AP PreCalculus Final Exam Review
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Function
Inputs related exactly to one output. Use vertical line test.
domain
x - values left and right
Range
y - values up and down
interval
A set of real numbers between two endpoints, often used to describe the domain or range of a function.
Graph increasing
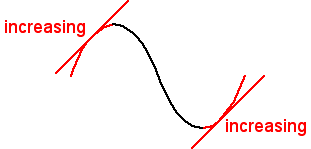
Graph decreasing
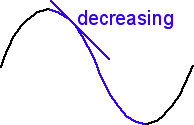
Constant graph
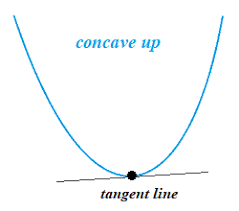
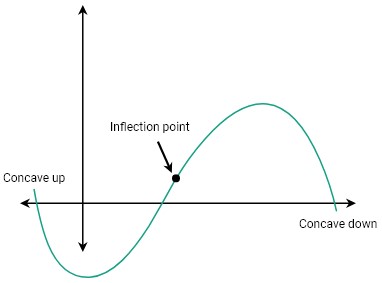
Concave up (ROC increasing)
Concave down (ROC decreasing)
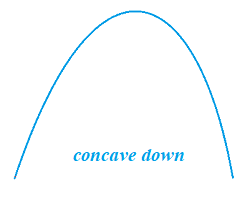
point of inflection
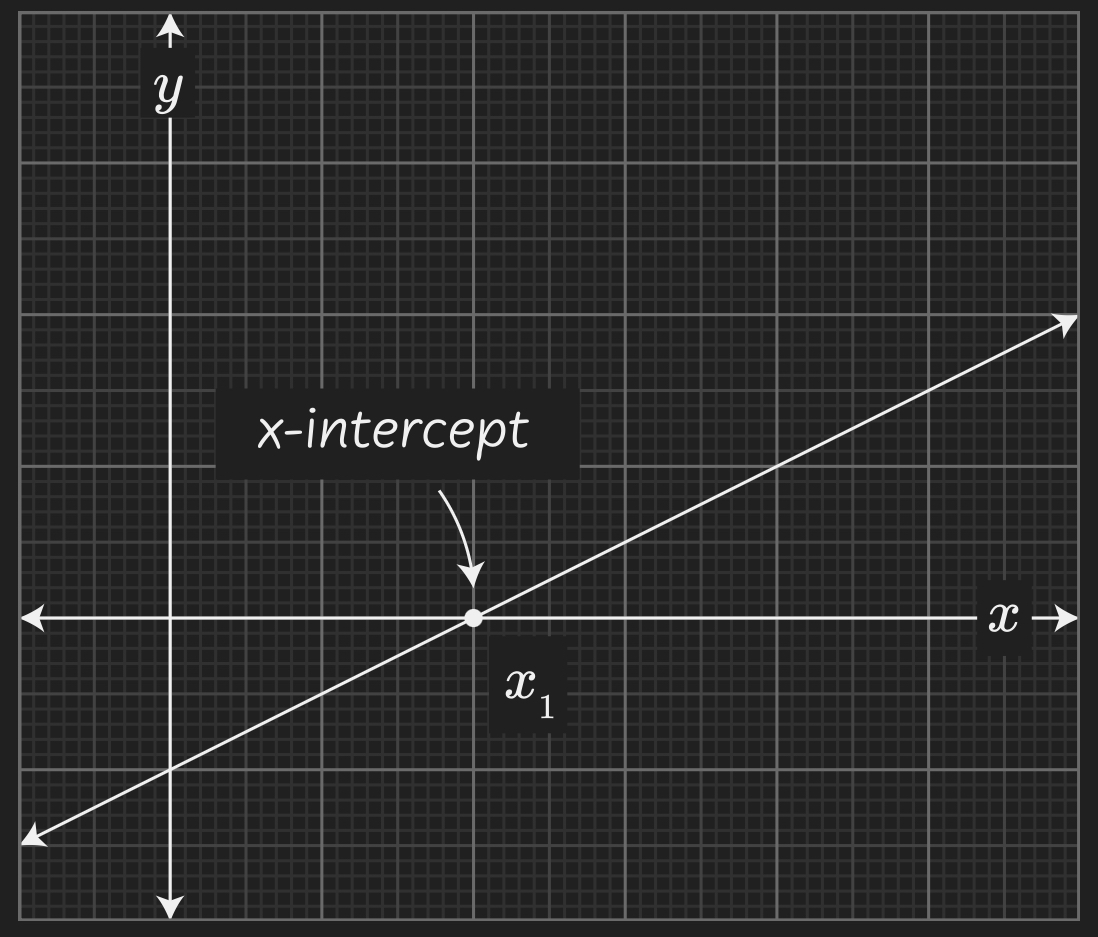
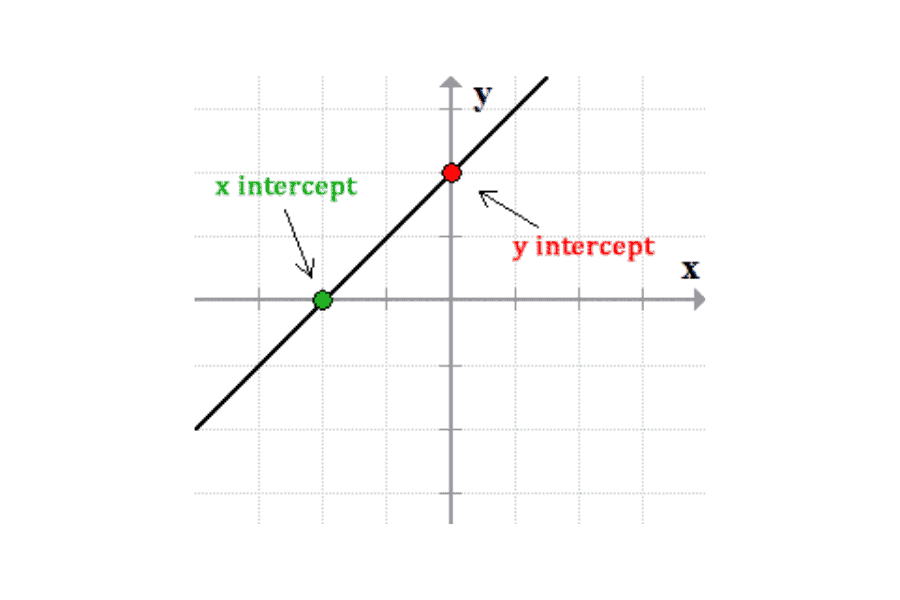
x-intercept
y-intercept
Slope
Change in y / x
AROC
average rate of change. Change in y / x
secant line
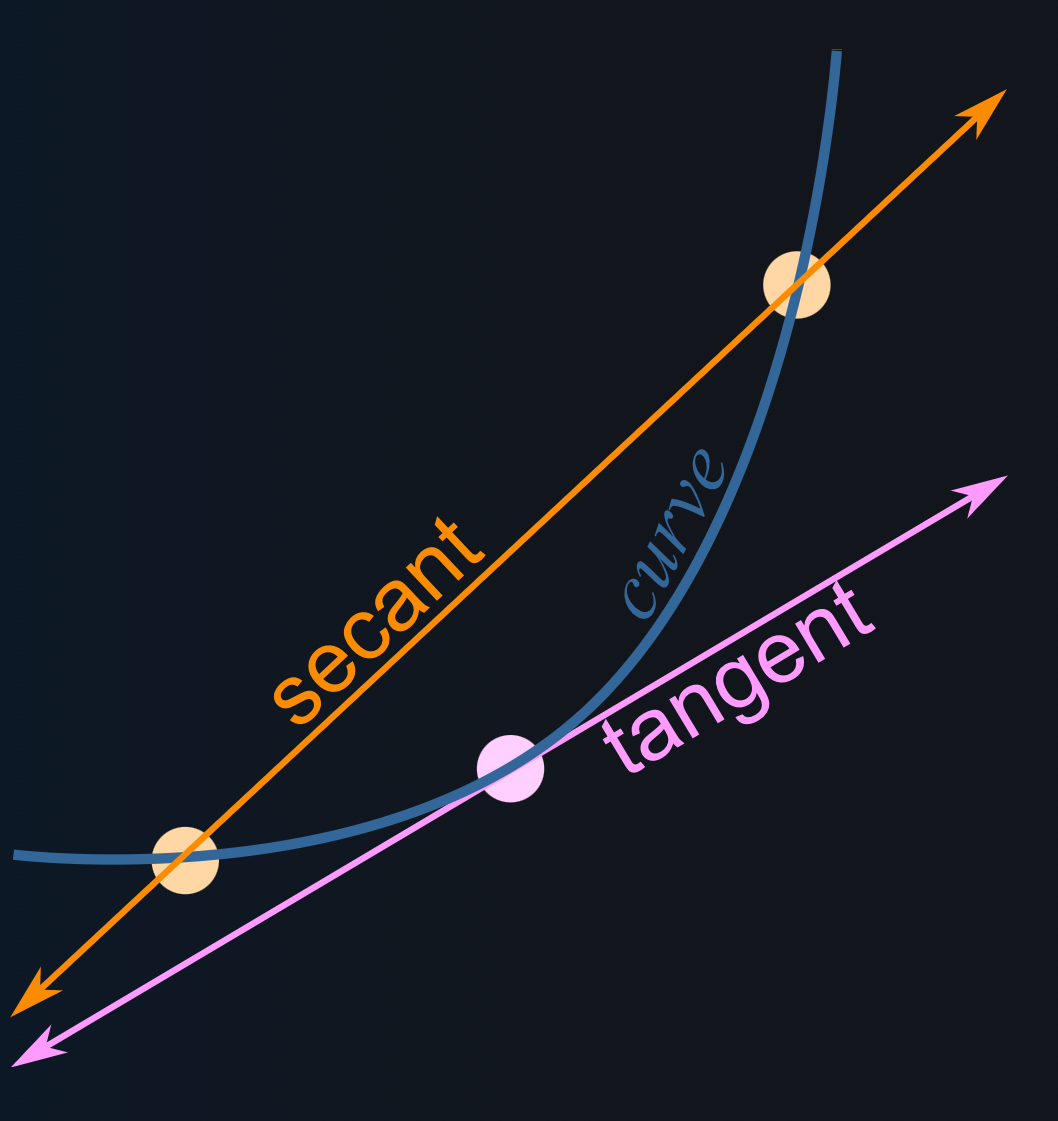
consecutive equal-length intervals
A method used to approximate the slope of a curve by using a secant line through points that are evenly spaced.
Degree
A unit of measurement for angles, equal to 1/360 of a complete rotation.
Leading coefficient
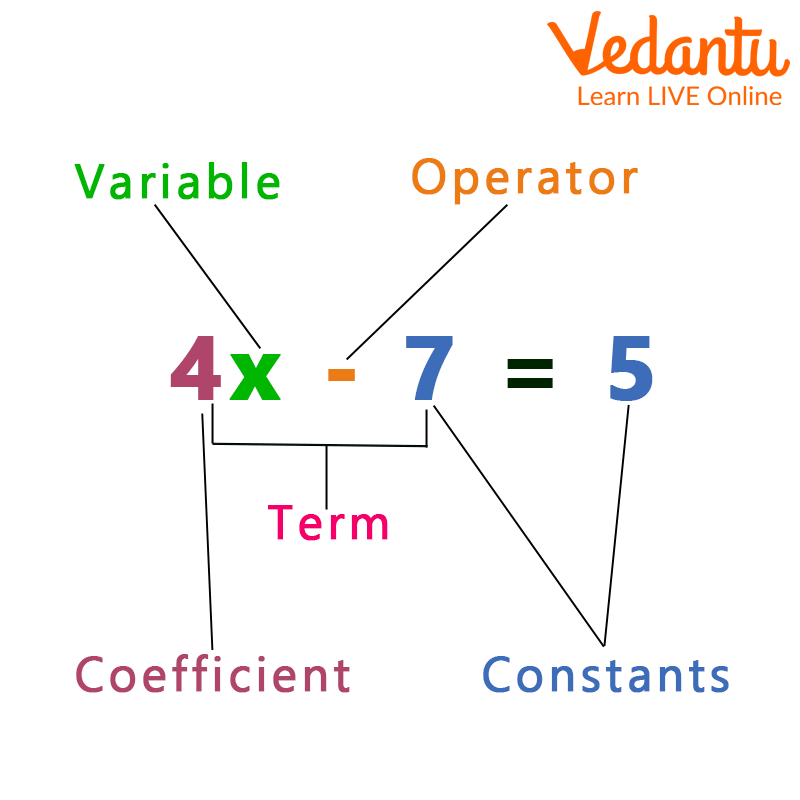
end behavior
The behavior of a function as the input values approach positive or negative infinity, often described by the limits of the function.
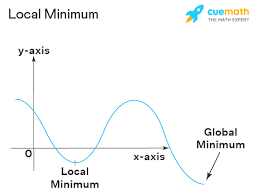
local / relative maximum
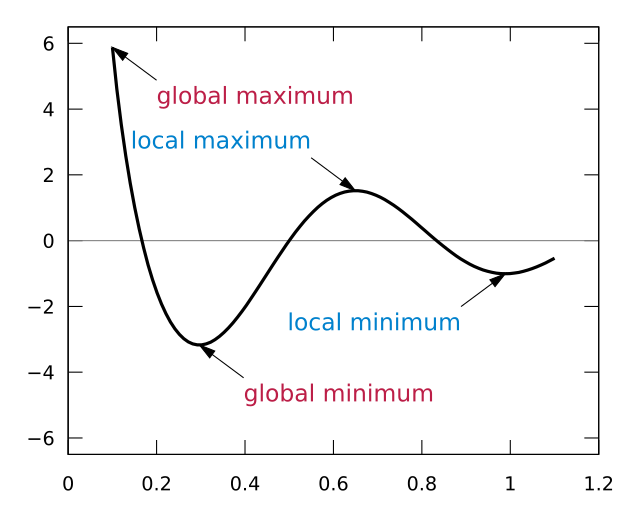

local / relative minimum
Global / absolute maximum
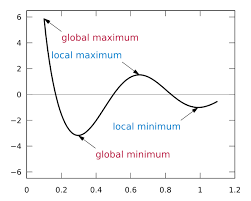
global absolute minimum
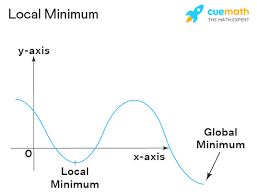
Extrema
The maximum or minimum values of a function. Absolute (global) extrema and local (relative) extrema.
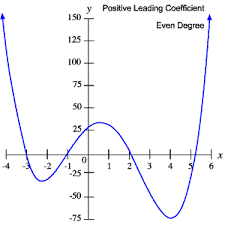
even degree function
End points both point up or both point down
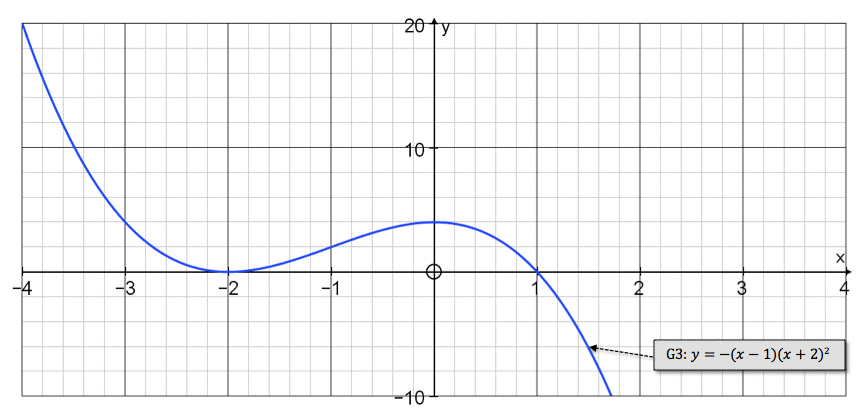
odd degree function
Graph whose ends points in opposite directions
imaginary number
Product of a real number and the imaginary unit i, defined by its property i²
complex number
Imaginary units expressed in the form a+bi
complex polynomial
conjugate root theorem
if the complex number a + bi is a root of a polynomial P(x) in one variable with real coefficients, then the complex conjugate a - bi is also a root of that polynomial.
zero
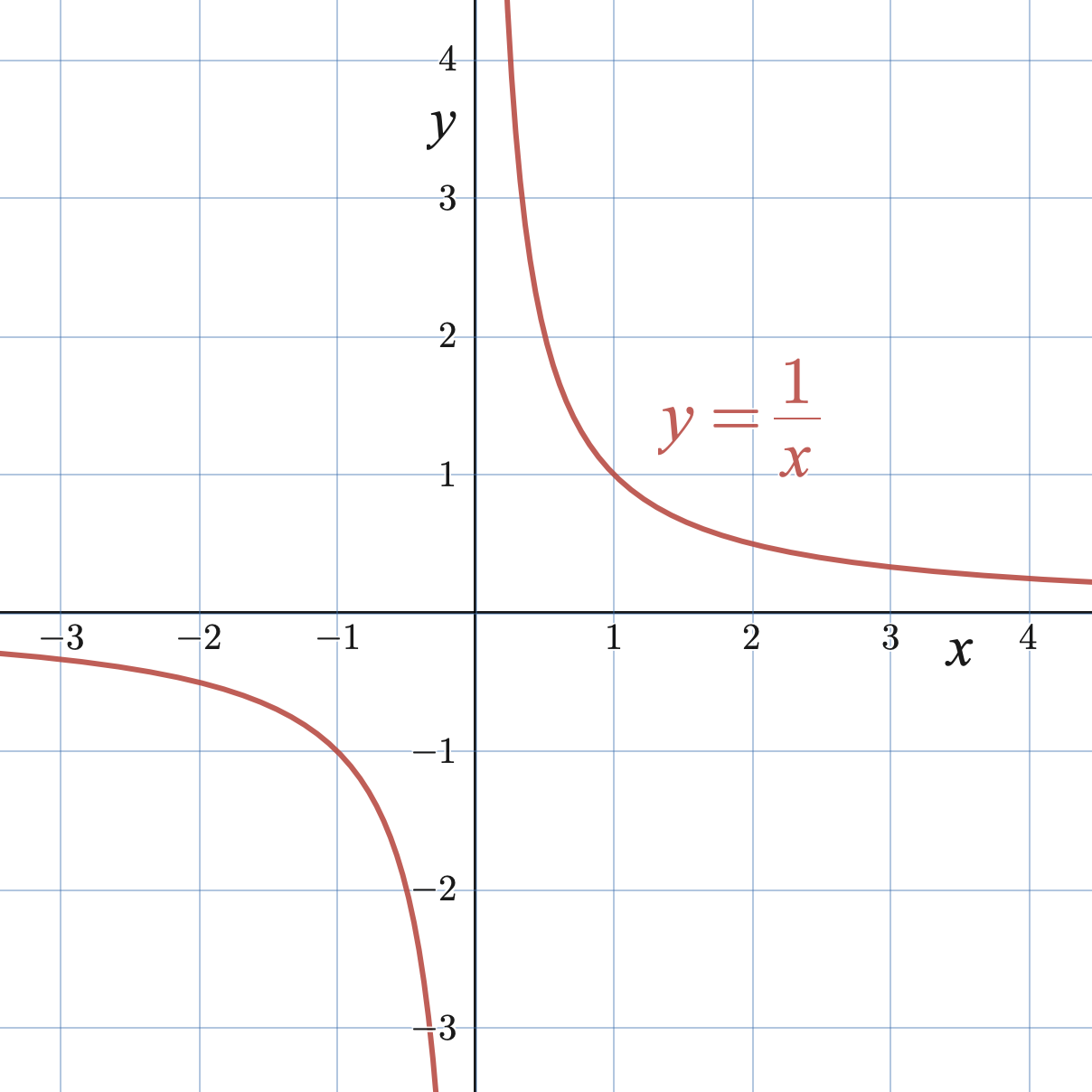
even function
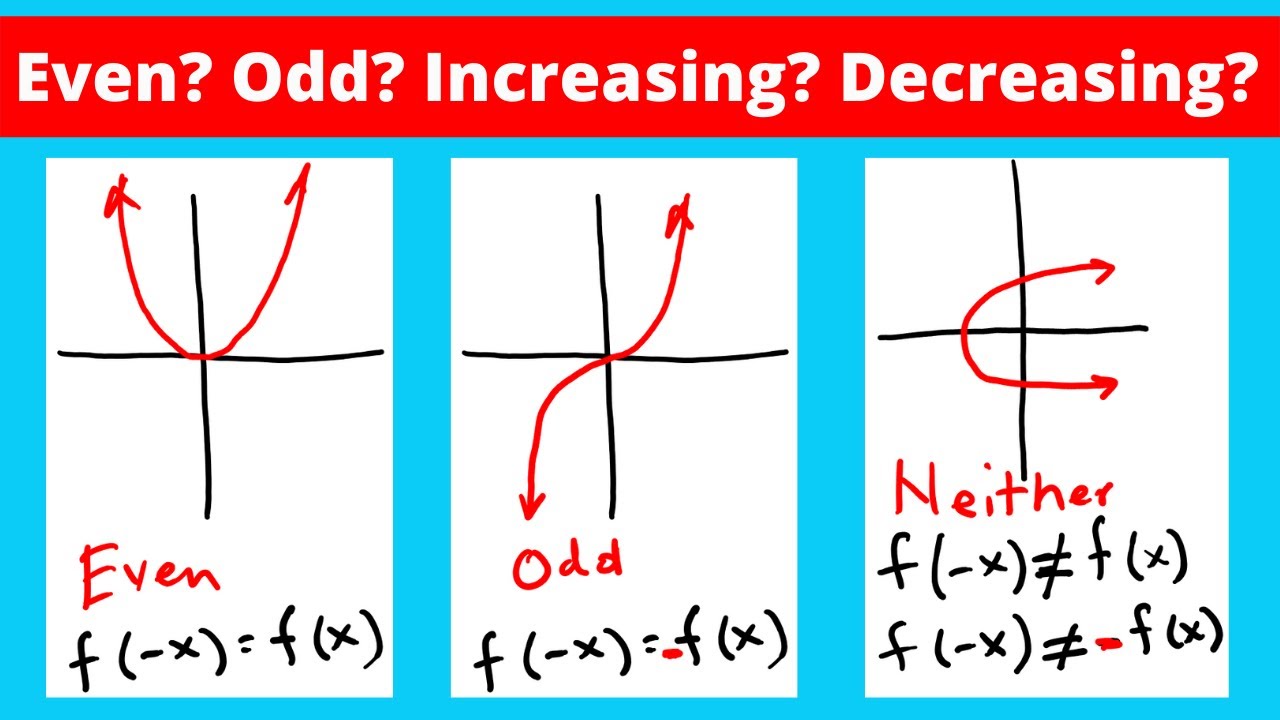
odd function
limit notation
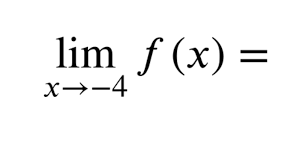
multiplicities
the degree (exponent) of each factor, or the amount of times a factor appears
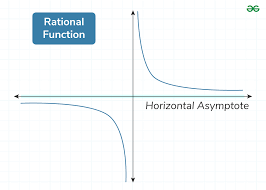
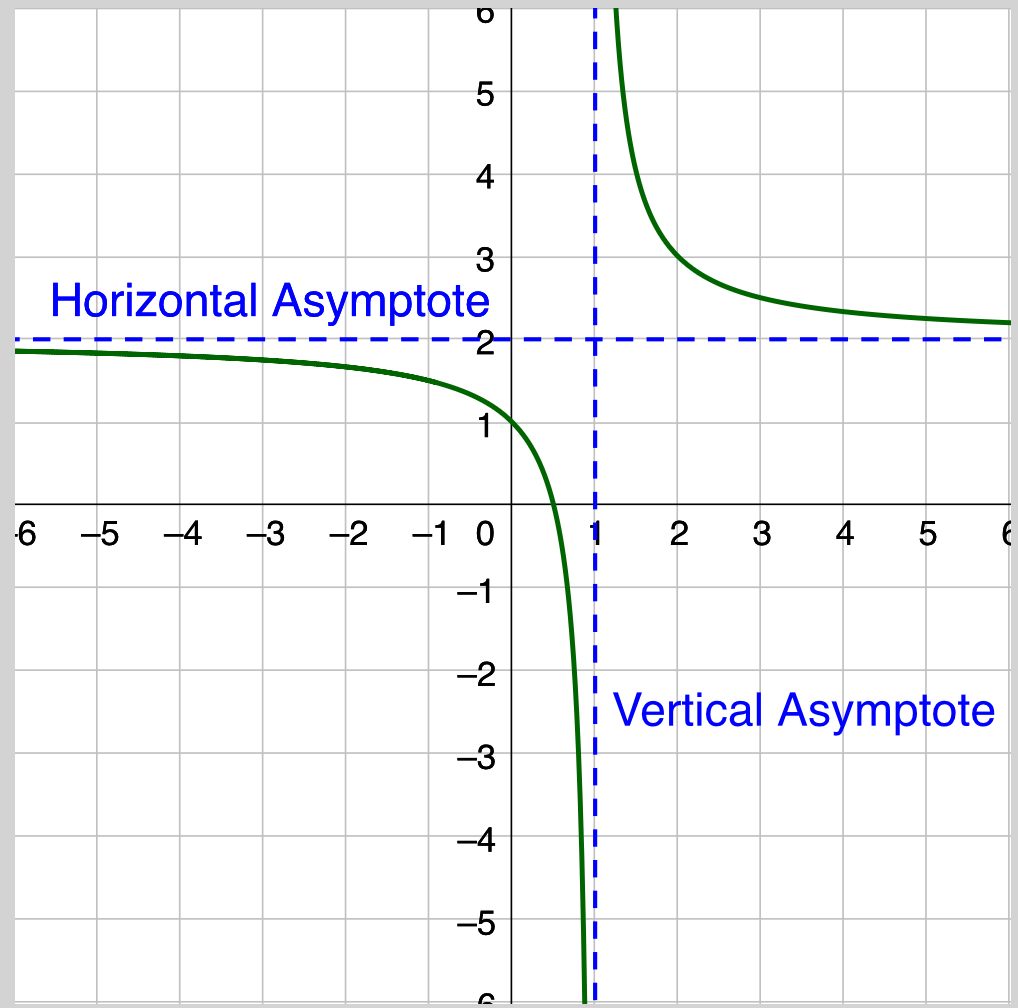
Horizontal asymptote
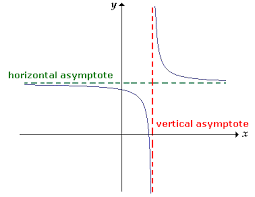
vertical asymptote
Oblique / slant asymptote
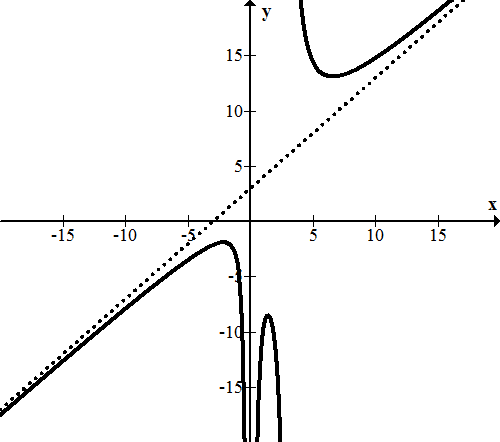
rational function
ratio of two polynomial functions where the denominator polynomial is not equal to zero
undefined
the denominator of the expression is equal to zero. Therefore, the expression cannot be determined at that value.
domain restrictions
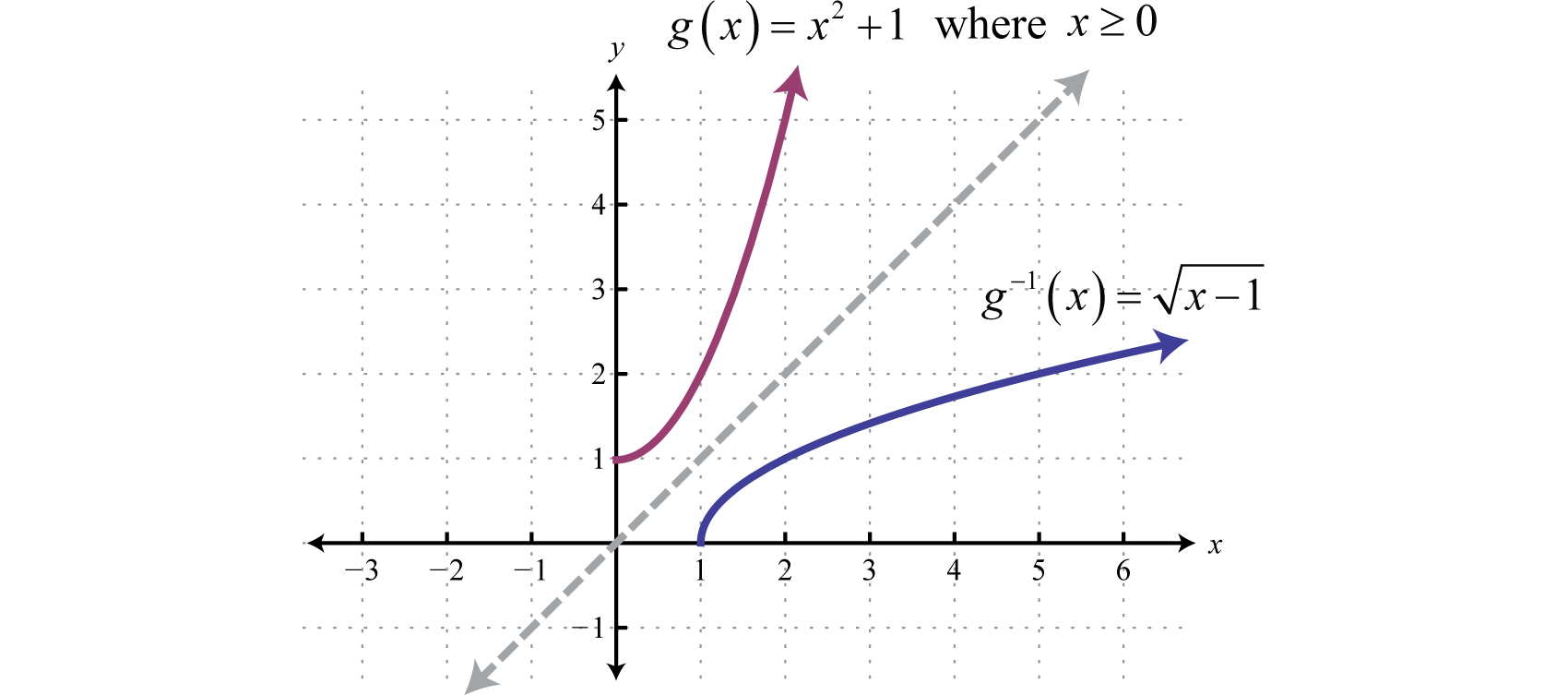
test points
The test point method can be used to solve quadratic inequalities that have a real number solution. It can also be used for linear inequalities, but it's not the most efficient method.
Hole
binomial theorem
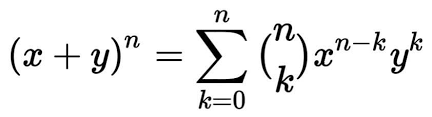
Regression
aims to find a linear relationship to describe the correlation between an independent and possibly dependent variable
residual
the difference between predicted values of y (dependent variable) and observed values of Y
predicted data
used to forecast future outcomes.
Sequence
an ordered set of numbers, i.e., a set of numbers that “occur one after the other.” For instance, the numbers 2 , 4 , 6 , 8 , … , form a sequence
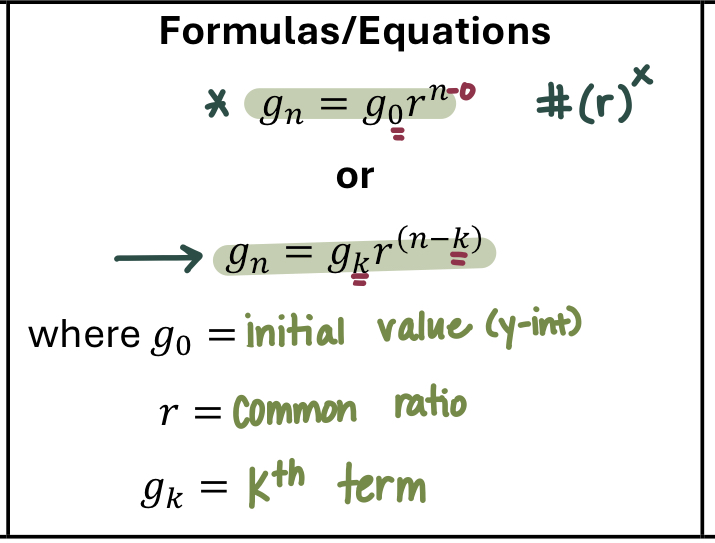
geometric sequence
Geometric sequences behave like exponential functions, except they are not continuous. Increasing geometric sequences increase by a larger amount each step. (% increase always stays the same!)
Geometric sequence equation
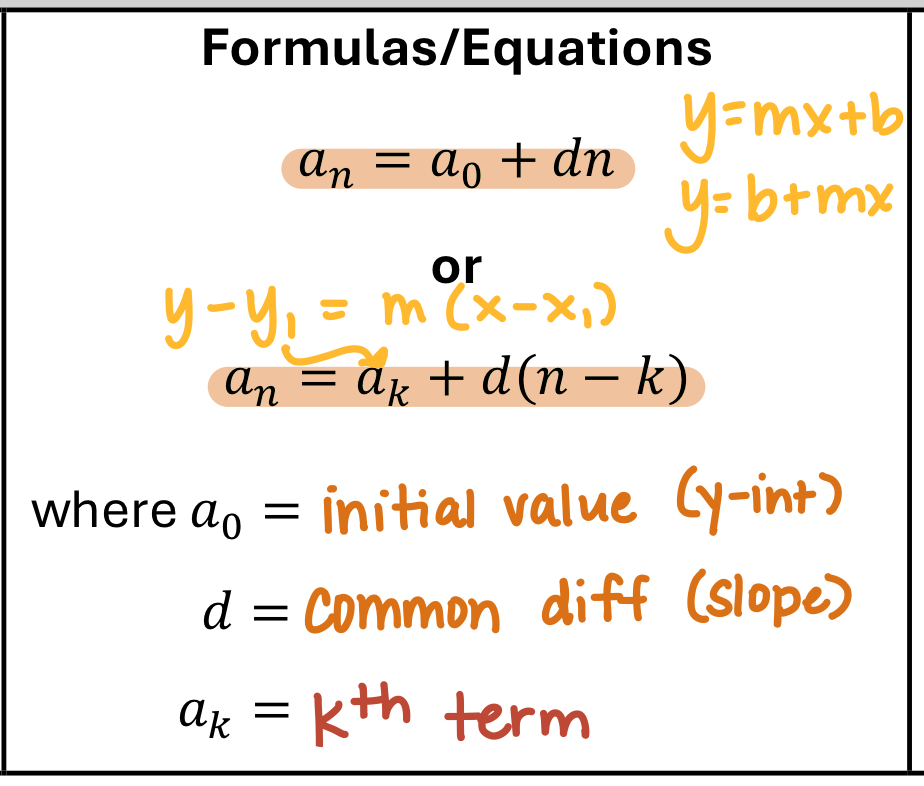
Arithmetic sequence
Arithmetic sequences behave like linear functions, except they are not continuous. Increasing arithmetic sequences increase equally each step. (Slope always stays the same!)
Arithmetic sequence equation
common difference
Constant rate of change in successive terms.
common ratio
Constant proportional change
Exponential growth
growth whose rate becomes ever more rapid in proportion to the growing total number or size.
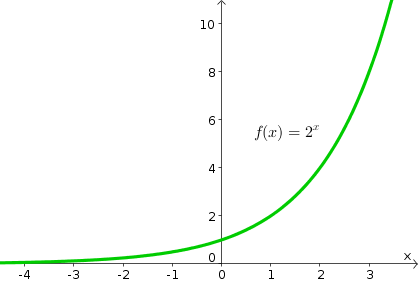
Exponential decay
decay if it decreases at a rate proportional to its current value
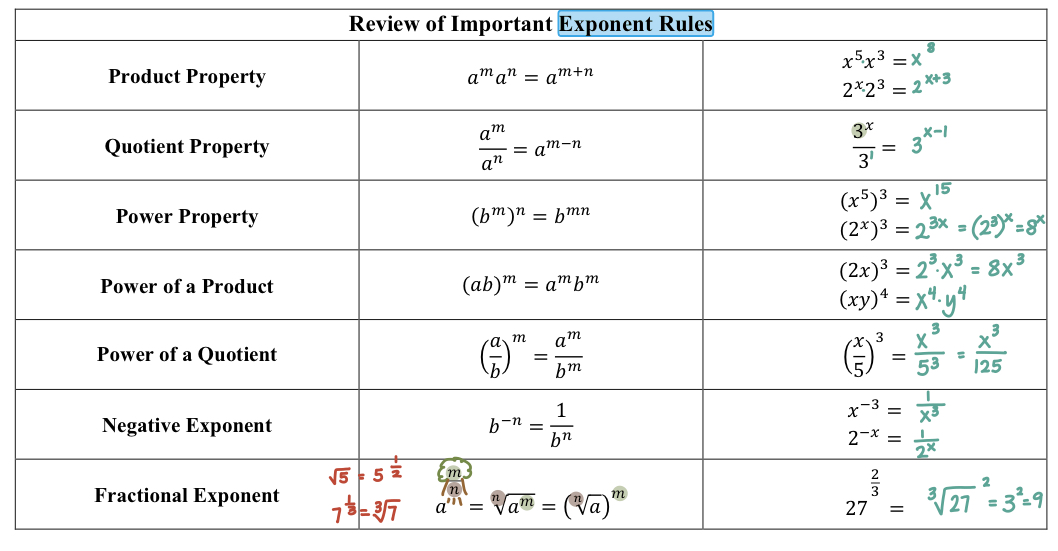
exponent rules
natural base
The natural base, or e, is a fundamental irrational number used in calculus to model exponential growth and decay, and is the base for the natural logarithm
composite function
complex function created by two or more functions
inverse
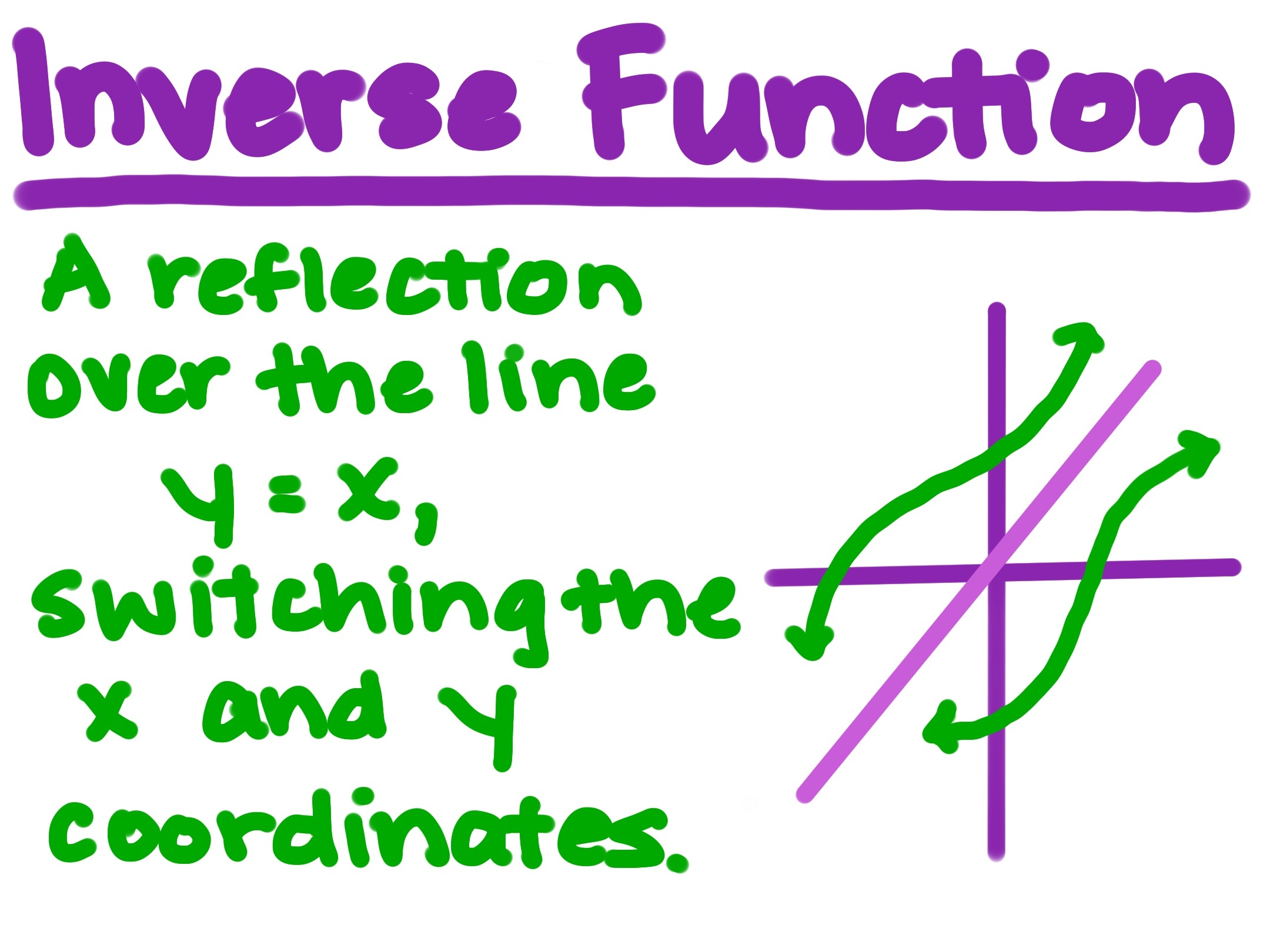
y = x line
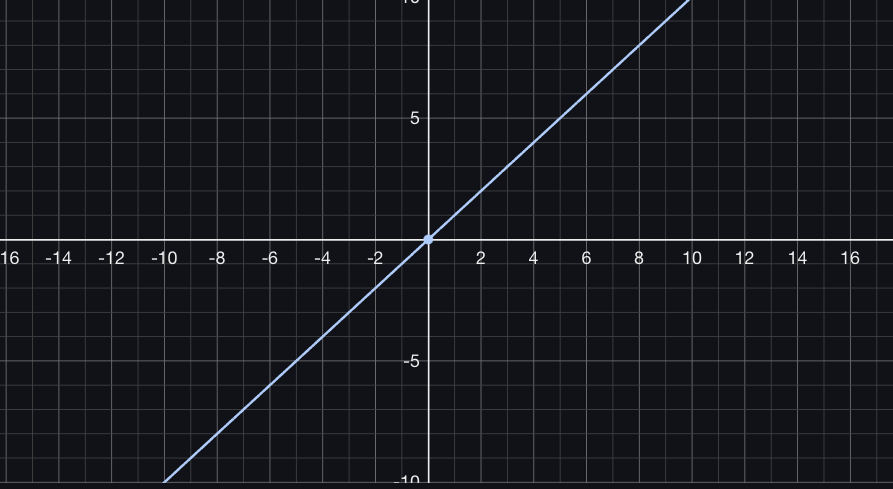
Logarithm
the exponent or power to which a base must be raised to yield a given number
base of a log
Any number greater than 0, but not 1. If base isn’t written it’s understood as a base of 10.
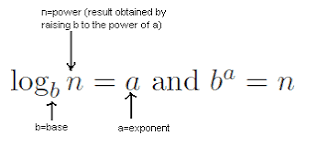
argument of a logarithm
The number that you are taking the logarithm of.
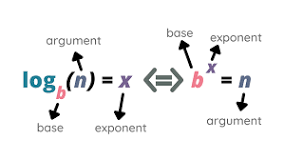
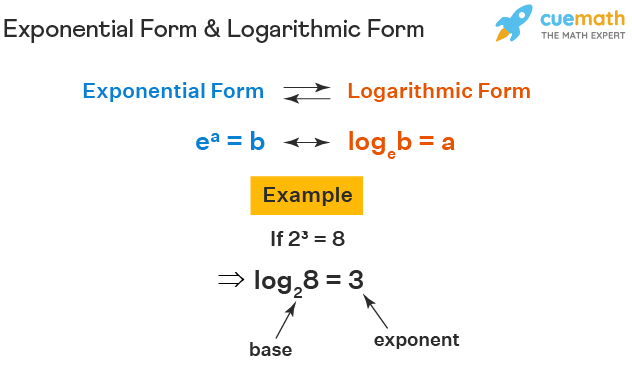
exponential form
A way of writing a number that is multiplied by itself more than once.
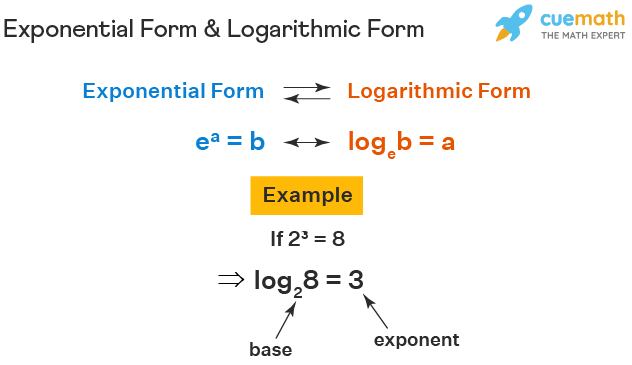
logarithmic form
semi-log plot
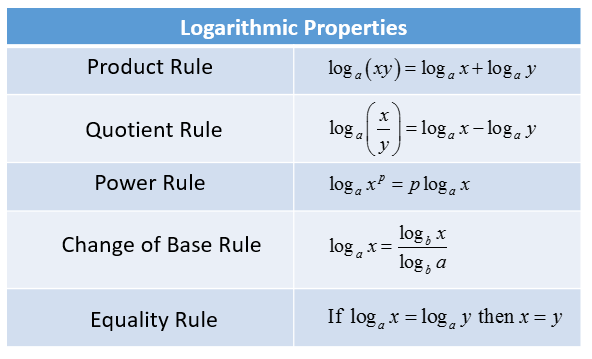
log properties
Change of base
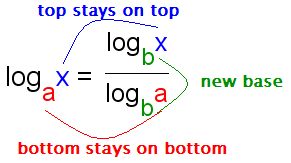
Natural log
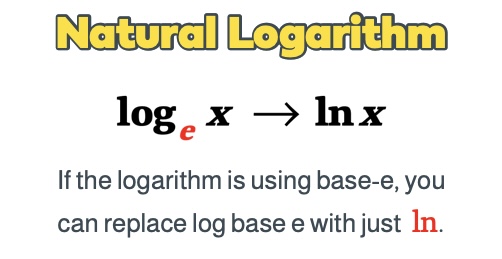
convert log to exponential
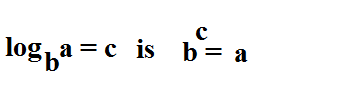
Convert exponential to log
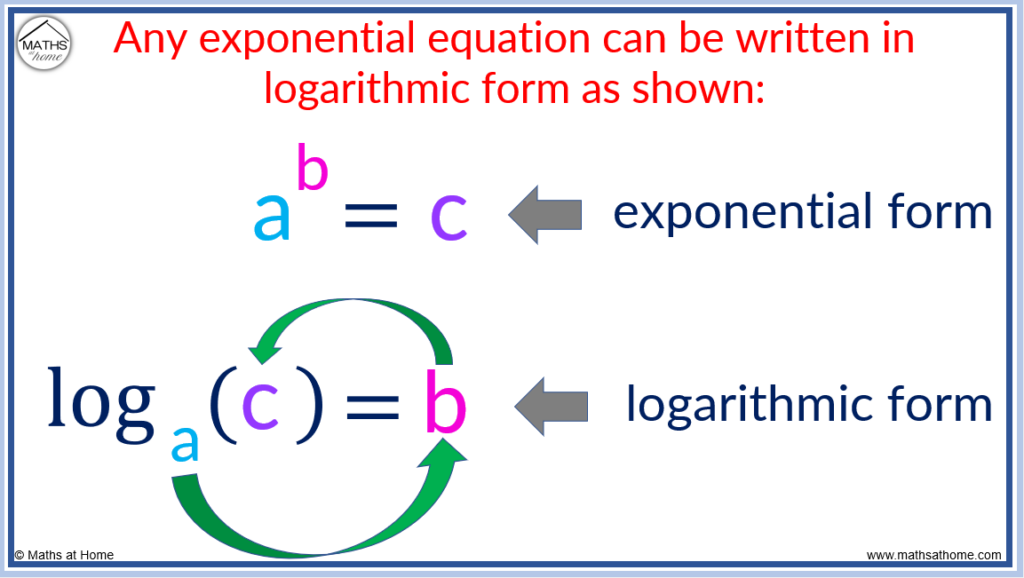
Linear equation
Y=mx+b
linear shape
linear asymptotes
A straight line that approaches a curve
linear domain and range
Domain: All real numbers
Range: all real numbers
Absolute value equation
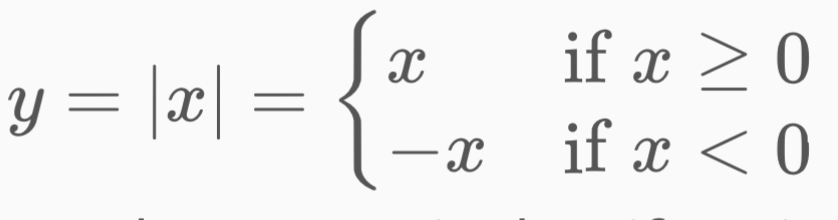
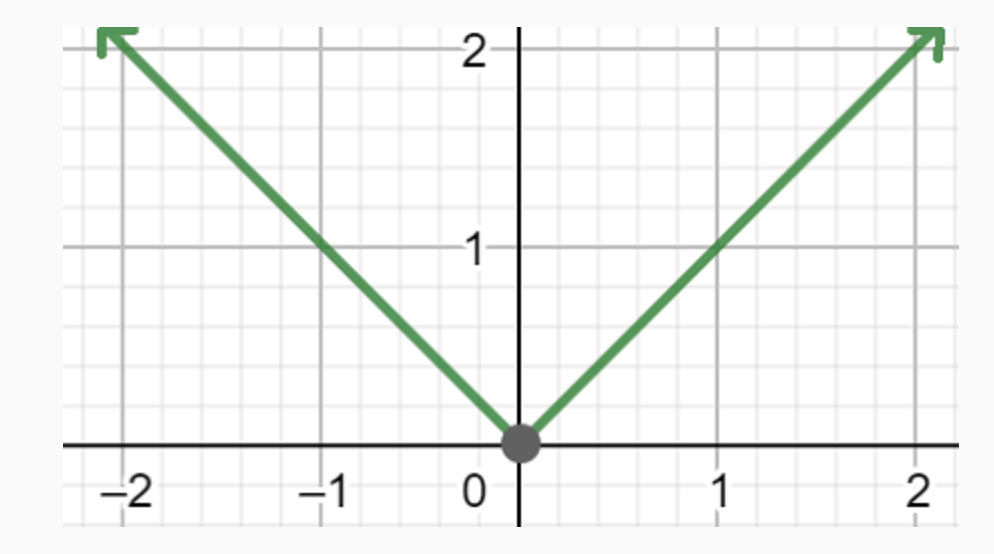
absolute value shape
absolute value asymptote
None
absolute value domain and range
Domain: all real numbers
Range: [0,∞]
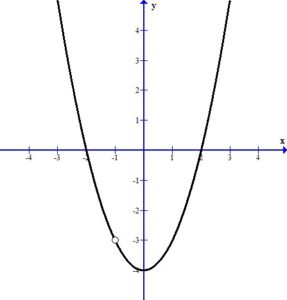
quadratic equation
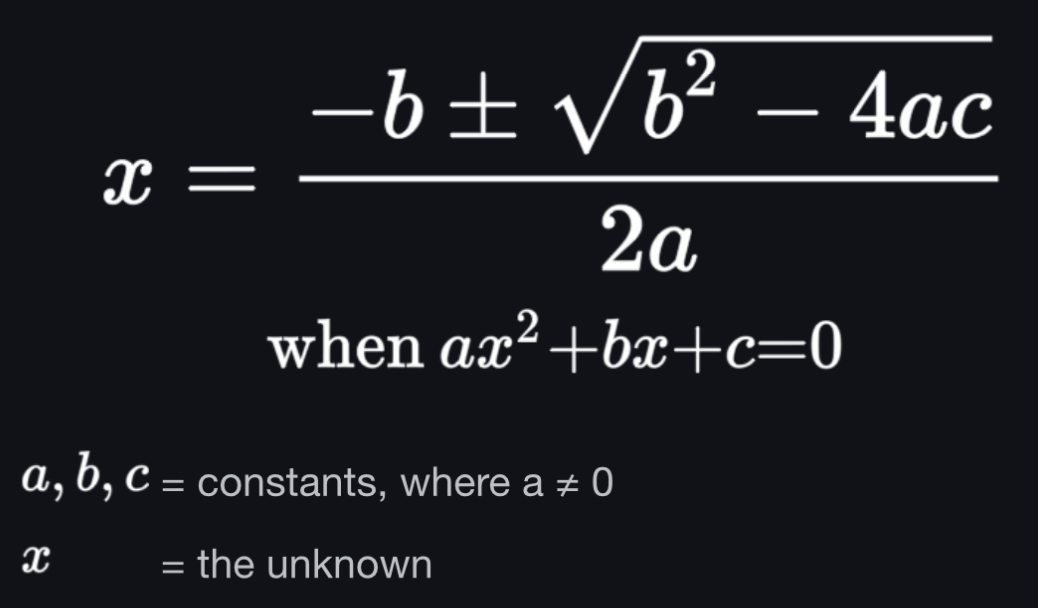
quadratic shape
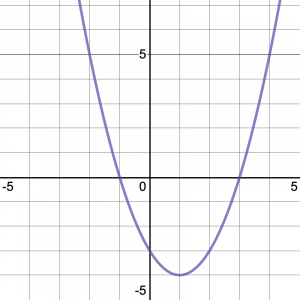
Quadratic asymptotes
No asymptotes
Quadratic domain and range
Domain: all real numbers
Range: depends if concave down or up… ez tho 😛
square root equation
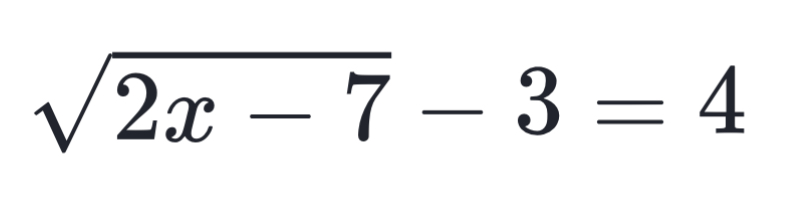
square root shape
square root asymptotes
No asymptotes
square root domain and range
domain is [0, ∞)
range is [0, ∞)
Cubic equation
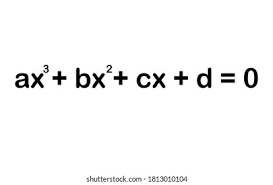
Cubic shape
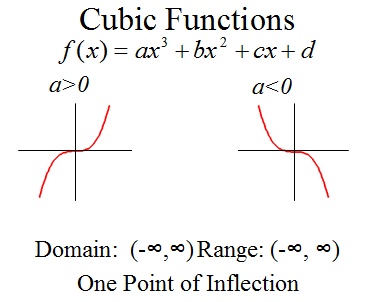
cubic asymptotes
No asymptotes
cubic domain and range
Domain: all real numbers
Range: all real numbers
cube root equation
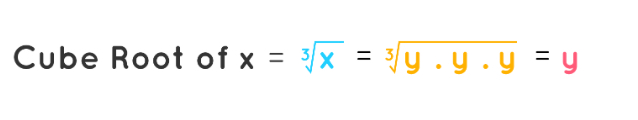
Cube root shape
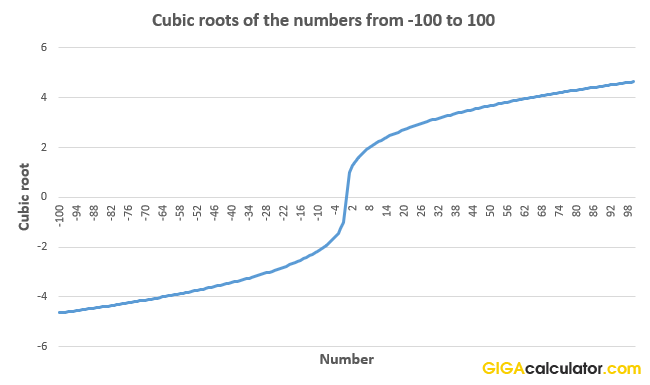
cube root asymptotes
No asymptotes
cube root domain and range
Domain: all real numbers
Range: all real numbers
exponential equation
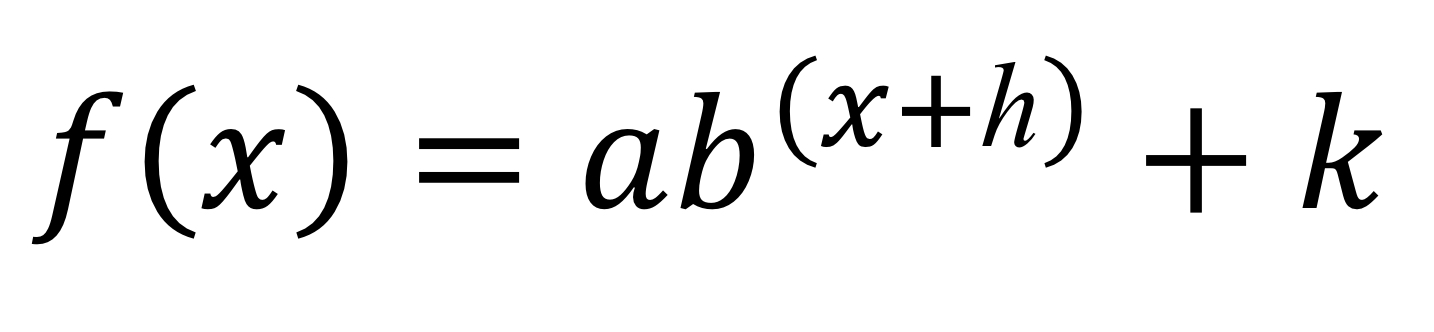
exponential shape
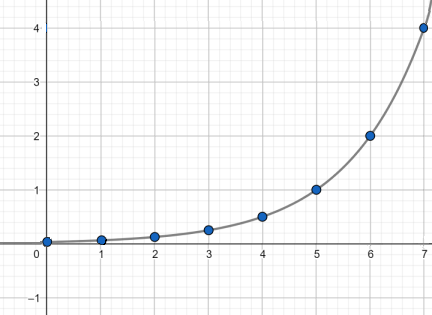
exponential asymptote
Horizontal asymptote
exponential domain and range
Domain: All real numbers
Range: range bounded by the horizontal asymptote