cgs 2301 - hemispheres
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
lateralization
the idea that some brain functions are specialized to either the left or ride side of the brain
left brain
logical, calculating, lingustic
right brain
emotional, holistic, intuitive
damage to left hemisphere?
pessimistic, overly emotional, overly noticing even nonserious problems
damage to right hemisphere?
optimistic, unemotional, anosognosia (oblivious to serious injury/illness/disability)
lateralized left brain function
language, broca and wernicke’s areas
lateralized right brain function
faces, visual motor tasks
contralateral
left hemisphere → right side of body, right visual field
right hemisphere → left side of body, left visual field
localization
specific brain regions are responsible for specific functions
evidence of localization (3)
selective amnesia
aperceptive amnesia
associative amnesia
selective anmnesia
selective memory loss, can’t remember certain specific details
aperceptive amnesia
vision intact
impaired recognition of shapes/forms
diffuse and widespread damage
ex: in the video, the woman can’t mimic the shapes drawn

associative amnesia
vision intact
shapes/forms intact
recognition impaired (perception is correct but deeper association with label is severed)
damage to dorsal (?)
scope of deficit varies
ex: could perfectly mimic drawing but wouldn’t be able to say what it is
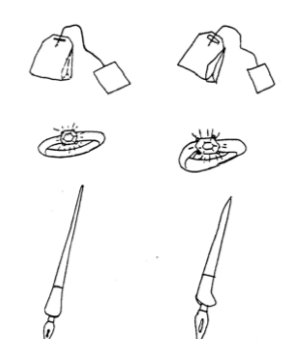
localized vs lateralized
contiguous (bordering) area controls the task
dyscalculia
can’t do simple math calculations
alexia
can’t read
note: alexia is caused by brain damage vs dyslexia which is a developmental disorder caused by genetics/environment
agraphia
can’t write
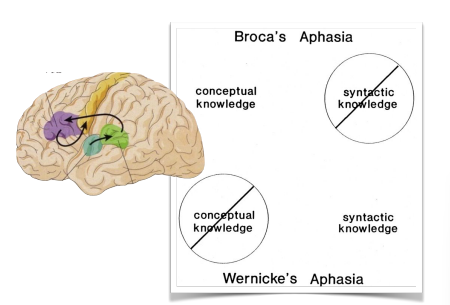
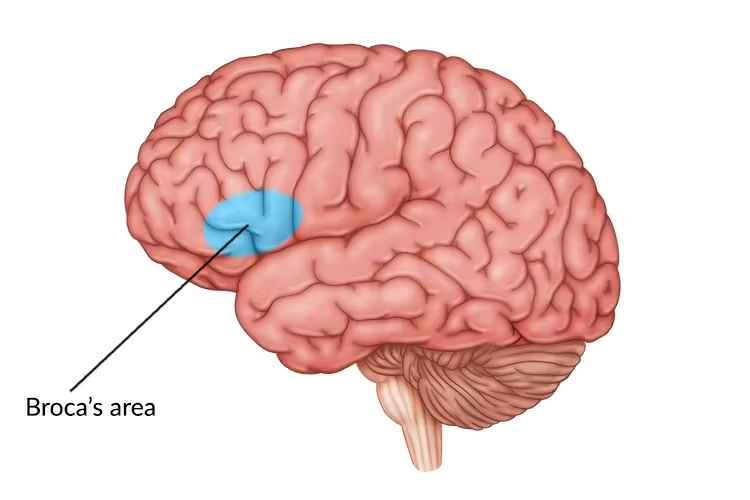
broca’s aphasia
can’t produce language
note: broca sounds like “boca” = mouth in spanish → you can’t produce language w your mouth
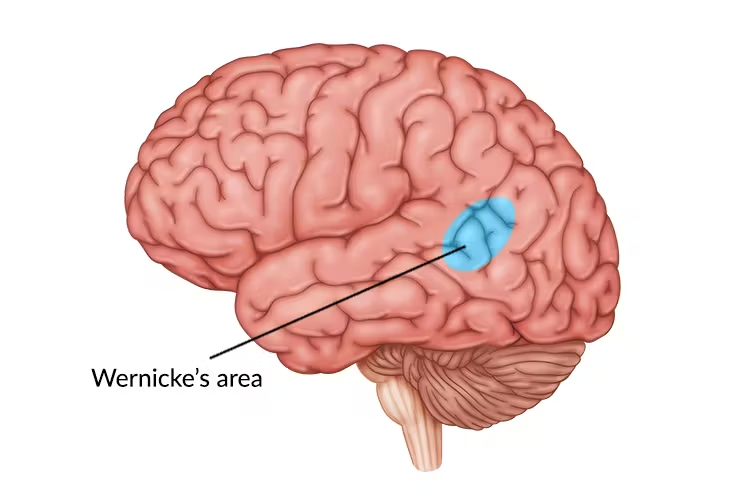
wernicke’s aphasia
can’t comprehend language
prosopagnosia
selective memory impairment
inability to recognize faces
capgras syndrome
believe someone you love has been replaced by an imposter
decussation
crossing of nerve fibers from one side of CNS to other side
areas of decussation (4)
corpus callosum
optic chiasm
super olivary complex
spinal cord
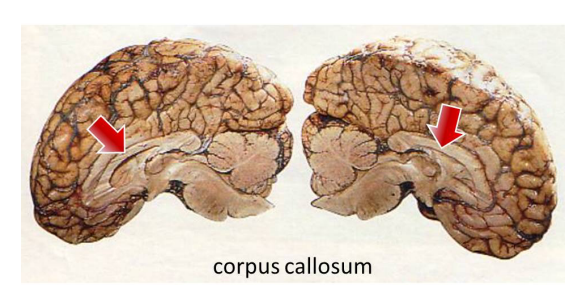
corpus callosum
bridge of ~200 mil fibers
connects left and right hemispheres
severed in split brain patients
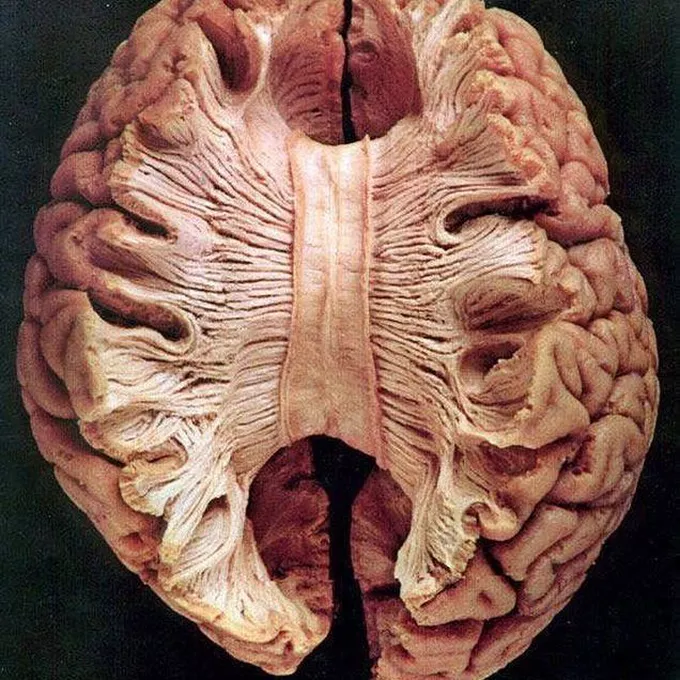
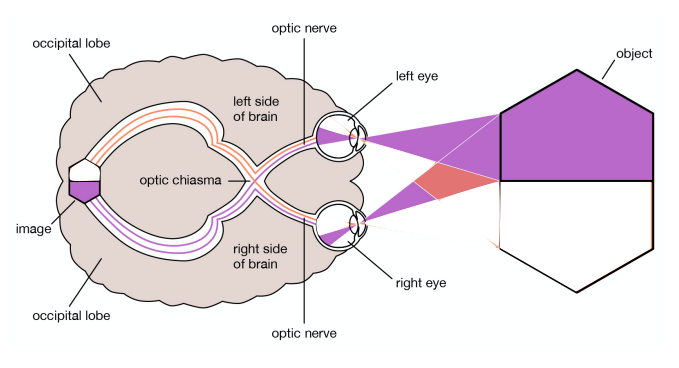
optic chiasm
vision
left visual field info → right visual cortex
right visual field info → left visual cortex
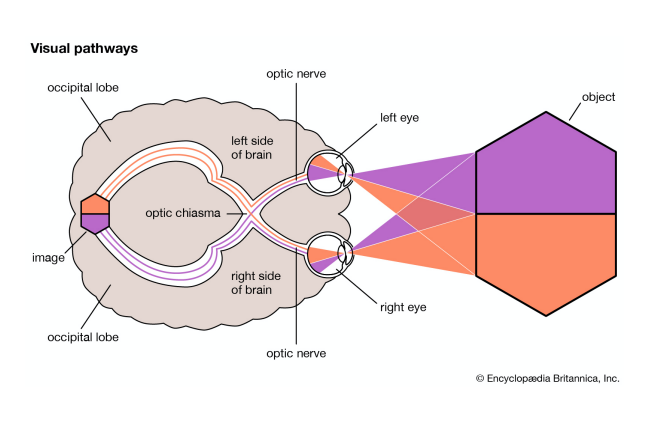
superior olivary complex
auditory pathways
a bunch of subcortical areas
decussation in superior olivary complex after cochlear nucleus (so not complete crossover)
auditory pathway
auditory nerve → cochlear nuclei → superior olivary nucleus → inferior colliculus → medial geniculate nucleus of thalamus → auditory cortex
mnemonic: Manny Is Super Cute (medial → inferior → superior → cochlea) (it’s backwards tho rip)
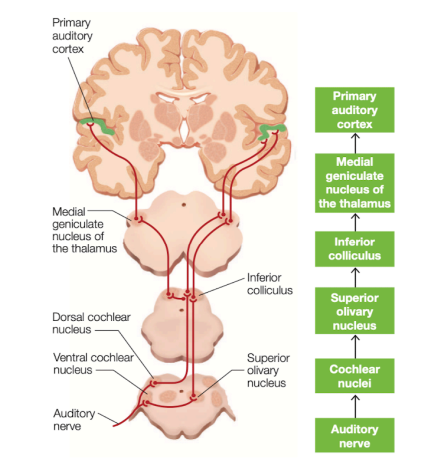
spinal cord
pain and temperature
touch and vibration
motor output
multiple points of decussation
what do split brain patients have?
severed corpus callosum
what can a severed corpus callosum tell us?
verbal, verbal, and tactile info transfer
emotion
motor coordination
how do the hemispheres exist independently?
who conducted the verbal, verbal, and tactile info transfer experiment in split brain patients?
Roger Sperry and Michael Gazzaniga
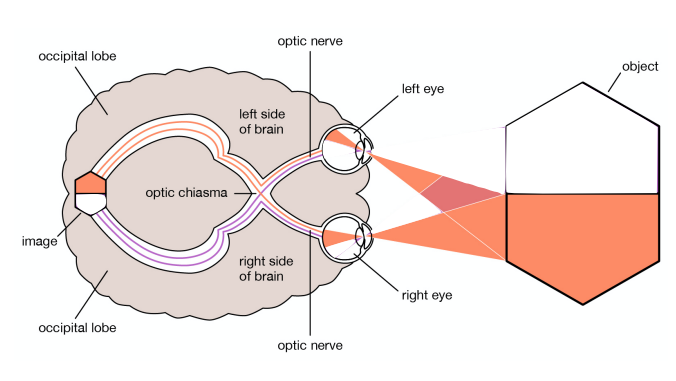
part 1: patient is shown cup in the right visual field
when asked what they saw, the patient said a cup
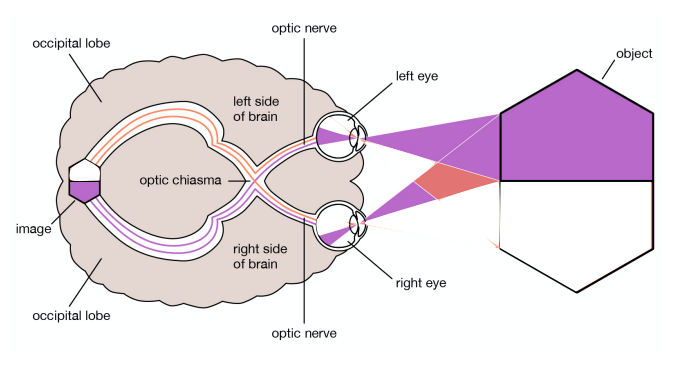
part 2: patient was shown a spoon in the left visual field
when asked what they saw, the patient said they didn’t know
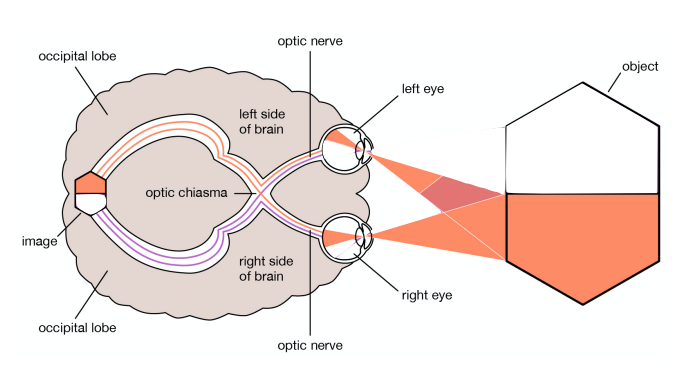
part 3: spoon was shown again in the left visual field
when asked what they saw the patient still didn’t know
however when asked to find the object they saw from a bag of objects, they picked the spoon
who conducted the emotional info transfer experiment in split brain patients?
Gazzaniga and LeDoux (1978)
patient PS
part 1: patient is shown emotionally charged word (ex: DEVIL) to left hemisphere
when asked if the word was good or bad, the patient said bad
when asked what the word was, the patient said devil
part 2: patient is shown emotionally charged word (ex: DEVIL) to right hemisphere
patient said word is bad
however didn’t know what the word was
motor coordination (1930s)
Kurt Goldstein
alien hand phenomenon
middle-aged woman with suicidal tendencies
would try to strangle herself with her left hand.
would fight off her left hand with her right.
autopsy revealed CC lesion.
right hemisphere (more emotional?) tried to commit suicide - left hemisphere not aware of this intention.
implications
what does this say about the will and self?
are there two of us?