The Life and death of the Cell
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Eukaryotic cell cycle includes four phases
G1
S
G2
M phase
G1
the cell grows so it can split
grow a lot of proteins so when they split their daughter cells can have a good amount of proteins
are told to split —> response to extracellular cues whether or not they should divide
cell repair
high metabolic activity
Metabolic activity
the sum of all chemical reactions in an organism that sustain life, converting food into energy for processes like breathing, cell repair, and growth
S phase
DNA synthesis —> dna is being replicated
92 total chromosomes —> double the 46 chromosome
G2
prevents division if the DNA is incorrectly or improperly repaired
checks if there is the right number of chromosomes
M phase
the actually cellular division
cells divide at different rates
G0
An arrested state for non-divdiing, mature cells. Cells will carry normal cellular function
most cells stay in this stage of the cycle ex: heart cells
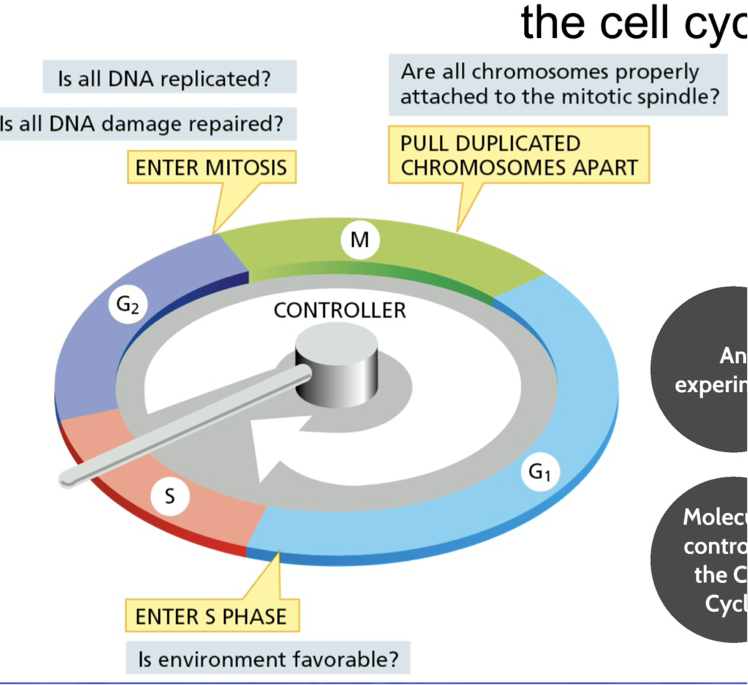
How are the cell cycle control system regulated?
They have checkpoints
what are the three check points at certain critical steps
G1 to S phase
G2 to M phase
M phase
what is the first check point G1 to S phase do?
confirms whether environment is favorable before it enters the s phase
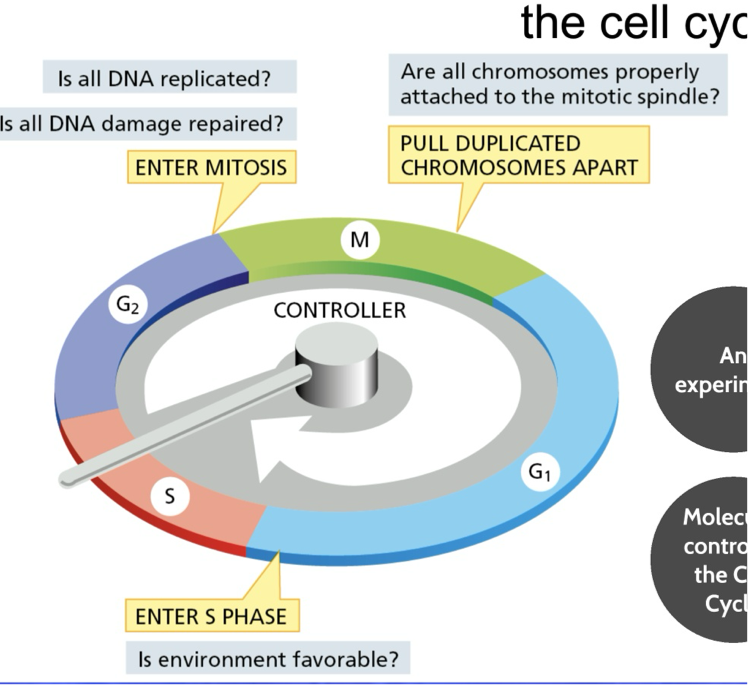
what is the second check point G2 to M phase do?
confirms that the DNA is undamaged and fully replicated before entering mitosis
Asks:
Is all the DNA replicated? Is all the DNA damaged repaired?
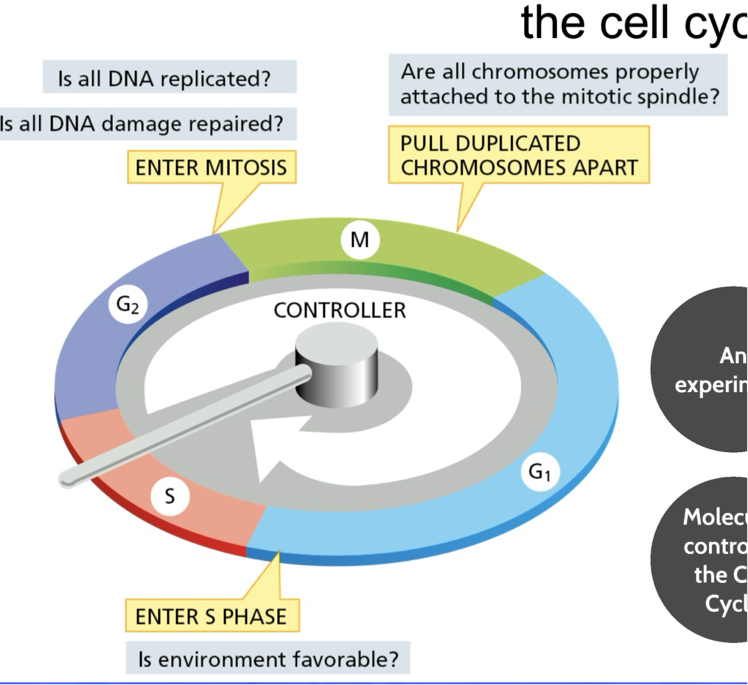
What is the third check point M phase do?
confirm chromosomes are attached to mitotic spindle before pulling the duplicated chromosomes apart
Asks:
Are all the chromosomes properly attached to mitotic spindle?
cell cycle control system
network of regulatory proteins ensures that cells replicate their DNA and organelles, and divide in an orderly fashion
What does the cell cycle depend on?
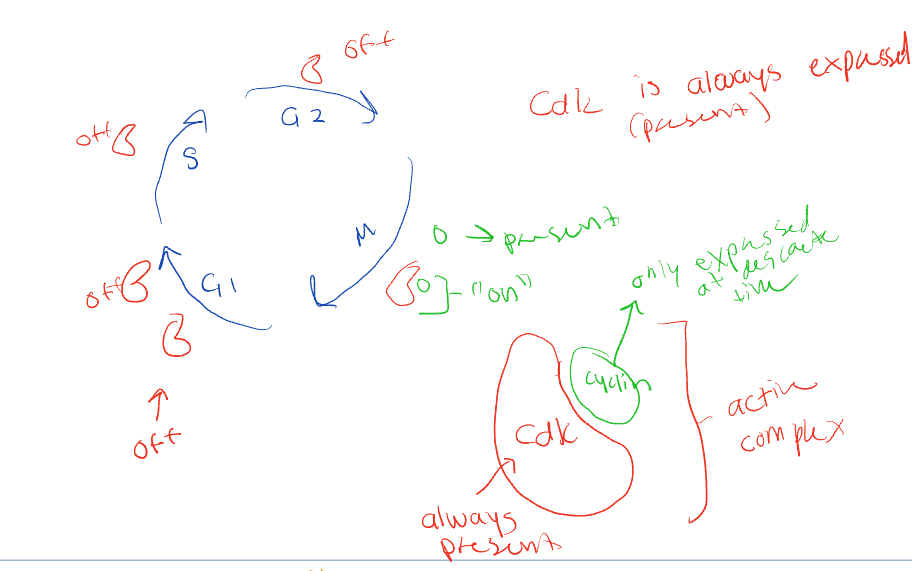
cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdks)
cyclin-dependent protein kinase ( cdk)
protein kinases that are present in proliferating cells throughout the cell cycle
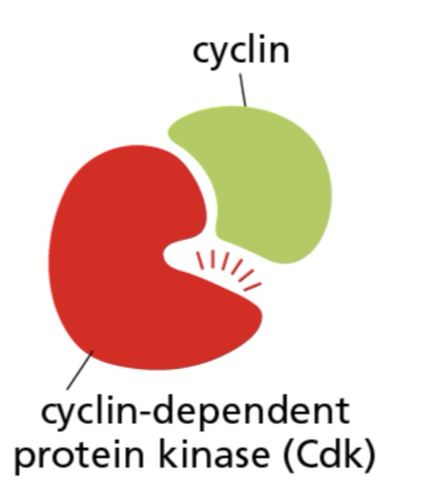
kinase
a protein enzyme that takes a phosphate from atp and sticks it to another molecule
Cyclins
switching kinases on/off is
concentraction vary over course of cell cycle
activated complexes help trigger various cell cycle events
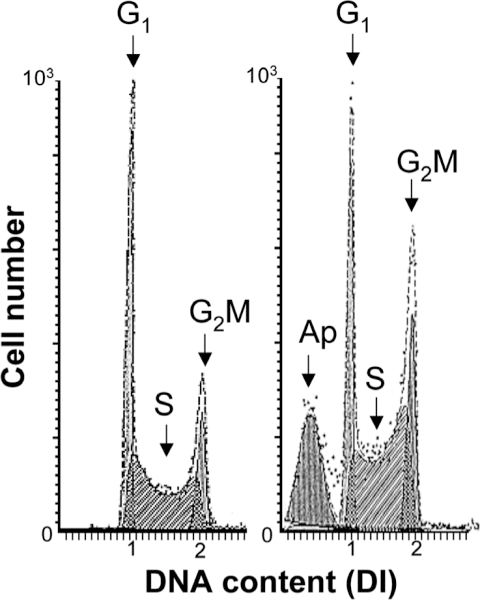
flow cytometry:
1) Which peak corresponds to each phase of cell cycle?
2) Which phase of cell cycle is the longest
G1 is always the first peak
G2 and M are the second, but s phase is never on the chart

Why is the fluorescence doubled in g2 and m phase?
there is double the DNA, and in this experiment there are labeled with flourescence light. Thus, they have more light
Why is there no peak for s phase?
There is no distinct peak for S phase in flow cytometry histograms because cells in this phase are actively synthesizing DNA, meaning their DNA content is continuously changing from the
2N2 cap N
2𝑁
(G1) to
4N4 cap N
4𝑁
(G2) levels
The Rb protein
hibits e2f and when it does it cant make the proteins to grow
happens in G1 phase
when phosphate is attached to it changes shape and can no longer attach to the e2f and floats away
mitogen
extracellular signal encourages mitosis
what is the signal that attaches to the RAS and what does it do?
signal transduction
goes to nucleus to make cyclin
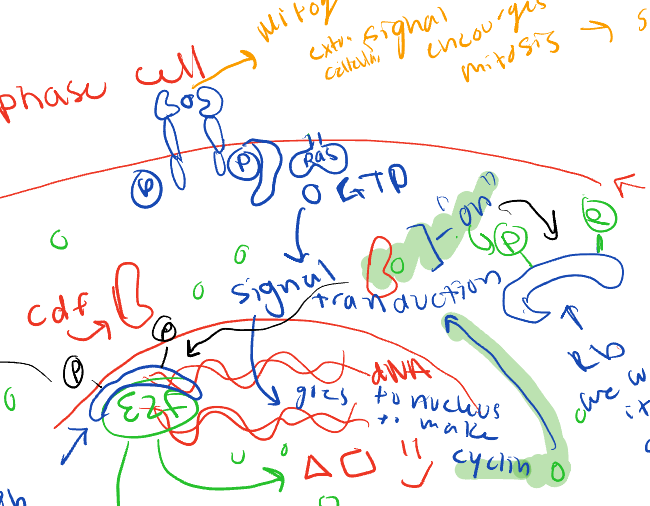
explain the process of the RB protein and to enter mitosios
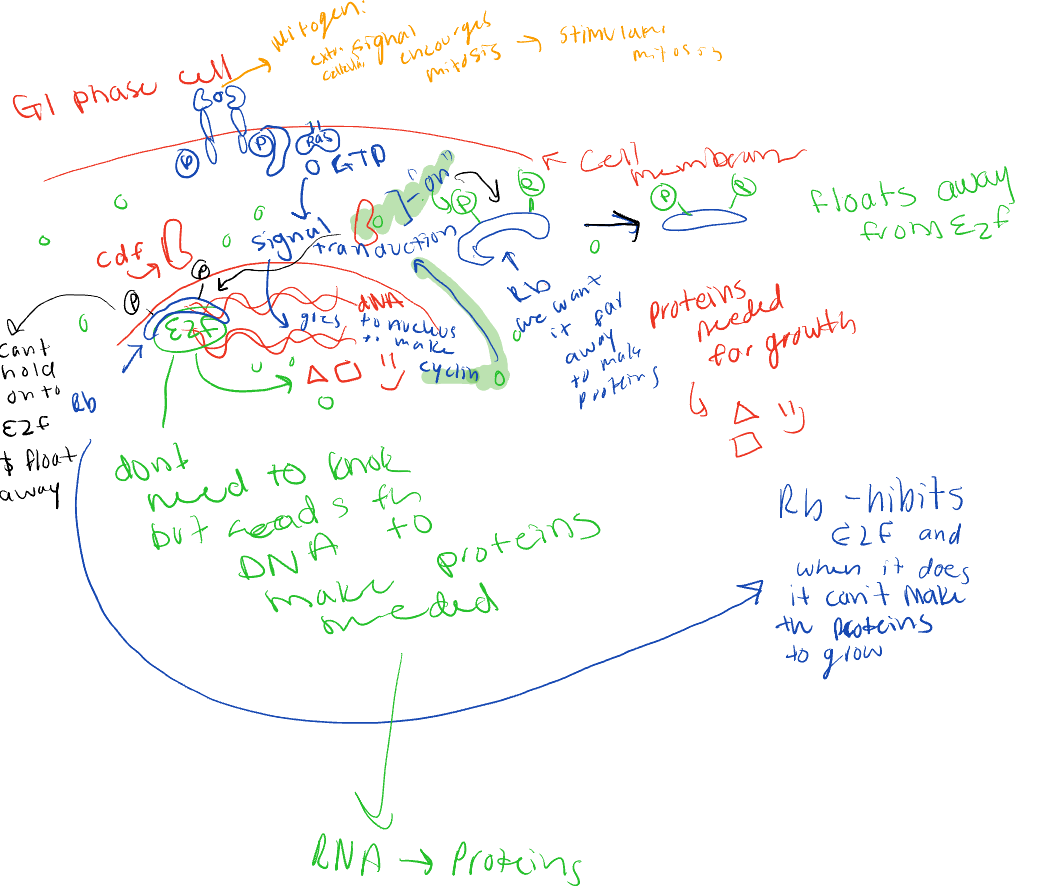
what happens if there is no RP
the cell keeps growing and the cell cycle is on a loop and cant stop
What would the effect be from overexpressing Rb in every human cell? Potential cancer therapy or more harm than good?
harder for them to grow and overwork the cell