Urinary and Digestive Systems Study Guide for Lab Practical
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Parts of a Nephron
Renal corpuscle
- Glomerulus
- Glomerular capsule ( or Bowman's capsule)
Proximal convoluted tubule
Nephron loop
- Descending limb of nephron loop
-Ascending limb of nephron loop
Distal convoluted loop
Collecting duct
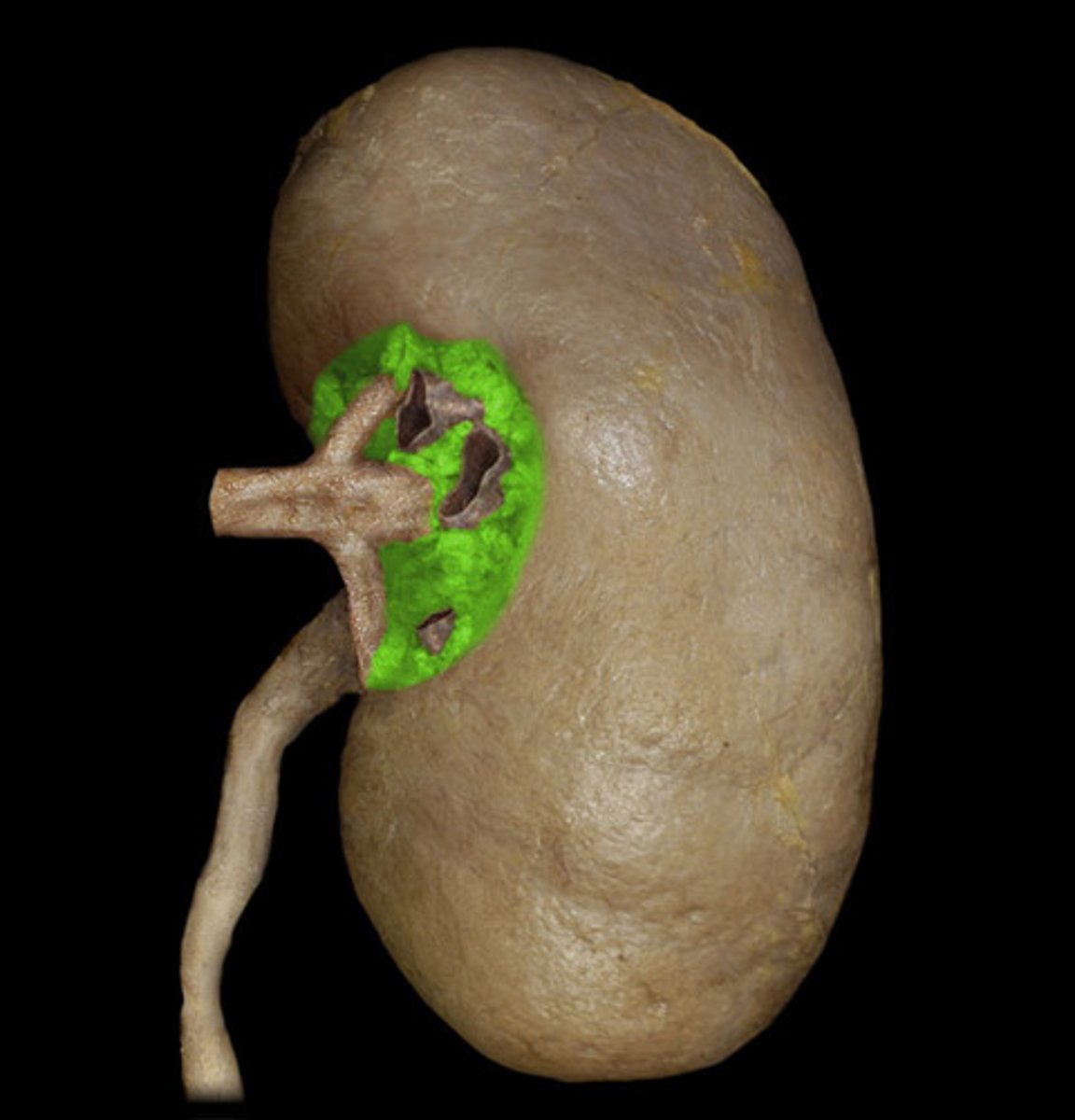
hilum
indented opening in the kidney where vessels (and nerves) enter and leave; indentation on the medial side of the kidney where the ureter leaves the kidney.
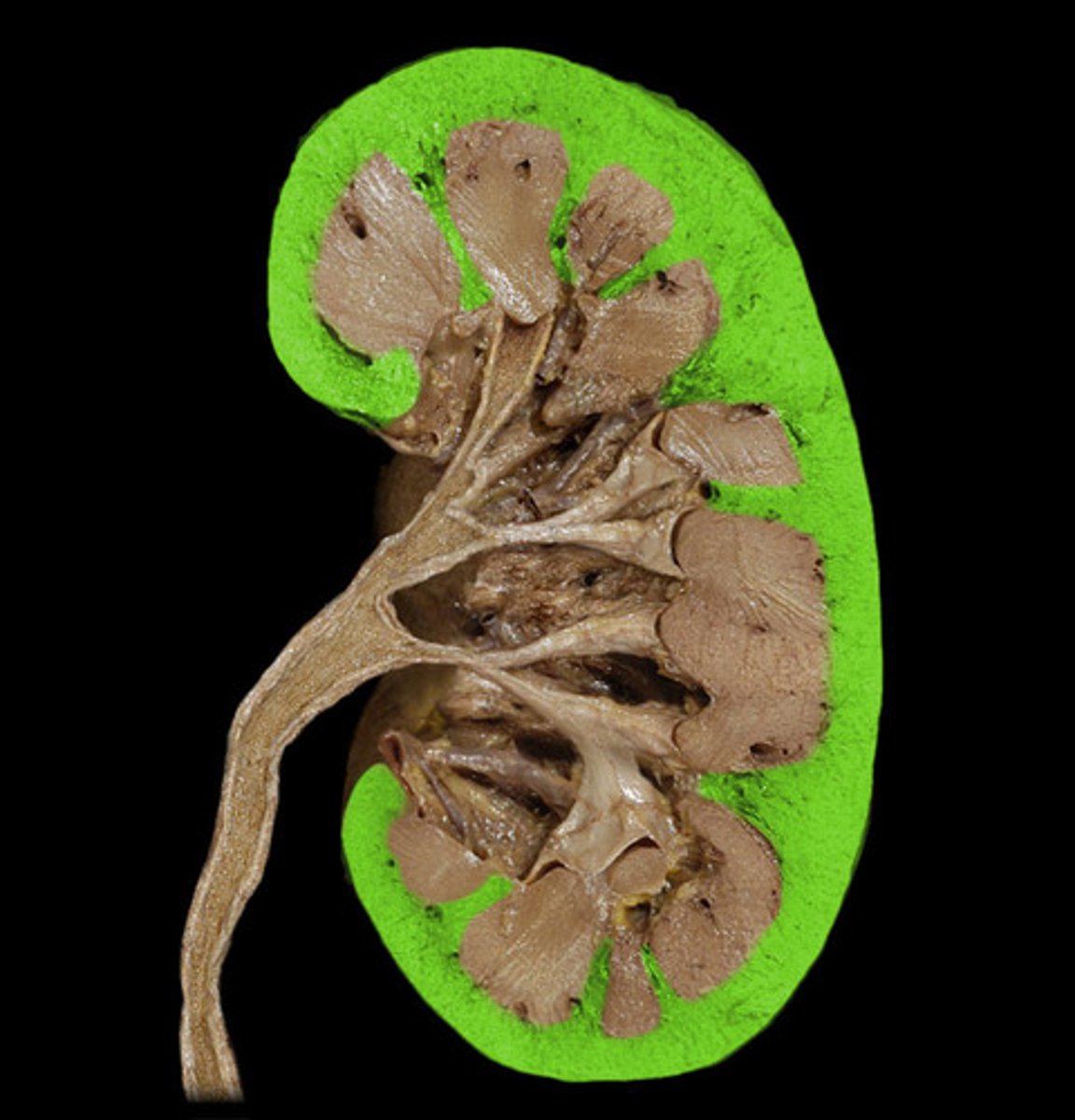
renal cortex
outer layer/region of the kidney
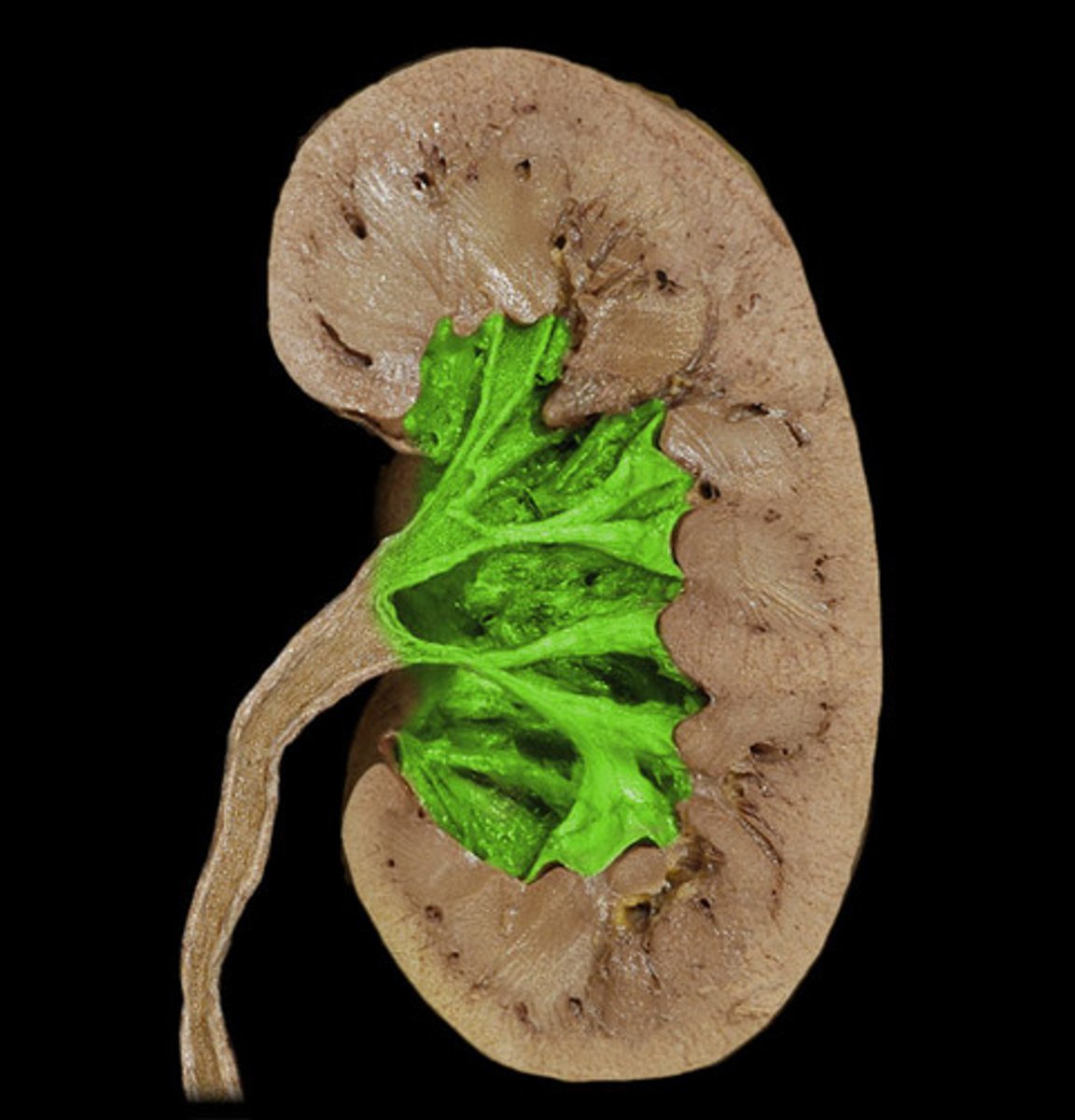
renal sinus
space (hollow chamber) within kidney that is adjacent to renal medulla, contains calyces and renal pelvis
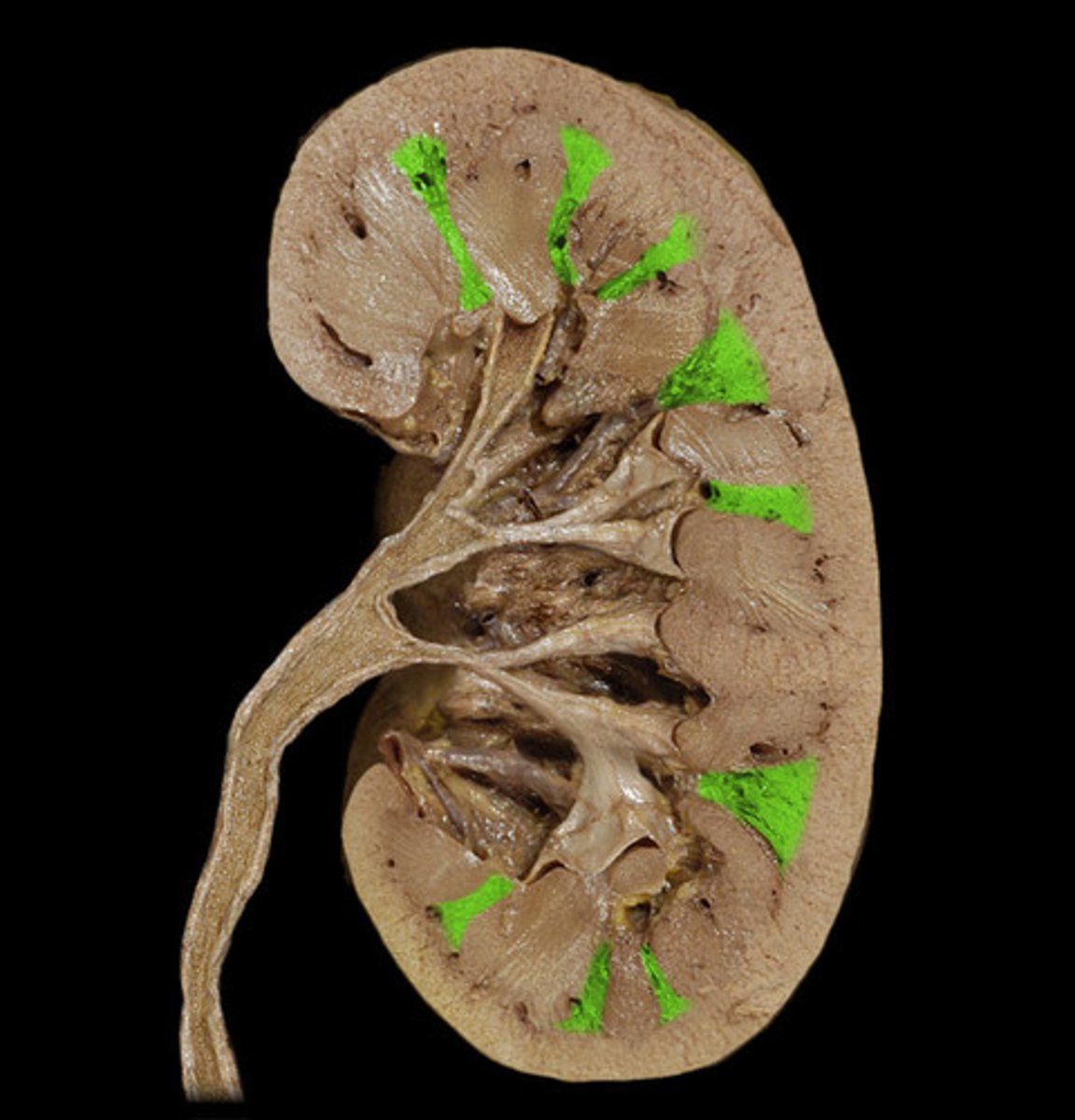
renal column
area of cortical tissue running between the medullary pyramids; inward extensions of the cortex tissue separating the renal pyramids.
renal medulla made of renal pyramids
the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids; Renal pyramids are cone-shaped tissues of the kidney. the renal medulla is made up of 10 to 18 of these conical subdivisions. The broad base of each pyramid faces the renal cortex, papilla (apex), and points internally towards the pelvis.
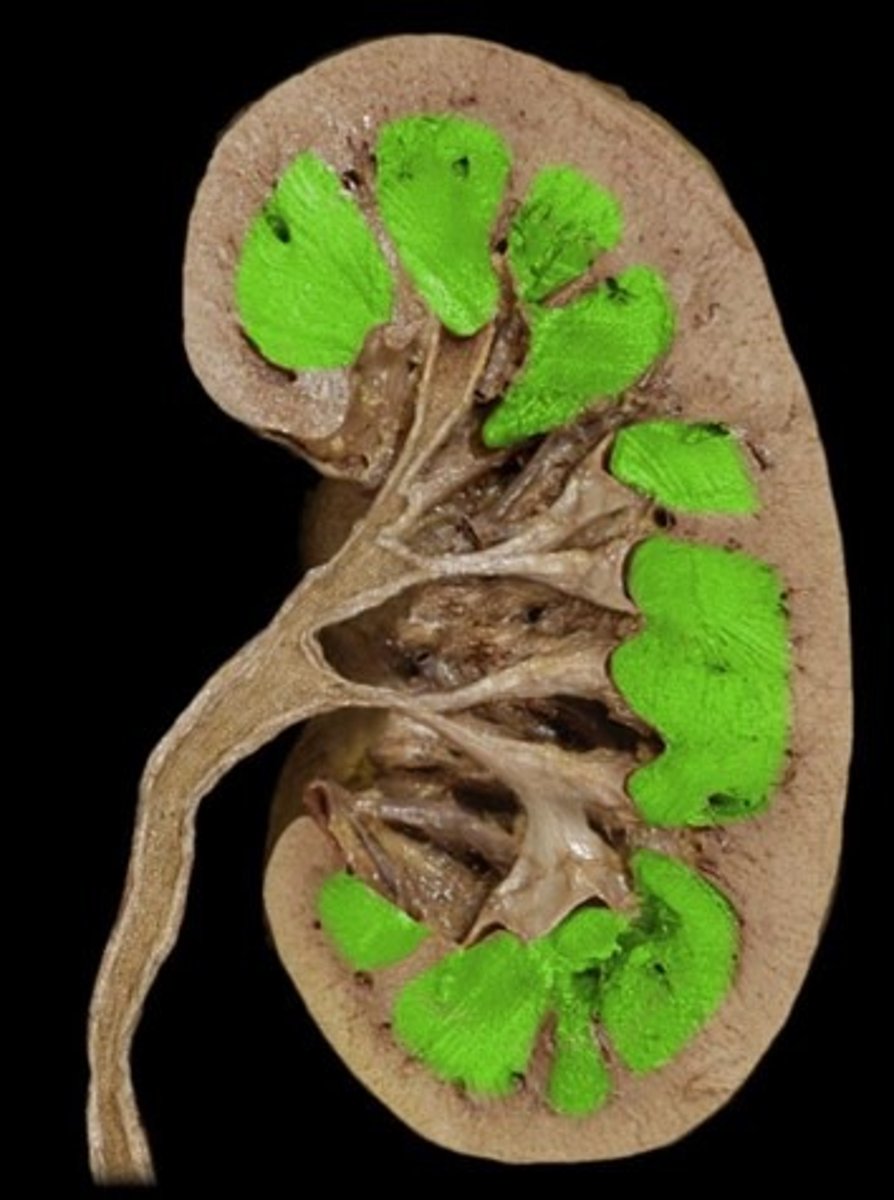
renal papilla
apex or tip of renal pyramid
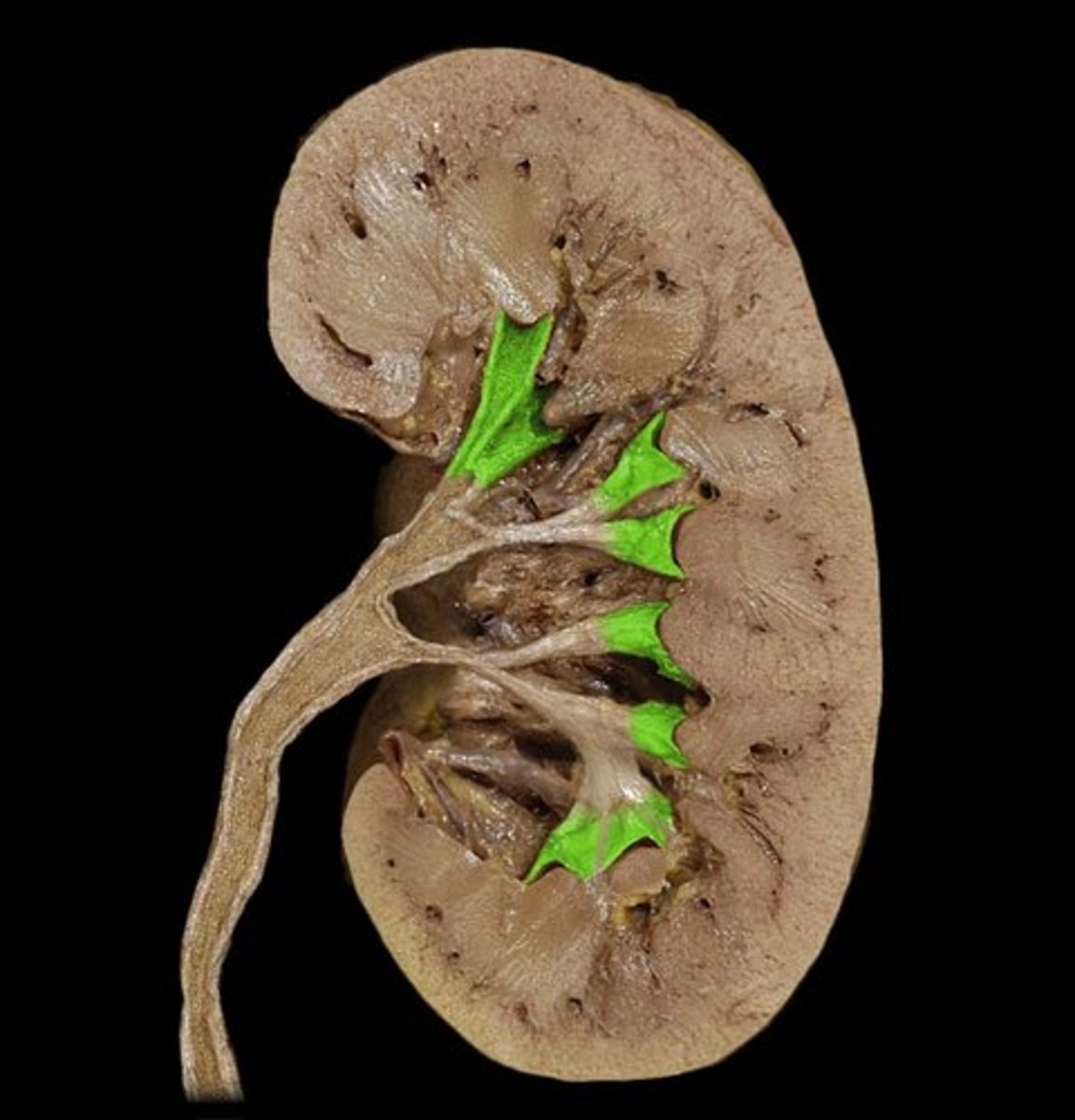
major calyx
urine passageway: The cavity formed by the convergence of several minor calyces, which drain urine from the minor calyxes into the renal pelvis
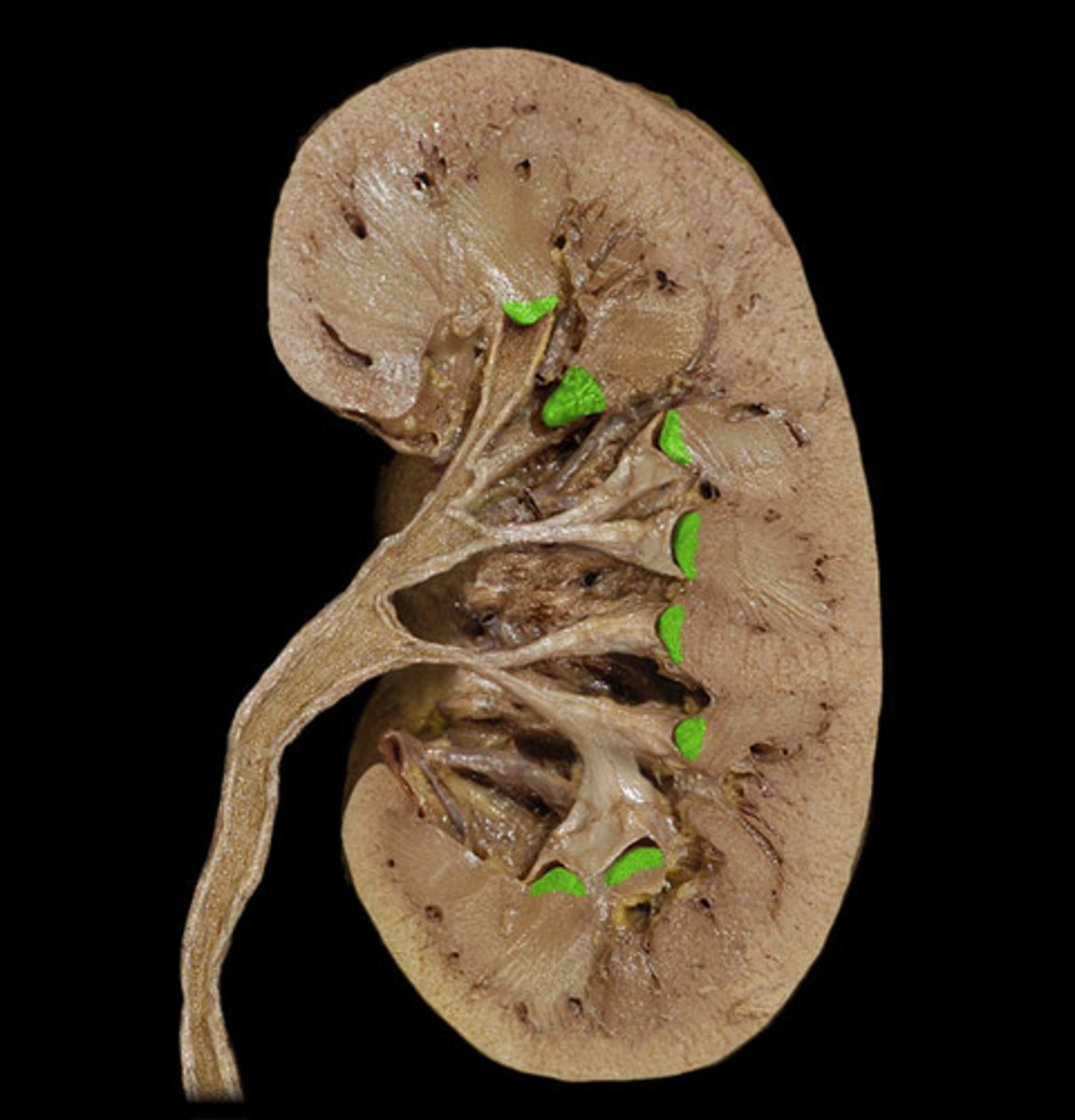
minor calyx
cup-shape that surrounds pyramids and encircles the papilla of each pyramid; collects its urine.
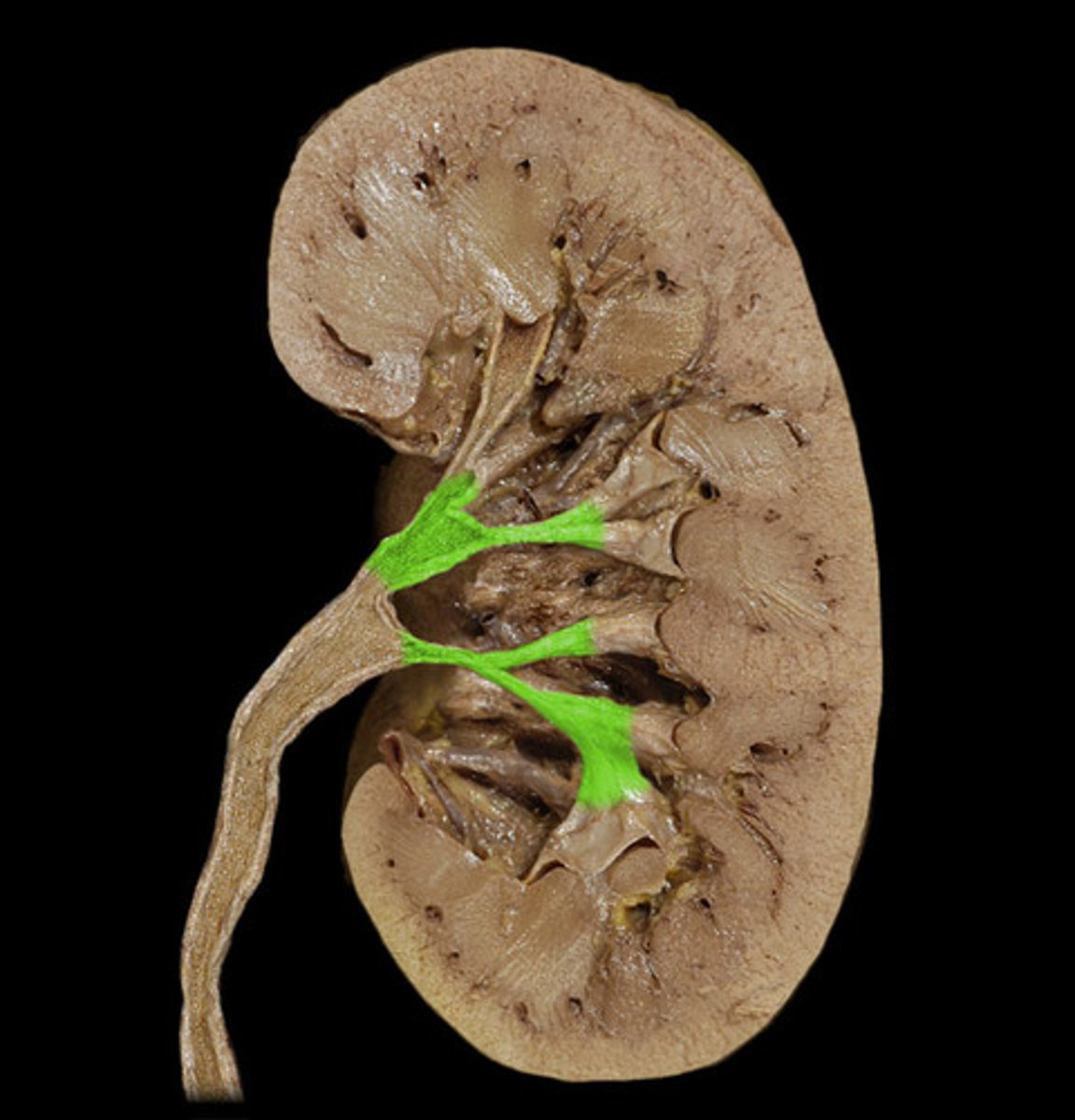
renal pelvis
funnel-shaped reservoir that collects the urine and passes it to the ureter
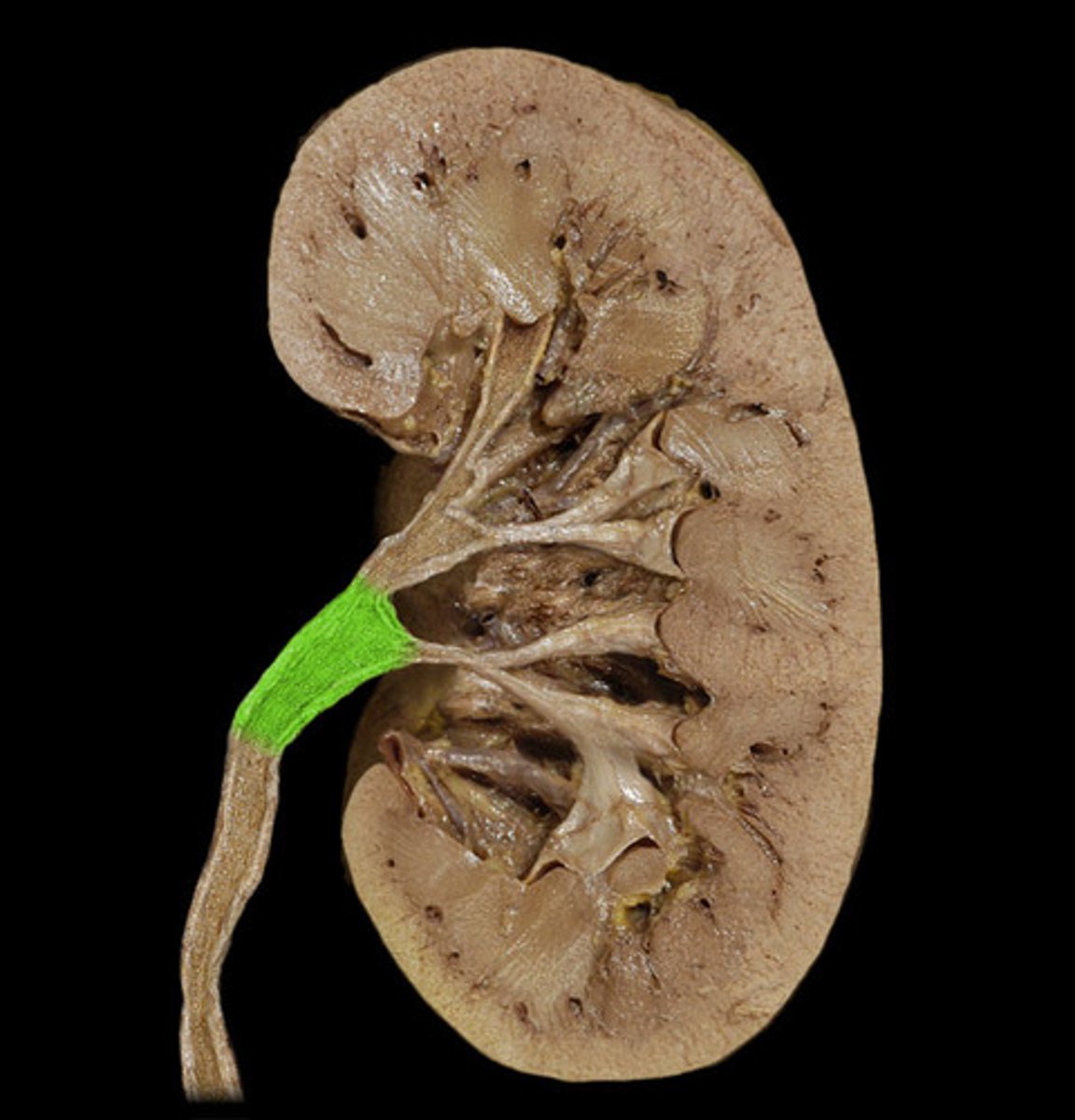
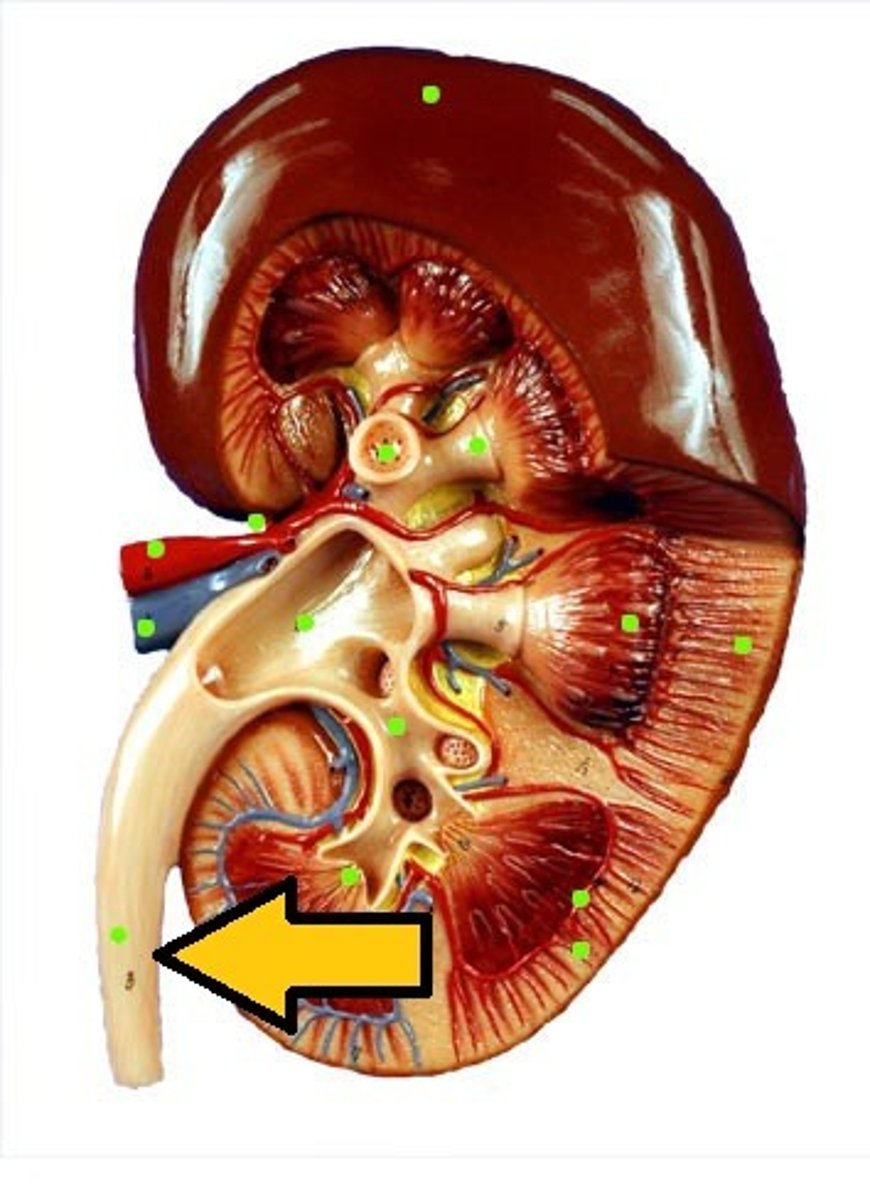
ureter
tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder
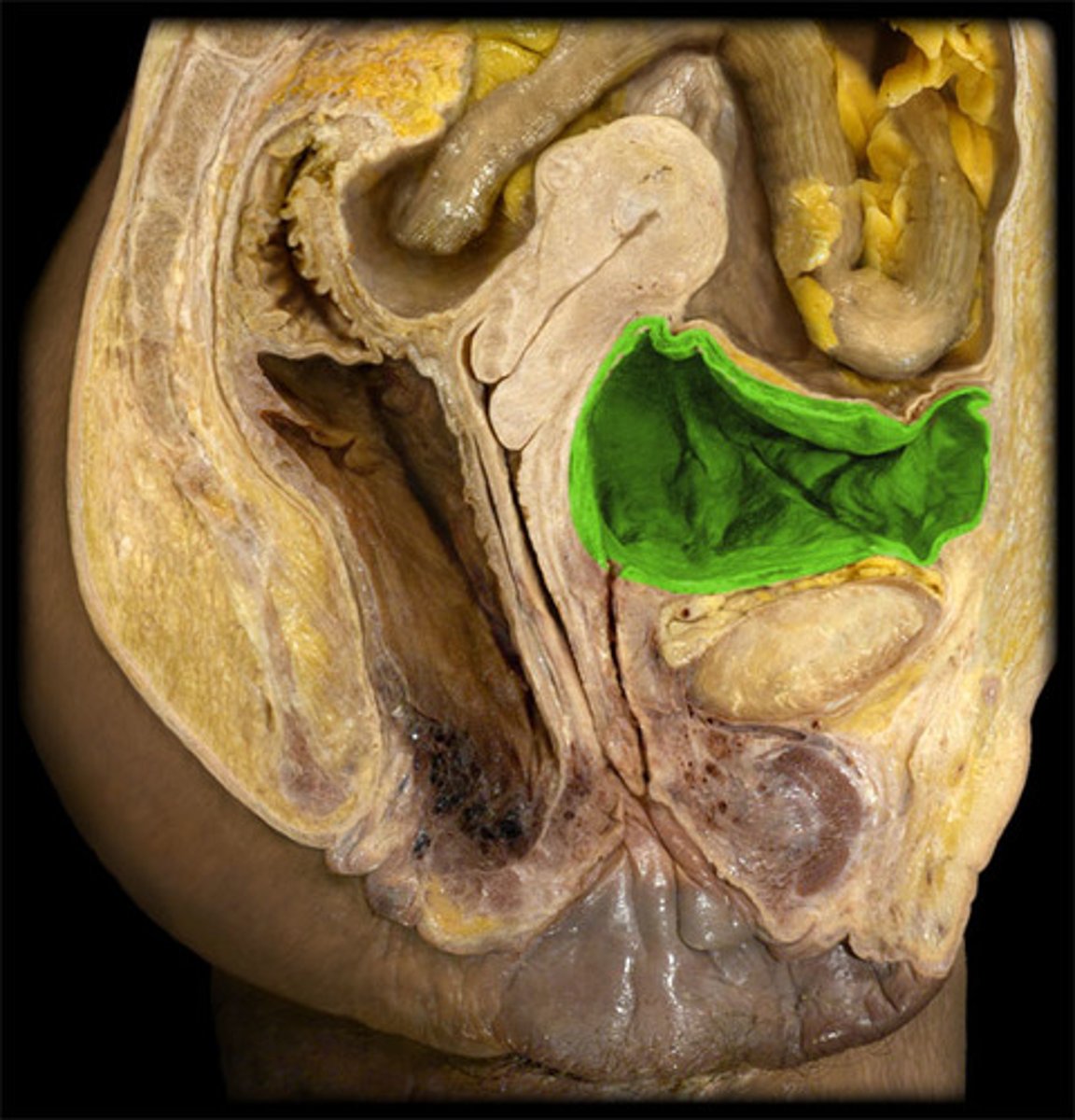
female urinary bladder
hollow, muscular sac that holds and stores urine
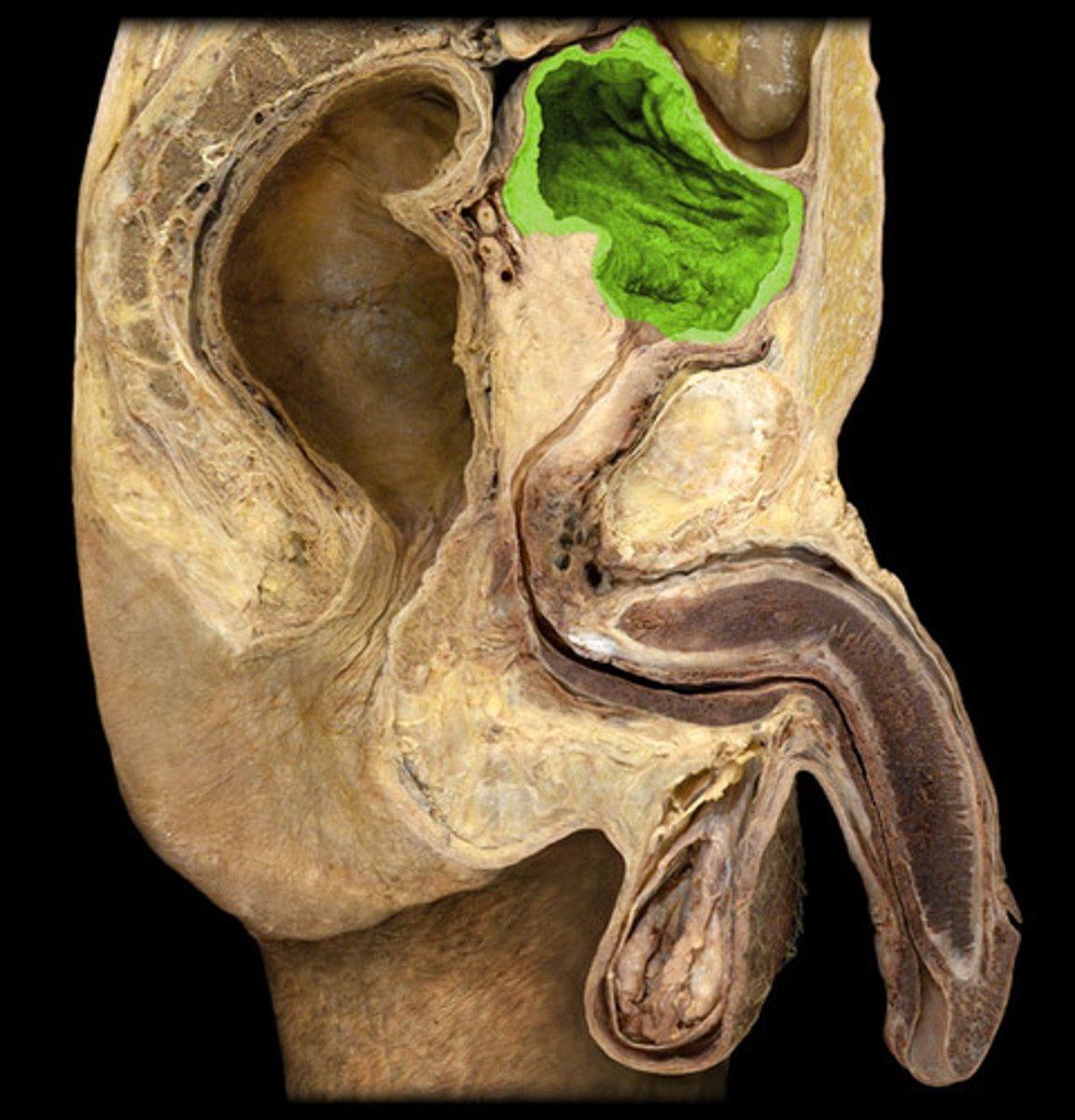
male urinary bladder
The base of the urinary bladder is between the rectum and the symphysis pubis; prostate gland surrounds the neck inferiorly.
female urethra
approximately 1.5 inches long
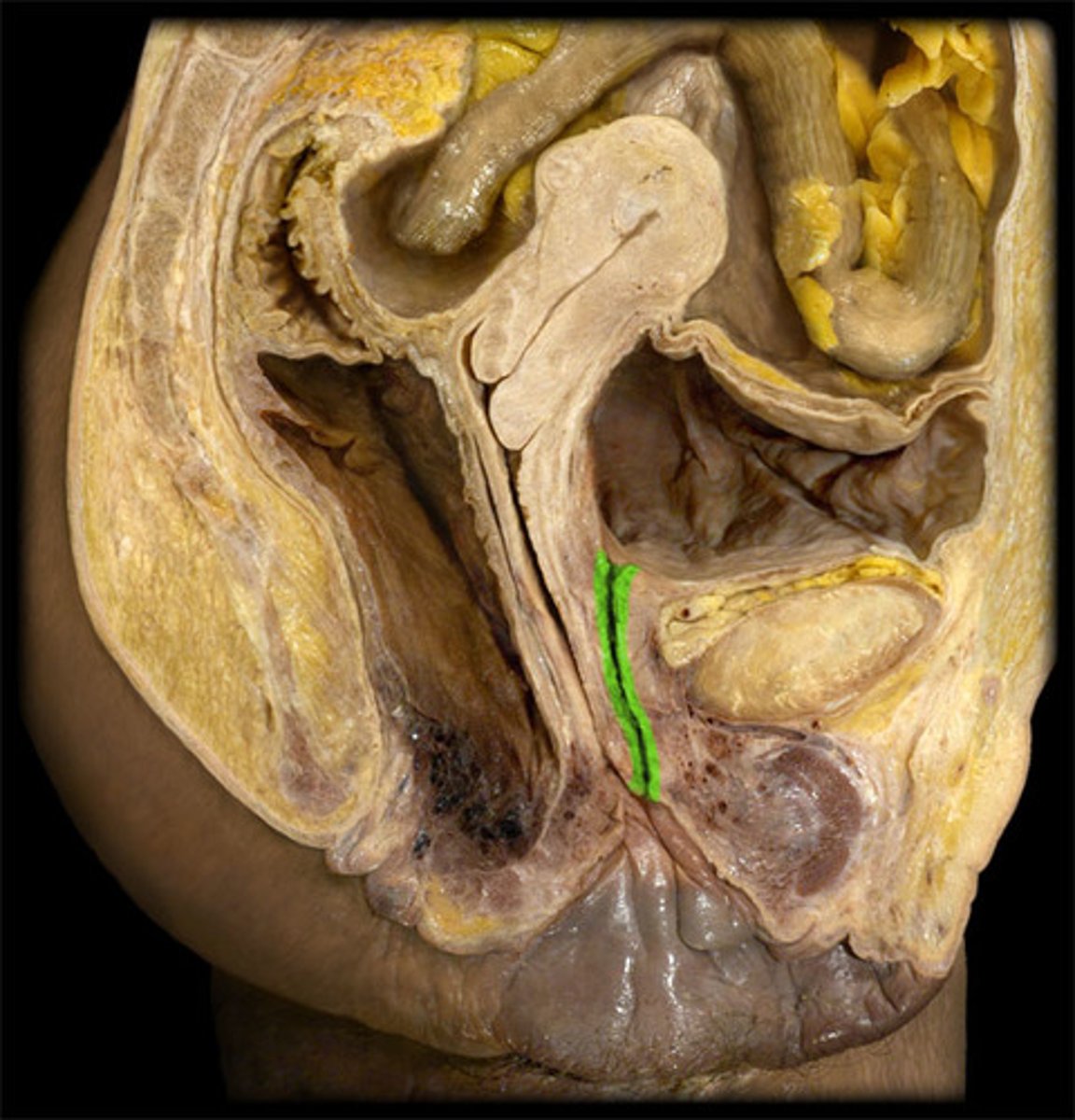
ureters
tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
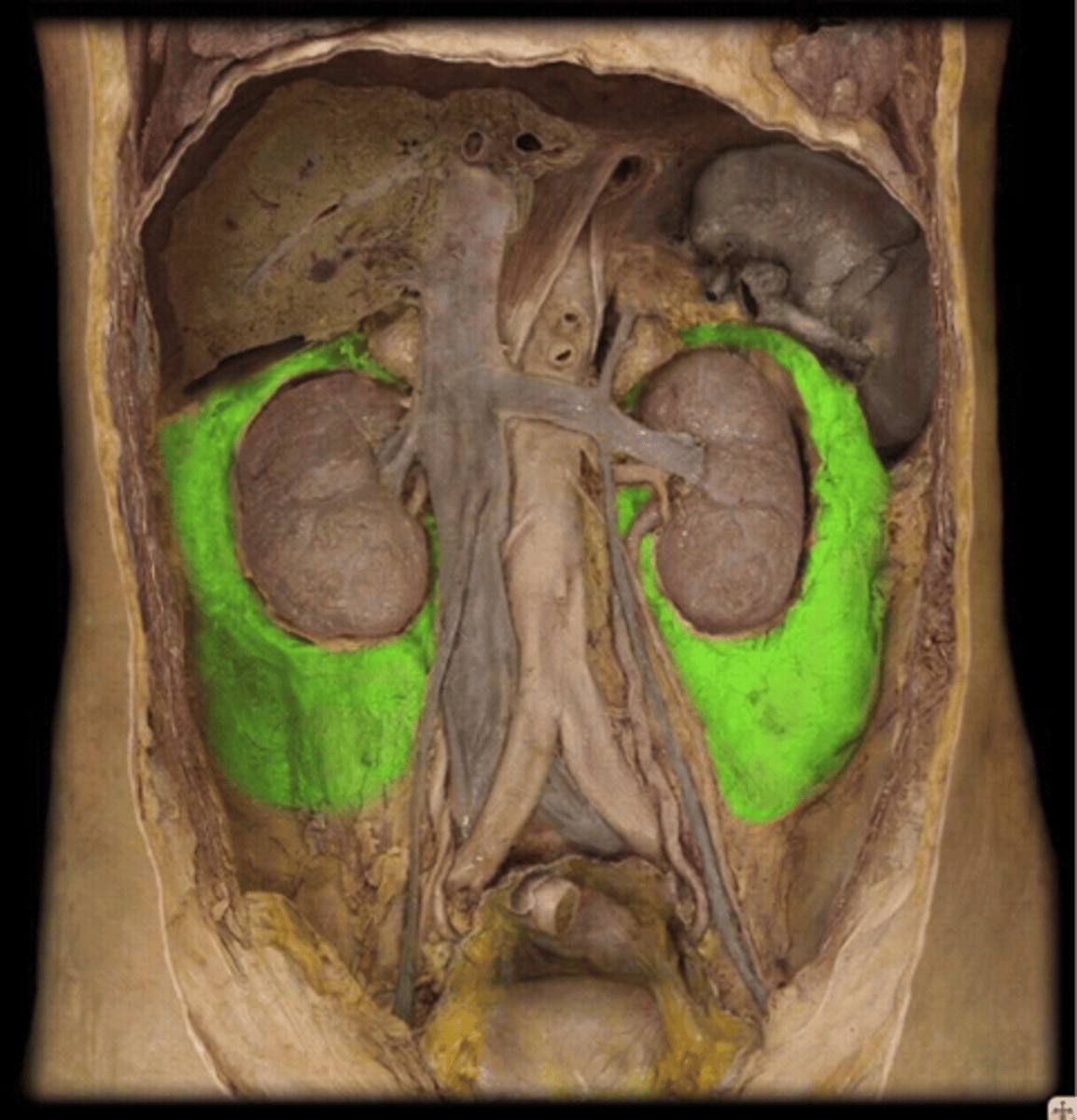
pararenal fat
outermost layer between renal fascia and peritoneum
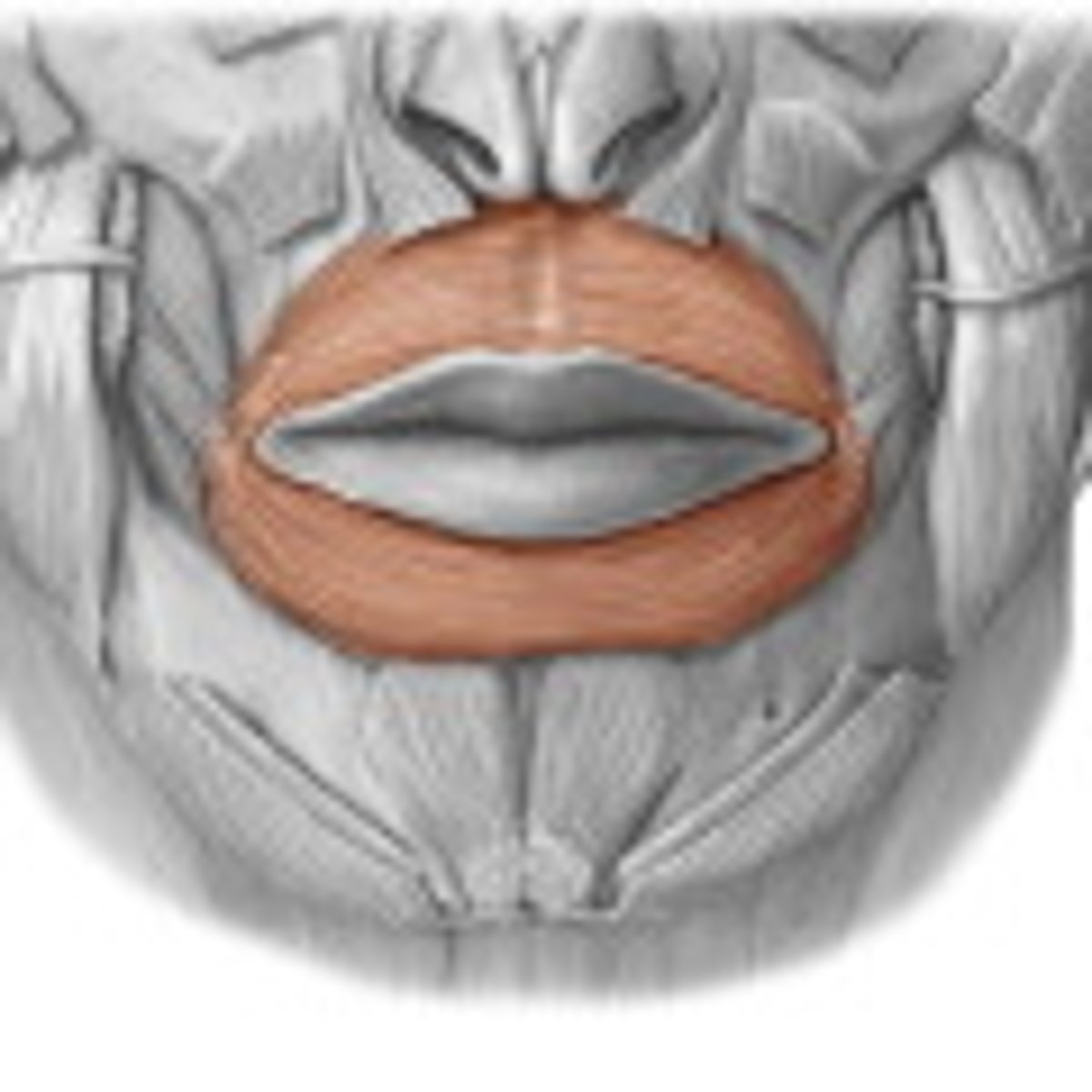
lips
form the opening to the oral cavity; cheil/o
oral cavity
The part of the mouth behind the gums and teeth that is bounded above by the hard and soft palates and below by the tongue and by the mucous membrane connecting it with the inner part of the mandible.
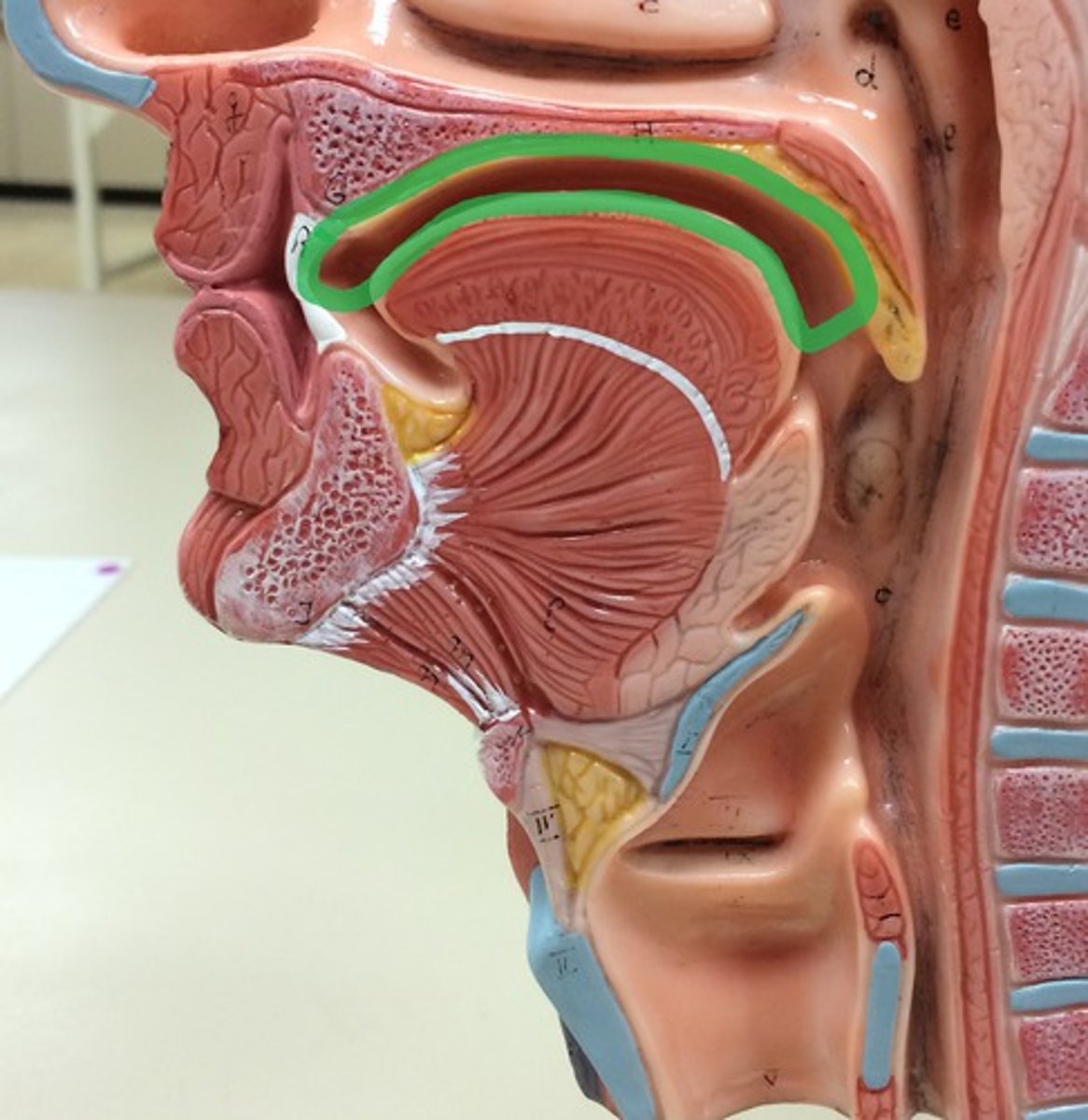
hard palate
bony anterior (front) portion of the palate
soft palate
muscular posterior (back) portion of the palate; not supported by bone
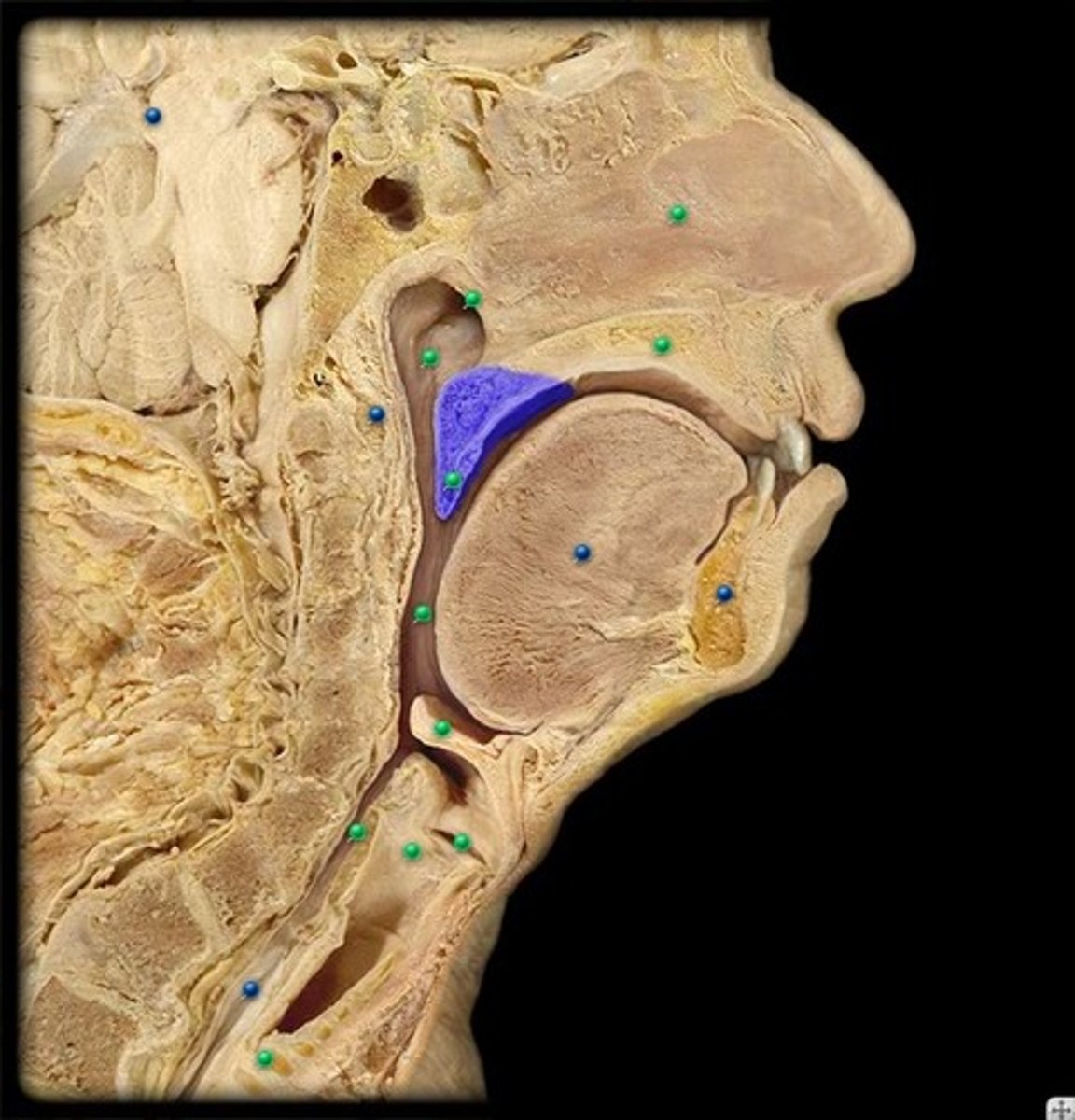
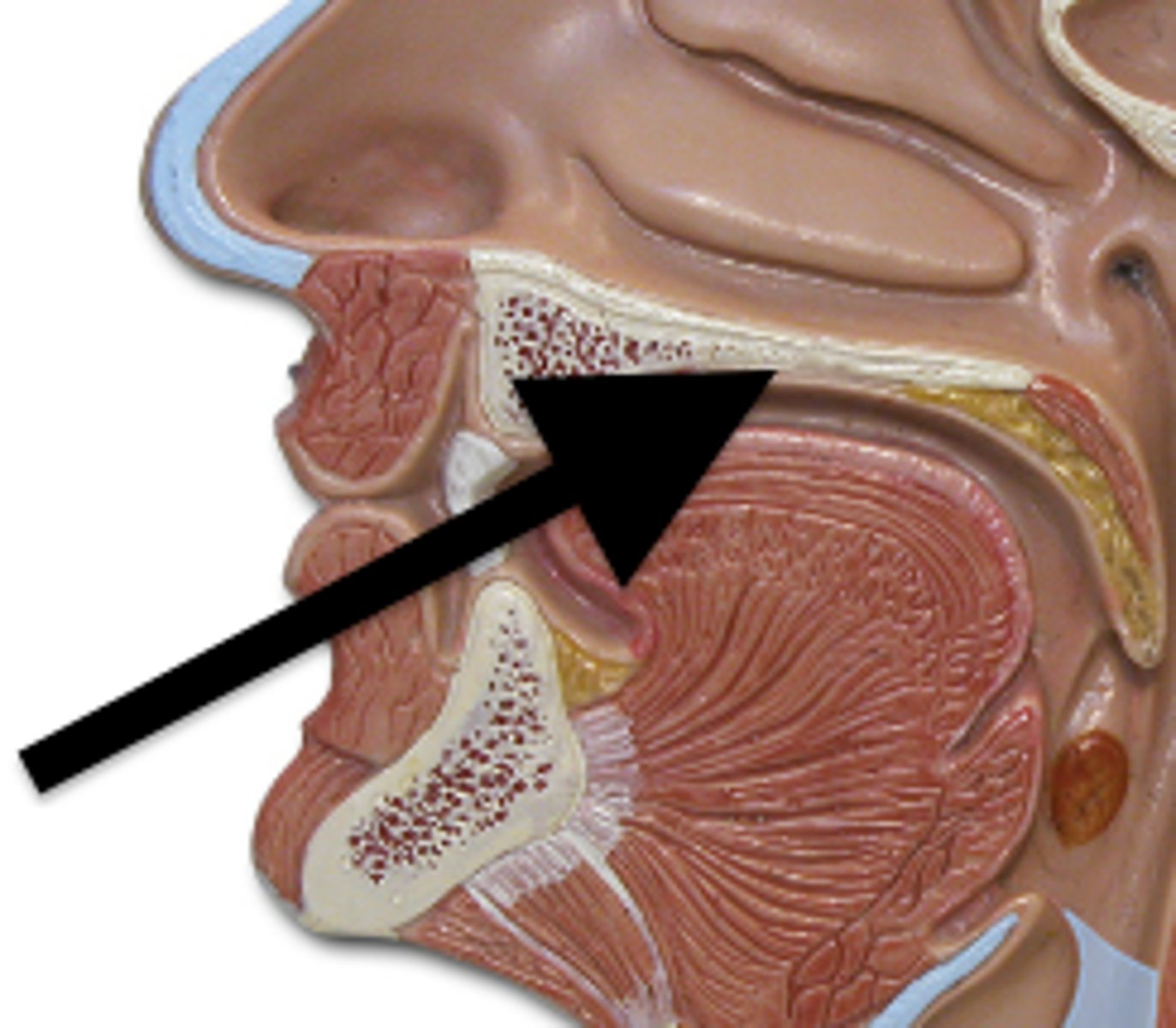
pharynx
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx; the membrane-lined cavity behind the nose and mouth, connecting them to the esophagus.
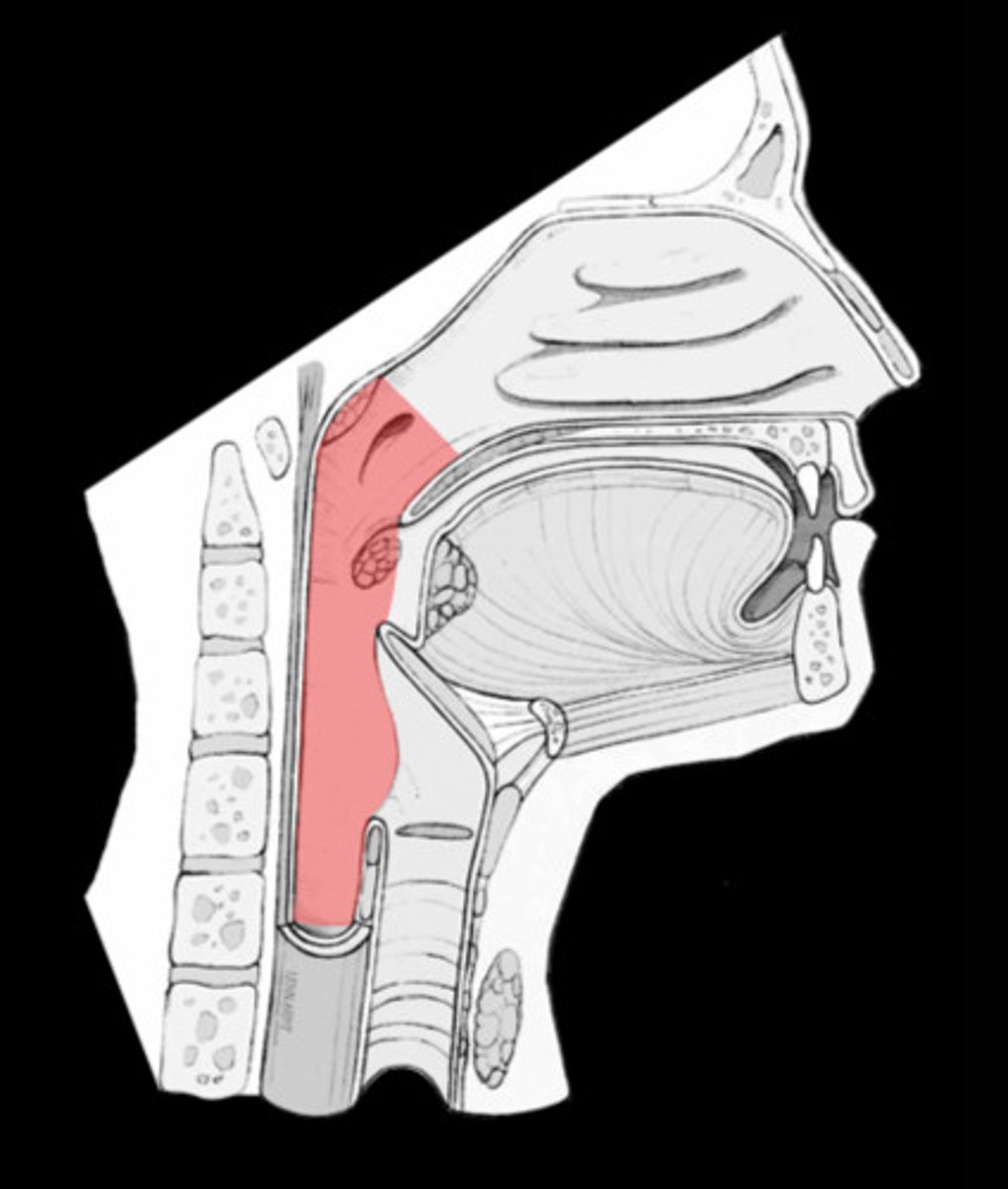
oropharynx
central portion of the pharynx between the roof of the mouth and the upper edge of the epiglottis
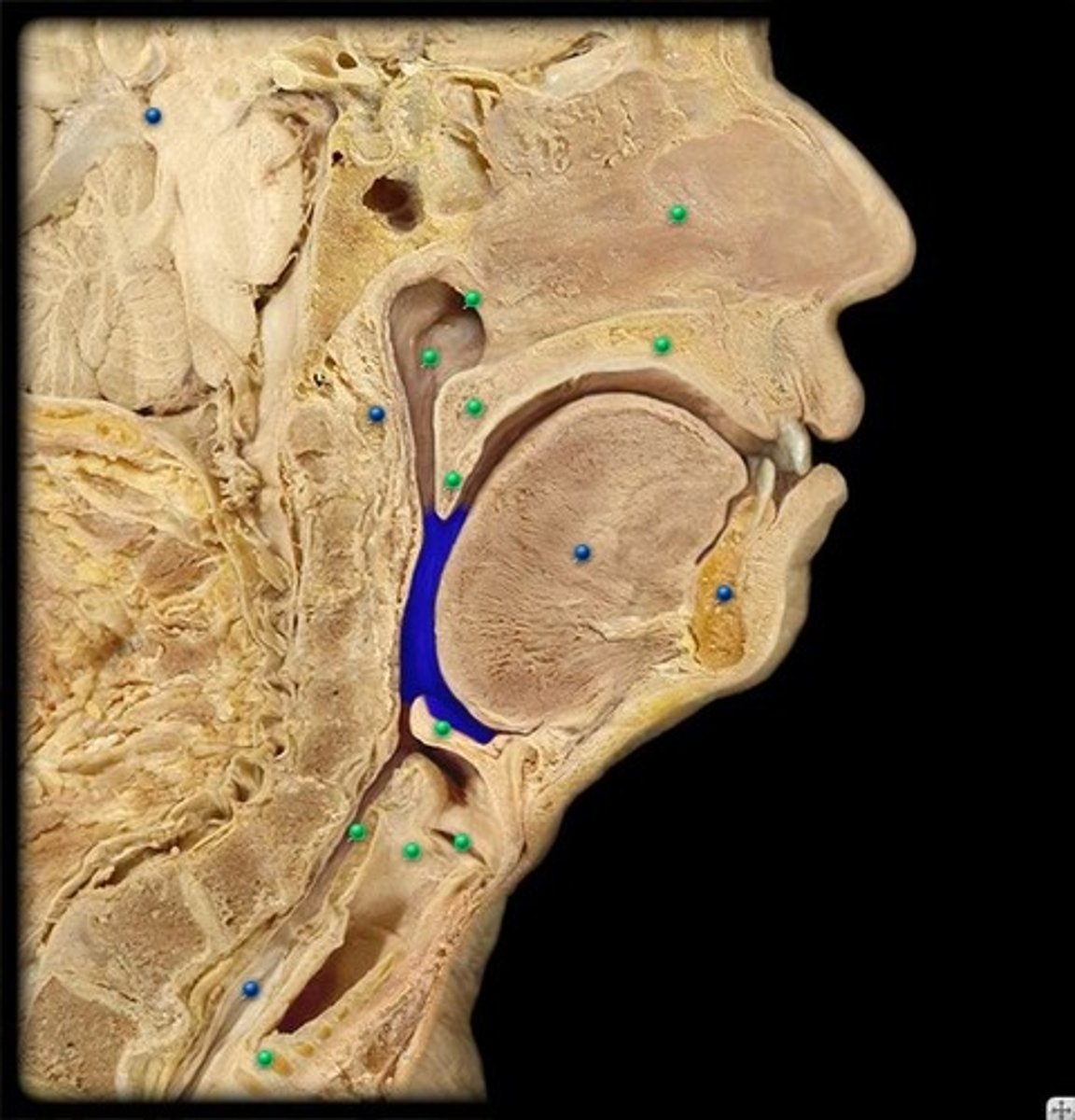
laryngopharynx
lower part of the pharynx, just below the oropharyngeal opening into the larynx and esophagus
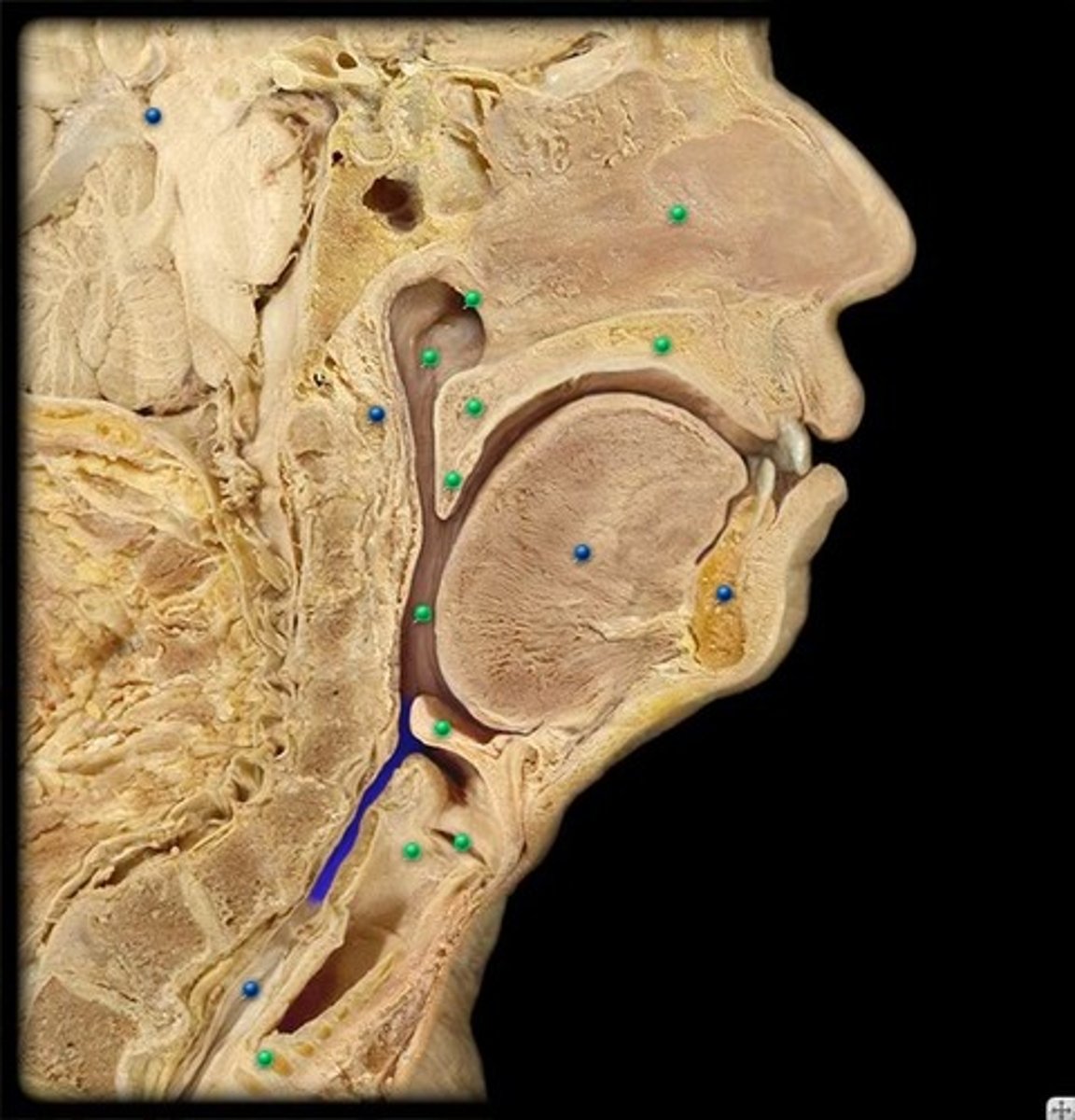
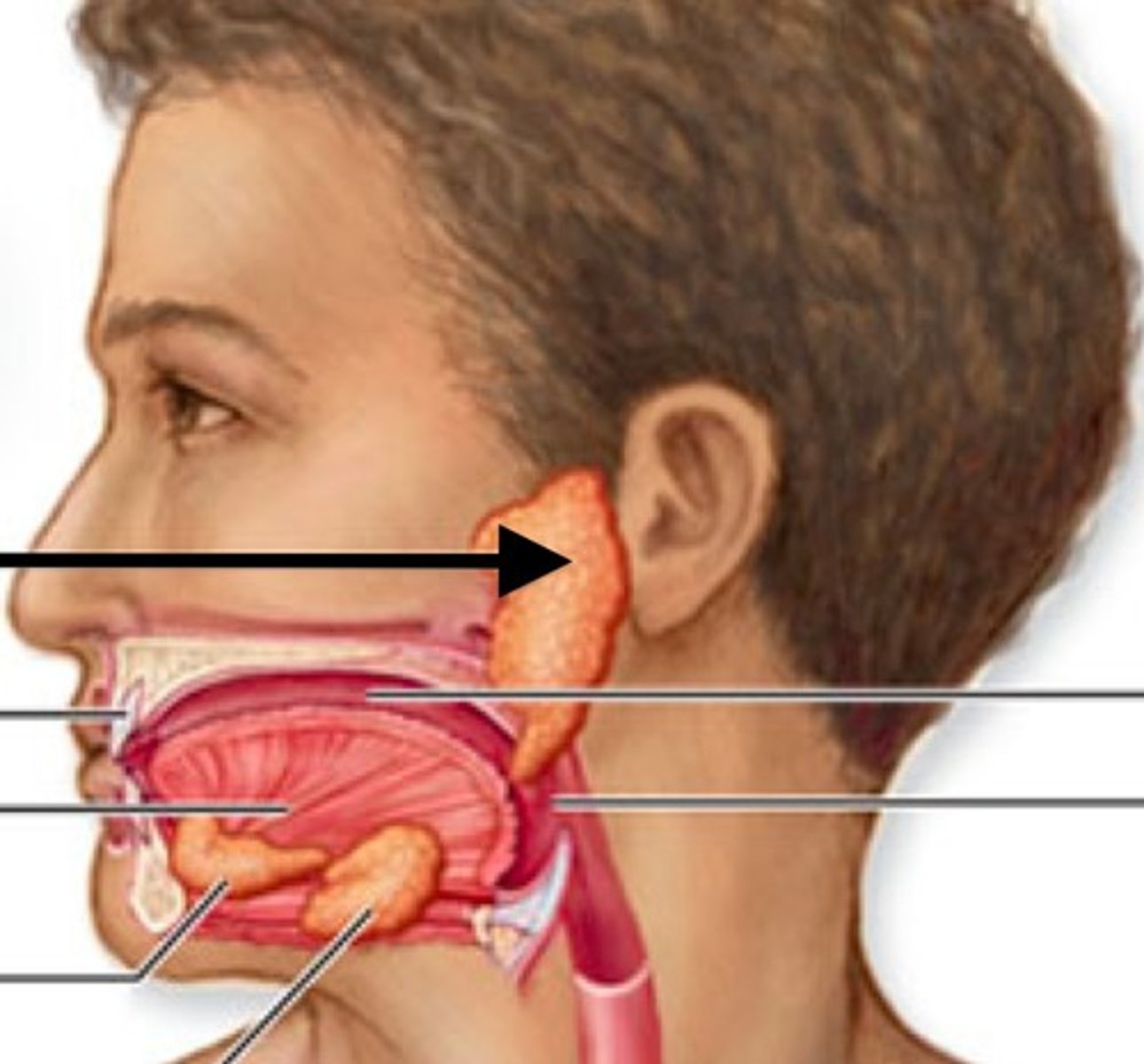
parotid salivary glands
ventral to the ear canals; located below the ears.
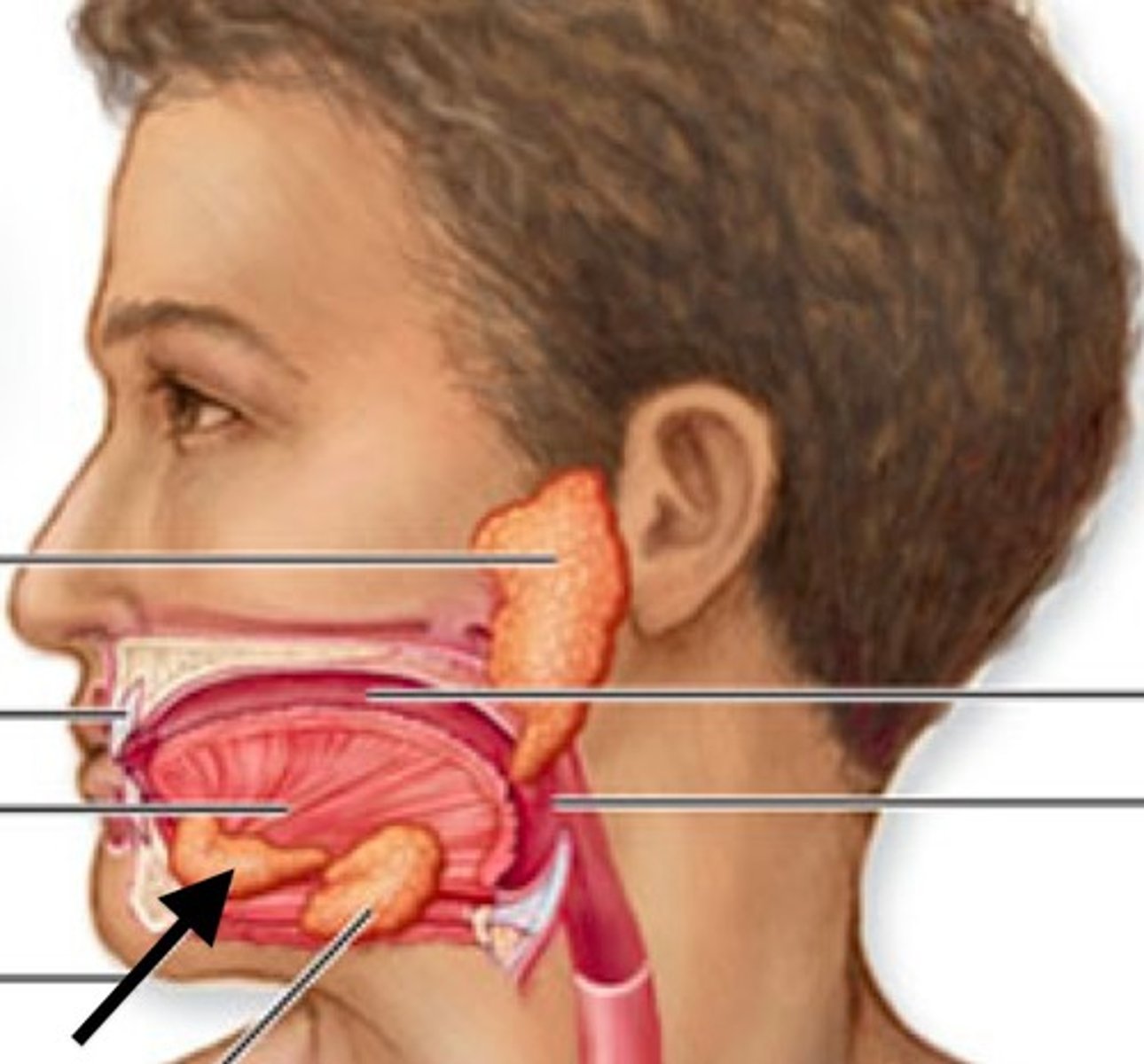
sublingual salivary glands
found under the tongue
submandibular salivary gland
under the mandible; salivary gland inside the lower jaw on either side that produces most of the nocturnal saliva;
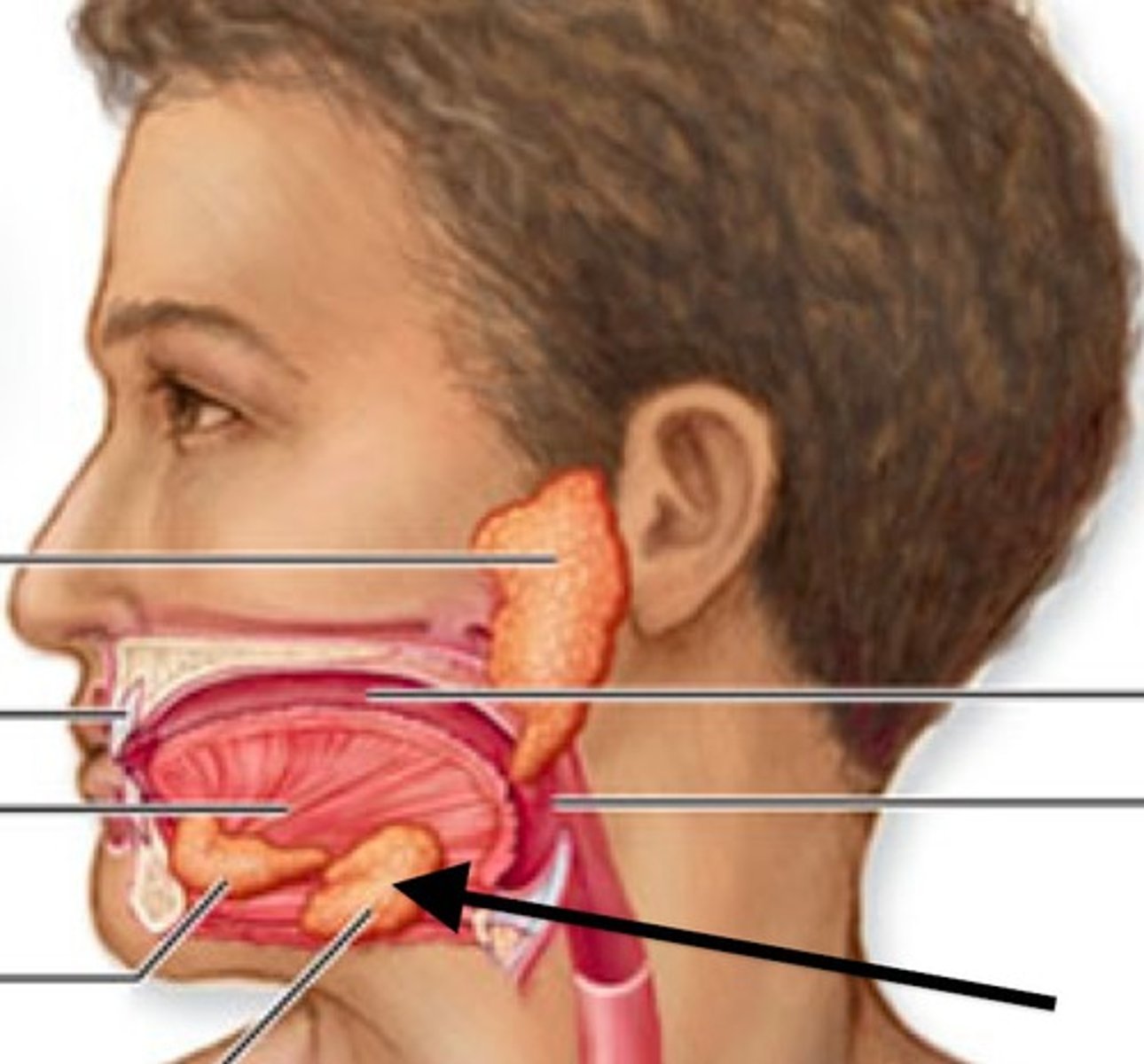
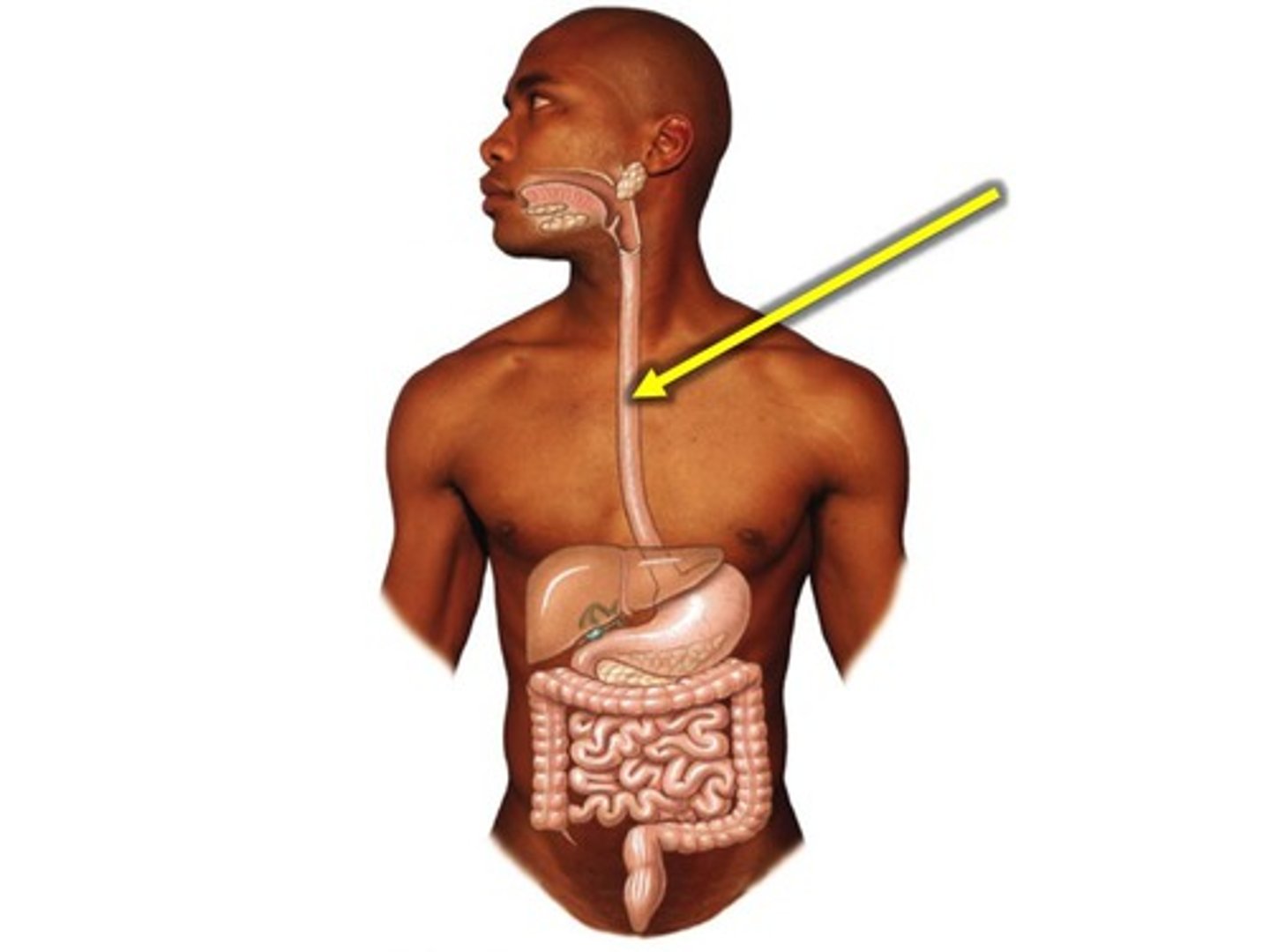
esophagus
muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.
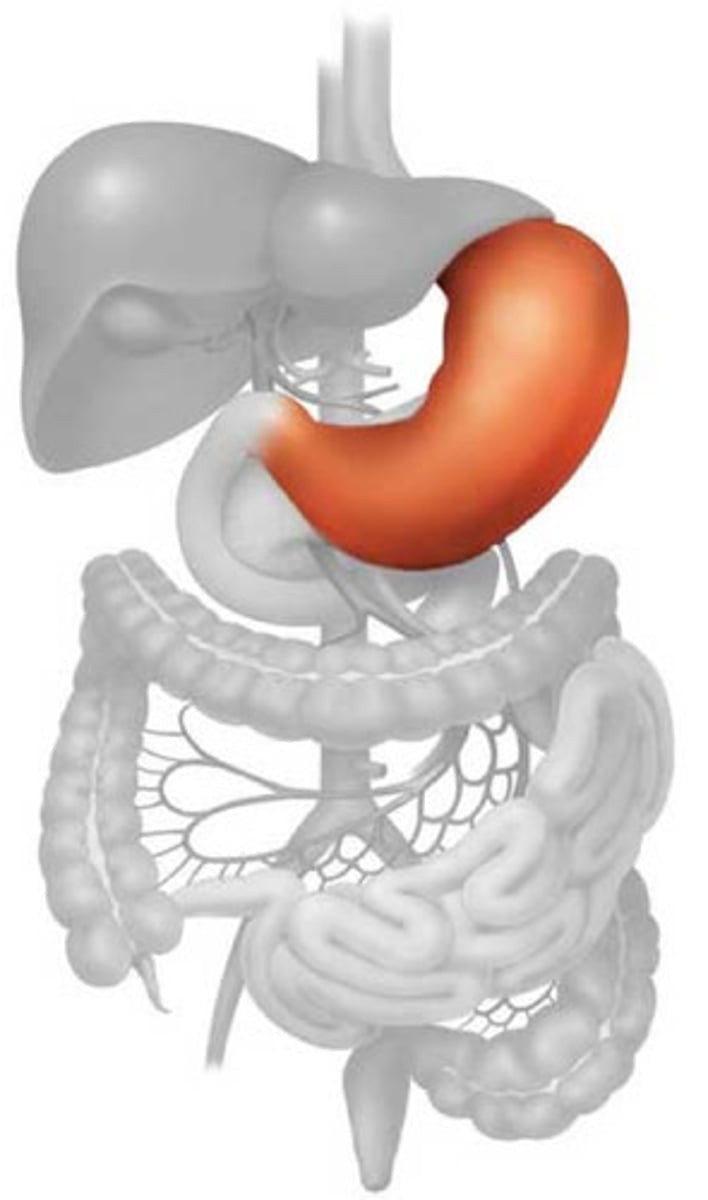
stomach
muscular and elastic sac that serves mainly to store food, break it up mechanically, and begin chemical digestion of proteins and fat; large muscular sac that continues the mechanical and chemical digestion of food
greater omentum
a fatty sheet that hangs like an apron over the abdominal viscera; large apron-like fold of visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach
duodenum
first section/part of the small intestine
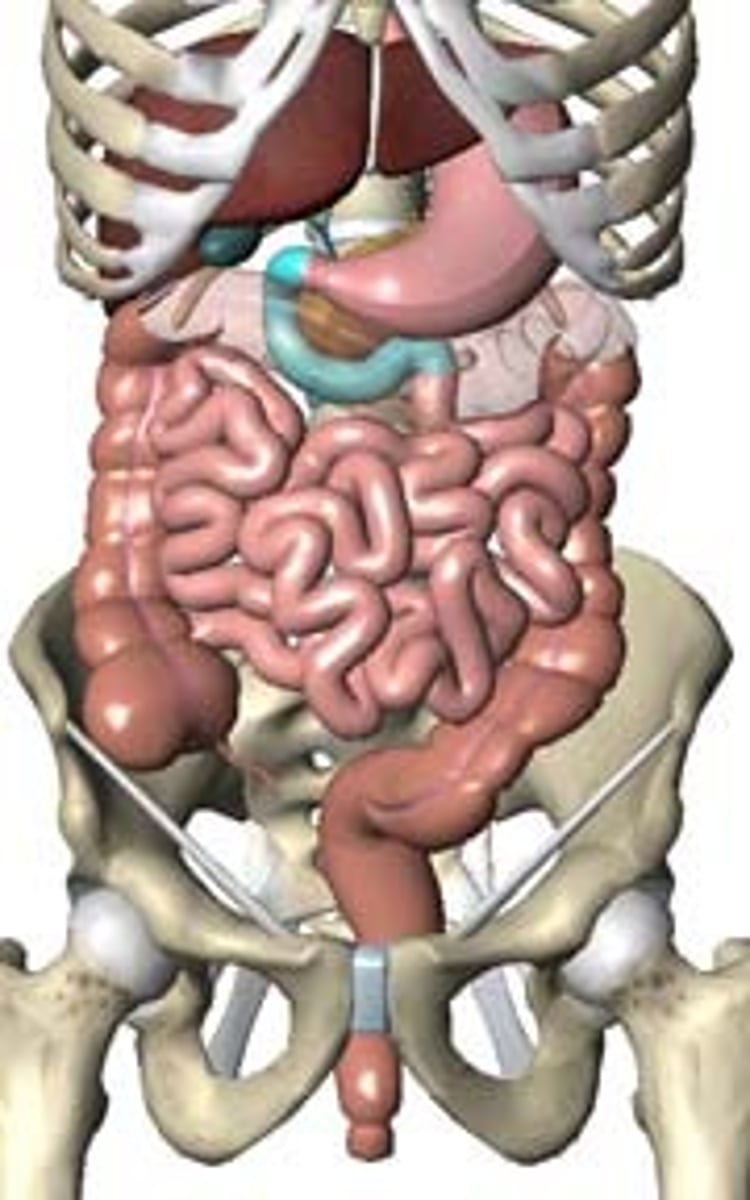
small intestine
Digestive organ where most chemical digestion and absorption of food takes place
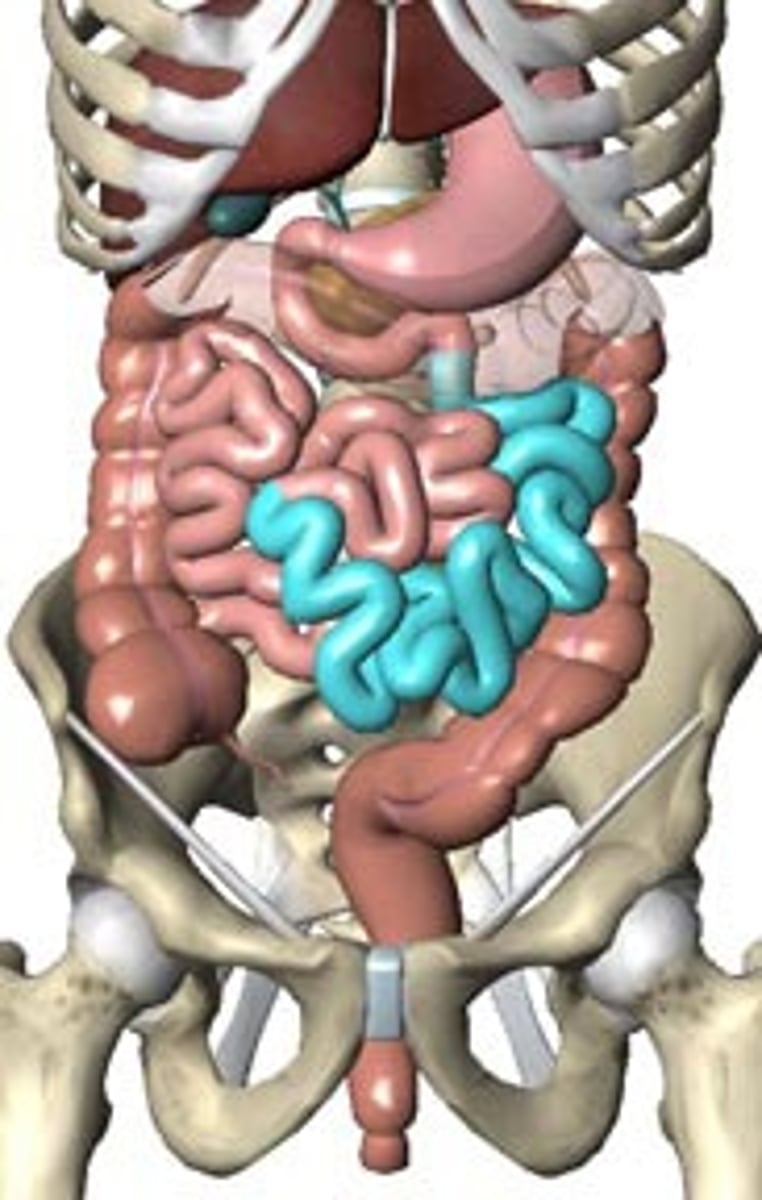
mesentery of small intestine
attaches the small intestine to the posterior abdominal wall; holds many blood vessels
ascending colon
the part of the large intestine that ascends from the cecum to the transverse colon; travels upward from the cecum to the undersurface of the liver
transverse colon
the middle part of the large intestine, passing across the abdomen from right to left toward the spleen and below the stomach.
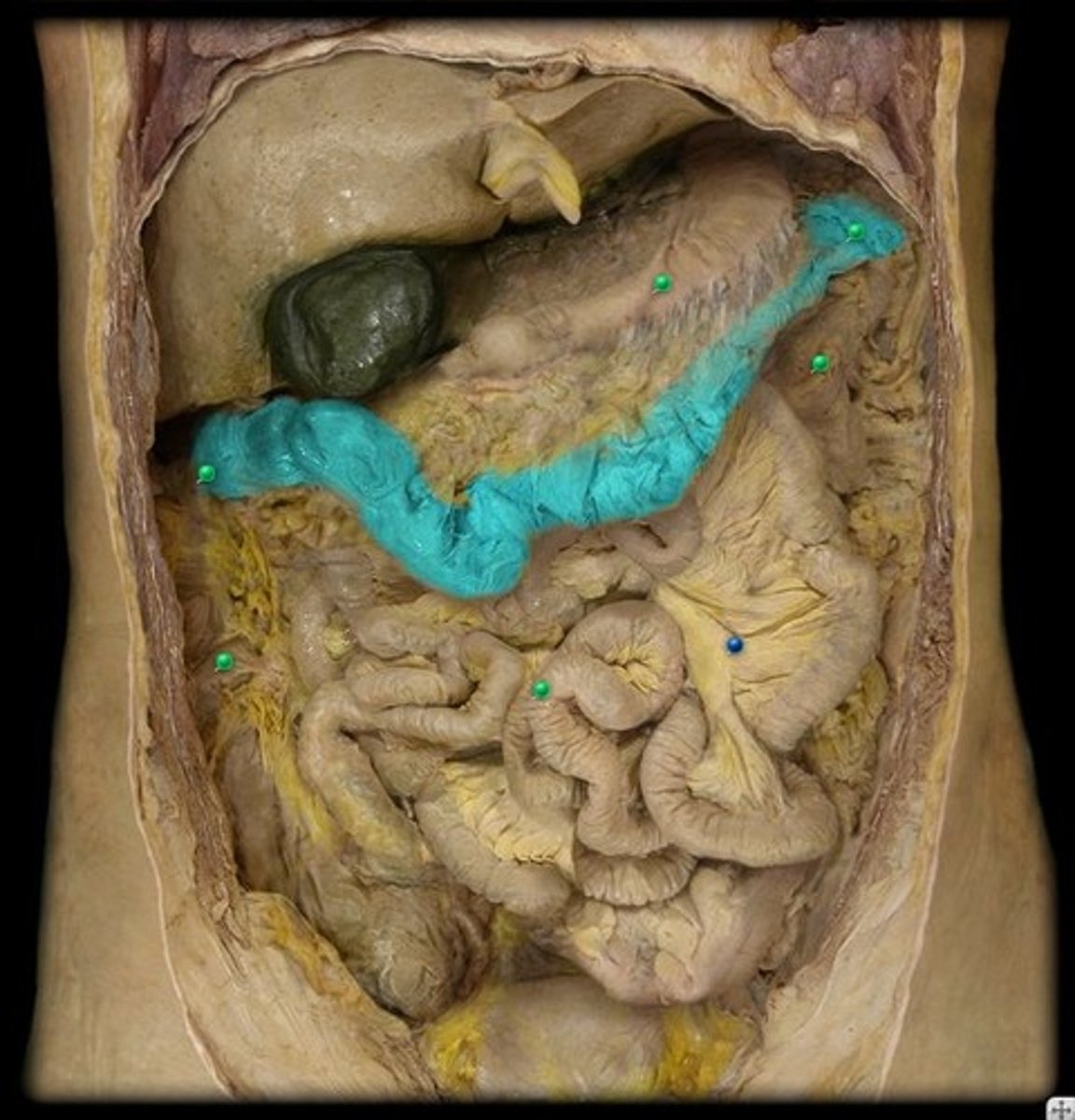
descending colon
the part of the large intestine that extends downward from the transverse colon on the left side of the abdominal cavity to the sigmoid colon
sigmoid colon
an S-shaped structure that continues from the descending colon above and joins with the rectum below
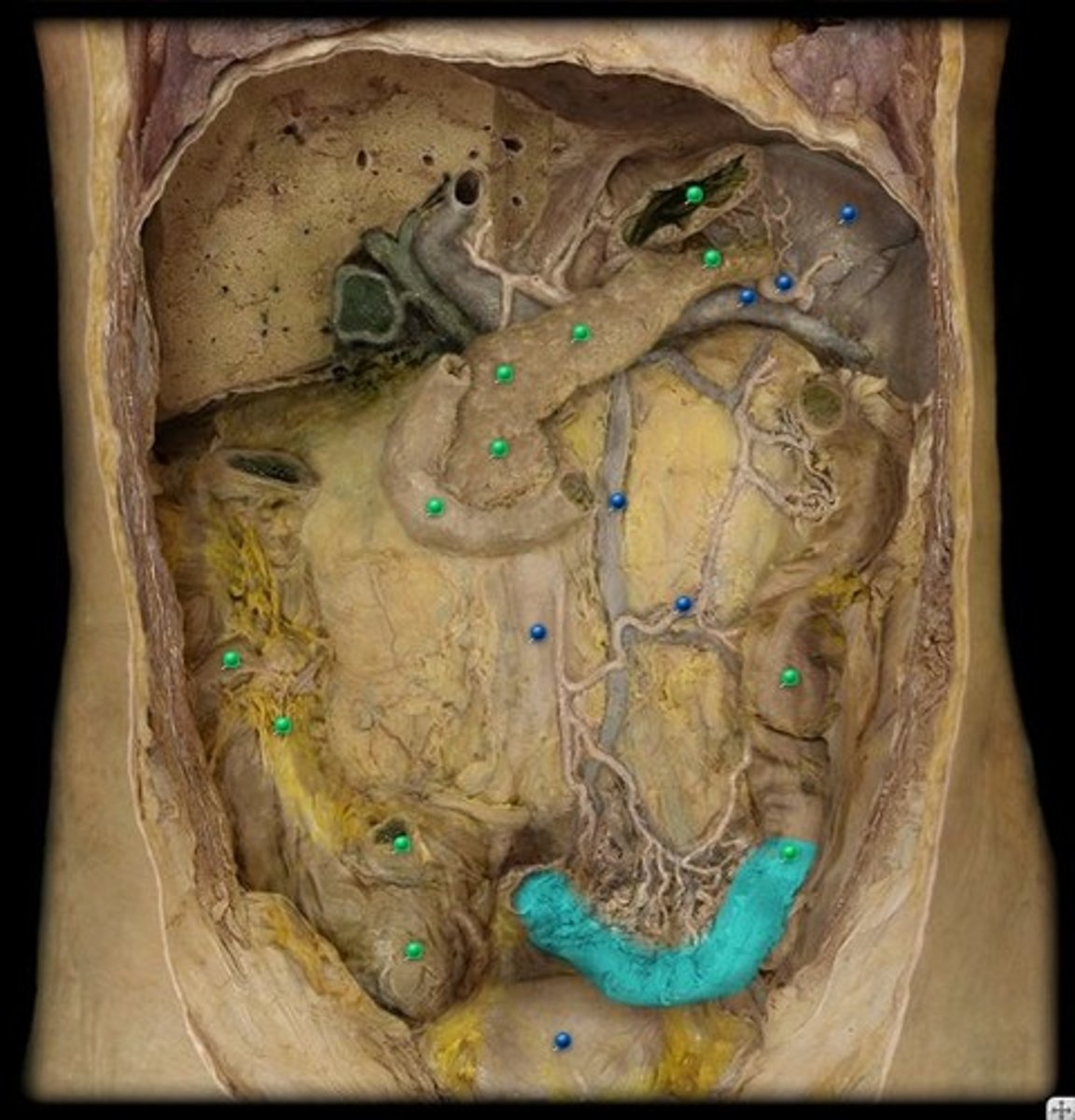
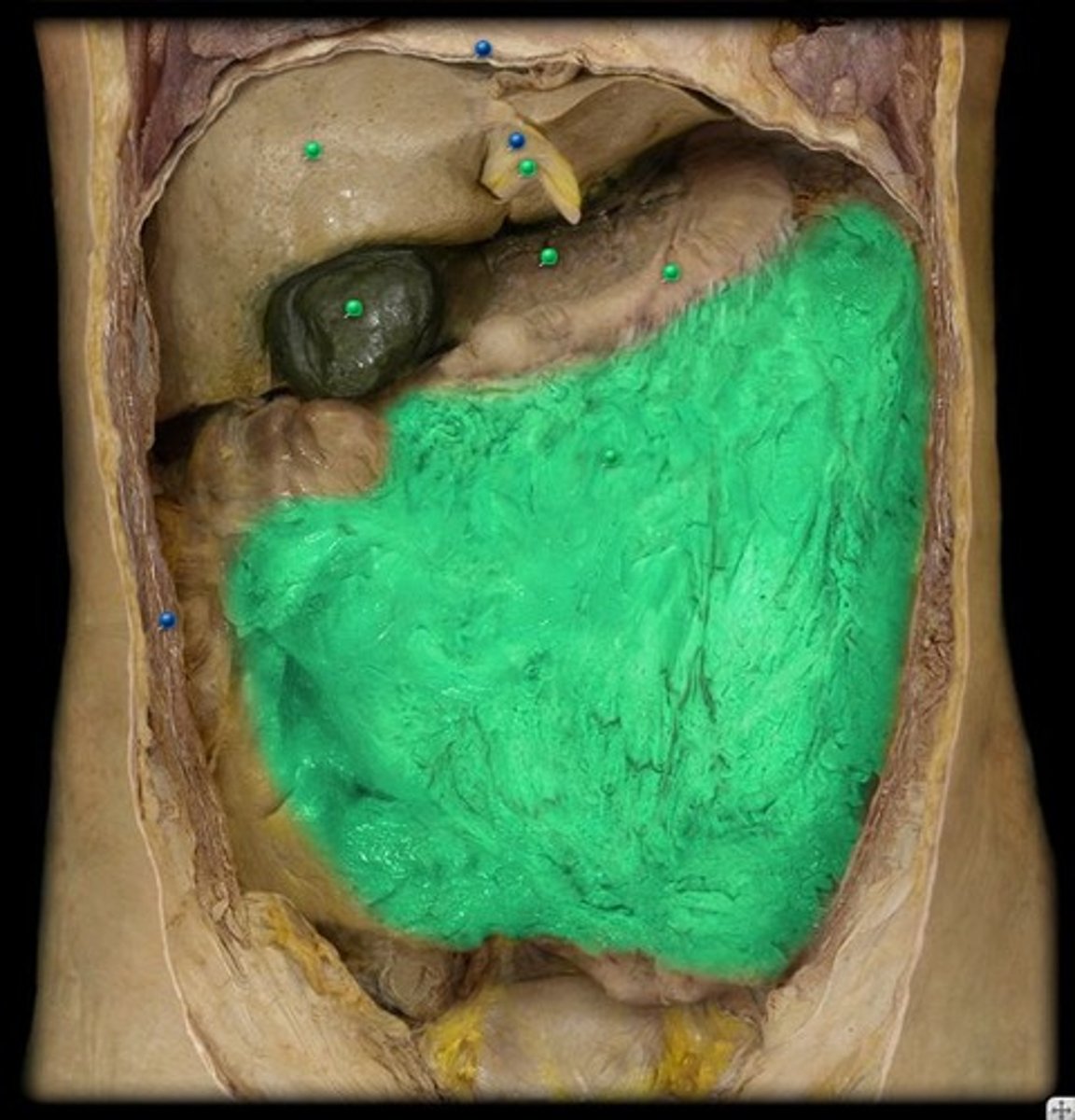
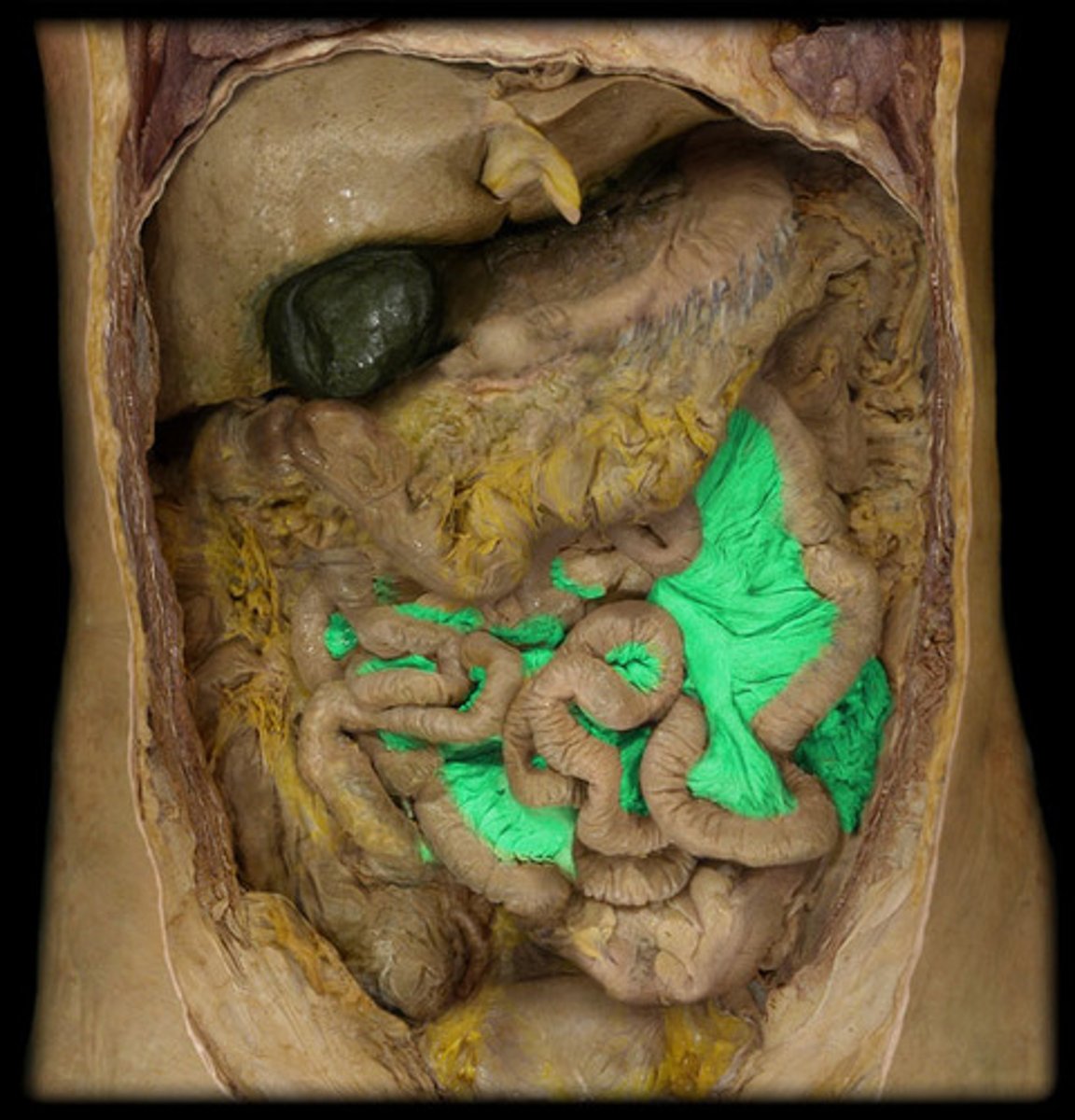
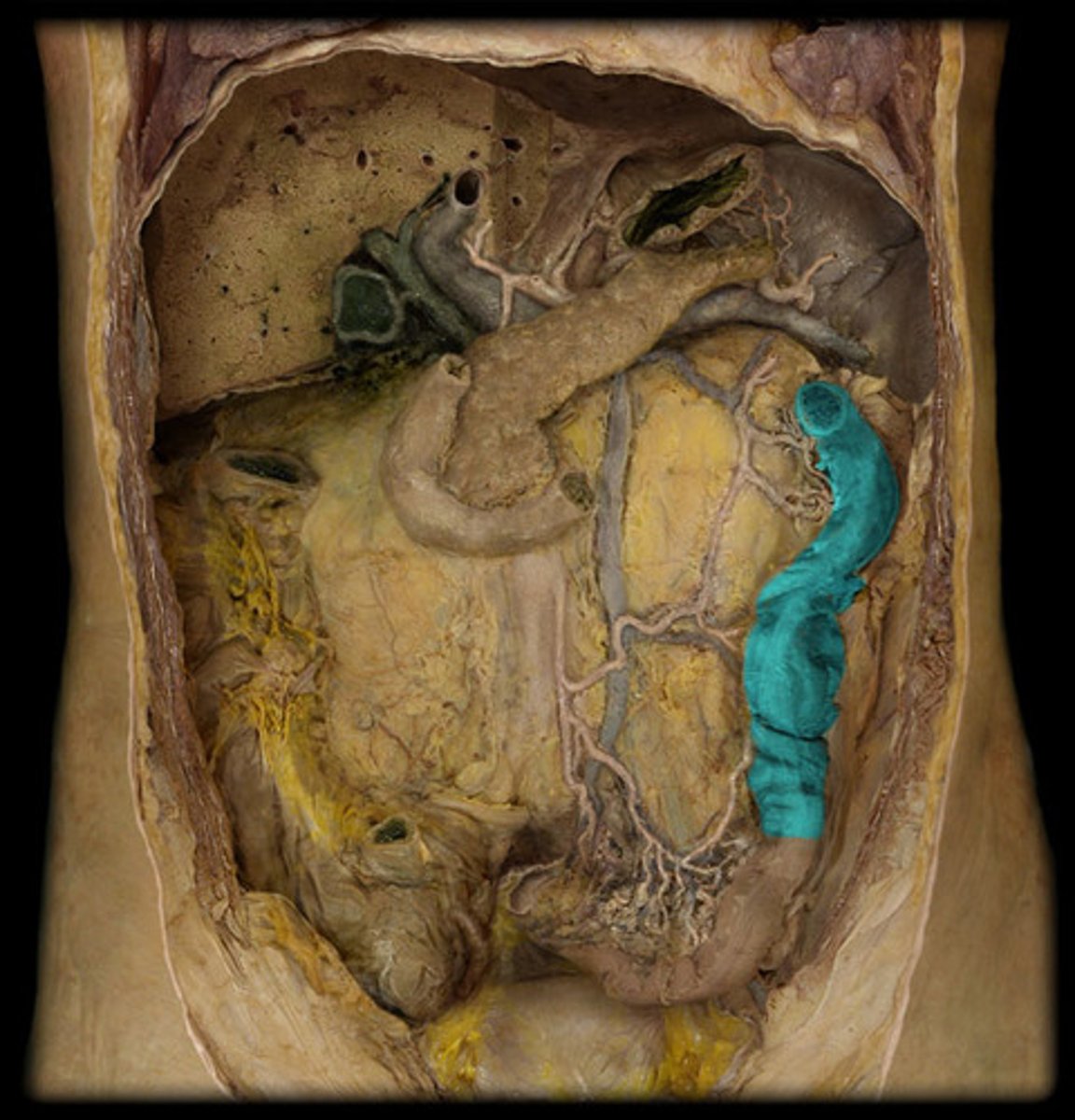
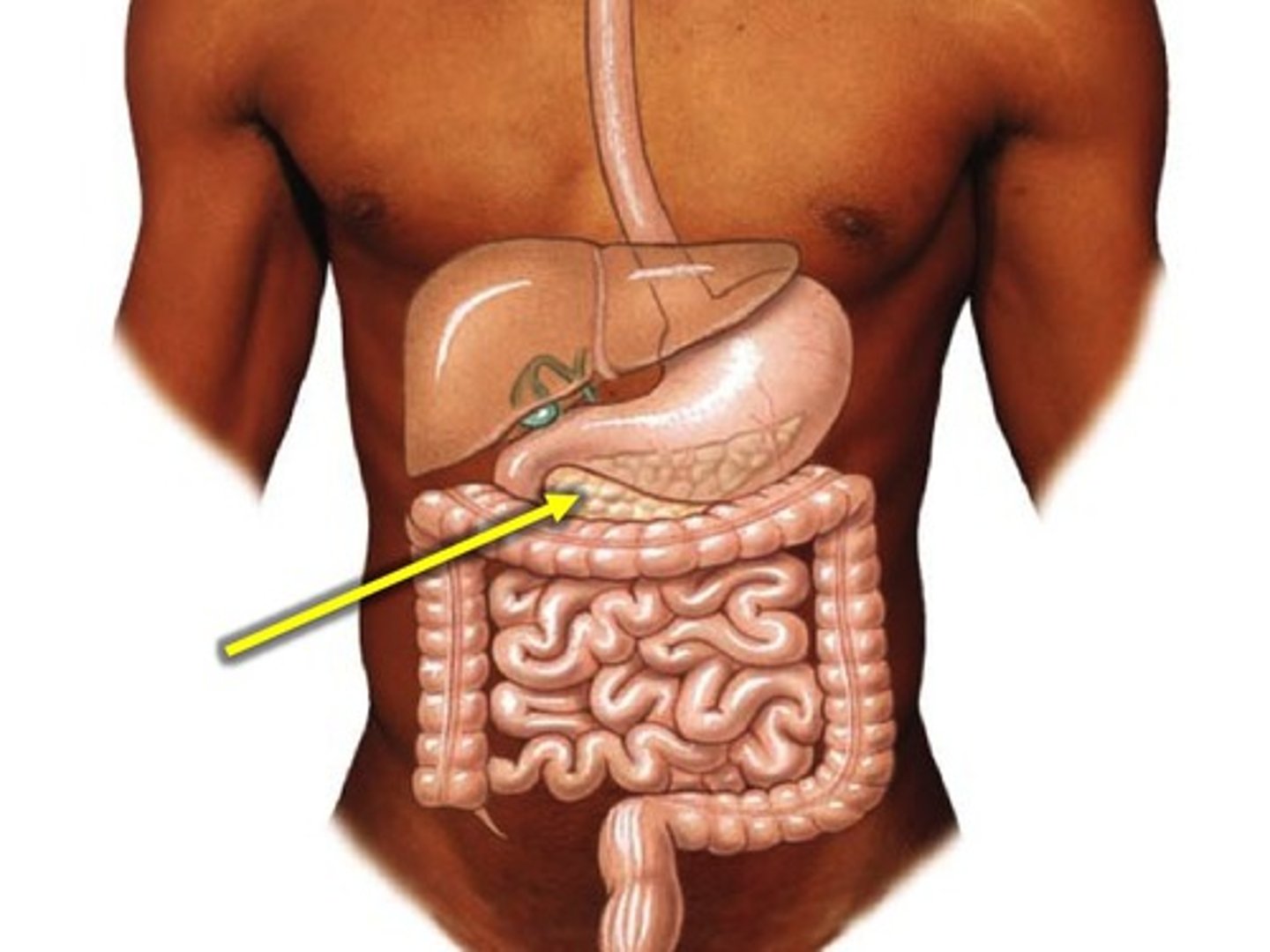
liver
produces bile (emulsifies fat) and stores glycogen
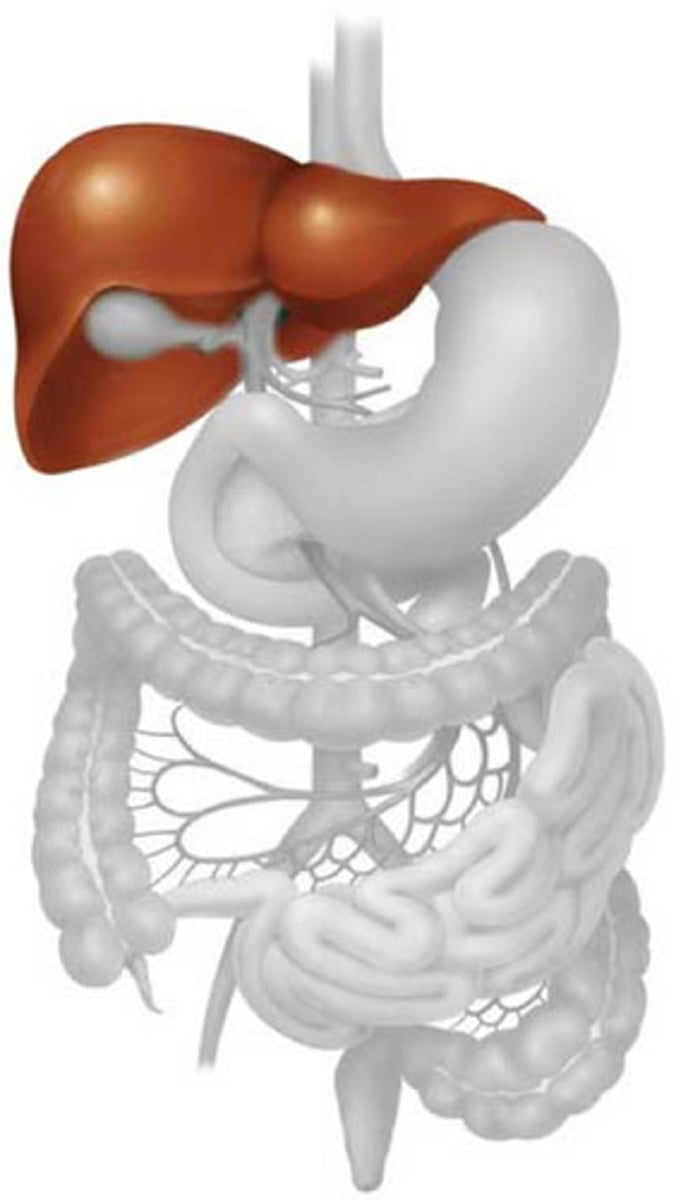
gallbladder
A muscular sac attached to the liver that secretes bile and stores it until needed for digestion
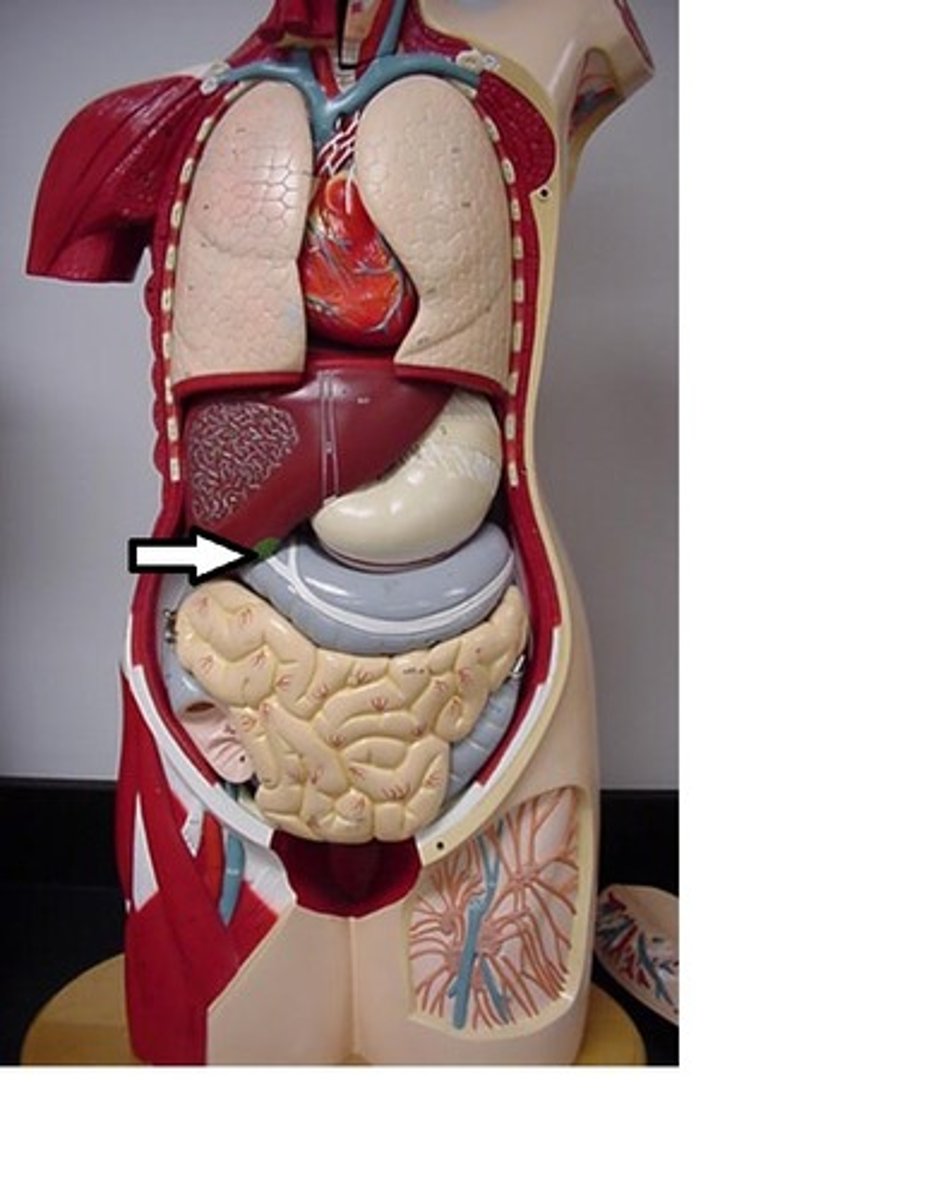
falciform ligament
Structure that separates right and left lobes of liver; ligament that attaches part of the liver to the diaphragm and the abdominal wall
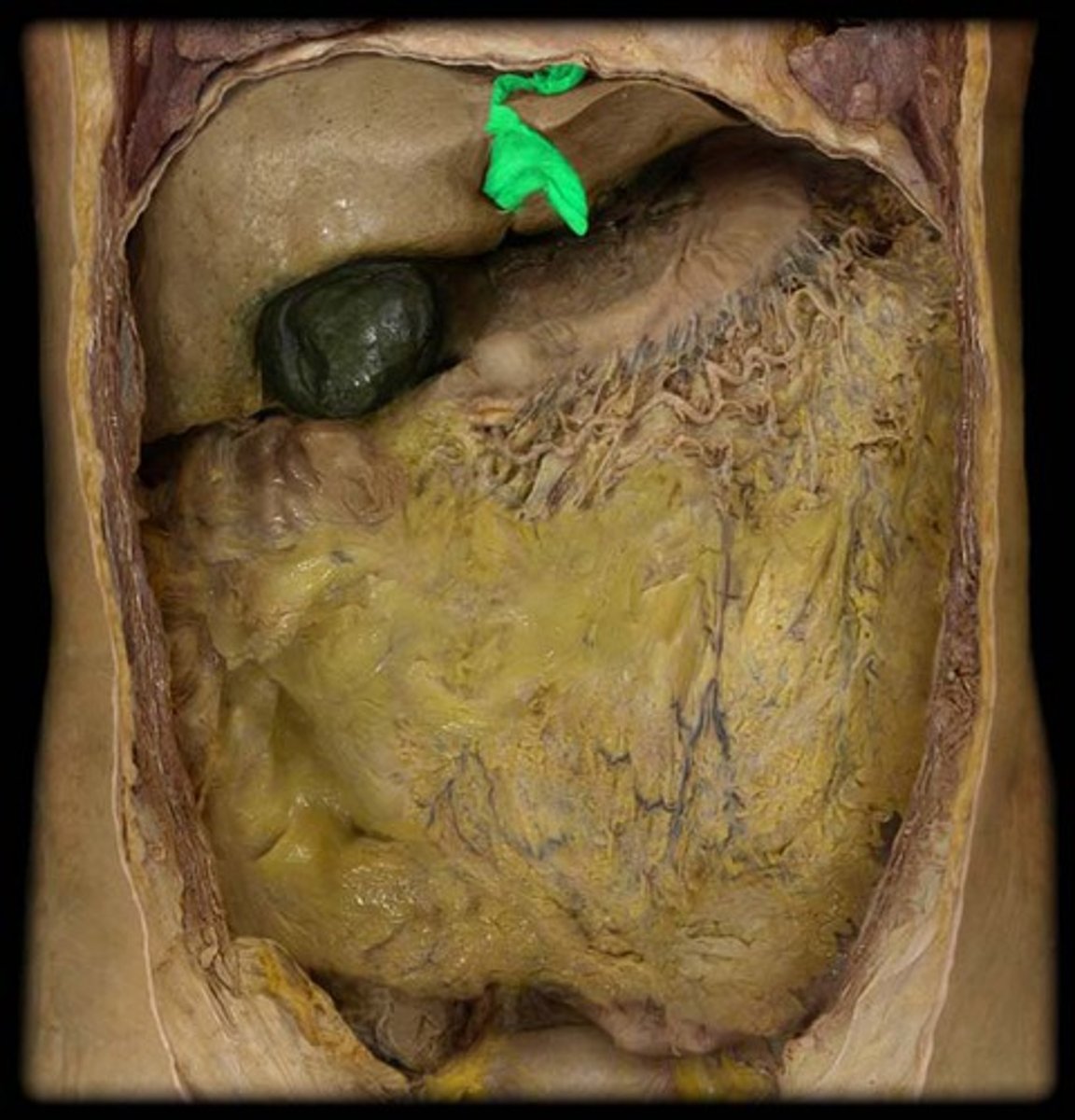
pancreas
organ in the abdominal cavity with two roles.
1. exocrine role: to produce digestive enzymes and bicarbonate, which are delivered to the small intestine via the pancreatic duct.
2. endocrine role: to secrete insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream to help regulate blood glucose levels.
rectum
short tube at the end of the large intestine where waste material is compressed into a solid form before being eliminated from the anus.