AQA A level Chemistry 3.3.12: Polymers
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What topic will you need to recap when revising for this topic? (1)
3.3.4 Alkenes (specifically the addition polymerisation sections)
What is a condensation polymer? (2)
- A polymer formed through a condensation reaction where molecules join
- Losing small molecules such as water as by-products.
What is the general reaction for forming esters from carboxylic acids and alcohols? (1)
CH₃COOH + CH₃OH → CH₃COOCH₃ + H₂O
What is the general reaction for forming esters from acyl chlorides and alcohols? (1)
CH₃COCl + CH₃OH → CH₃COOCH₃ + HCl
What is the general reaction for forming amides from acyl chlorides and amines? (1)
CH₃COCl + CH₃NH₂ → CH₃CONHCH₃ + HCl
Why do the condensation reactions above (esters, amides) not allow for polymerisation? (1)
The products formed are not able to react with each other to form larger molecules
What type of monomers are required for the formation of condensation polymers? (1)
Monomers with functional groups at both ends of the molecule e.g. diol or diacid
What two monomers are used in the formation of a polyester? (1)
A diacid and a diol
What is the repeating unit formed in polyester synthesis? (1)
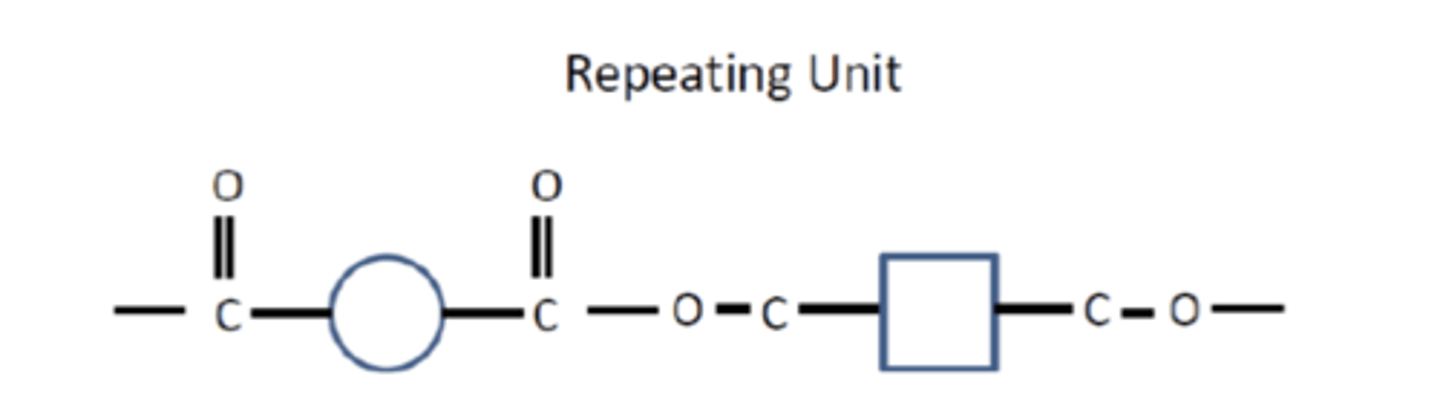
What is the by-product of polyester formation through condensation polymerisation? (1)
Water (H₂O) is the by-product
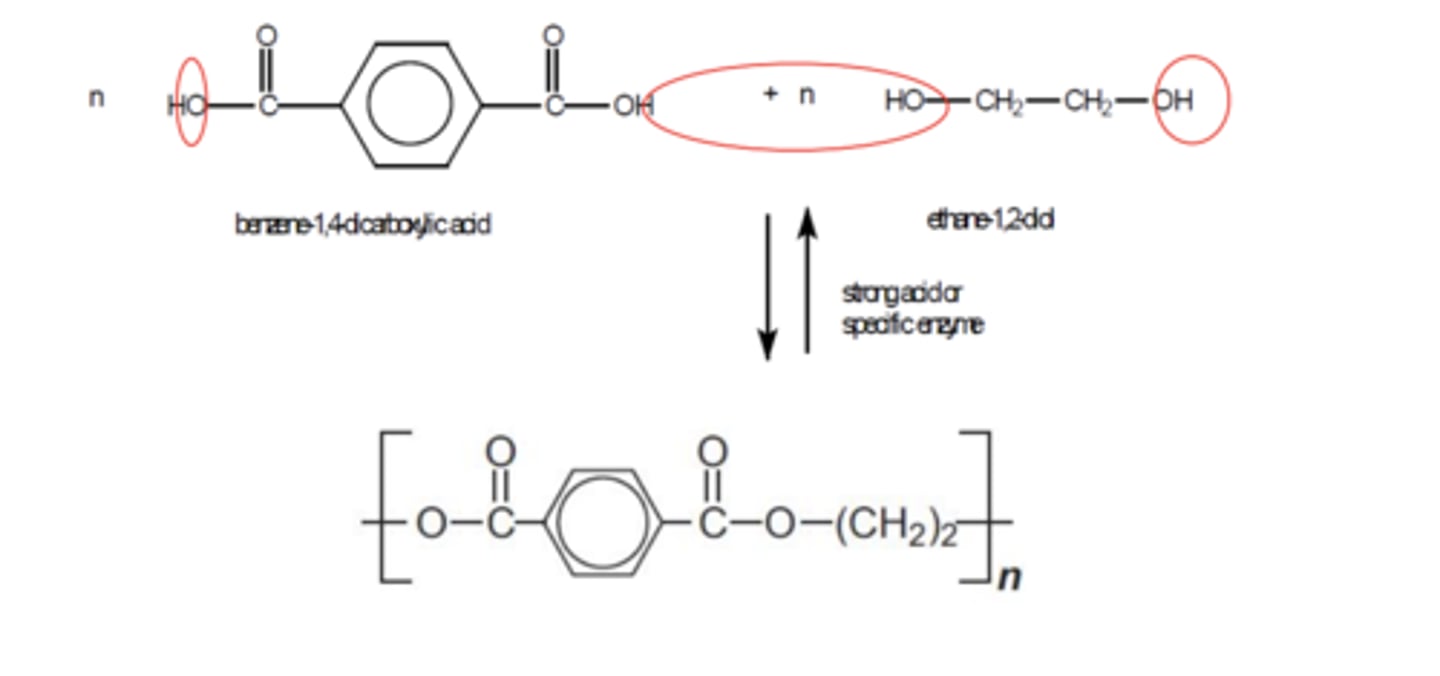
Draw the monomer unit and repeating unit of a polyester made by combining benzene-1,4-dioic acid and ethane-1,2-diol (3)
Terylene
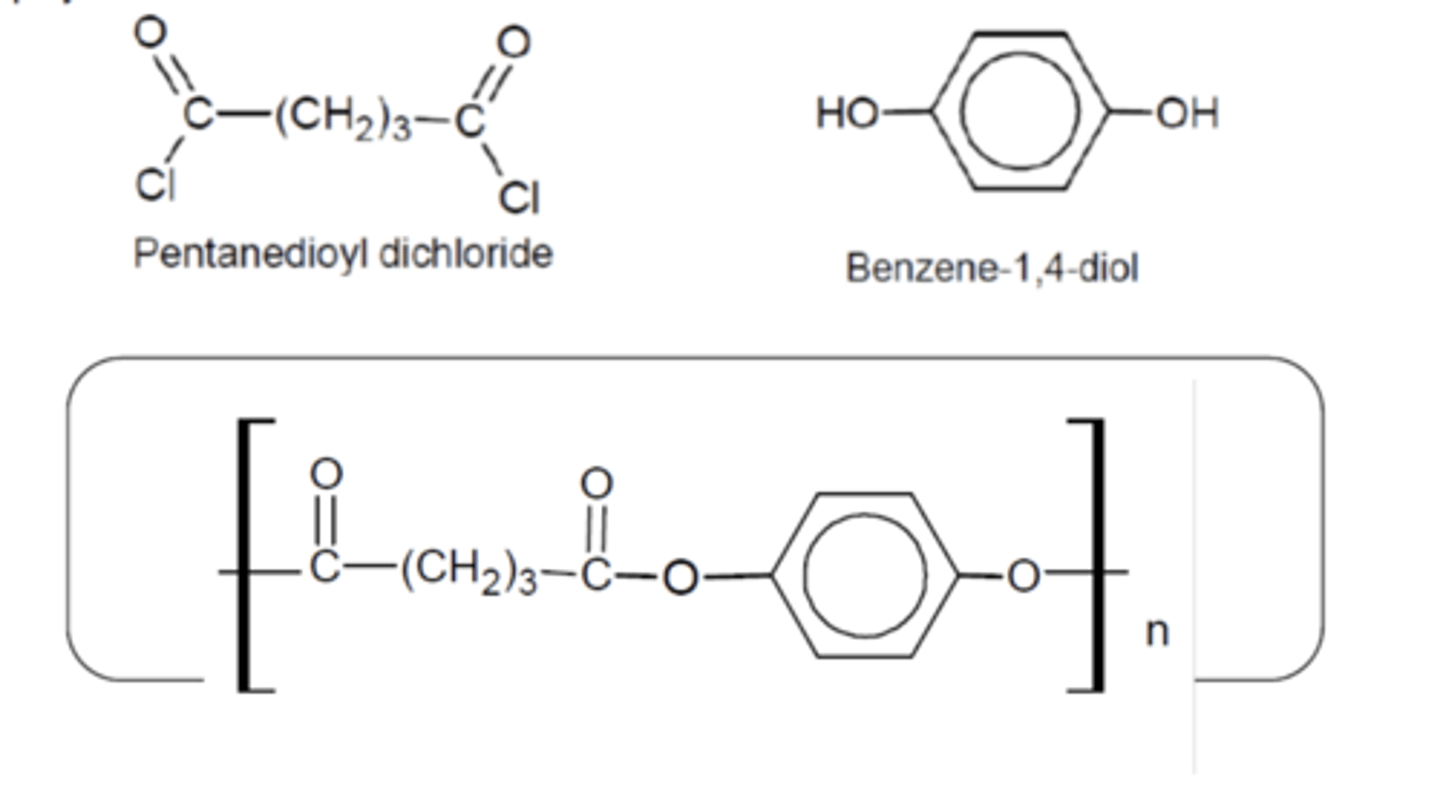
Draw the monomer unit and repeating unit of a polyester made by combining pentanedioyl dichloride and benzene-1,4-diol. (3)
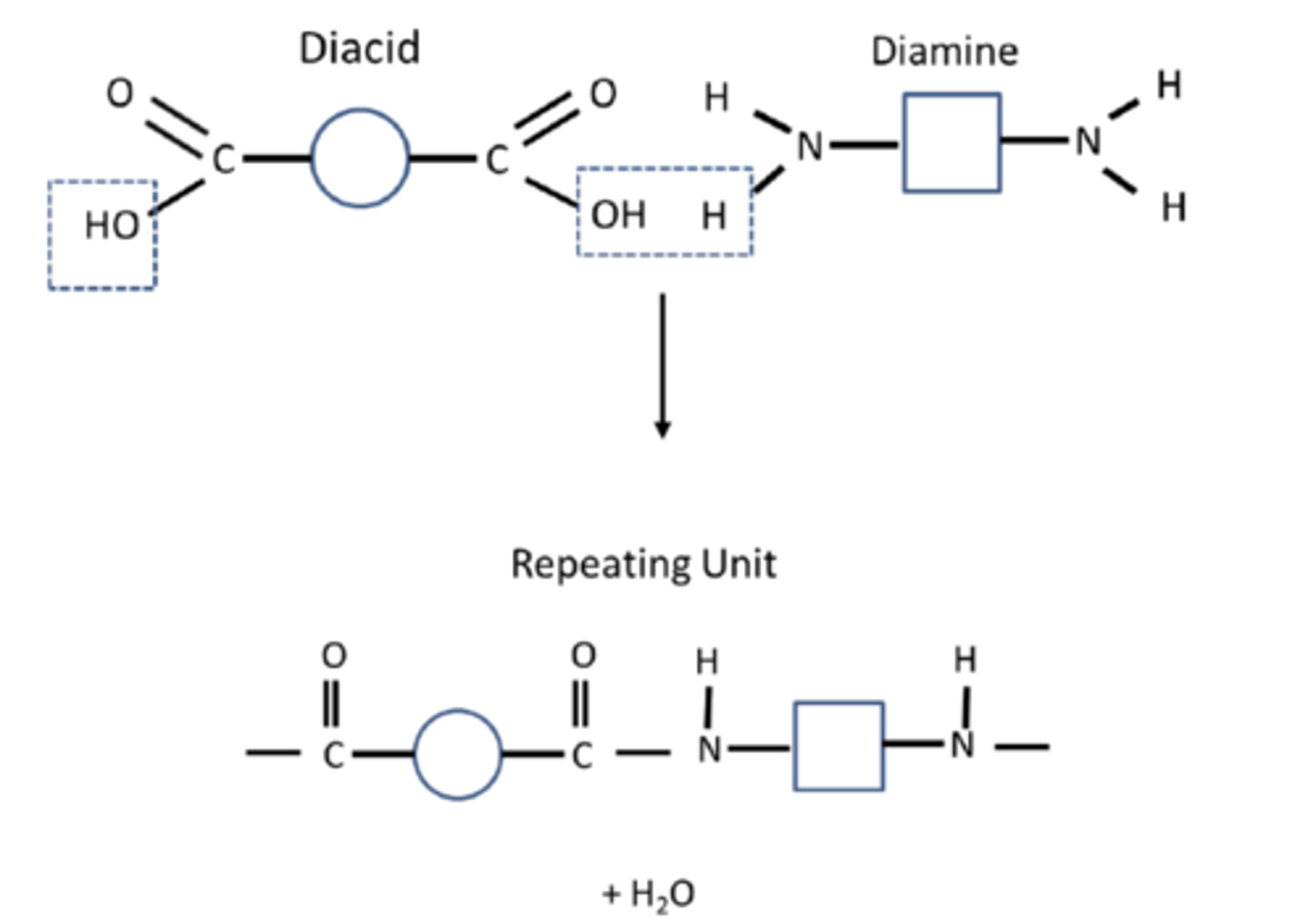
What are polyamides made from? (2)
Condensation of:
- Diacid and diamine
- Diacyl chloride and diamine
Draw an example of a polyamide repeating unit (2)
What are the two examples of polyamides that you must know? (2)
- Nylon-6,6 - made by combining hexanedioic acid and hexane-1,6-diamine
- Kevlar - Used in bullet proof vests
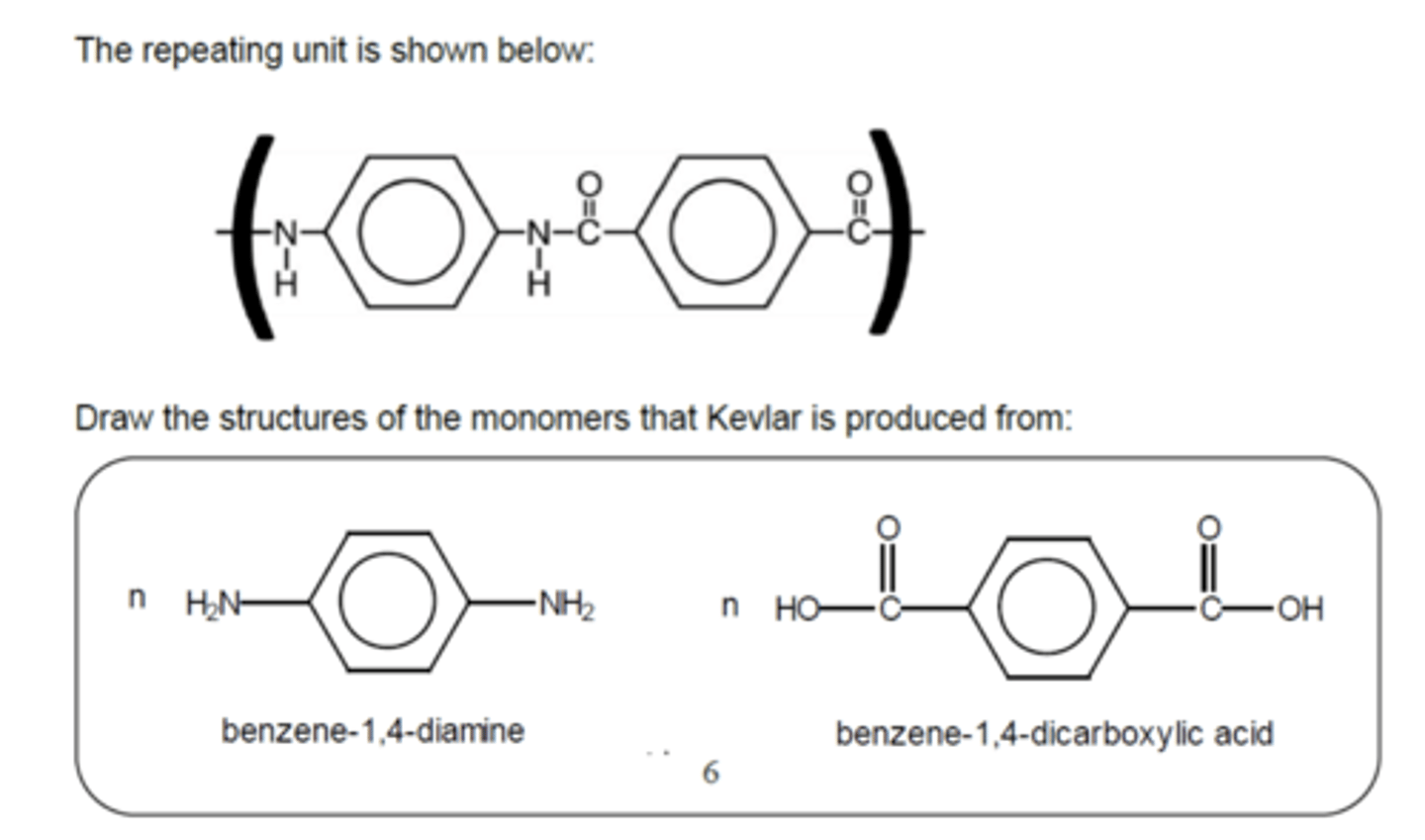
Draw the repeat unit for Kevlar and the monomers that it is produced from (3)
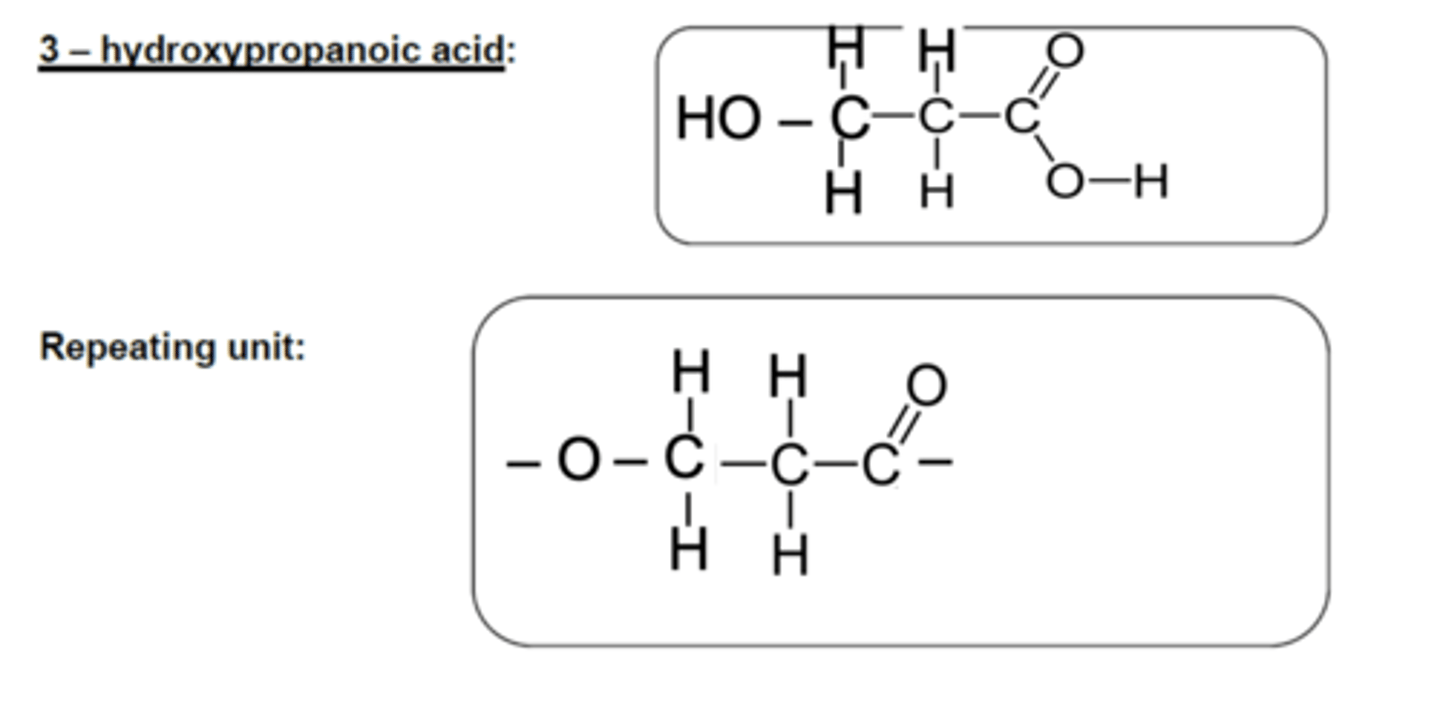
Draw the monomer unit and repeating unit of 3-hydroxypropanoic acid used to form a polyester. (3)
ONLY ONE MONOMER
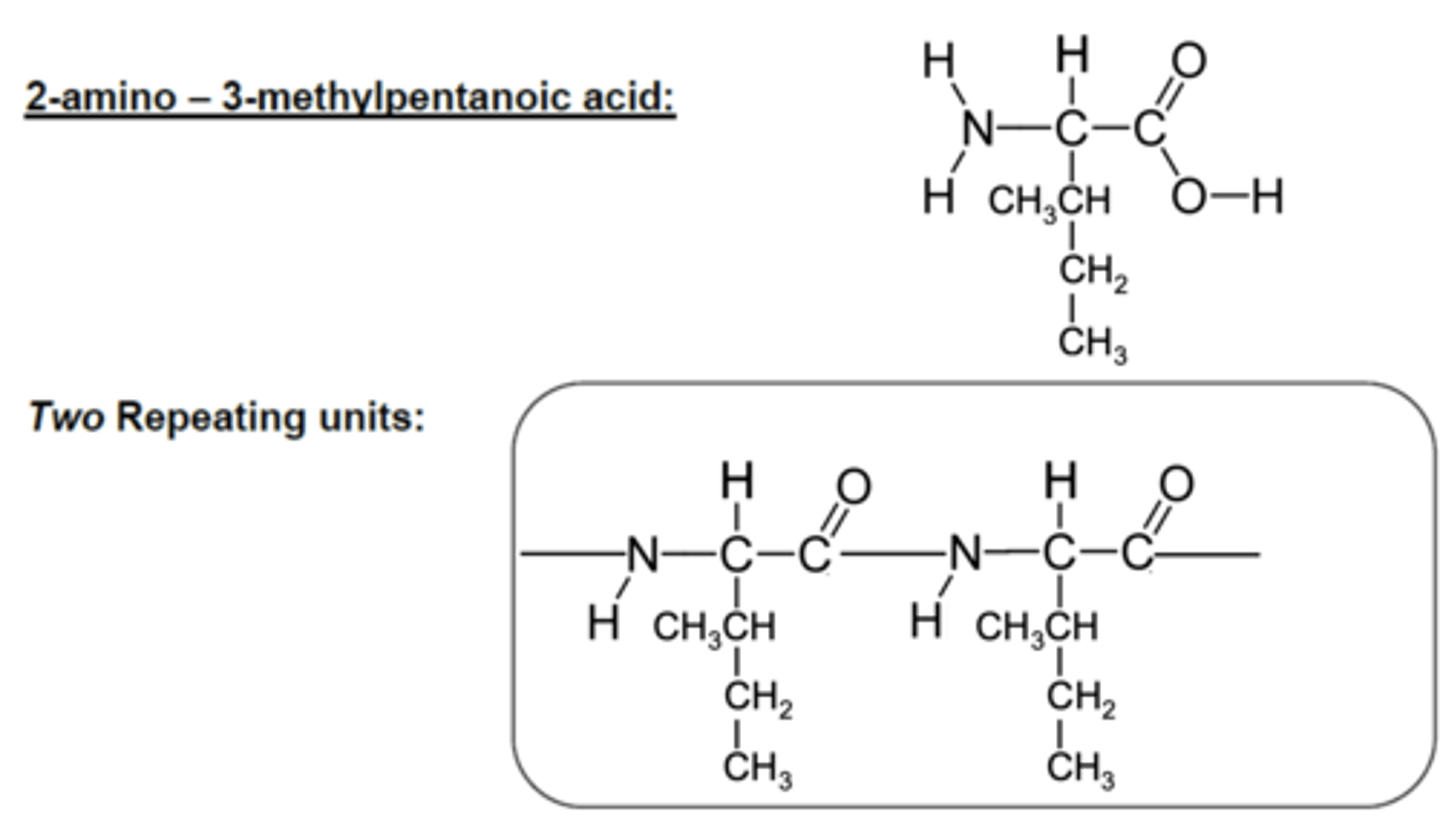
Draw the monomer unit and two repeating units of 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid used to form a polyamide. (3)
ONLY ONE MONOMER
Why are polyamides generally very strong? (2)
- Hydrogen bonding occurs both intermolecularly and intramolecularly
- Forming a helical structure
What are polyesters commonly used for? (2)
- Used as substitutes for wool and cotton
- In clothing, carpets, rugs, bullet-proof vests, and flame-retardant clothing
What are polyamides commonly used for? (1)
Used in underwear, fishing nets, and other elastic synthetic fibers
What is the key structural difference between condensation and addition polymers? (2)
- Condensation polymers contain polar bonds (C-N and C-O)
- Whereas addition polymers consist entirely of non-polar C-C bonds
Why are condensation polymers biodegradable? (2)
- Because their polar bonds (C-N and C-O) can be readily attacked by nucleophiles
- Breaking the polymer into monomers
Why are addition polymers non-biodegradable? (2)
- They consist entirely of non-polar C-C bonds
- Which are resistant to chemical attack
What is one advantage of recycling polymers related to resource use? (2)
- Recycling polymers saves using crude oil, a non-renewable resource
- As well as the energy required to refine it
What is one advantage of recycling polymers related to waste management? (1)
Recycling polymers prevents them from ending up in landfill sites
What is a disadvantage of recycling polymers related to the process? (2)
- Recycling polymers requires collection, transportation, and sorting
- Which uses energy, manpower, and is expensive