Musculoskeletal System Assessment Techniques
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Musculoskeletal System (MSK)
Structural components of the body including muscles and bones.
Screening MS Exam
Quick assessment of overall musculoskeletal structure.
Comprehensive MS Exam
Detailed examination typically performed by rheumatologists.
Regional MS Exam
Focused evaluation of specific joints or structures.
Palpation
Technique using pressure to identify musculoskeletal abnormalities.
Observation
Assessing visible abnormalities in skin and musculoskeletal components.
Range of Motion (ROM)
Measurement of joint movement, can be active or passive.
Active ROM
Patient-initiated movement to assess joint function.
Passive ROM
Examiner-initiated movement to evaluate joint flexibility.
Goniometer
Instrument used to measure joint angles and ROM.
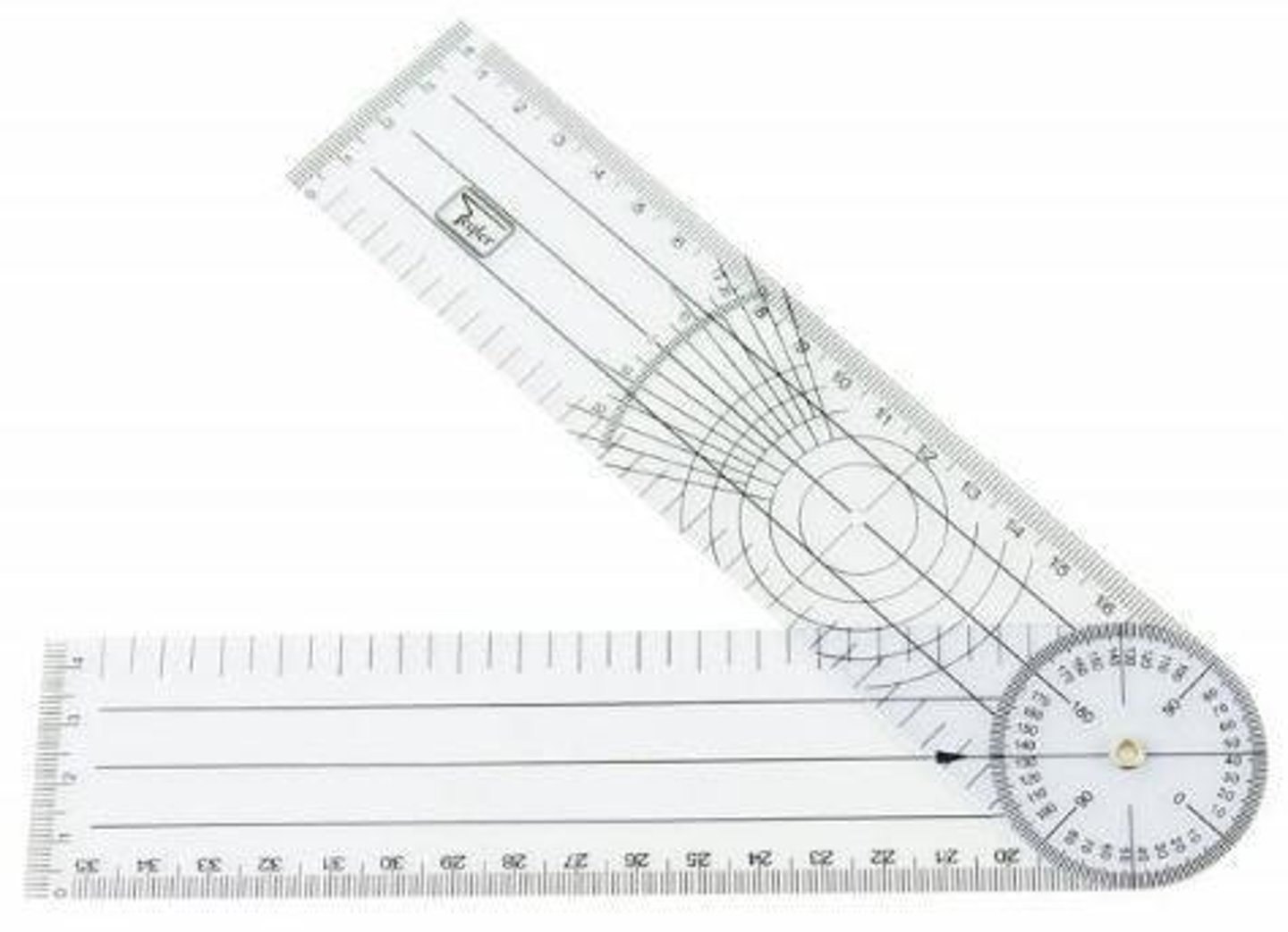
Skin-Marking Pencil
Tool for marking anatomical landmarks during examination.
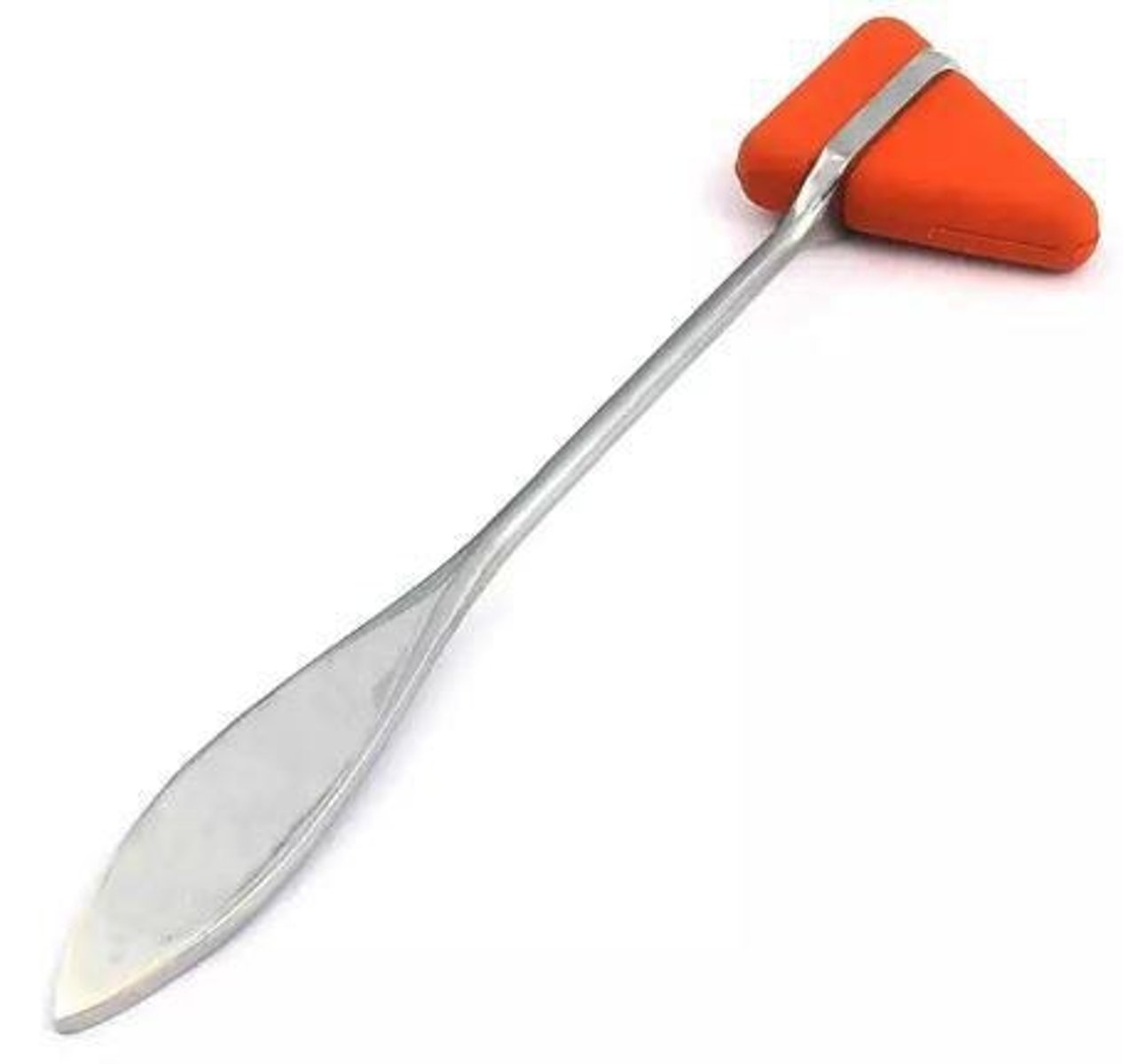
Reflex Hammer
Device used to test deep tendon reflexes.

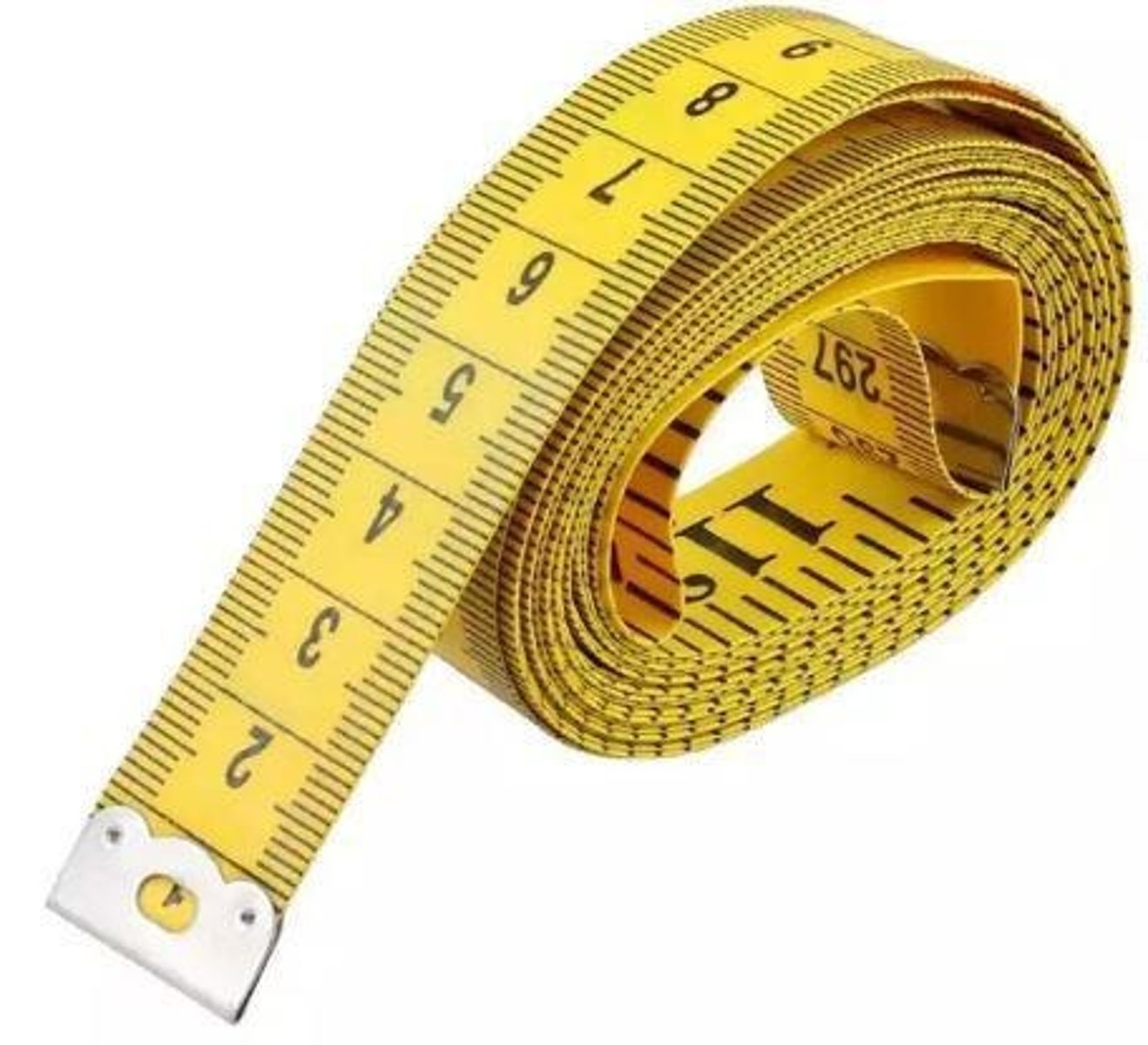
Tape Measure
Used to measure distances and dimensions during assessment.

Gait Analysis
Evaluation of walking patterns and locomotion functions.
Trigger Points
Sensitive areas in muscles indicating myofascial pain.
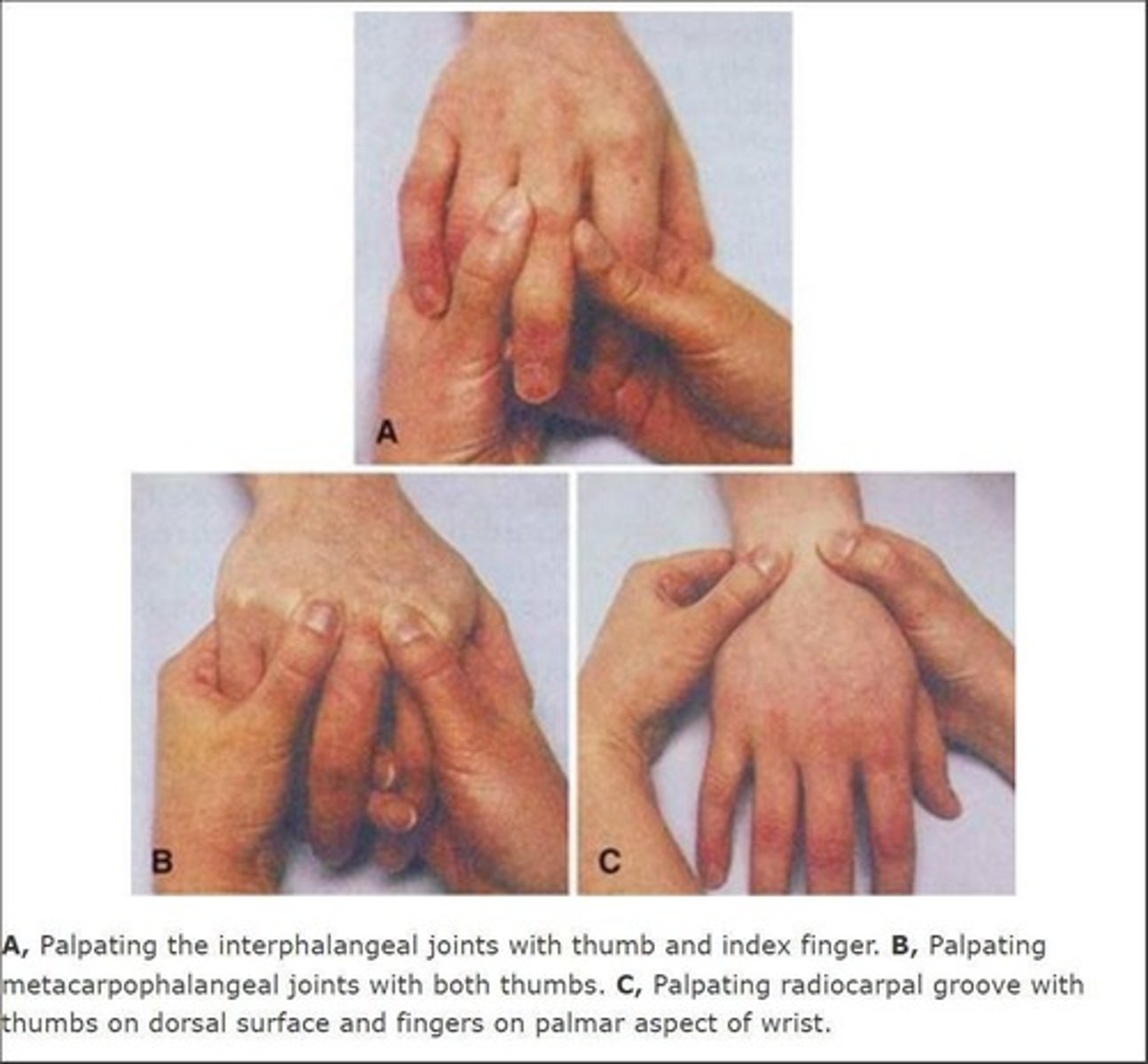
Symmetry/Asymmetry
Comparison of body parts for balanced development.
Muscle Atrophy
Decrease in muscle mass due to disuse or disease.
Kyphosis
Abnormal curvature of the spine, hunchback appearance.
Scoliosis
Lateral curvature of the spine, often in adolescents.
Drawer Sign
Test for knee ligament stability during examination.
Pediatric Variations
Changes in musculoskeletal findings during growth stages.
Subjective Documentation
Patient-reported symptoms and history during assessment.
Objective Documentation
Clinician-observed findings during physical examination.