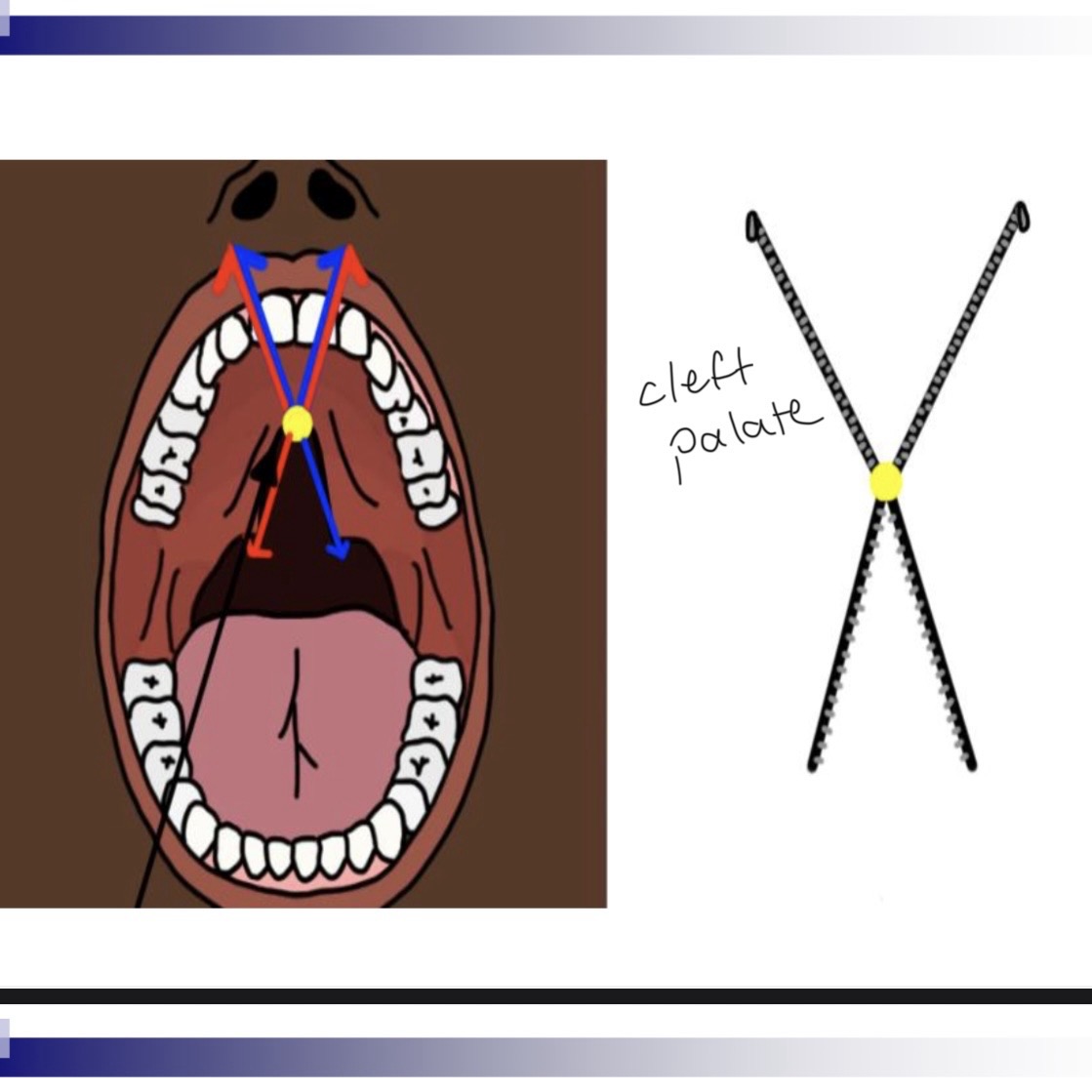
cleft palate
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Label

Label
What types of sounds might be easier for those with cleft palate/lip
Liquids and glides
What type of speech do those with cleft palate have
Distorted speech
Why do those with cleft palate have distorted speech
Bc air is escaping through the nostrils
What types of sounds will be easy for those with cleft palate
Nasals
Babies with cleft palate where will their feeding go
Up their nose
Label
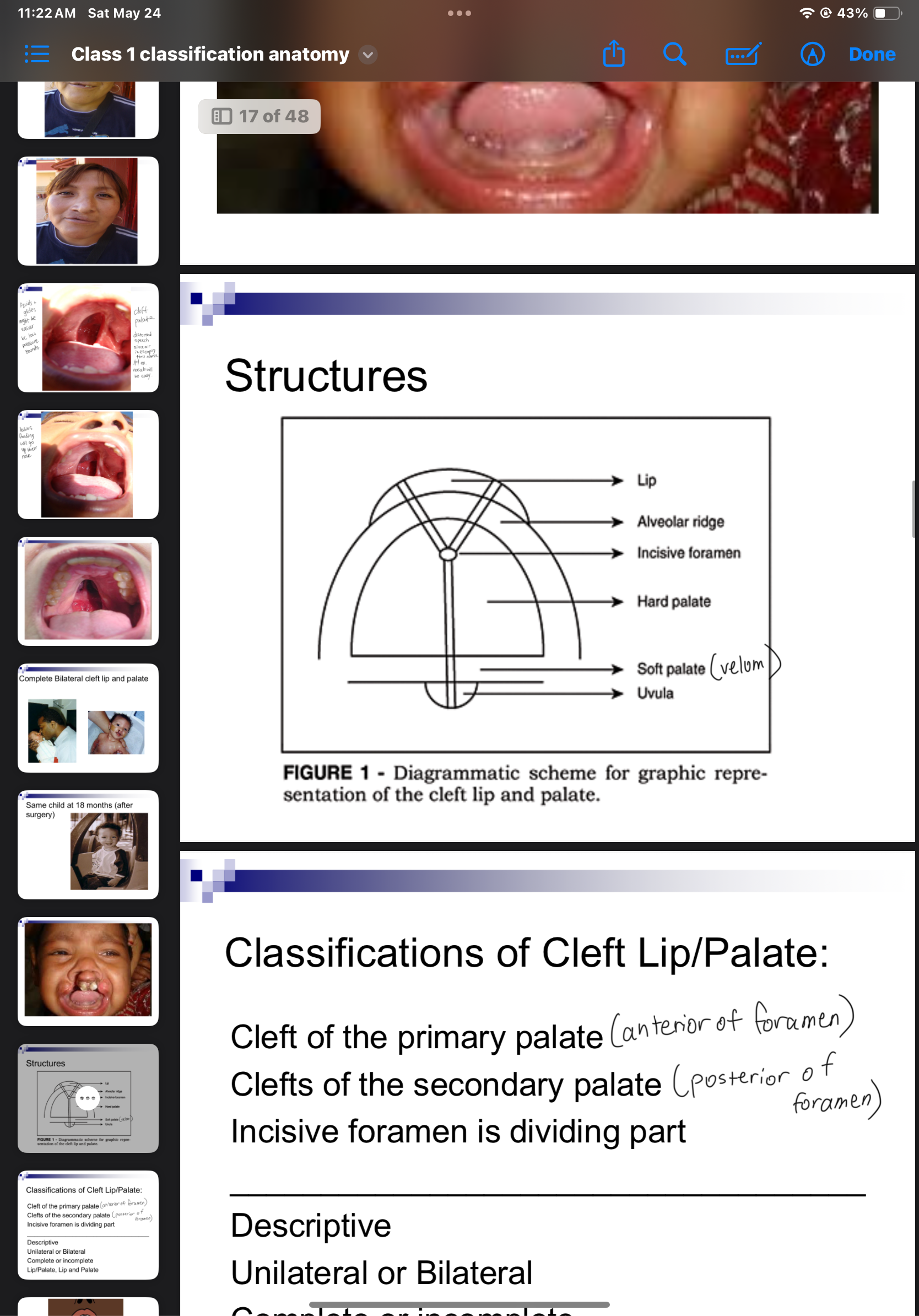
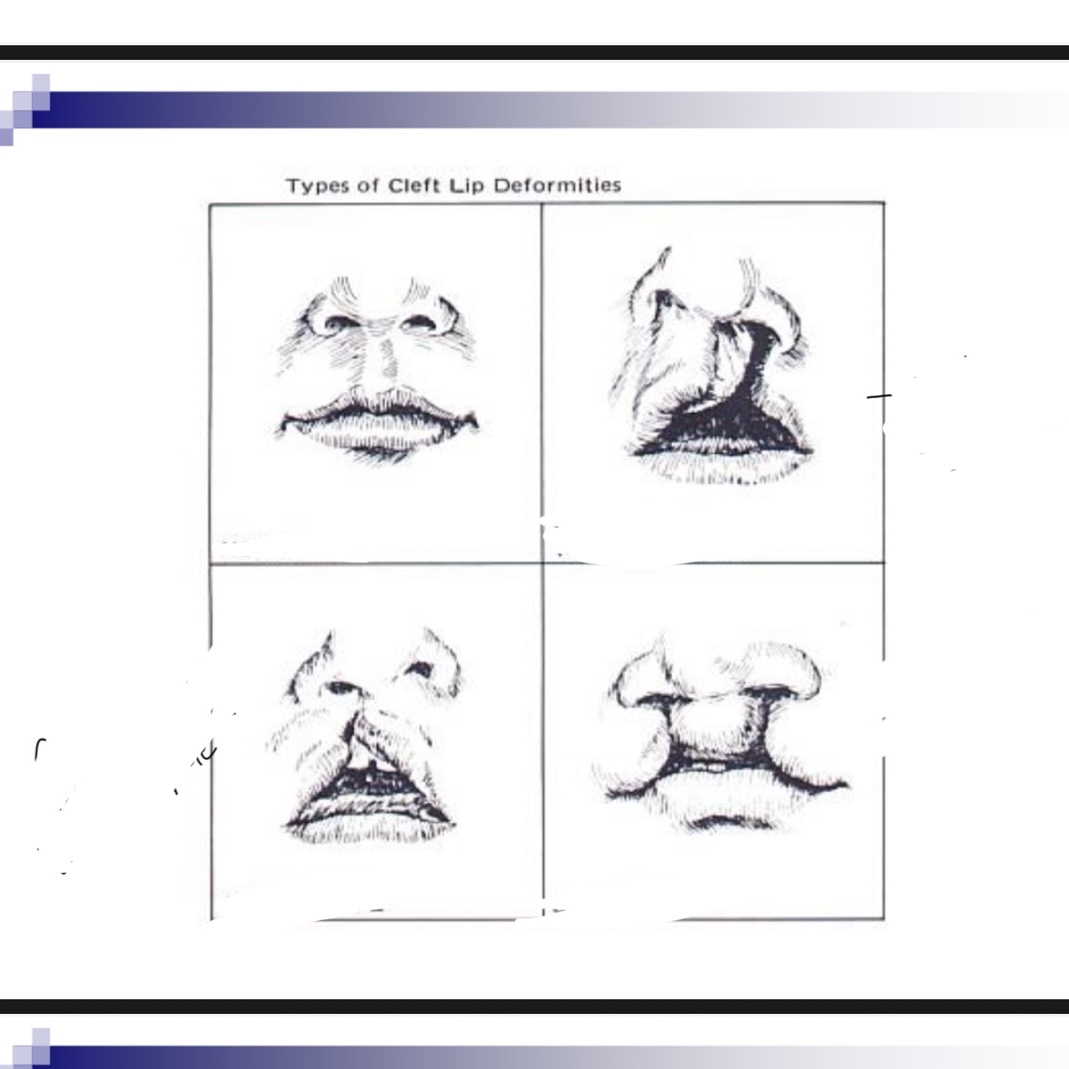
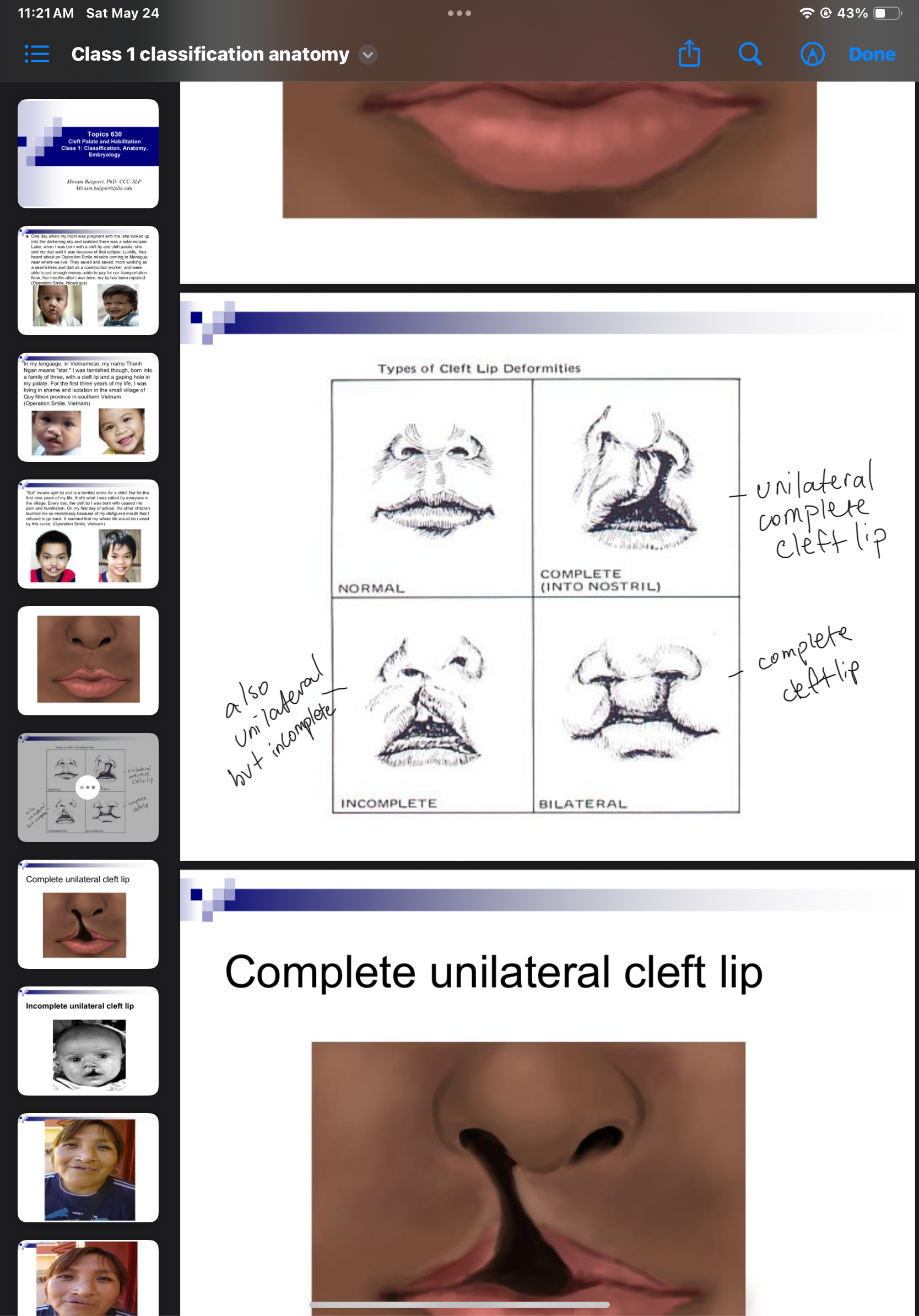
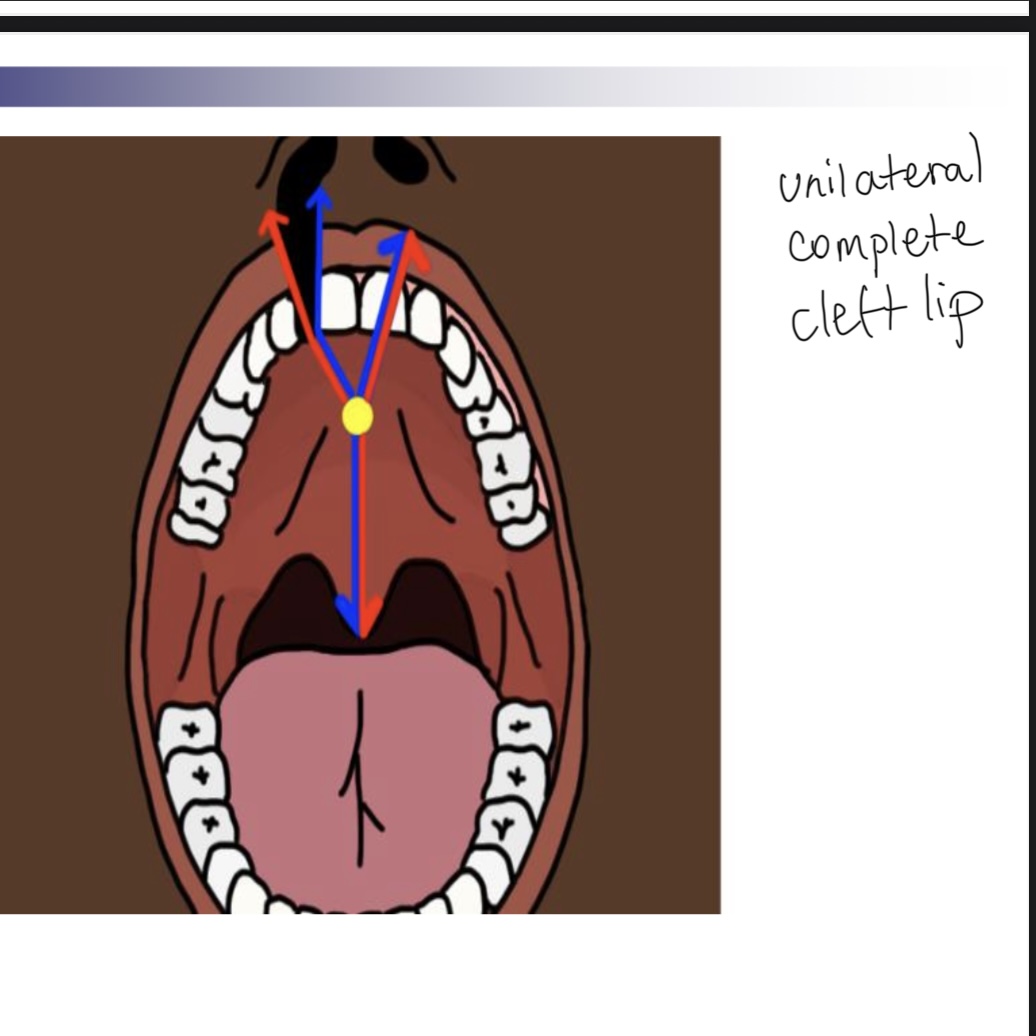
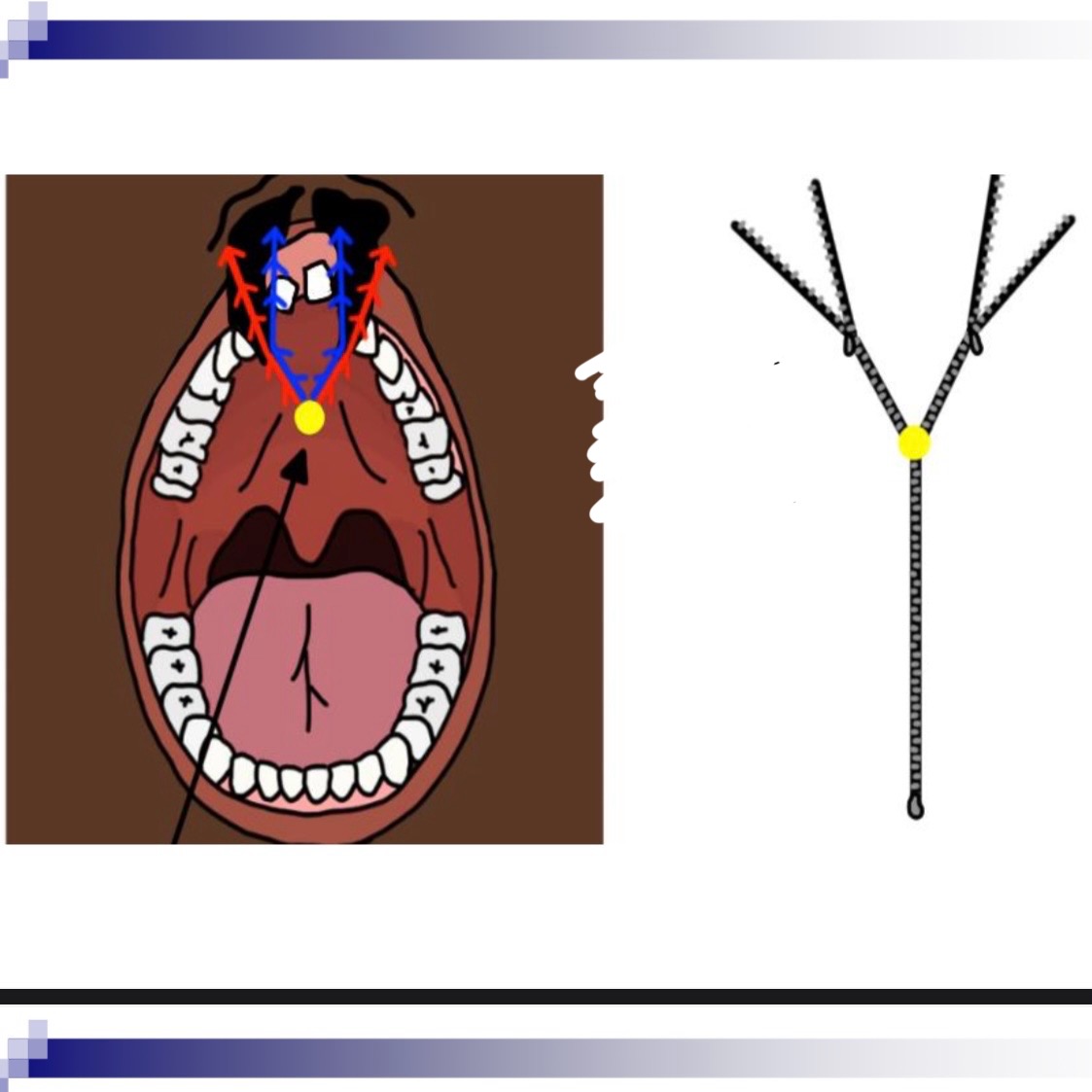
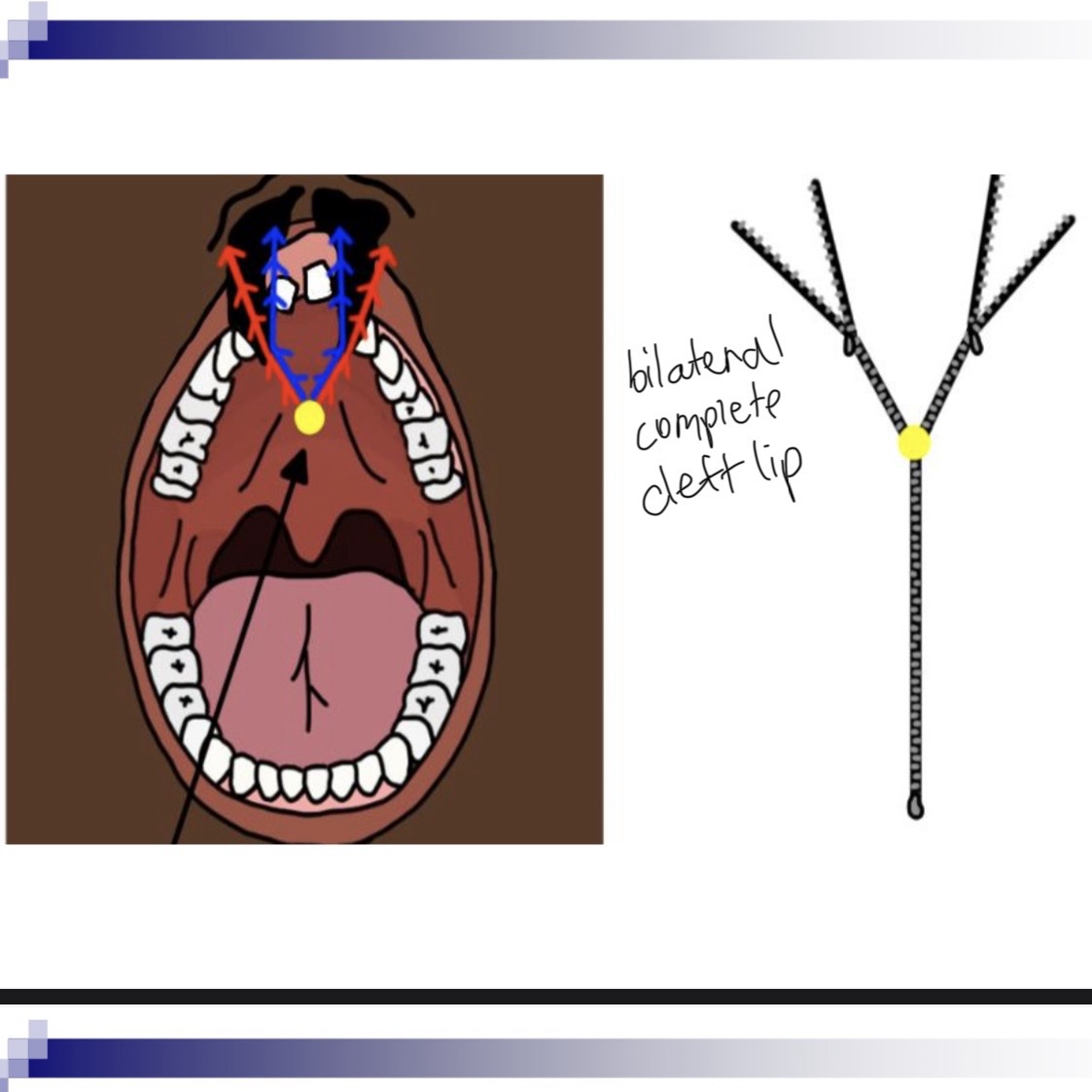
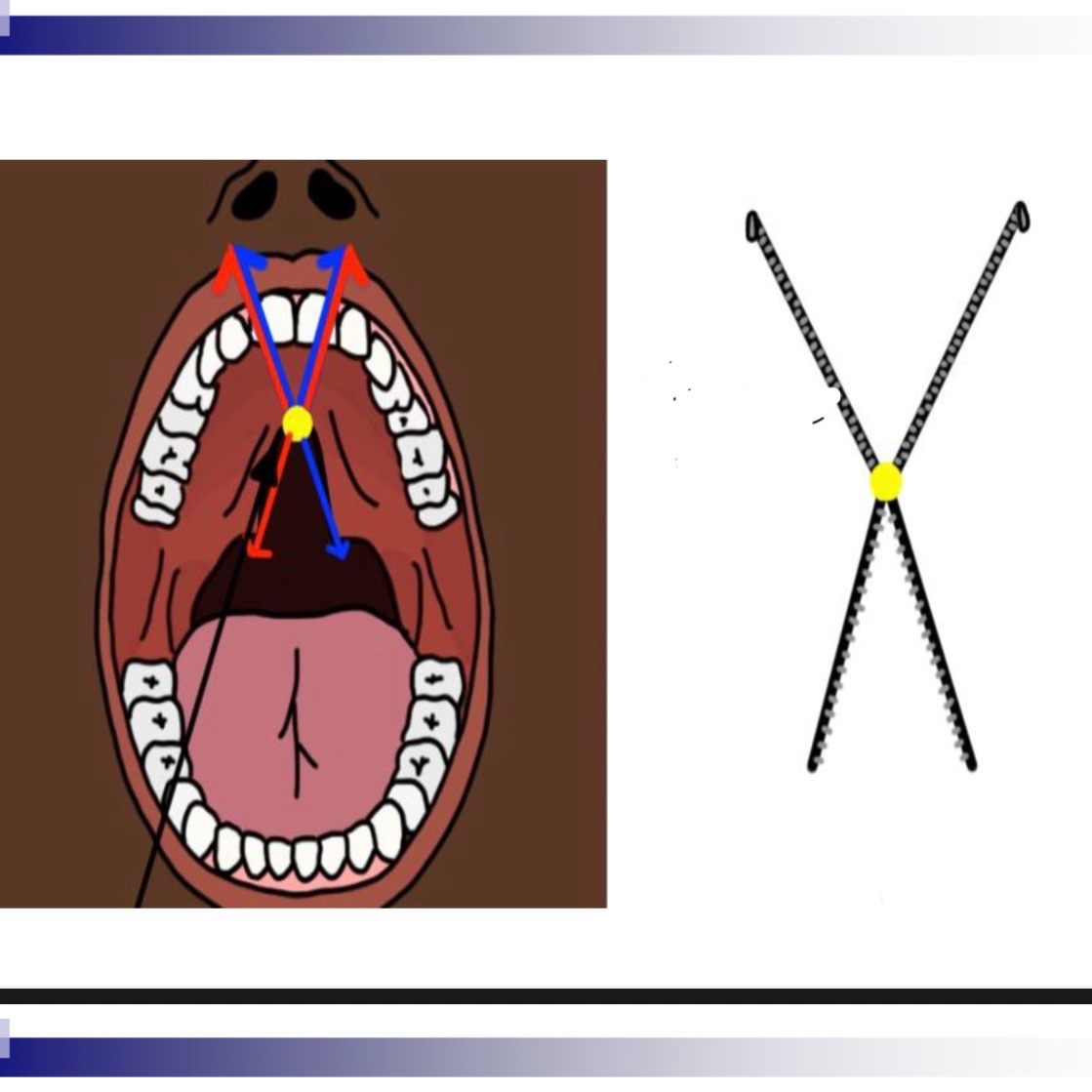
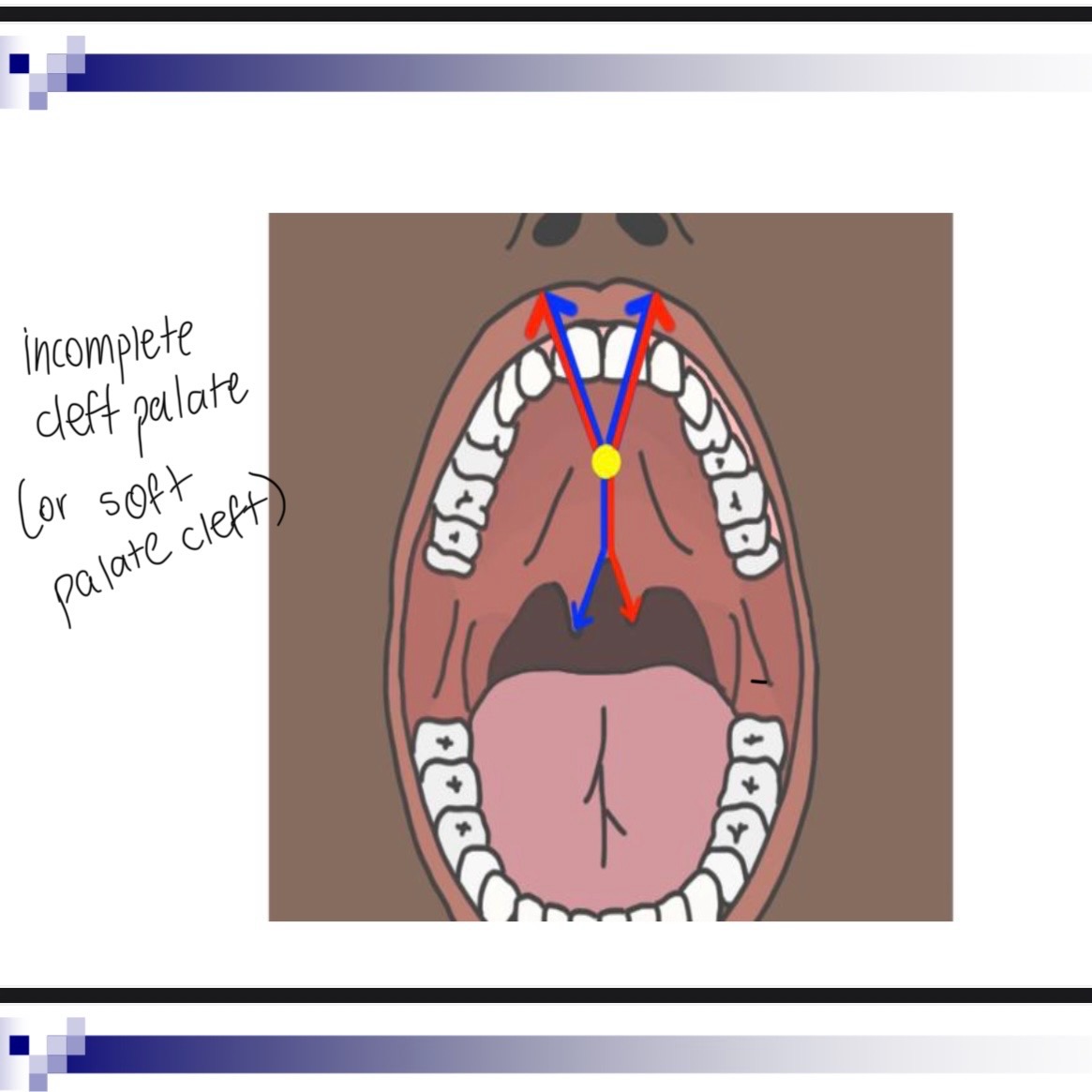
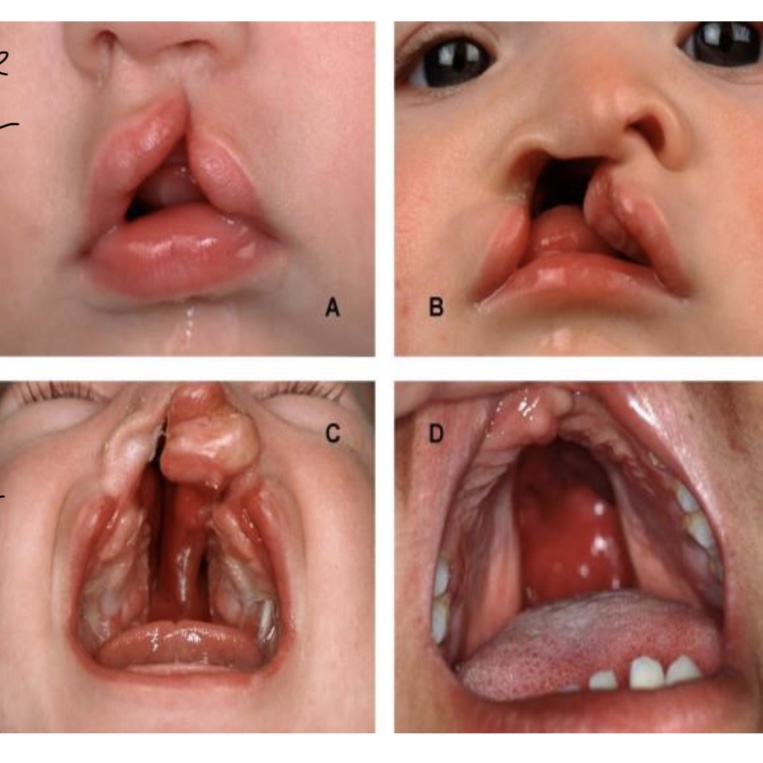
3 classifications of cleft lip/palafe
Cleft of the primary palate (anterior of foramen)
Clefts of the secondary palate (posterior of foramen)
Incisive foramen is dividing apart
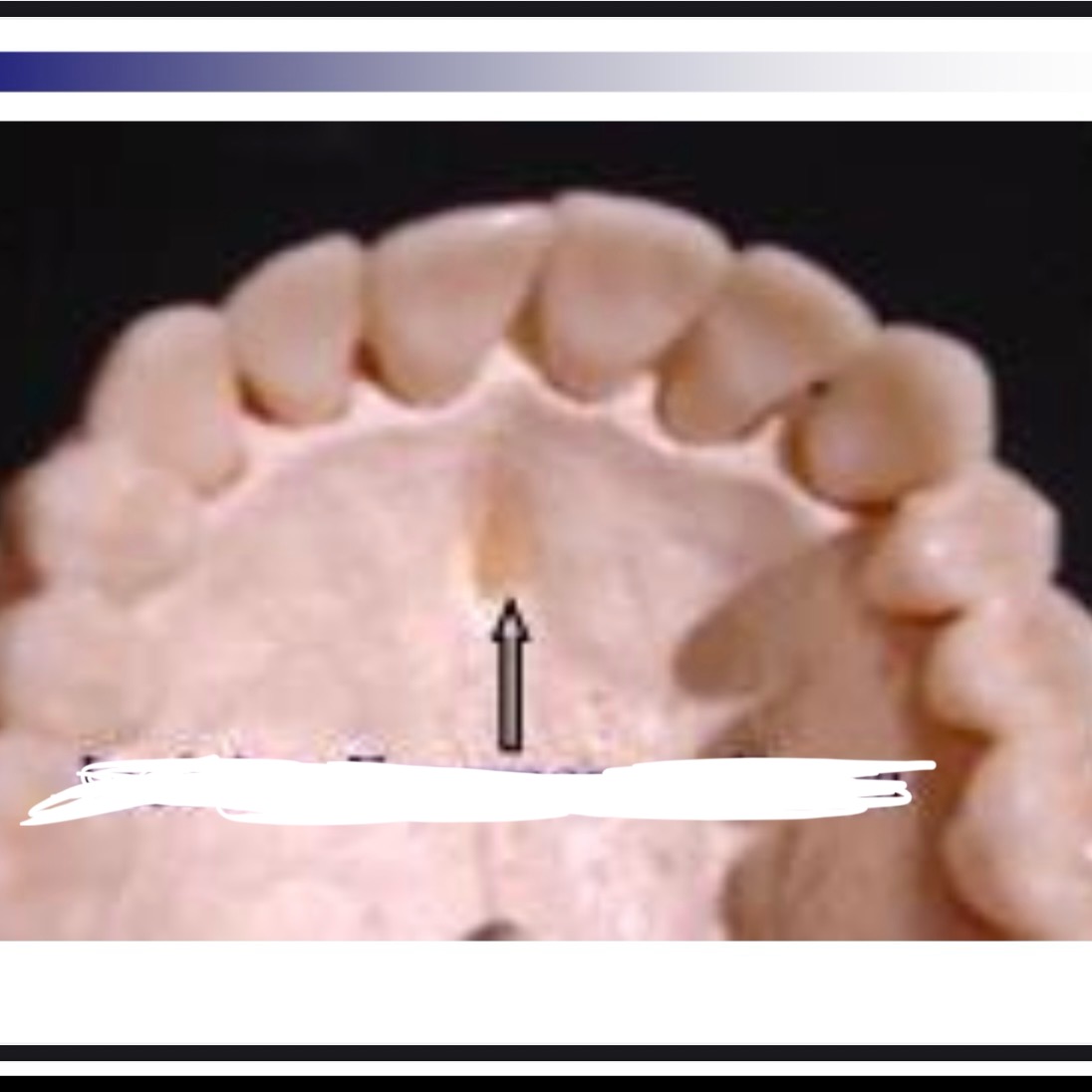
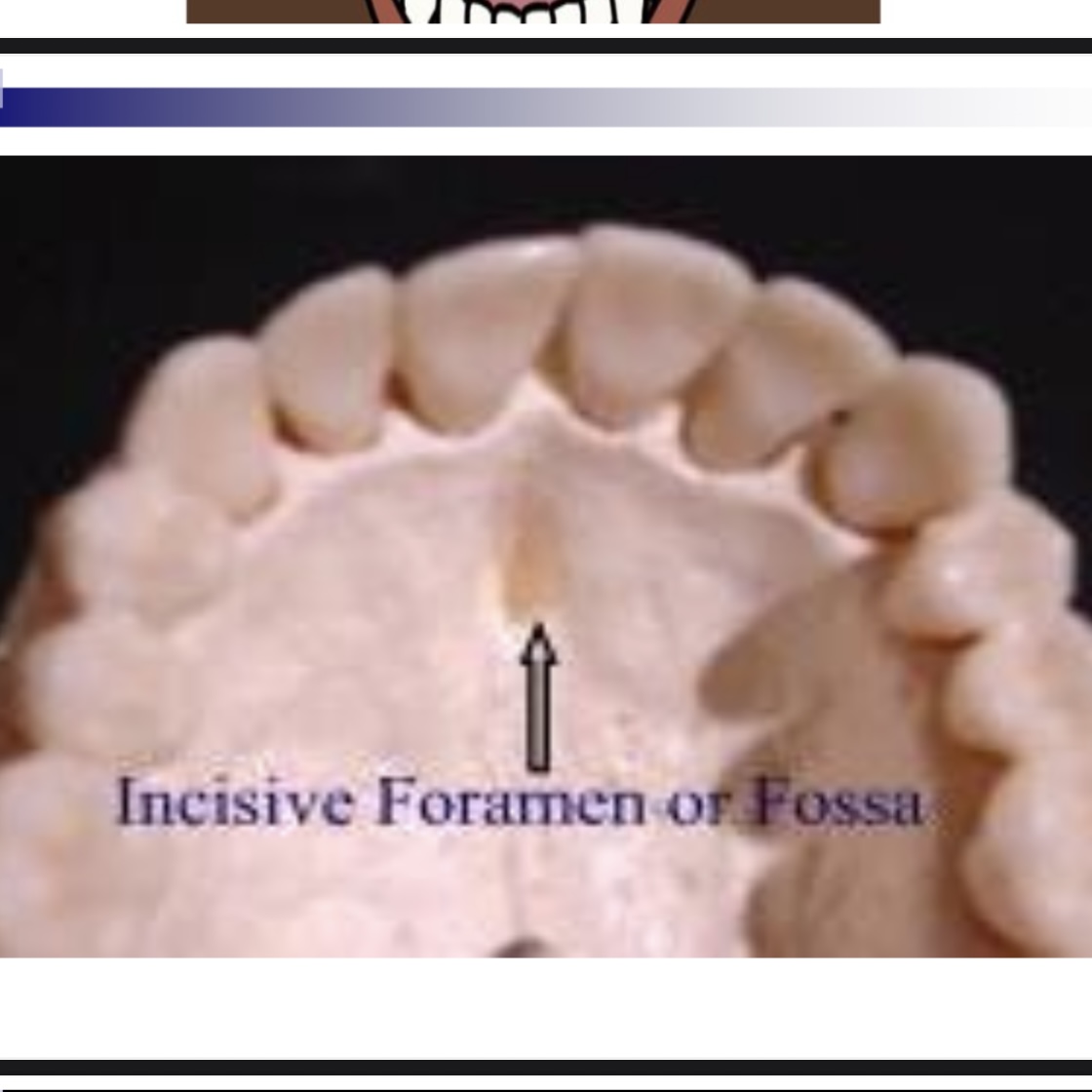
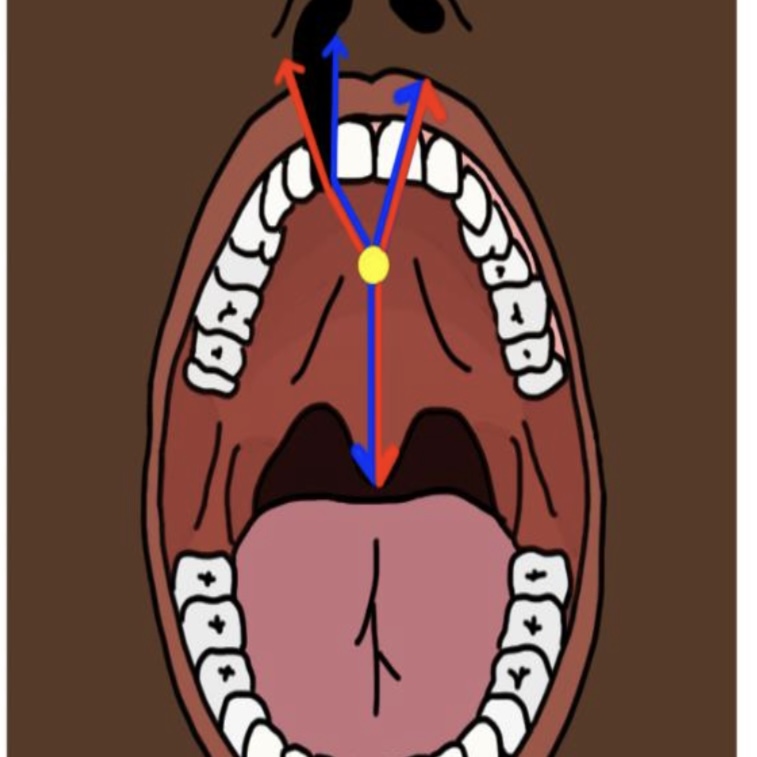

How might cleft palate affect phonation
Usually would not be affected but level of vocal folds can be damaged bc of a lot of glottal stops. Could sound hoarse and breathy
How might cleft palate affect resonance
Hyper nasal bc everything comes out of nose
How might cleft palate affect articulation
High pressure sounds will be difficult
/m/ /n/ sounds easy or hard for cleft palate
Easy
/p/ /b/ /t/ /d/ /k/ /g/ /f/ /v/ how will these be easy or hard for cleft palate
Hard
/h/ /l/ /r/ easy or hard cleft palate
Could be way
/s/ /z/ th sh easy or hard for cleft palate
Hard

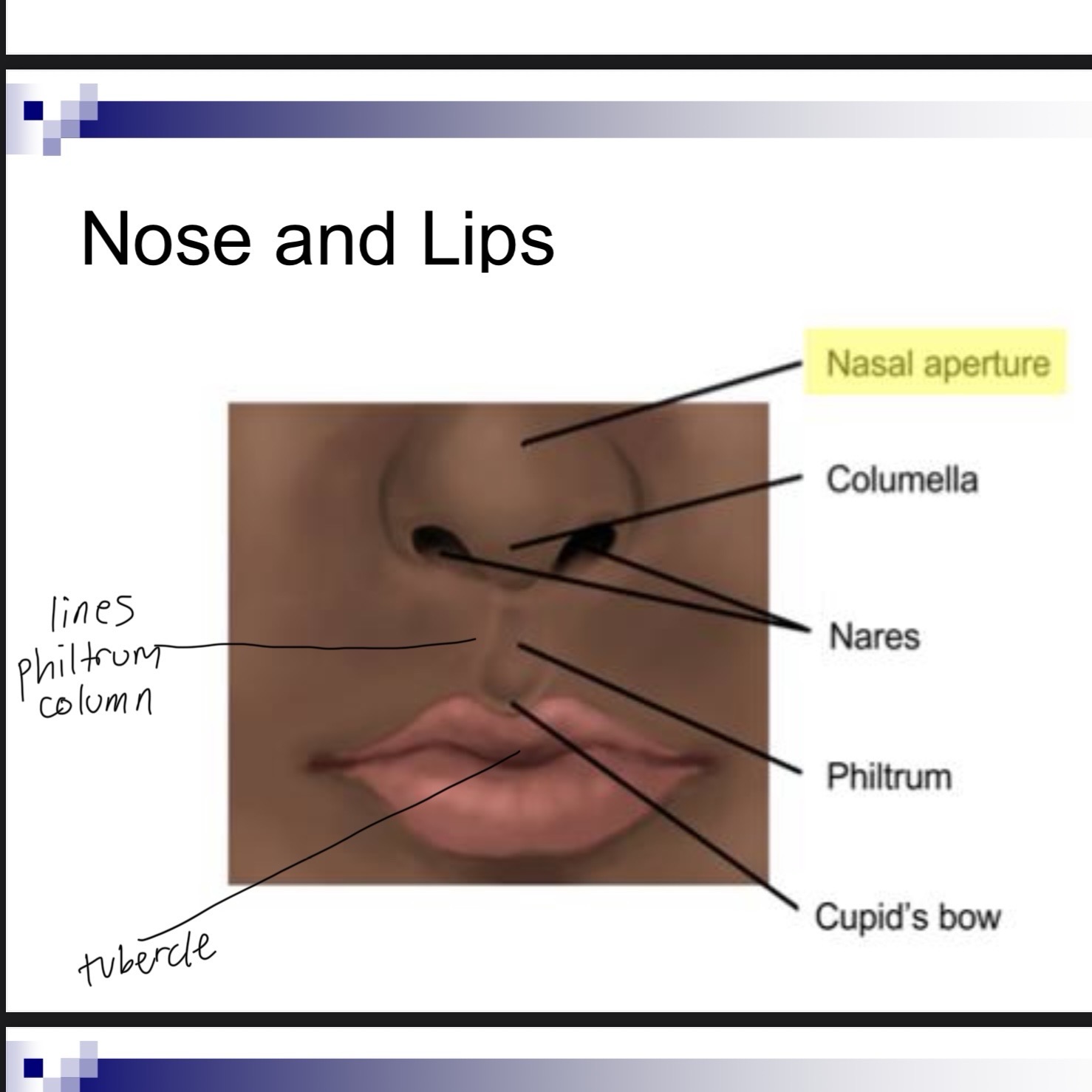
Vermillion in lips is
Color of lips
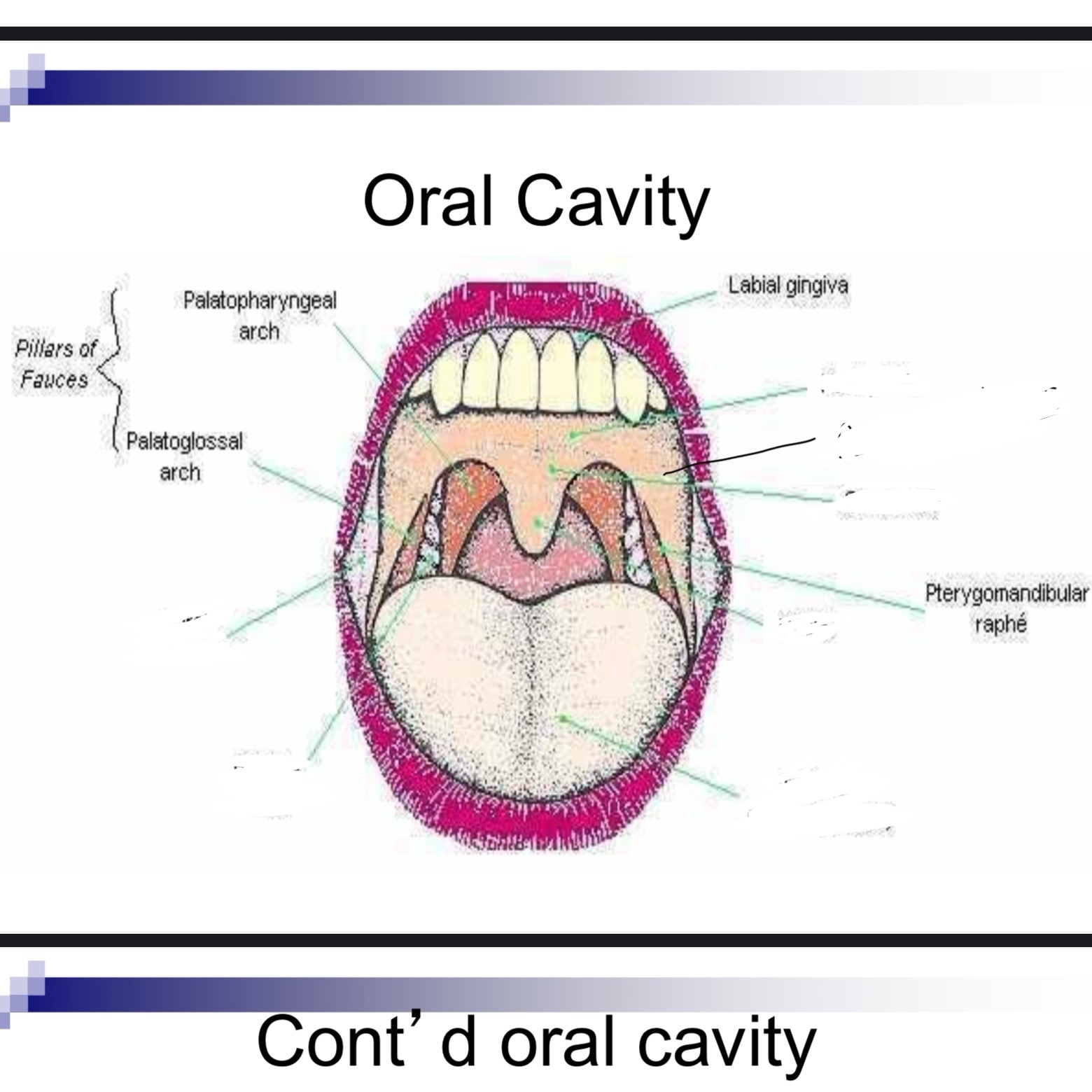
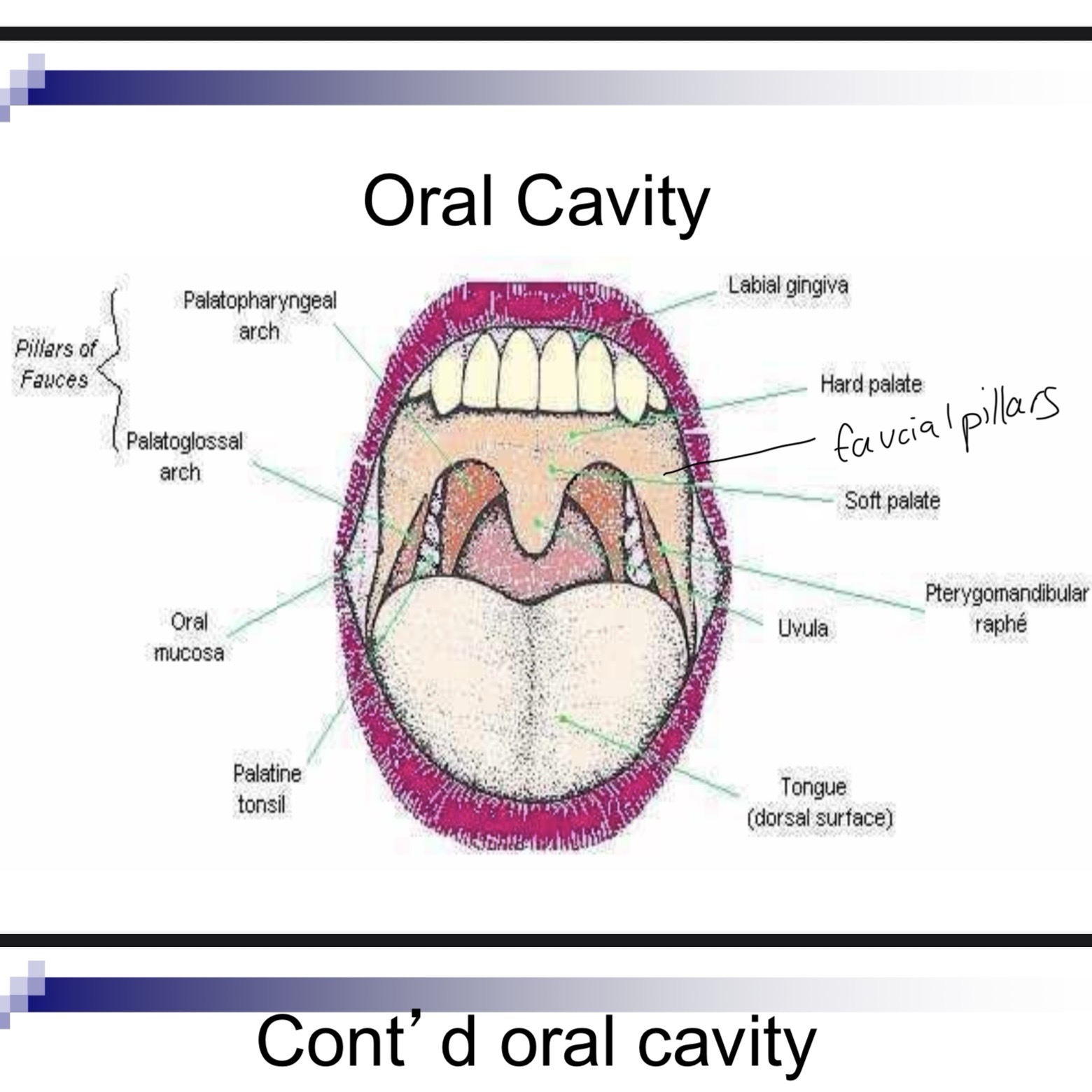
Faucial pillars
Curtain like structures that assist in velopharyngeal and lingual movement
Palatine tonsils
Between anterior and posterior faucial pillars
Lingual tonsils
Lymphoid tissue at base of tongue and extends to epiglottis
Oropharyngeal isthmus
Opening of oral cavity to pharynx
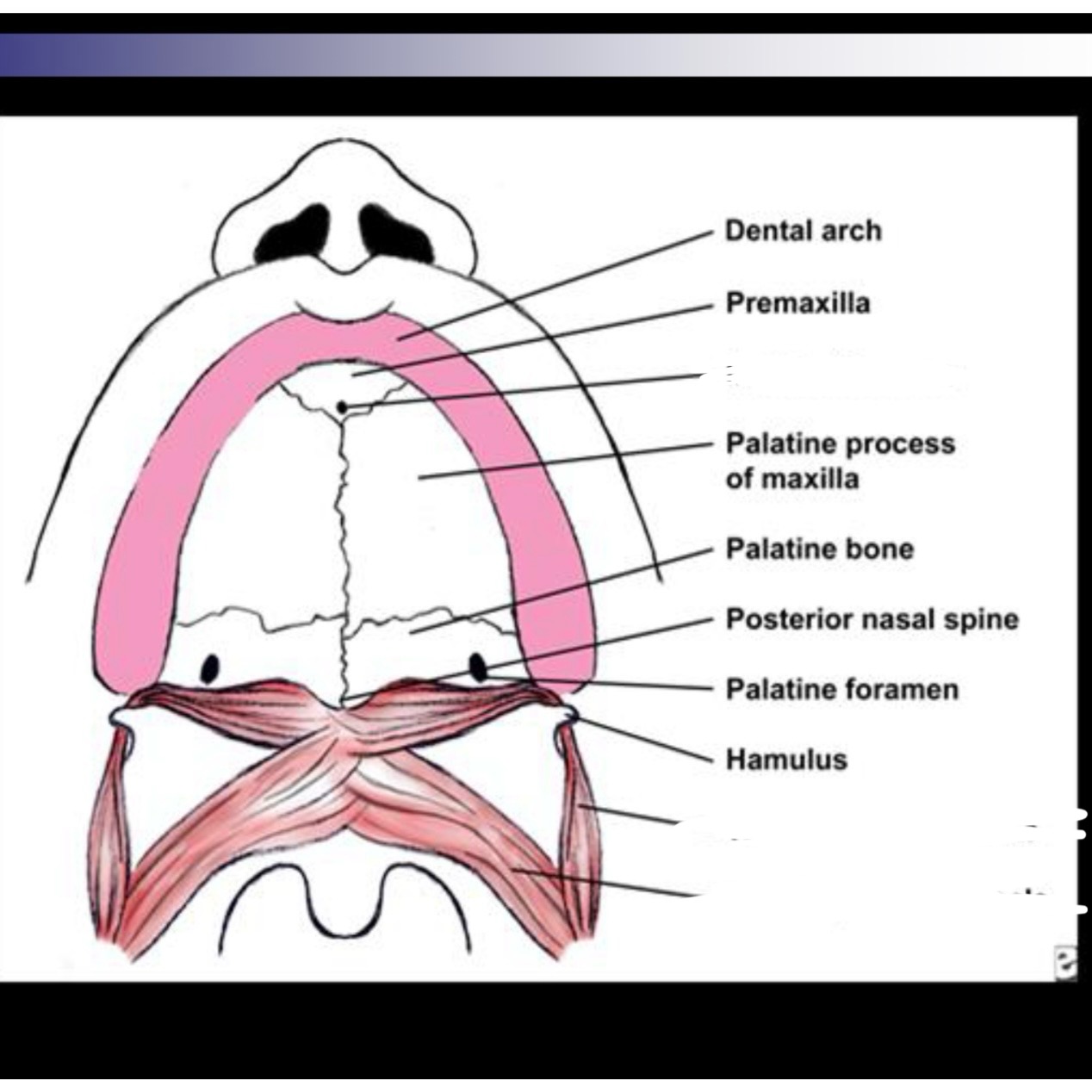
What is needed for pharyngeal closure
Movement of velum, posterior pharyngeal wall, and lateral pharyngeal wall are needed
Velar movement - nonpneumatic activities
Swallowing gagging vomiting
Velar movement - pneumatic activities
Blowing singing speech
Pharyngeal closure - lateral pharyngeal walls move
Medially
Pharyngeal closure - posterior pharyngeal wall movement
Moves anteriorly
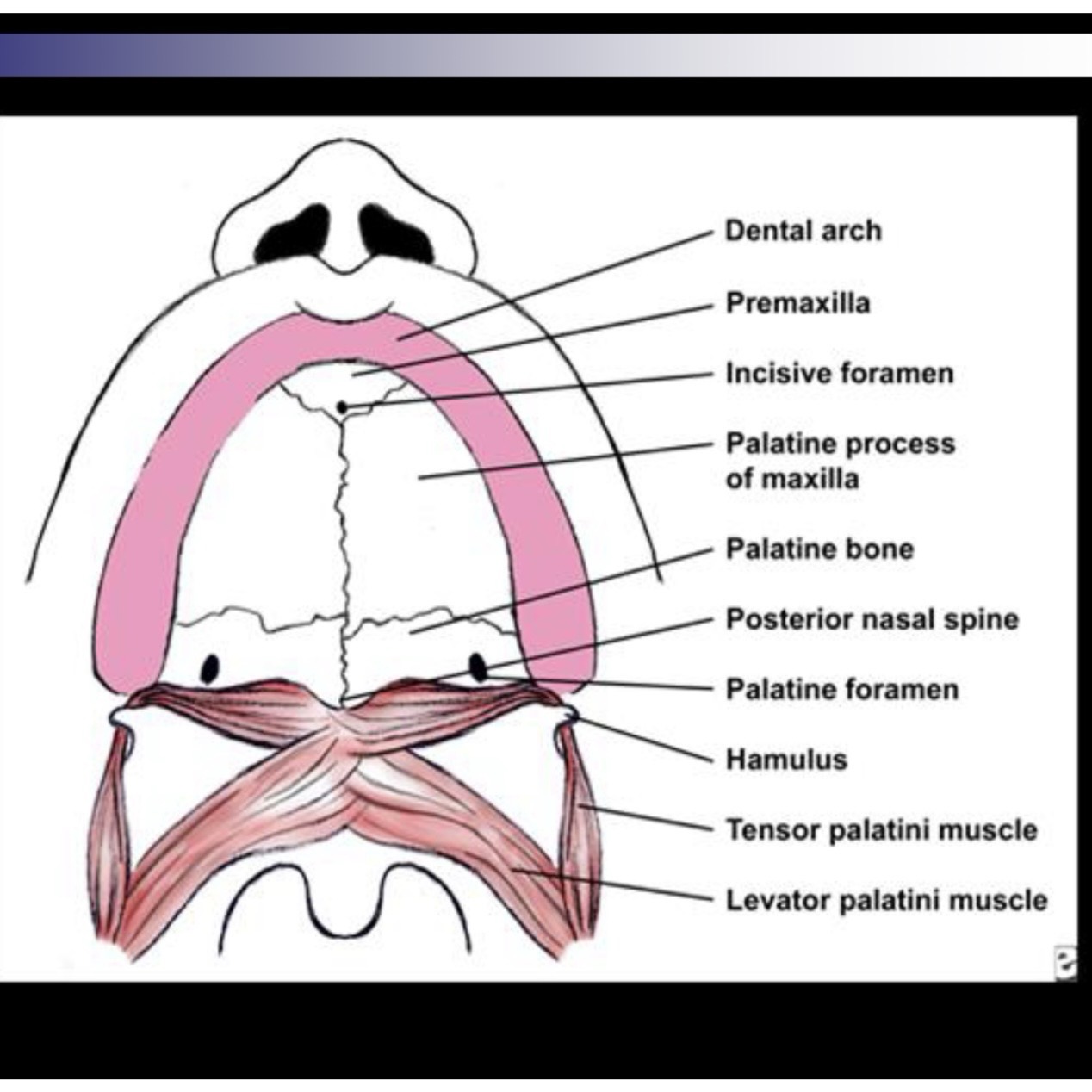
What muscles are involved in velopharyngeal closure
Levator veli palatini
Superior pharyngeal constrictor
Muscular uvulae
Palatoglossus muscles
Tensor veli palatini
Levator veli palatini
A sling. Two sides come together. Main muscle for velar elevation
Superior pharyngeal constrictor
Medial displacement of lateral pharyngeal walls
Musculus uvulae
Contracts during phonation and creates bulge on velum which adds stiffness
Palatoglossus muscles
Depresses velum
Tensor veli palatini
Opens the Eustachian tube for middle ear drainage, contributes little or nothing with velopharyngeal closure
Lips and alveolus embryological development
6-7 weeks of gestation, starts at incisive foramen
Hard palate embryological development
8-9 weeks of gestation
Velum and uvula embryological development
12 weeks gestation
Cleft lip w or w out palate African population
Approx. 1 in 2200
Cleft lip w or w out palate Caucasian
Approx. 1 in 1200
Cleft lip w or w out palate Asians
Approx. 1 in 800
Cleft lip w or w out palate Native Americans
Approx. 1 in 300
CPO incidence of clefting
Approx. same occurrence across all racial groups
Which is more common left or right cleft lip
Left
Which is more frequently occurring unilateral or bilateral cleft
Unilateral
Most cases of cleft lip are ___, that is with no associated syndromes or other birth defects.
Isolated
___ explains 20-50% of clefts
Genetics
External agents of cleft
Smoking, alcohol, too much vitamin A, drugs (Valium), retinoic acid (acne)
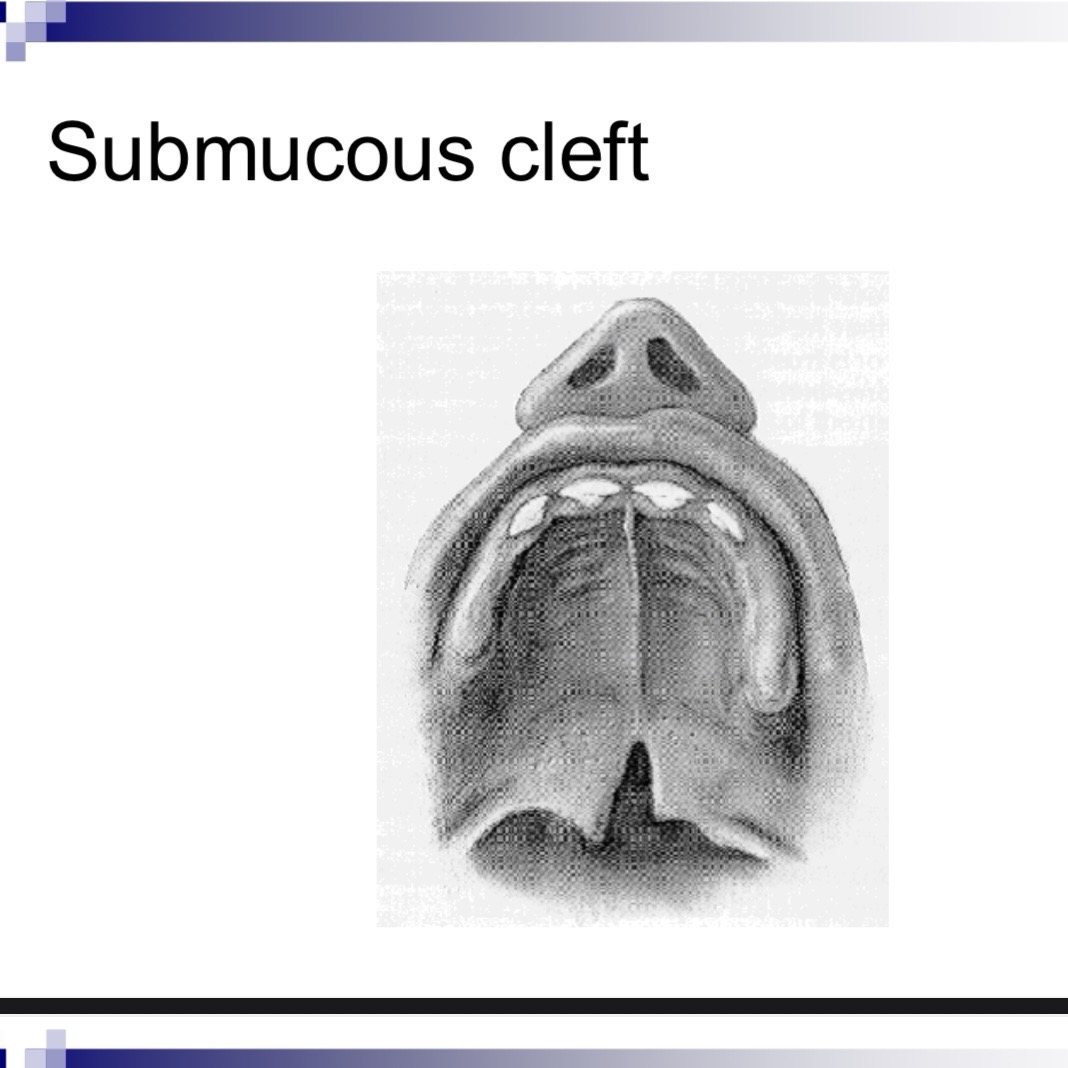
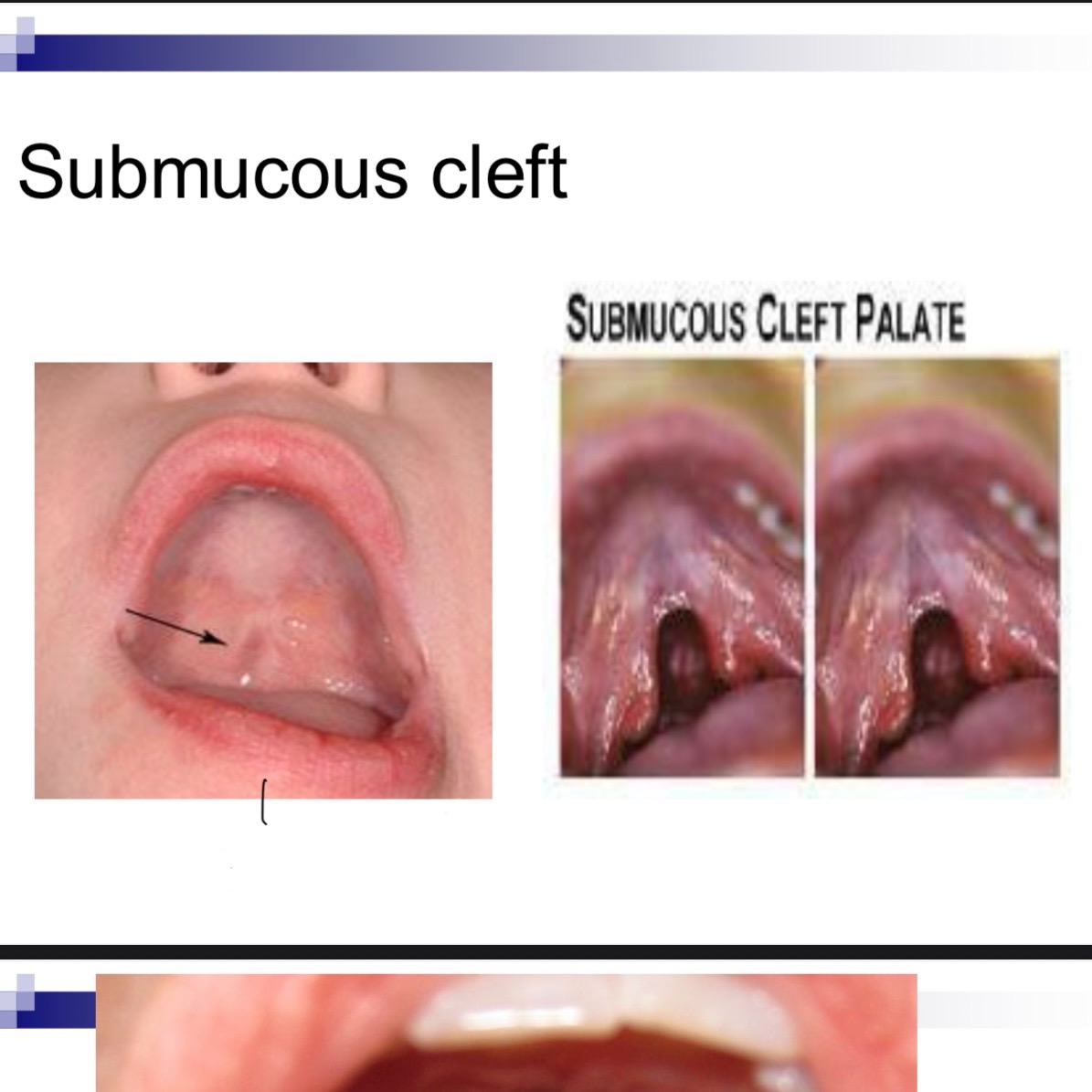
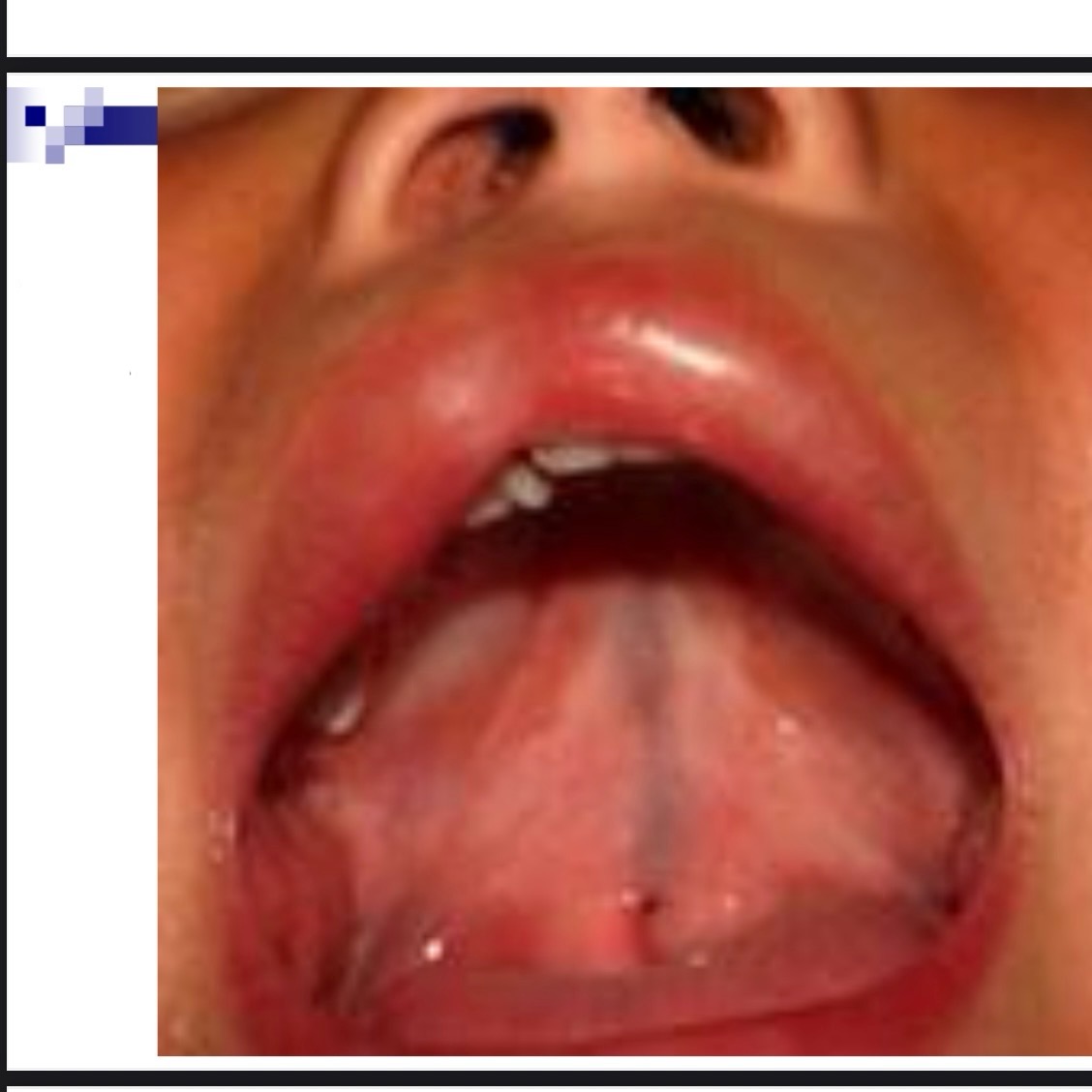
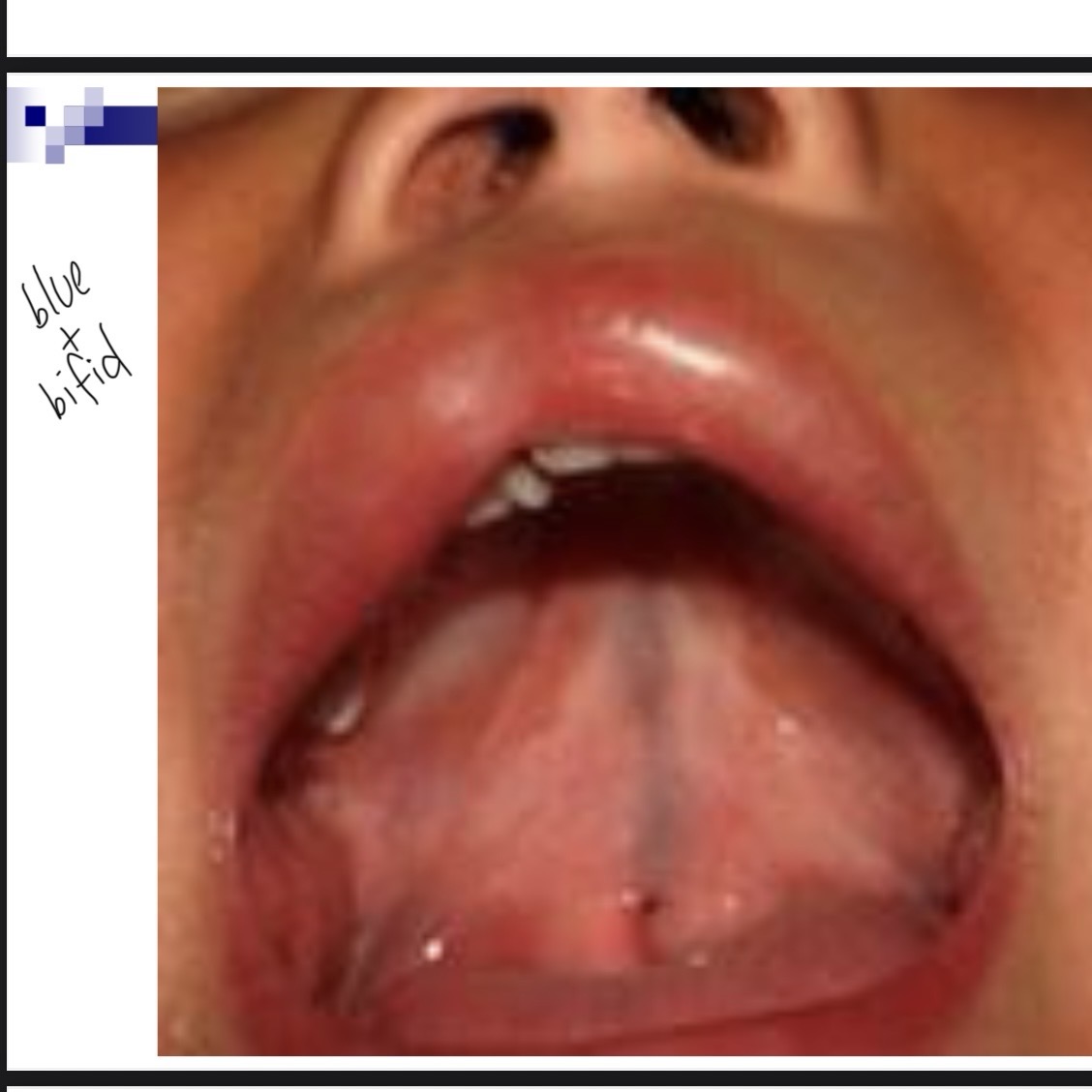
__ __ can indicate a submucous cleft
Bifid uvula
Submucous cleft palate is a congenital defect which means it
Happens at birth
Submucos cleft involved the muscles of
Of the velum and bony surfaces of hard palate
Diagnosis of submucous cleft (one or more of these)
Bifid uvula, zona pellucida (blue area in hard palate, notch in posterior border of hard palate
Bifid uvula may (4 characteristics)
May be split down middle w two pendulous structures
May appear as one structure with line down the center
May have simple indentation at posterior border
Uvula may appear small and underdeveloped-hypoplastic
Zona pellucida blue area
Bluish coloring caused by thin mucosa w lack of normal underlying muscle mass
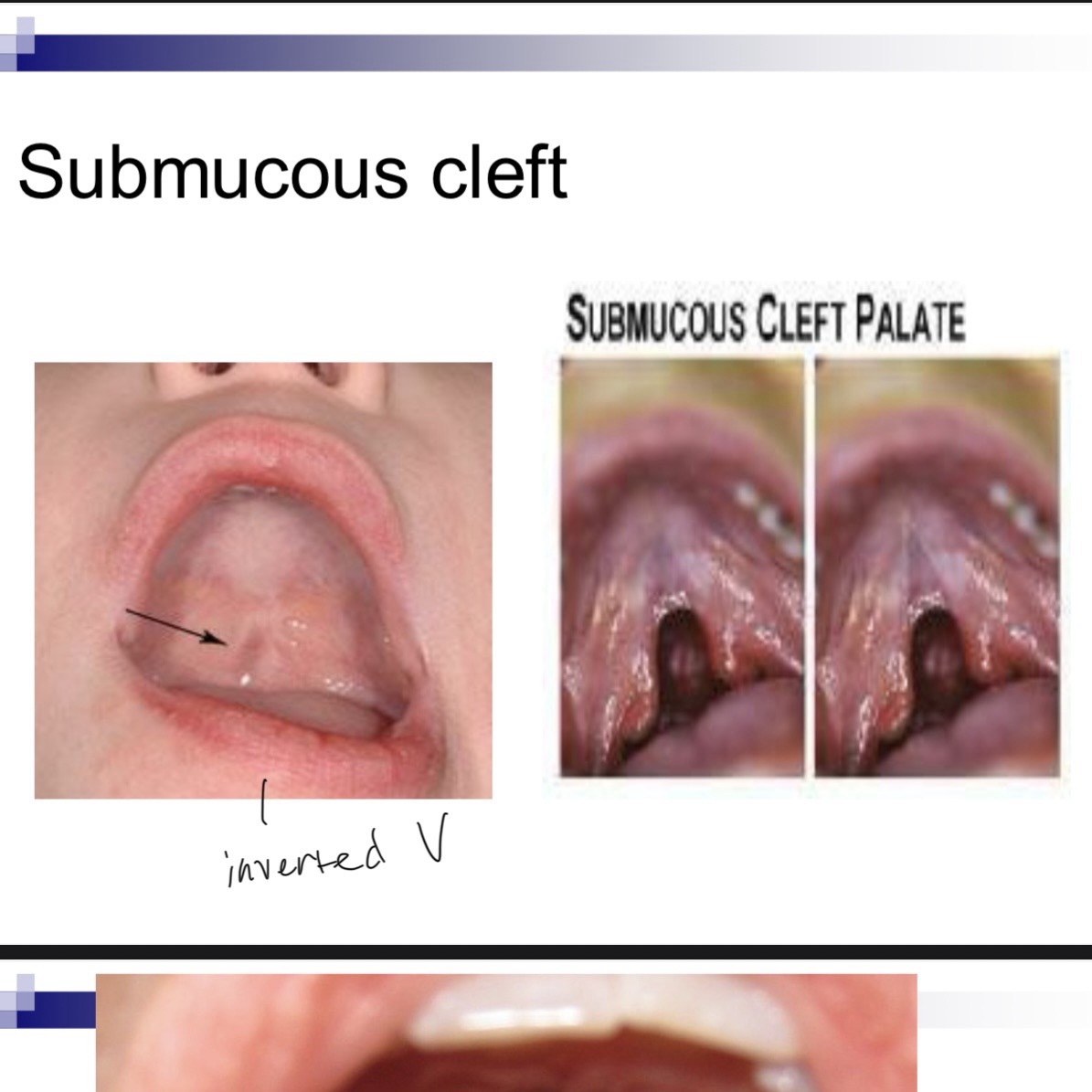
Zona pellucida inverted V
Velum may appear to be an inverted V, especially during phonation. V shape due to abnormal insertion of Levator palatini muscle in the posterior section of hard palate, rather than middle of velum.
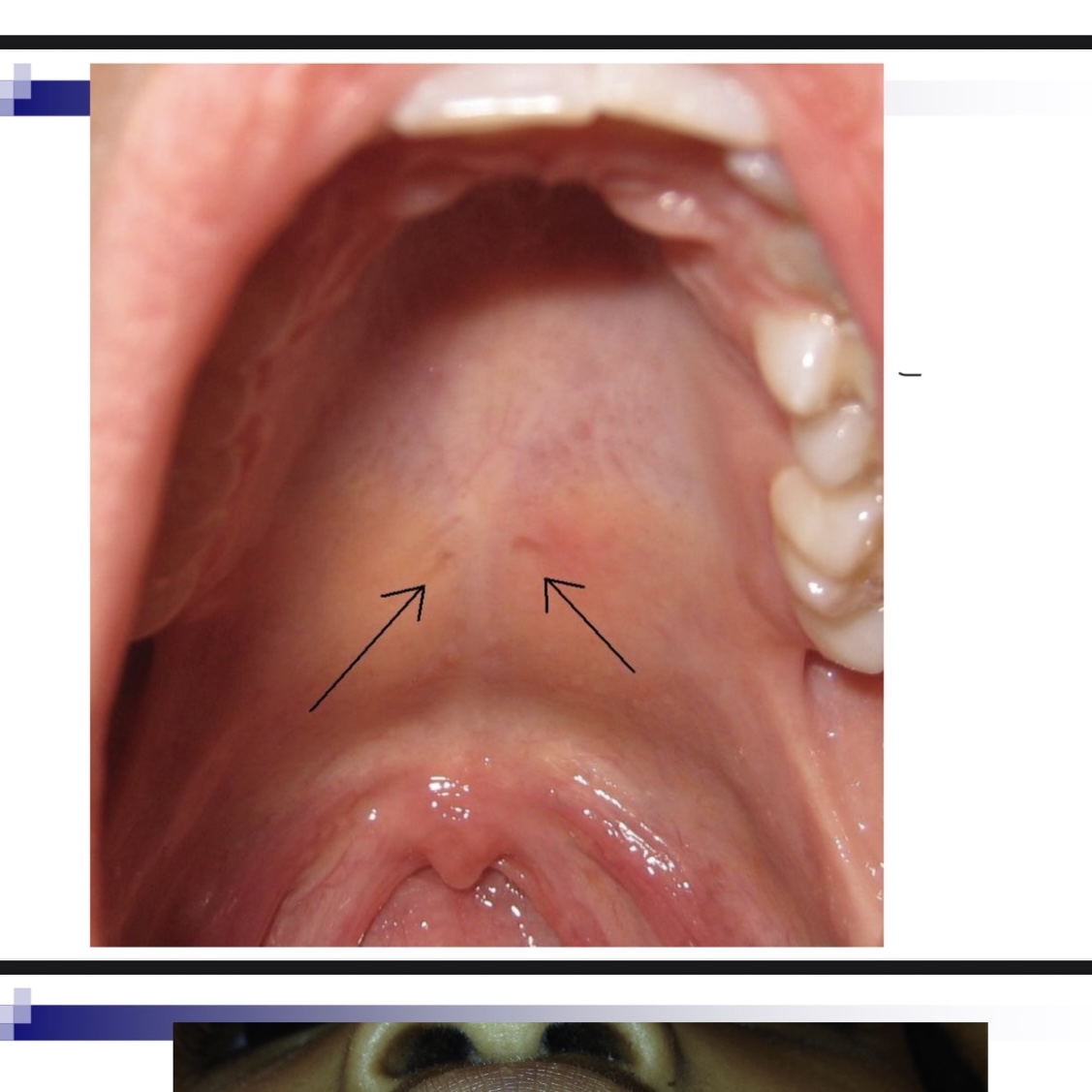
Notch in posterior border of hard palate
Can indicate submucous cleft.
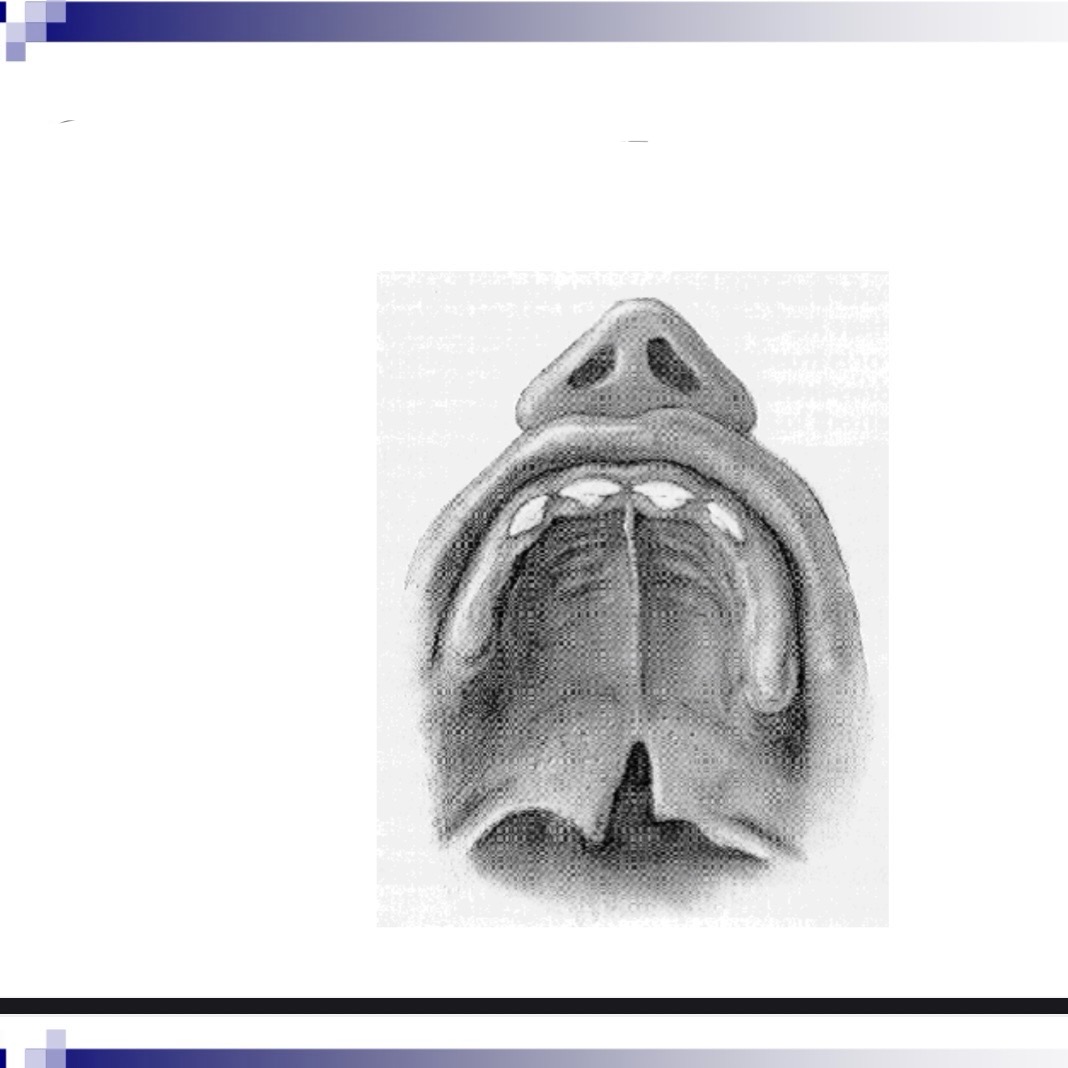
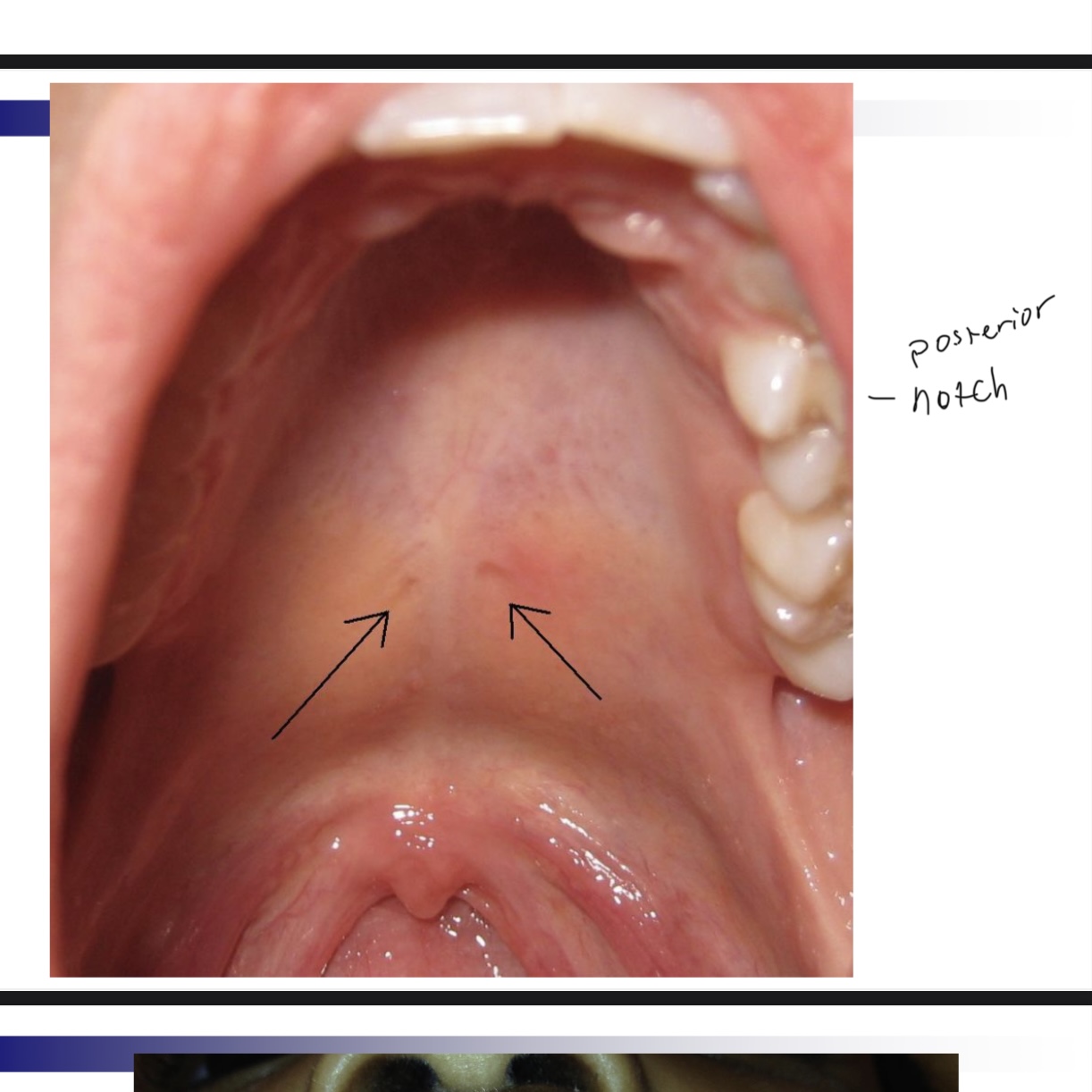
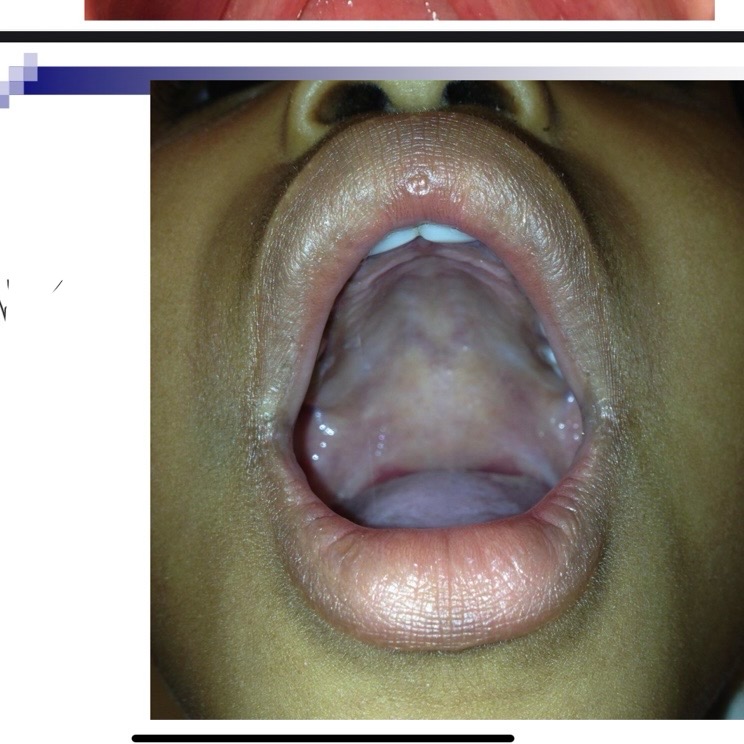
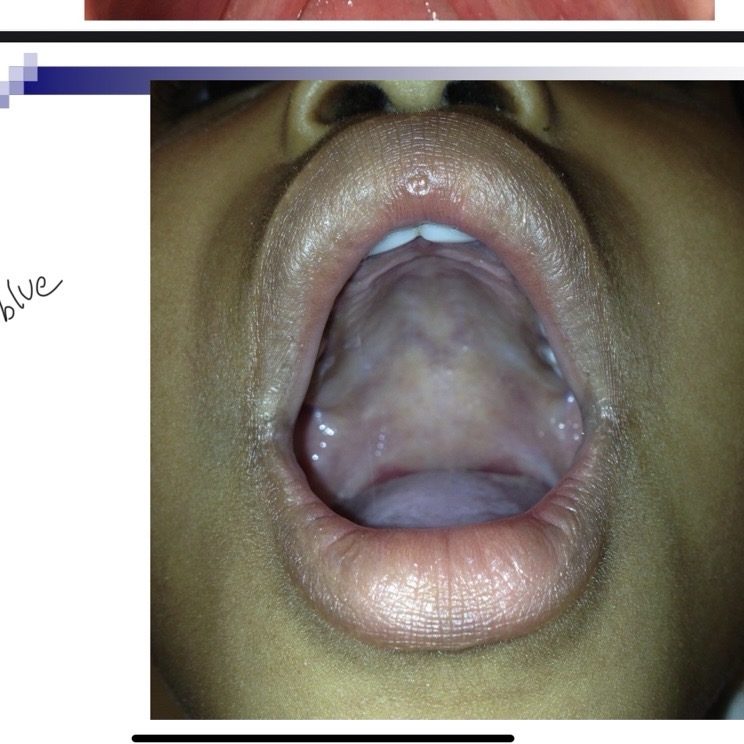
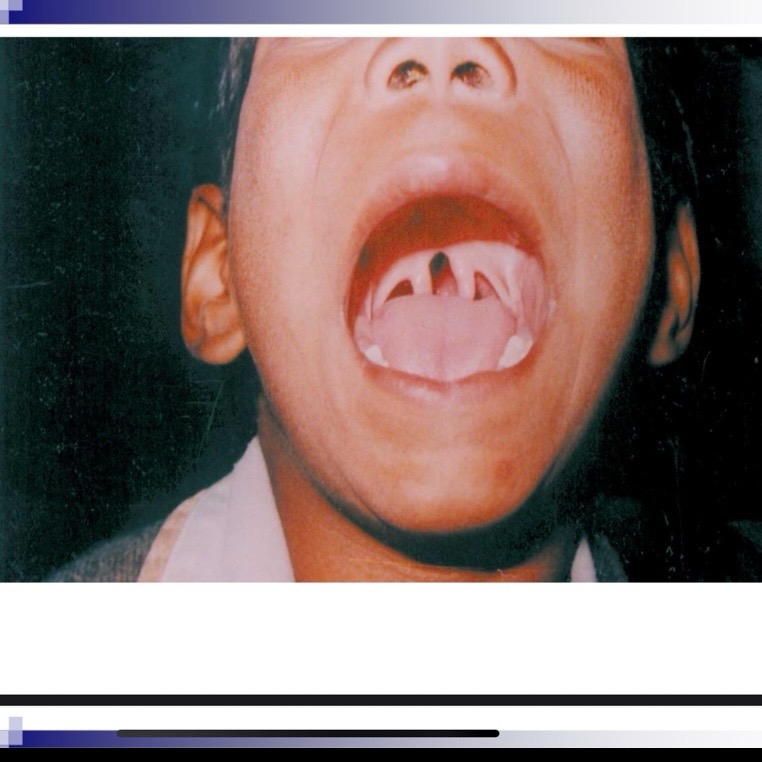
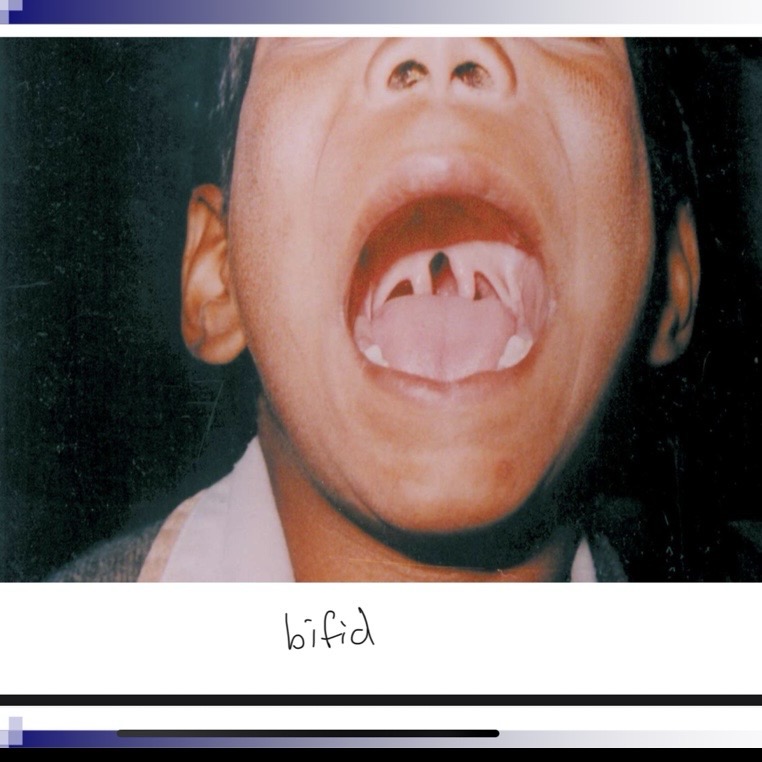
Occult submucous cleft is only apparent by
Viewing nasal surface of velum through nasopharyngoscopy
Occult submucous cleft is only pursued if patient has
Velophyangeal insufficiency or hypernasality and no cleft can be observed by oral and tactile examination
Effect of submucous cleft on function
Possible velopharyngeal dysfunction
Possible resulting speech problems
Possible nasal regurgitation when swallowing especially during first year
Increased risk for middle ear infections due to abnormal insertion of tensor veli palatini muscle, which can cause Eustachian tube dysfunction
When to treat submucous cleft
Speech and feeding affected
Why is feeding difficult for a baby with cleft lip
Compromised lip seal
Able to breastfeed and bottle feed w assistance
Why is feeding difficult for a baby with cleft palate
Difficulty creating suction/pressure needed to express milk
Breastfeeding is very difficult
Modifications are required for bottle feeding
Feeding issues related to cleft palate
Poor intake
Nasal regurgitation
Excessive air intake
Disruption in bonding between caretaker and infant
What are 2 feeding guidelines help for a baby with cleft palate
Modify nipple
Modify bottle
What is a feeding obturator
Acrylic plate which fits over the hard palate, providing a seal between nasal/oral cavity
Some disadvantages of feeding obturator
Hard to place since infant has no teeth
Irritation of oral tissue
Expensive
Hygiene
Why is cup drinking important for an infant with CP up to 10 months of age
After surgery, for healing, the pressure of drinking through a bottle could cause the sewn up part to open again
Methods of severe cases of CP
Nasogastric tube
Orogastric tube
Gastrostomy tube
Prior to 6 months, where are vocalizations produced
Pharynx and glottis
What differences are observed by 6 months for early vocal development for typical kids
Begin to produce anterior labial and alveolar consonants
Glottal stop production reduced
Speech production for infants with CP
Alveolar sounds not observed
Produce fewer total consonants
Glottal production persists
Nasals, glides, liquids may be produced easily
3 indicators of velopharyngeal dysfunction
Anatomical or structural defects that affect velopharygneal closure
Neuro motor or physical disorder
Inappropriate articulation patterns
What types of anatomical/structural defects can indicate velopharyngeal dysfunction
History of CP or submuc cleft
Short velum
Types of neuromotor or physical disorders that may indicate velopharyngeal dysfunction
Poor movement of velum/muscles function (Levator veli palatini)
Dysarthria
Apraxia
Velopharyngeal dysfunction leads to 2 types of errors
Compensatory errors and obligatory errors
Compensatory errors
SLPs work w these continuous errors after CP gets fixed
Obligatory errors
SLPs cannot work w these errors due to the anatomical issue of CP. surgeon needs to be involved first
Nasal air emission
Air leaks through nasal cavity during high pressure sounds
Example of nasal emission instead of saying sun
Thun
Glottal stop + example
Produced in larynx
Substitutes stops and sometimes fricative & affricates
Daddy - ?a?y
Pharyngeal stop + example
Further back than k and g
Substitutes for k and g sound
Tongue base meets with posterior pharyngeal wall
Pharyngeal fricative + example
Substitutes mostly w fricatives and affricates
Sounds like x - sun - xun
Pharyngeal affricate
Combination of pharyngeal fricative and glottal stop
Substitutes for affricates ch and j
Nasal fricative
Substitution for fricatives or affricates
All nasal, sun- no s at all
Mid dorsum palatal stop
Produced in the approximate place for “y” sound(/j/)
Substituted for /t/ /k/ /d/ /g/
Dysphonia + characteristic
voice disorder which common cause is vocal nodules
Breathiness, hoarseness, low intensity
Why children with history of CP or VP dysfunction have increased risk for dysphonia
All substitution errors they make are at the vocal fold level which causes the VFs to constantly bump into each other and can lead to dysphonia