Exponential Growth
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
what are the components of a closed system
no immigration, no emigration, births increase pop size, deaths decrease pop size
population growth models are used to estimate…
population size many generations in the future
life tables used to determine
population growth from one generation to the next generation
to determine a change in population size (N) from one point in time to sometime later:
N(later)=N(now) + Births - Deaths
what are the underlying assumptions of the exponential model
all individuals have the same average birth (b) and death (d) rates
b and d are constant through time
births and deaths occur continuously throughout year
no migration (I or E) - the pop is closed
resources are unlimited
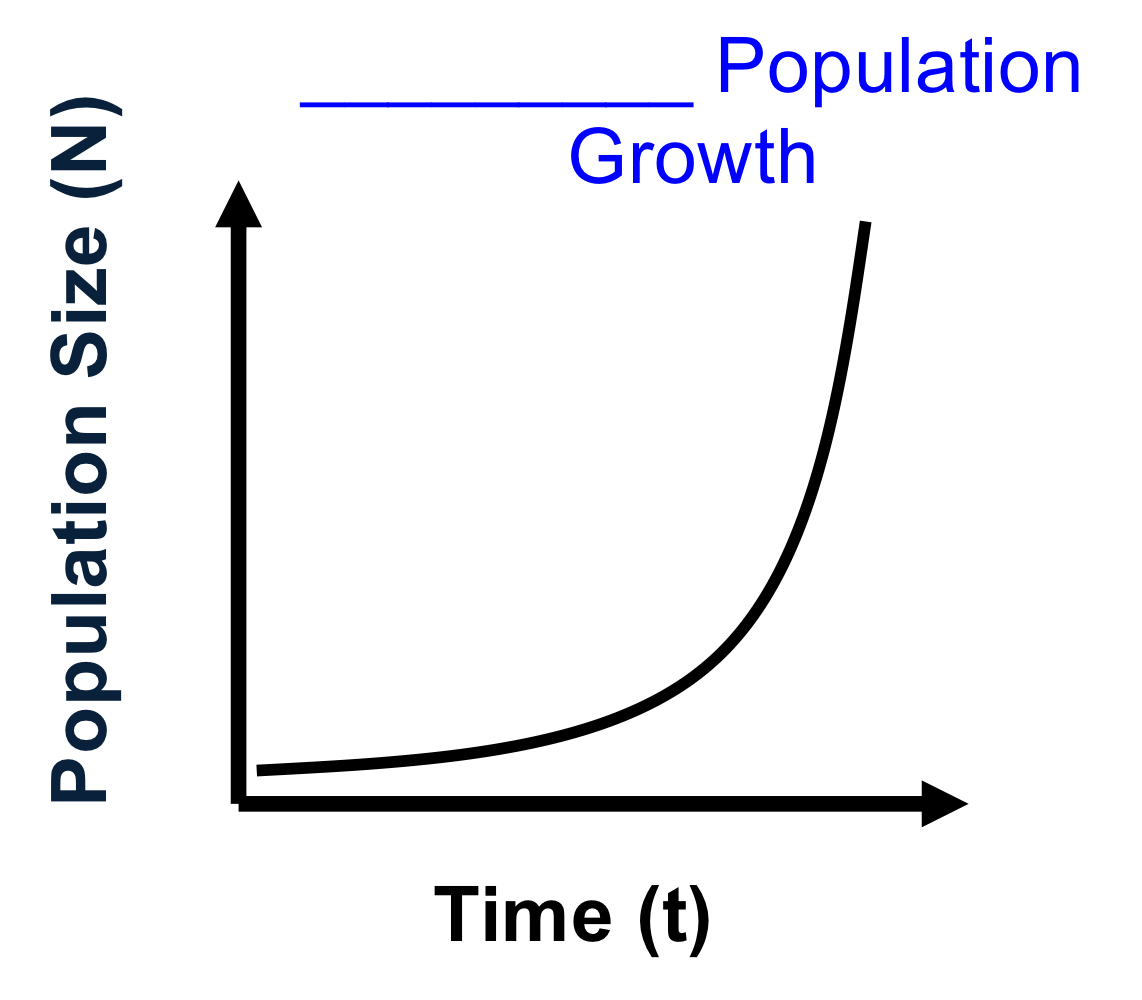
what is the name
exponential population growth
what does the geometric model assume
discrete breeding (population only grows during breeding season) but similar equation to exponential model
variable for population size
N
variable for change in time
∆t
variable for birth
b
variable for death
d
variable for number of inds in the pop at t=0
No
per capita growth rate
r=b-d
exponential growth rate
r is an instantaneous per capita rate of increase
exponential growth equation
dN/dt = rN
for the per capita growth rate, rate of change in the pop size changes _____
continuously
the rate of change in pop size over a _____ time interval is equal to the ____ multiplied by ______
short, per capita rate of change, the number of inds in population N at t
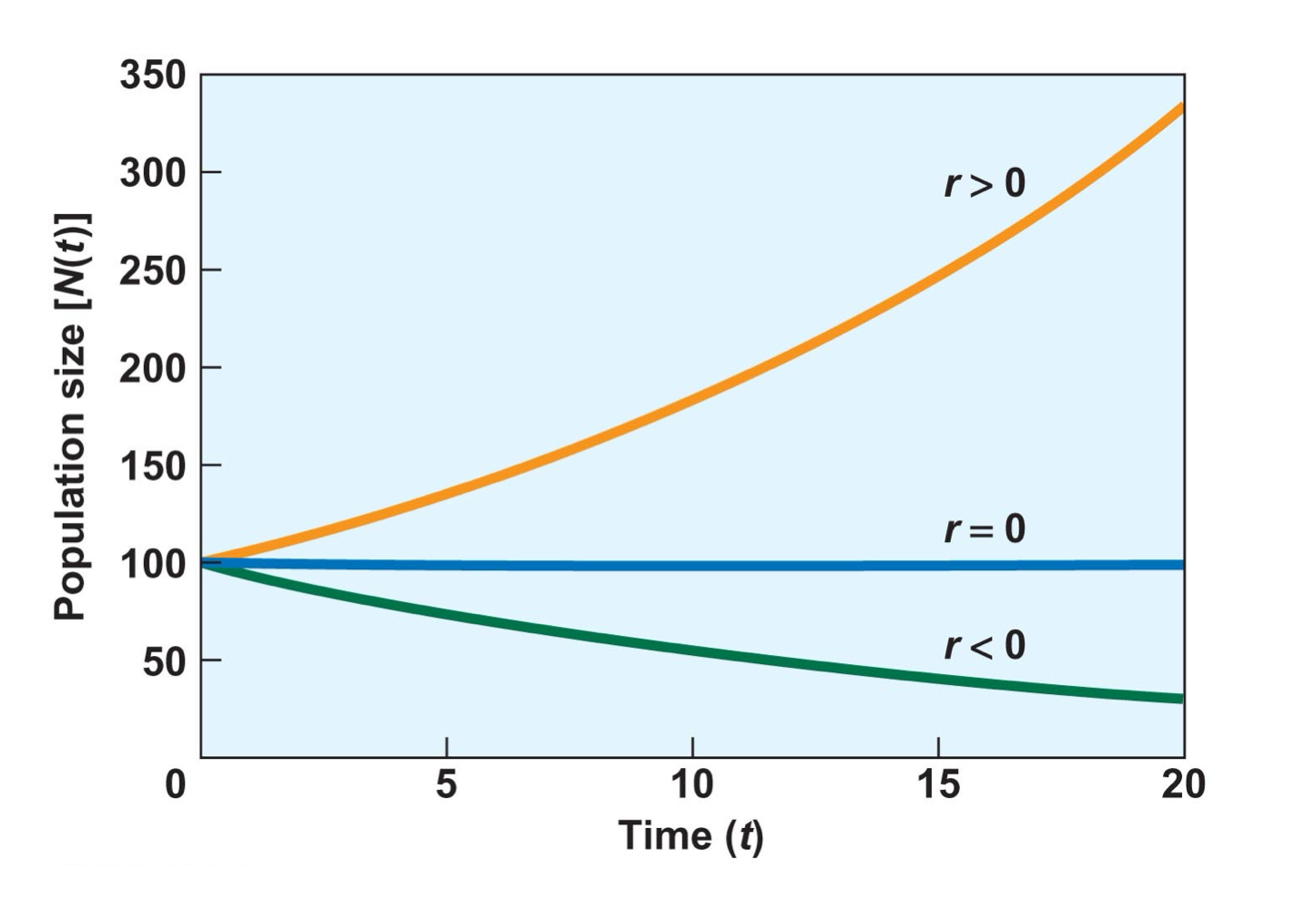
r=+ _____ r=- _____ r=0______
increase, decrease, constant
do we typically observe exponential growth in nature
no because underlying assumption are often violated
what is violated in the assumption that all individuals have the same average b and d rates
different age classes generally have different b and d (life tables)
what is violated in the assumption that r(b and d) are constant through time
it’s rare because
age structure of a pop changes through time(ie the number of inds in each age class change through time)
environmental conditions change through time and continuously influence b, d, and r
(r the highest growth rate that the pop has potential to achieve if a stable age distribution and constant b and d)
what is violated in the assumption that there is no migration (I and E) - the population is closed
populations are rarely closed (except in the laboratory)
what is violated in the assumption that resources are unlimited
resources usually become limited
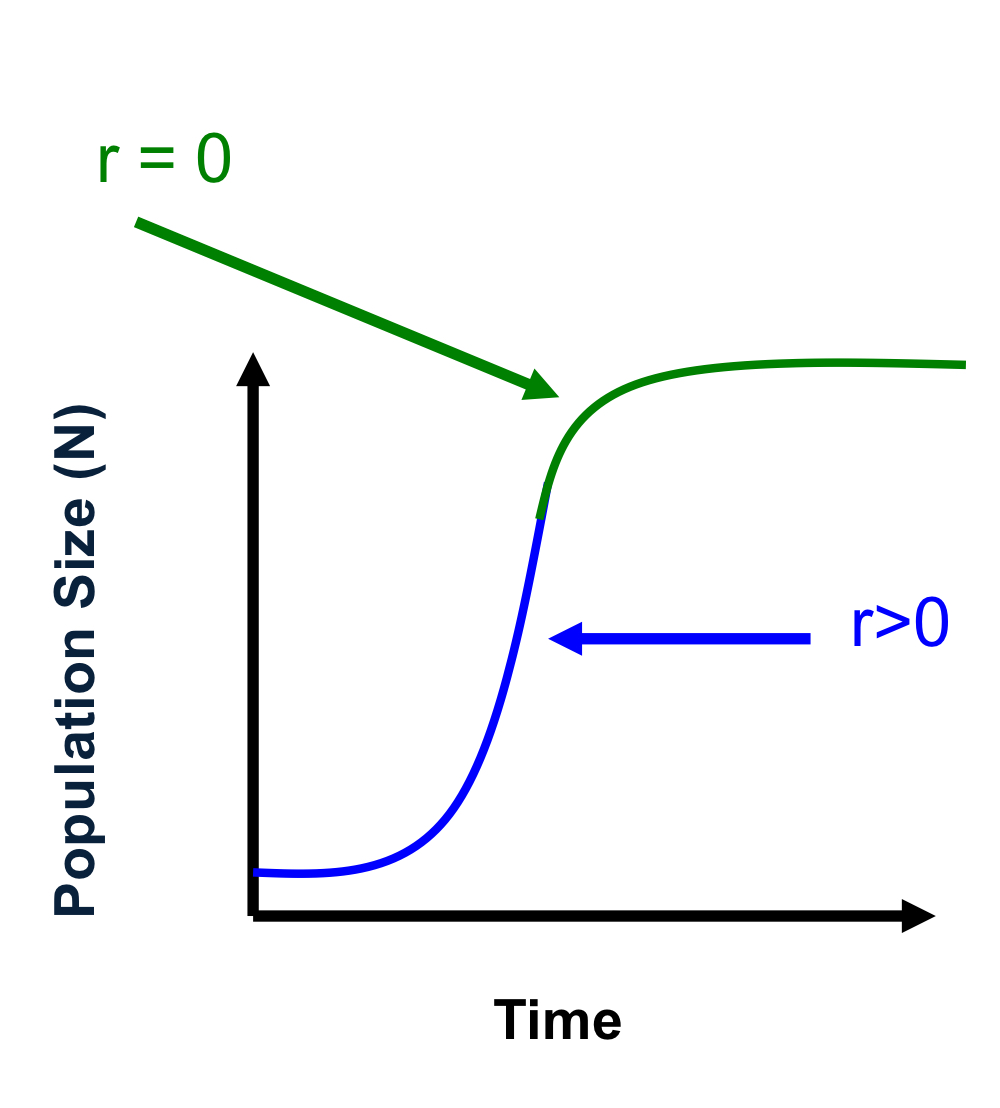
when population size is low:
no competition (resources are unlimited)
population grows at the intrinsic rate of increase, r (exponential growth) = highest growth potential
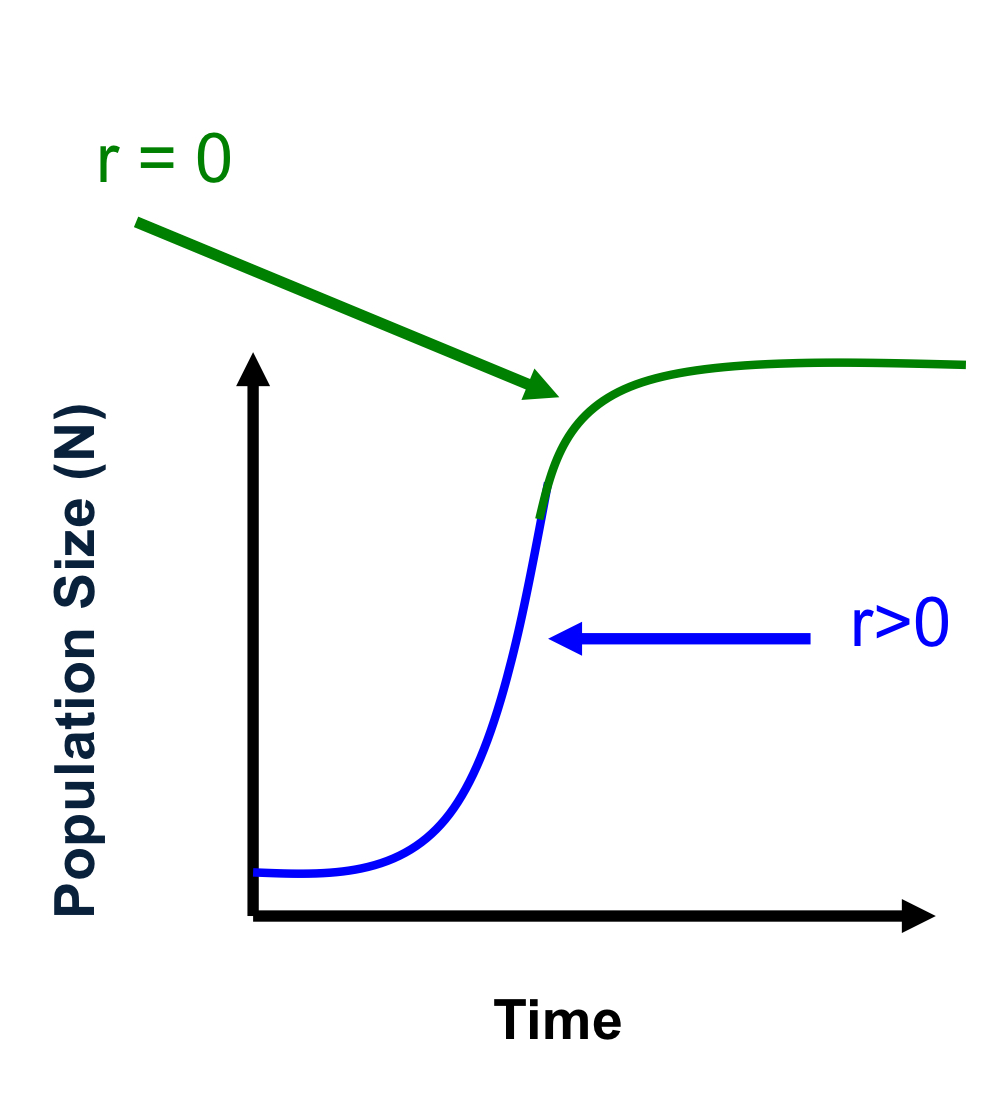
when population size is high
intraspecific competition increases (resources become limited)
competition decreases r (b ↓ and d ↑) as N increases (=density dependence)
N levels off and r=0
why has the human pop size not leveled off
medical advances (less death more birth)
technological advances (agriculture, aquaculture, unlimited food supply)
we can determine whether a population grows from one generation to the next using age specific survival and fecundity data from
life tables
to determine population size many generations in the future, we must use mathematical models such as
exponential (& geometric) models
the exponential (& geometric) models require the knowledge of ____, _____ and ______
average b, average d, pop size (N)
most species violate the assumptions in the exponential model for many reasons: ______, _______, ________
b, d ( r ) vary through time
populations are not closed
resources are usually limited
exponential growth rates, or intrinsic rates of increase ( r ), will only be accurate over the long term if ____ and ______
age structure is stable
b and d do not vary