Dean, Pollard (2001): Application of Demand-Control Theory to Sign Language Interpreting: Implications for Stress and Interpreter Training
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Demand-control theory (Karasek, 1979)
two phenomenon are at play: demand and control, and the “strength” of each ranges from low to high
What are the demands in the interpreting profession?
linguistic
environmental
interpersonal
intrapersonal
Decision latitude
control
CTD
Cumulative trauma disorder
Workplace (occupational) stress is linked to
injury
disease
absenteeism
low productivity
Physical environment changes meant to help reduce stress at work
noise reduction barries
ergonomic seating and keyboards
glare-reducing lights
open space in office buildins
Employee-focused changes meant to help reduce stress at work
“brown bag” seminars on nutrition and stress reduction
gym membership discounts
on-site gyms
on-site daycare
interactional viewpoint
the individual and the work environment are both considered in the definition of the problem and potential solutions (interventions)
Who developed demand-control model?
Robert Karasek (1979) in collaboration with Tores Theorell
Demand
requirements of a job
environment
actual task being performed
other factors that “act upon” the person
Control
the degree to which the person has the power to “act upon” the demands
make decisions
using skills/resources relevant to task
altering the environment
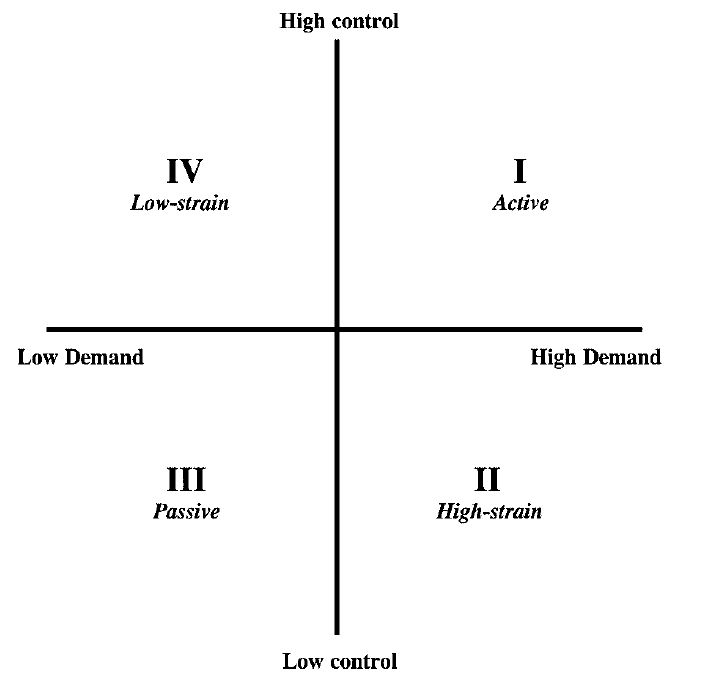
Quadrant 1: Active
High demand, high control
well trained nurse who can adequately respond to job demands
Quadrant 2: High-strain
high degree of demands, limited control of demands
factory worker with little control over the pace of the assembly line
Quadrant 4: low-strain
high control, low demand
college professor proctoring a final exam
Quadrant 3: Passive
low demand, low control
assembling fast-food hamburgers at a dead restaurant
What are two prominent factors cited in interpreter stress and burnout?
inadequate training for working in the real world
lack of professional support after graduation
Role strain
static, restrictive nature of the interpreter’s role
Role strain comes from
working conditions
unattainable high performance expectations
conflicting views among understanding of interpreter’s role
no outlet for emotional reactions and duress
limited ability to help consumers
real or perceived skill inadequacies
CTD examples
carpal-tunnel syndrome
tendinitis
bursitis
Psychological CTD prevention
self-exploration
constructive thinking
reflection
venting
prayer
Linguistic demand
directly or indirectly related to language
language fluency of parties involved
clarity in articulation
interpreter’s own knowledge and fluency in each language
Environmental demand
factors related to the setting in which the interpreting assignment takes place
interpersonal deman
factors related to the interaction of individuals participating in the communication process and other parties present
intrapersonal demand
physical and psychological factors pertaining to the interpreter alone1.
What are the 3 challenges in applying the demand-control model to interpreting?
identifying the demands interpreters face
recognizing the simultaneous contribution of demands from each of the 4 categories to the total degree of demand experienced
recognize the shift in demands that can happen from assignment to assignment or even within one single assignment
Even if Q1 is intense, it is often considered worthwhile because it stimulates
learning
Demands and control have
a relationship
Job control components
skills/resources
decision authority
In a profession, decision latitude is determined by
education and experience
freedoms attributed to that role by society
professional code of conduct
Which quadrant is most preferred and associated with less psycho physiological risk
Q1: Active
This paper indirectly argues that interpreting is in what quadrant?
High demand, low control - Q2: High-Strain
What are two factors currently contributing to illness, injury (CTD), high turnover, and burnout rates in the interpreting profession?
lack of decision latitude (perception and in CPC)
lack of other control resources
formally sanctioned, confidential supervision
There is a positive correlation between higher job satisfaction and
more training and effective supervision
This paper argues for
extended supervised training periods after graduate (like in medical and legal professions)
problem-based learning approaches
emphasizes early student exposure to practice challenges with real consumers and merges acquisition of knowledge with developing professional practice and judgement skills WITH seasoned teachers/mentors
competency-based education
knowledge is demonstrated in “real-world setting” over a period of time
frequent feedback
immediate opportunity to incorporate feedback in real practice