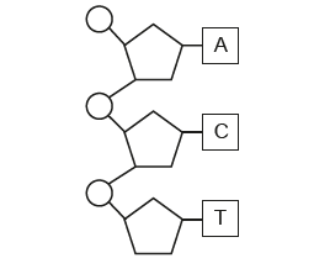
Sketch the complementary strand to complete the section of a DNA diagram (3)

Distinguish between the structures of DNA and RNA (3)
DNA is double stranded, RNA is singe stranded
DNA: deoxyribose, RNA: ribose
DNA: thymine, RNA: uracil
DNA: helical RNA: variety of forms → mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
draw a labelled nucleotide (3)