Lecture 11 Key Concepts/Terms
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
1
New cards
what are the two characteristics of life?
1.) organization
2.) can replicate itself
2.) can replicate itself
2
New cards
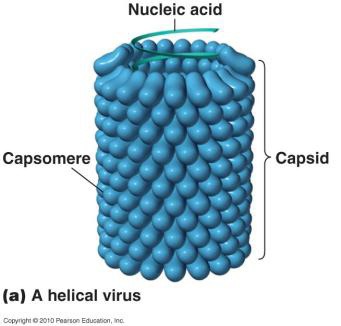
helical capsid
virus structure
continuous helix of capsomers forming a cylindrical nucleocapsid
RNA strand inside
continuous helix of capsomers forming a cylindrical nucleocapsid
RNA strand inside
3
New cards
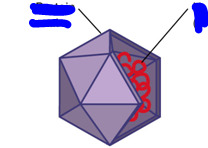
icosahedral capsid
virus structure
3D, 20 sided figure
DNA inside
3D, 20 sided figure
DNA inside
4
New cards
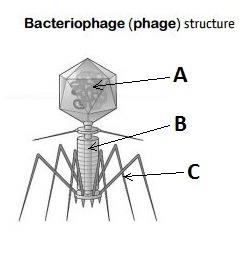
Icosahedral head: helical tail
bacteriophage/bacterial virus structure
capsid at the head containing DNA
capsid at the head containing DNA
5
New cards
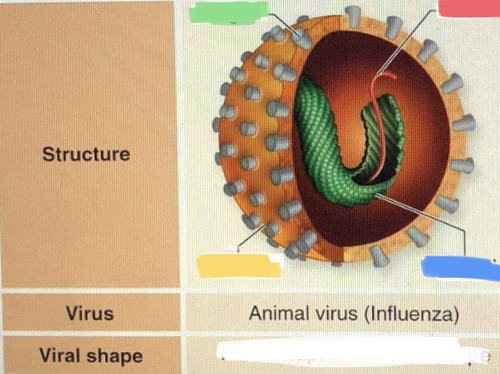
helical capsid within envelope
virus structure
capsid containing RNA
capsid containing RNA
6
New cards
what structure is an adenovirus
icosahedral capsid
7
New cards
capsid/protein coat
encloses genetic material
8
New cards
Can a virus contain both DNA and RNA?
no, one or the other
9
New cards
what two configurations can viral genetic material have
circular or linear
10
New cards
can a virus have single or double stranded DNA/RNA?
yes
11
New cards
viruses evolve ________ from other organisms
independently
12
New cards
what is a binal virus
irregular in shape and have complex structures
13
New cards
what kind of virus structure is binal?
bacteriophage
14
New cards
helical viruses
rod-shaped viruses

15
New cards
icosahedral viruses
viruses with a polyhedral capsid with 20 triangular facets
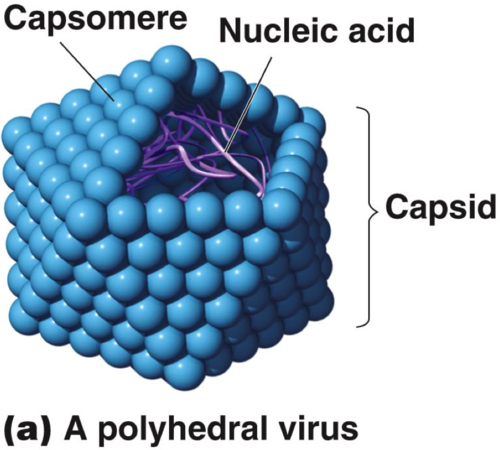
16
New cards
bacteriophage
kind of virus that infects bacteria
cylindrical body with icosahedral capsid on tail fibers (alien looking)
cylindrical body with icosahedral capsid on tail fibers (alien looking)
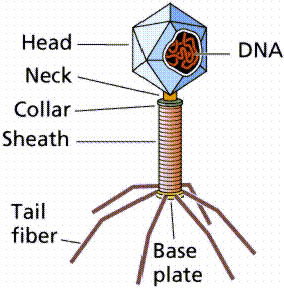
17
New cards
viral replication is _______
independent of the host cell's DNA but dependent on the host cell's enzymes and metabolism (parasitic)
18
New cards
why do some scientists argue that viruses are not alive?
they can't multiply on their own to make offspring viruses
19
New cards
what is the significance of TSEs (transmissible spongiform encephalopathies) in this lecture?
they used to be referred to as "slow viruses" because they used to be undetectable until years after infection. TSEs are prions and prions have no genetic material. Bc of this, expression is restricted
20
New cards
what are some examples of TSEs?
Kuru, mad cow disease, scrapie, chronic wasting disease, creutzfeldt-jakob disease
21
New cards
how are prions different from viruses?
they only contain protein and they lack DNA or RNA
22
New cards
prion
abnormal pathogenic agents that are transmissible and induce abnormal folding of specific normal cellular proteins found mostly in the brain
23
New cards
How are prions transmitted?
ingestion, transplant, and surgical instruments
24
New cards
how is the traditional tree of life misleading?
it looks monophyletic, but it's not, it's paraphyletic
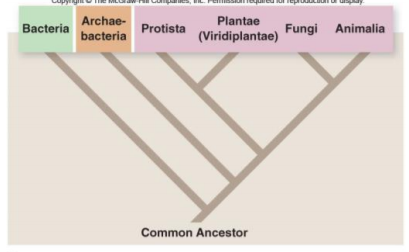
25
New cards
how should we think of the tree of life?
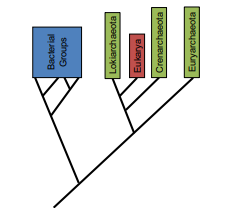
26
New cards
LUCA
last universal common ancestor; only on the tree of life
27
New cards
what are the traits shared by all life forms (before LUCA)
-plasma membrane bound cells
-ribosomes
-semi-conservative DNA replication
-similar genetic codes for proteins
-transcription and translation
-metabolic pathways
-ribosomes
-semi-conservative DNA replication
-similar genetic codes for proteins
-transcription and translation
-metabolic pathways
28
New cards
Are prokaryotes unicellular or multicellular?
always unicellular
29
New cards
How do prokaryotes divide?
binary fission
30
New cards
configuration of DNA in prokaryotes
circular chromosome, unenclosed DNA
31
New cards
do prokaryotes have organelles?
no
32
New cards
do prokaryotes sexually or asexually reproduce?
asexually
33
New cards
what are the three defining traits of eukaryotes?
they are multicellular
they have organelles (compartmentalized)
they are mostly sexual
they have organelles (compartmentalized)
they are mostly sexual
34
New cards
How is the new eukaryotic tree different from older views?
you can find plants fungi and animals as tips on tree, other tips include protists