Processing Display and Storage
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
raw data
whatever the system obtained before any sort of processing occured
when does pre processing occyre
before image is displayed
what is pre-processing
automatic fast function of imaging system that makes graph of exposure data we have and compares it to a preset forum and cleans it up
Analog-to-DIgital Converter
digitation of electronic signalh
how many digits are in the biinary code
2 (0 & 1)
Digitization process
scanning
receptor is divided into a matrix of pixels
Digitization process
sampling
measures each pixel for the amount of exposure
Digitization process
quantization
assigns a numerical value to each density
dynamic range
number of shades an imaging system can produce
dynamic range is identified by…
bit depth of each picel
increase in display of greater shades in grey has ______ dynamic range and _____ contrast resoluition
greater; better
as exposure increase _____ increases
densities
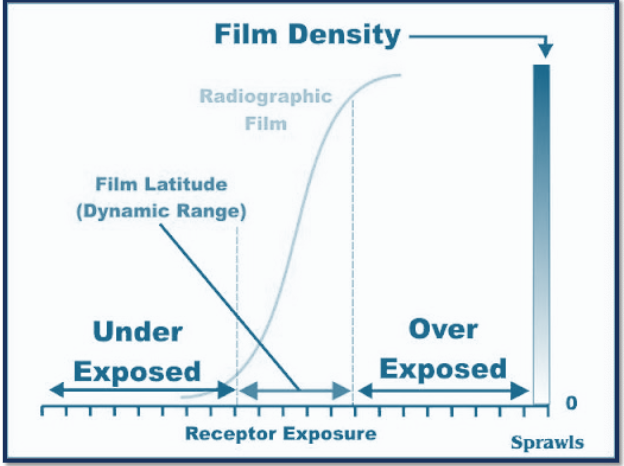
body
useful range of densities
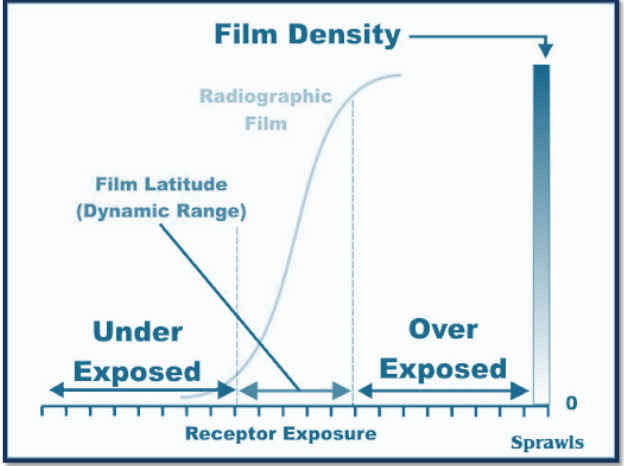
toe
underexposed
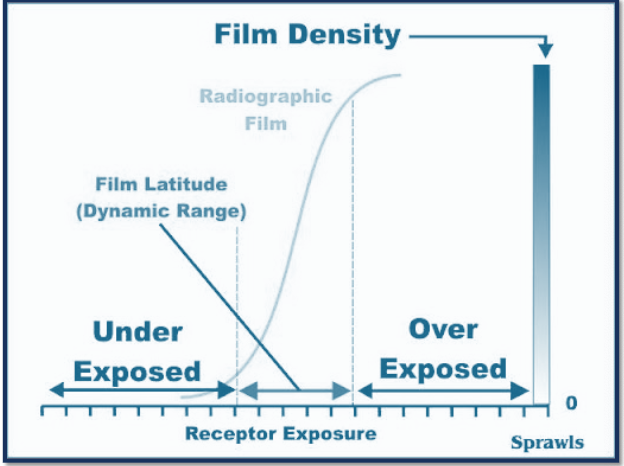
shoulder
overexposed
digital exposure lattitude is
wide
in digital exposure you can underexposure by%
50%
in digital exposure you can overexpose by:
400%
when are pixel values counted
during sampling
how are values arranged in a bar graph
according to frequency
Histogram analysis
prior
reference histograms within system
Histogram analysis
neural
based on exams taken, it will start averaging so that it is more specific to your department
Exposure field recognition (EFR)
identifies edges of exposed area; recognizes sudden change in pixel values
What are the requirements for exposure field recognition
accurate collimation
alignment of exposure field with the image receptor
exposure field recognition errors
histogram analysis error
re-mapping error
landmark identification
identifies edges of anatomical part; densities outside of anatomical landmarks are discarded prior to histogram analysis
value of interest
determines what info can be removed and can staylo
lookup table
biggest influence for contrast with digital imaging due to anatomic rescaling (fixes contrast)
rescaling
evens out exposure and remaps it based on lookup table
flat fielding
even out densities so that it is more uniformed; smooths out tiles
interpolation
eliminates missing pixel information
segmentation
ability of PSP plate to identify multiple exposures on one plate
soft marker
annotated markerhar
hard marker
lead marker
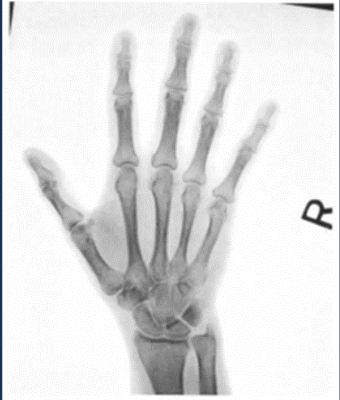
image inversion
reverse colors
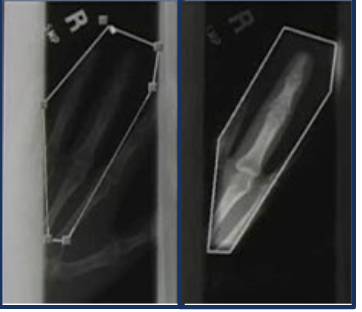
region of interest
calculated pixel value for a selected area of interest
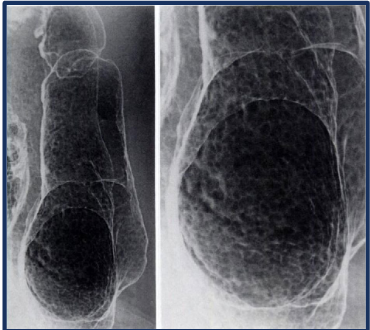
magnifiction
zooming in on an image
edge enhancement
enhances edge of structureswhat i
what is the effect of using too much edge enhancement
halo effect
loss of detail
High pass filterig
makes the edges of the structure stand out to the background; introduces some noise
equalization
compression of dynamic range; removes lightest and darkest exposures
masking
blacking out white background
smoothing
noise reduction; suppresses mottle on image (decreases contrast)
subtraction
leaving some structures in an image while eliminating others
low passing filters
computer only keeps low frequency in an image
window width and level
adjusts darkness and contrastwi
window width
number of shades displayed
Window level
where on the scale the window is set
computer processing unit (CPU)
“brains” or “Control Panel” of computer system
Motherboard
main circuit board
software
application that make certain operations ‘run’ on a computer system
computer network
chain of computers and components that all work in conjunction with one another
Health Level 7 (HL7)
standardized computer language for transmission of hospital information
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM)
standarized computer language for transmission of images
What enables imaging systems from different manufacturers to communicate
DICOM
DICOM Commands
retrieve (query) images for a specific patient
worklist of images
send images
print images
DICOM Header
series of text info attached to the image
local area network (LAN)
transmit images within a hospital
Wide area network (WAN)
multiple LAN interconnected (spans large area)
Information Flow
HIS
RIS
Acquisition Workstation
PACS
Diagnostic Workstation
HIS
store and display hospital and patient info (umbrella)
RIS
specific to radiology
Teleradiology
remote transmission and viewing images
storage classification
online
data stored on hard drives with quick access and transfer times
Storage classification
nearline
jukebox uses robotic arms to retrieve tapes and insert them into a drive to read or write data
storage classification
offline
a removable tape or optical media that is manually stored and retrieved
storage short-term
online; active
storage long term
nearline; archive
byte
combined group of 8-bits
Random Access Memory (RAM)
data can be stored at random (‘active storage’)
Read only Memory (ROM)
contains info supplied by manufactured
Redundant array of independent discs (RAID)
large storage system
secondary memory
flash drive
juke box
Picture Archiving & Communications System (PACS)
electronic network for communication between image modalities, display stations. & storage
PACS advantage
archiving capability
transmit or move images throughout facility
ability of system to pre-fetch studies
average digital radiography study
about 5 MB
CRT Monitor
converts electrical signal into visible image
spatial resolution of CRT Monitor
1-2 lp/mm
Plasma Monitor
modern display monitor
pixel layer
made up of 3
red
green
blue