Bacterial Genome Replication
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
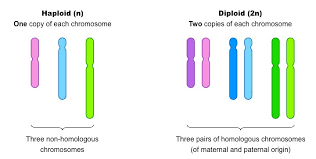
What is a chromosome, a haploid, and a diploid?
DNA package made of DNA and proteins
haploid - one set of chromosomes
diploid - 2 sets of chromosomes, one from each parent, formed through mitosis
Define the types of RNA (mRNa, rRNA, and tRNA)
mRNA - messenger RNA, carries the genetic instructions from DNA to the ribosome, where proteins are made.
rRNA - ribosomal RNA, combines with proteins to form ribosomes, helps read mRNA and link amino acids together during translation
tRNA - transfer RNA, transfers amino acid to protein chain during translation by matching to mRNA codon
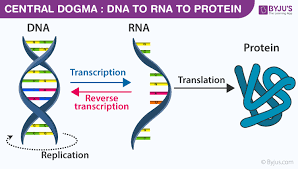
What is the central dogma?
genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to protein, through transcription and translation
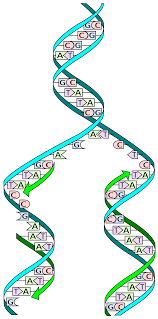
What is replication?
DNA copied
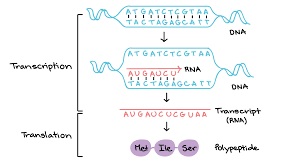
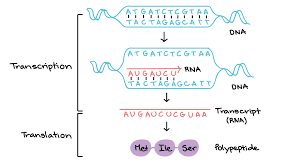
What is transcription and translation?
transcription - genetic information contained within DNA is re-written into messenger RNA
translation - genetic code contained within a mRNA molecule is decoded to produce a specific sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
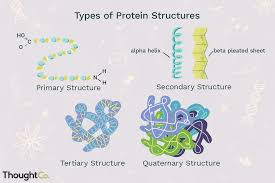
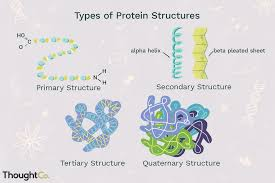
What are the 4 levels of protein structure?
primary structure – the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Secondary structure – local folding into structures, held by hydrogen bonds.
Tertiary structure – the overall 3D shape of a single polypeptide, formed by interactions between R-groups (like ionic bonds, disulfide bridges, hydrophobic interactions).
Quaternary structure – the structure formed when multiple polypeptide chains (subunits) come together to form a functional protein.
what is a plasmid?
extracellular DNA not vital for existence, can be transferred to other organisms
Describe the basic structure of DNA
sugar/phosphate backbone and nitrogenous bases

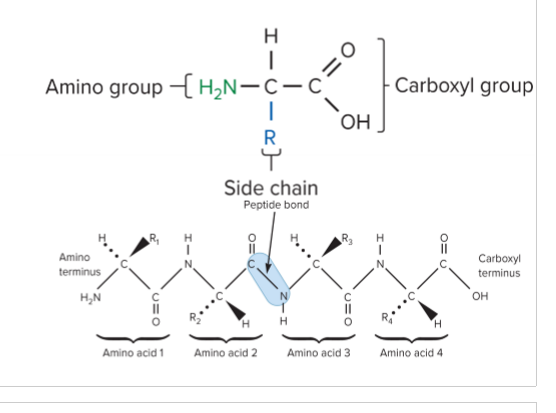
Describe the basic structure of amino acids
amino group, side chain, carboxyl group
What is semi-conservative replication?
During replication, each new DNA molecuel has one strand from the parent and one new daughter strand.
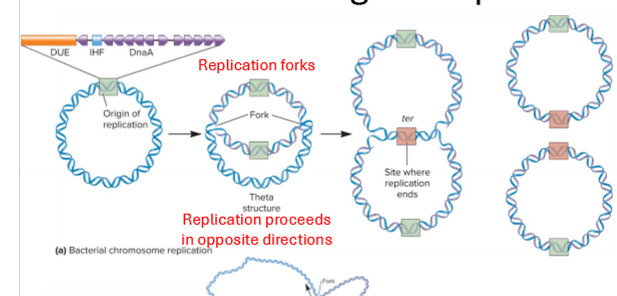
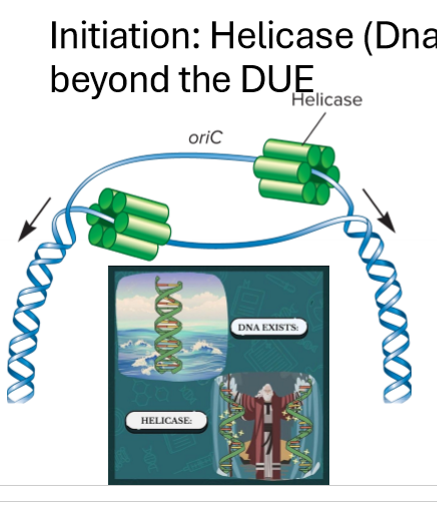
Describe initiation of replication in bacteria
initiation at single origin of replication (oriC) with IHF protein binding site
unwinding begins at DUE (DNA unwinding element) site which is AT rich, done by helicase
unwinds and starts replication forks
2 replication forks move out away from the origin until they have copied the whole region, helicase enzyme continues unwinding
IHF protein helps stabilize
DnaA protein (the initatior) binds to segments on OriC to repeat
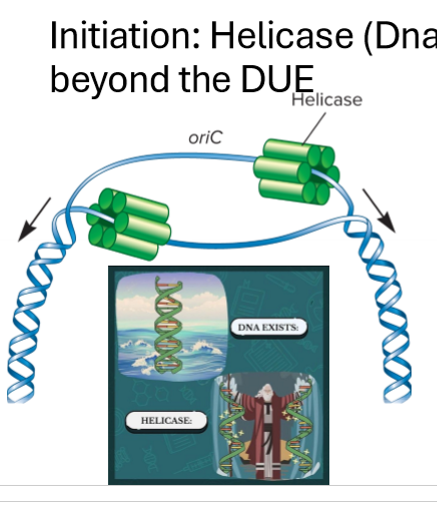
Describe the helicase (DNAB) enzyme
unwinds beginigng at DUE
breaks h bonds and provides force for replisome
6 subunit ring, surrounds DNA
requires ATP and proteins
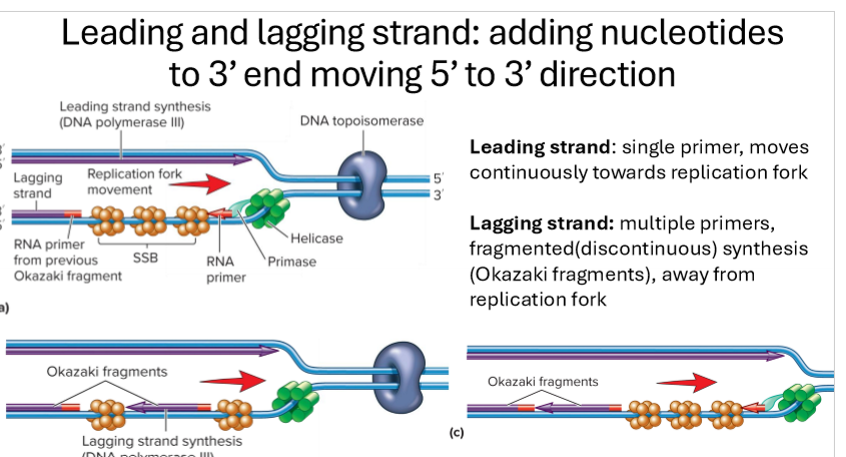
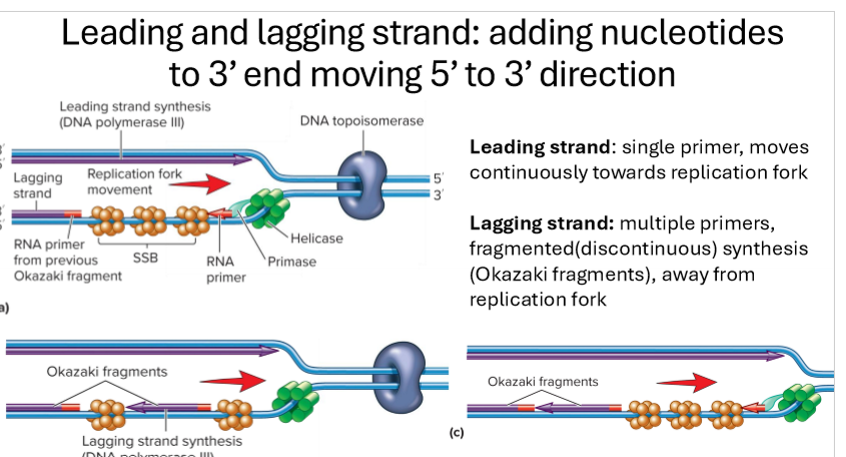
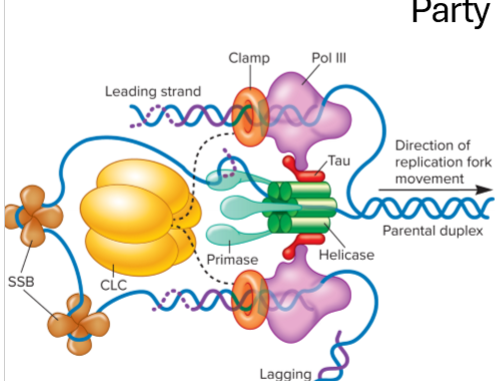
Describe elongation in bacteria
primase adds short RNA primer once template (parent strand) is free to make free 3’OH group on growing strand
Tau connects DNA polymerase 3 to primosome (helicase and primase)
DNA polymerase 3 adds nucelotides to the 3’ end of the RNA primer, building in 5’ to 3’ direction
leading strand synthesis is continuous
lagging strand is discontinous, short Okazaki fragments heading away from replication fork
clamp/clc stabilizes DNA polymerase 3
Topoisomerase relieves supercoiling
SSB stabilizes strands
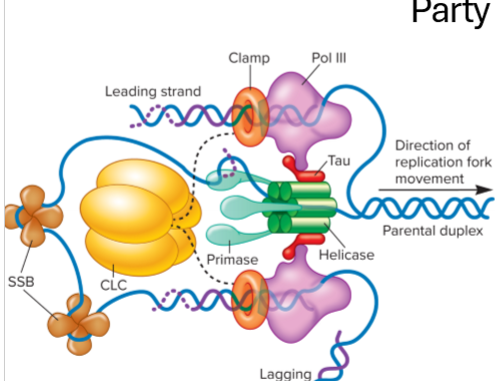
What are the roles of the all the proteins involved in DNA replication at the replication fork?
helicase - unwinds
primase - primes, synthesizes a complementary RNA primer
DNA polymerase adds nucleotides with help from primase
tau connects DNA polymerase 3 to primosome (heliase + primase_
clamp - stabilized pol 3
SSB - single strand binding proteins stabilizie strands
topoisomerase - relieves supercoiling
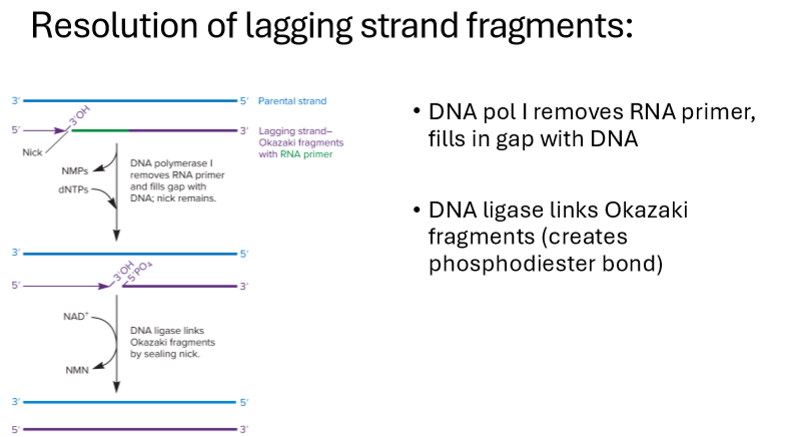
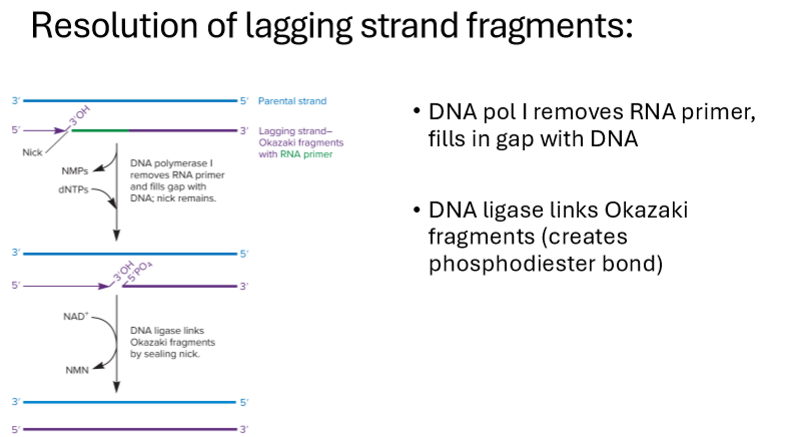
How are lagging strands resolved?
DNA polymerase 1 removes RNA primer, fills in gap with DNA
DNA ligase links okazaki fragments, creating phosphodiester bonds
Describe lagging vs leading strand replication
leading strand - synthesis is continuous with a single primer moving continuously towards replication fork
lagging strand- discontinous synthesis, with multiple primers forming short fragments called Okazaki fragments, heading away from replication fork.
Describe DNA polymerase 3 proofreading
after wrong H-bond formed, DNA pol stalls
3’ to 5’ exonuclease enzyme removes mismatch
DNA poly resumes, fills in correct nucleotide

Describe DNA replication termination
topoisomerase induces DNA break to separate daughter chromosomes, then fixes them

Briefly describe the 3 steps of bacterial DNA replication
initiation - proceeds from origin of replication, DUE unwinds at A-T rich site. 2 forks move out in opposite directions. helicase continues unwinding
Elongation -primase adds RNA primer, DNA polymerase 3 extends strand in 5’ to 3’ direction, lagging and leading strand, clamp stabilizes, topoisomerase relieves super coiling
Termination - topoisomerase induces DNA break to separate daughter chromosomes then fixes them
Compare bacteria and eukarya DNA replication, inclduing
origin
replisome
speed
errors
bacteria single origin, eukarya multiple origins
bacteria fewer proteins at replisome, eukarya more complicated replisome
bacteria faster than eukaryotes
similar error rate
Does archaea replication more resemble bacteria or eukaryotes?
more resembles eukaryote, can have multiple origins
What is Taq polymerase?
thermostable DNA polymerase
discovered by Alice Chien
used in original PCR techniaue
What is IHF in DNA?
integration Host Factor
DNA-binding protein that helps bring protein together
What is the role of the DnaA protein?
DnaA binds to OriC, bends the DNA, and helps initiate strand separation at the DUE.
What is the role of the RNA primer?
It provides a 3′-OH group for DNA polymerase to begin synthesis.
What enzyme seals the gaps between Okazaki fragments?
DNA ligase
What are the three key DNA elements at the bacterial origin of replication (OriC)?
DUE – DNA Unwinding Element (AT-rich)
IHF binding site – site for the DNA-bending protein IHF
DnaA boxes – repeat sequences where initiator protein DnaA binds