Theory - Ultrasonic Instrumentation
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Objectives of Periodontal Debridement
- Disruption and removal of subgingival biofilm
- Removal of plaque retentive factors
- Conservation of tooth structure
- Resolution of inflammation
Ultrasonic Instrumentation Mechanisms of Action
Mechanical
Irrigation
Cavitation
Acoustic microstreaming
Mechanical
Primary action
Irrigation
irrigant (usually water) is used with ultrasonic instruments to counteract any frictional heat generated by oscillating tip moving against tooth surface
Cavitation
Formation and explosive collapse of microscopic bubbles in a flowing liquid resulting from forces acting on liquid
acoustic microstreaming
swirling effect produced within the pocket by stream of fluid flowing over vibrating tip
occurs near any object in oscillatory motion in liquid
Magnetostrictive Components
**Cavitron is considered this
Insert
Handpiece
Base unit
Foot switch
Piezoelectric Components
Tip
Handpiece
Base unit
Foot switch
What is oscillation?
Forward and backward movement
The high-frequency oscillating action of the blunt tip contacting the deposit (biofilm or calculus) mechanically disrupts or fractures the deposit.
The conversion of electrical current into high-frequency mechanical vibrations is attained by what?
a transducer that is either magnetostrictive or piezoelectric in nature.
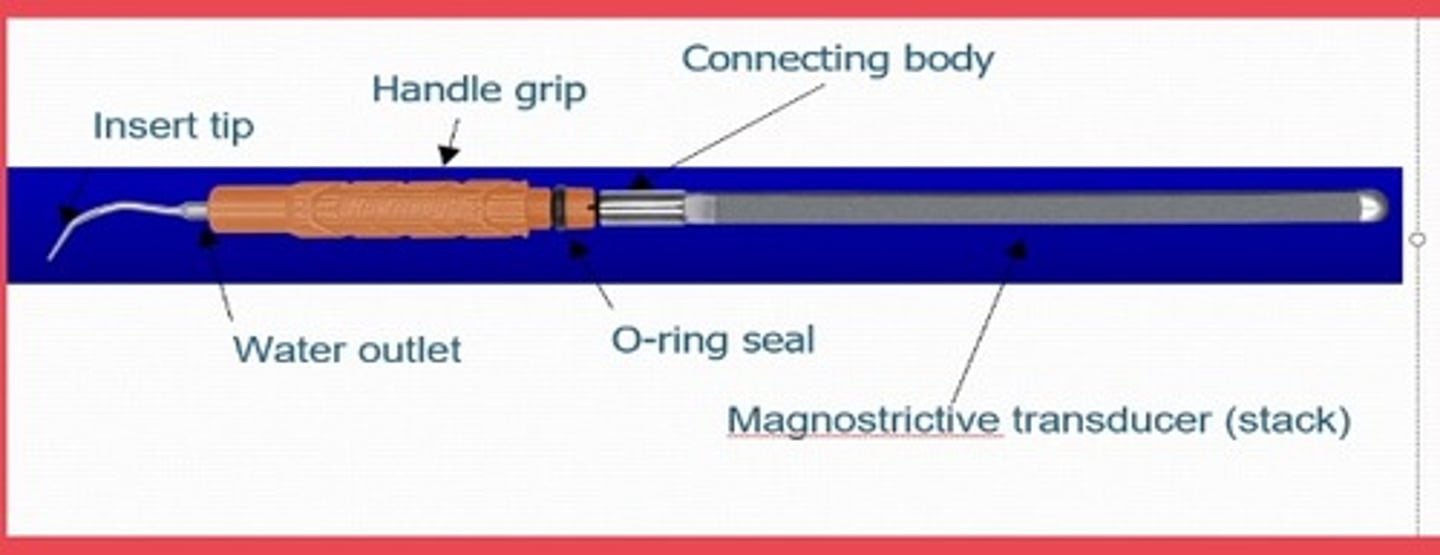
distinguishing components of a magnetostrictive ultrasonic scaler
insert and handpiece.
What is the insert in a magnetostrictive ultrasonic scaler composed of?
a stack of thin nickel strips soldered together at the ends and attached by a connecting body to a tip.
Hand piece of magnetostrictive ultrasonic scaler
The handpiece surrounds the nickel stack of the insert with copper wire, which generates an alternating magnetic field upon application of electrical current.
A piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler is differentiated by what?
a tip which screws onto the handpiece using a torque wrench.
Ultrasonic Operational Variables
Operating frequency
Power input
Water flow rate
Tip diameter
Tip shape
What is the operating frequency of the unit?
the number of complete back-and-forth cycles (strokes) the oscillating tip completes per second, measured in kilohertz.
T/F: the amount of electrical power input to the transducer is adjustable
TRUE
it is adjustable by manipulating the power setting of the unit.
The power setting used influences what?
the range of movement, or stroke length
What angulation do you use with ultrasonic scaler?
0 - 15 degree angulation
Stroke length is measured as what?
the displacement amplitude, meaning how far the tip is displaced from a position of zero movement.
Why is an adequate supply of water to the tip needed?
to minimize the production of frictional heat and to generate a lavage and the mechanisms of cavitation and acoustic microstreaming.
The diameter and shape of the tip used have a direct impact on what?
both the mechanical and biophysical (cavitation/microstreaming) mechanisms of action
Function produced by ultrasonic scaler is a function of
Efficiency of mechanical mechanism of action
Amount of cavitation and microstreaming activity
Factors influencing appropriate level of acoustic power
Displacement amplitude
Tip diameter
Tip shape
The net force exerted by the oscillating tip directly correlates to what?
the tip's mass (diameter) and to the distance the tip moves (displacement amplitude).
The efficacy and extent of biofilm disruption is relative to what?
the amount of cavitational and acoustic microstreaming occurring in the water surrounding the oscillating tip.
In order to accomplish efficient deposit removal without overinstrumentation of the root surface, it essential for the clinician to do what?
operate the ultrasonic scaler at the minimum effective acoustic power level.
Key features of ultrasonic tips
Diameter ( width)
Shape ( cross-section, circular or rectangular)
Geometry( number of places crossed by the shank)
Profile ( number of bends in active area)
When to replace tips
Manufacturers suggest replacement when 2mm of tip length is lost
What tips do you use on implants?
Carbon fiber or plastic tips are safe for use on the smooth titanium portion of implants
Types of ultrasonic tips
Straight
Contrangled
Periodontal
Straight tips
Slightly curved in only one direction
Universal use
Contrangled Tips
Paired instruments used in specific areas
Periodontal Tips
Thin straight
Designed for subgingival areas
Slimline
Thicker blue and green tips
an be used on higher settings and typically used for moderate to heavy calculus
Purple tip
thinner, can be used for light calc or biofilm disruption (good for gingivitis pts) and should be used on lower power
Adaptation for ultrasonic
Vertical
Horizontal
Oblique
What is the primary adaptation technique used during ultrasonic debridement?
vertical orientation
Horizontal adaptation
positions the active area of the tip perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth.
Oblique adaptation
the orientation required to remove deposits with a bladed instrument
Instrumentation and advancement of ultrasonic
With channeling, tip is advanced to base of pocket using stroke pattern indicated
Grasp of ultrasonic
Correct placement of grasp is determined by first balancing handpiece between thumb and forefinger
Sequence of Ultrasonic
Work by sextant
Why is it good to work by sextant with ultrasonic?
- More efficient
- Reduces frequency of changing tip
- Requires fewer changes in operation position
Clinical preparation for ultrasonic
Flush water lines 60 seconds
Fill handpiece with water
Insert appropriate tip
Adjust water supply to a fine mist
Preprocedural rinse
Standard precautions
Communicate with your patient
Tip adaptation
- Parallel to tooth surface
- Tip angulation near zero degrees
- Little to no lateral pressure
- Keep tip moving at ALL times
Medical Considerations
- Communicable Disease
- Immunocompromised patients (Kidney disease, chemo tx, organ transplant)
- Respiratory (COPD, emphysema, uncontrolled asthma, cystic fibrosis)
- Dysphagia or those who gag easily (Risks for aspiration pneumonia &
MS, Parkinson's, Muscular Dystrophy, post-stroke)
- Pacemakers (No cavitron if unshielded)