Anatomy Final Exam
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
study of joints and their movements
arthrology
a point of contact between bones, bone/cartilage, between bone/teeth
articulation
covers the ends of bones
articular cartilage
protective structure surrounding a synovial joint, composed of an outer fibrous layer and an inner synovial membrane that secretes synovial fluid.
articular capsule
reduces friction between strucutres in a joint
bursa
located outside the articular capsule; ex: patellar ligament
extracapsular ligaments
located within the articular capsule but the folds of the synovial membrane separate it from the synovial capsule
intracapsular ligament
pads of fibrocartilage that are between the meeting surfaces of bones and attached to the fibrous capsule
articular disc/meniscus
ligaments are overstretched or torn
sprain
bones come out of alignment
dislocation
the structural classification of joints in based on what two criteria
presence/absence of a synovial cavity
type of connective tissue that binds the bonds together
bones held together by fibrous connective tissue, contain collagen fibers
fibrous joints
bones are held together by cartilage with no synovial cavity
cartilaginous joints
joints that have a synovial cavity, joined by dense inrregular connective tissue, and often gave accesory ligaments
synovial joints
immovable joint
synarthrosis
slightly moveable joint
amphiarthrosis
freely moveable joint that permits several different types of movement
diarthrosis
fibrous joint with a greater space between two connecting bones and with more fibrous connective tissue
syndesmosis
fibrous joint composes of a thin layer of dense fibrous connective tissue; interlocking edges decreases chances of breaking
suture
a cone shaped peg fits in a socket; such as teeth
gomphosis
cartilaginous joint where the connecting material in hyaline cartilage
synchondrosis
cartilaginous joint where the ends of articulating bones are covered with hyaline cartilage but bones are connected by a flat disc of fibrocartilage, all occur at the midline of the body
symphysis
carpals and tarsals
undergo gliding movements (side/side or back/forth)
articulating sides are flat/curved
planar joint
convex side of one bone interlocks with the concave side of another bone
elbow, fingers/phalanges, knee
motion around a single axis
go through flexion/extension only
hinge joint
radius, ulna, neck
rounded portion of one bone connects with the ring of another bone
rotation around a longitudinal axis
pivot joint
oval shaped projection fits into depression of another bone
flexion/extension and adduction/abduction
condyloid joint
side/side and back/front
one bone is saddle shaped and sits on top of the rounded portion of another bone
ankle
motions are biaxial
saddle joint
multiaxial/all planes of movement
shoulder and hip
ball like portion of one bone fits into the socket of another
ball and socket joint
flat bone surfaces move side/side and front/back, takes place at planar joints only
gliding
decreasing the angle of a joint
flexion
increasing the angle of a joint
extension
pulling/moving a bone away from the midline
abduction
adding bone/moving bone back towards the midline
adduction
movement of the distal end of a body part in a circle
circumduction
bones rotating around a longitudinal axis
rotation
pulling of toes up/bending ankle up
dorsiflexion
pointing toes; pulling toes more distal
plantar flexion
turning of palms anteriorly; palms up
supination
turning of palms posteriorly; palms down
pronation
what are the two intracapsular ligaments of the knee
ACL and PCL
4 main tendons that encircle the shoulder joint
rotator cuff
allows for a deeper cavity/movement in the shoulder
glenoid labrum
study of muscles
myology
muscle tension without shortening the muscle
isometric contraction
muscle tension that is constant and shortens the muscle
isotonic contraction
connects muscle to bone and attaches to periosteum of bone
tendon
flat connective tissue that functions as a tendon
aponeurosis
occurs during muscle contraction in which myosin heads pull actin filaments toward the center of the sarcomere
powerstroke
muscle in charge of the major force in the movement
prime mover
supporting muscles that aid the prime mover and help add force
synergist
opposing muscle working in reverse
anatagonist
4 properties of muscle tissue
electrical excitablity
contractility
extensibility
elasticity
smallest in diameter
fewest myofibrils
least powerful of muscle fibers
dark red in appearance (heavy myoglobin)
heavy on mitochondria/ATP
slow oxidative fibers
intermediate in diameter
large amounts of myoglobin (pink in color)
generates ATP through aerobic respiration
more power contractions
fast oxidative fibers
largest in diameter
white in appearance
low myoglobin
most power contractions
fatigues most quickly
uses glucose to produce ATP
fast glycolytic fibers
oxygen storage for muscle tissue
myoglobin
muscle shortens pulling on another structure to produce movement
concentric isotonic contraction
length of muscle is increasing during contraction; controlled movement against tension
eccentric isotonic contraction
how we name muscles
location
shape
function
direction of fibers
number of origins
location of attachments
supporting cells of the nervous system
neuroglial cells
has myelinated axons
white matter
has unmyelinated axons
gray matter
helps maintain homeostasis and regaining original ionic conditions for a neuron
sodium potassium pump
no gates are open, no movement of ions, no action potential
resting membrane potential
working memory, closed neuronal circuit, circuit is stimulated over and over, when impulse flow ceases so does memory
short term memory
changes structure/function of neurons, enhances synaptic function
long term memory
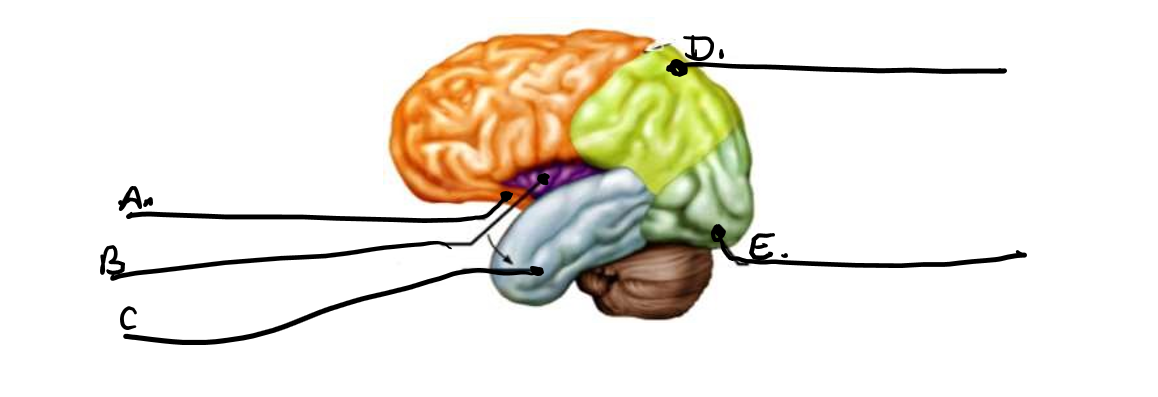
what is a
frontal lobe
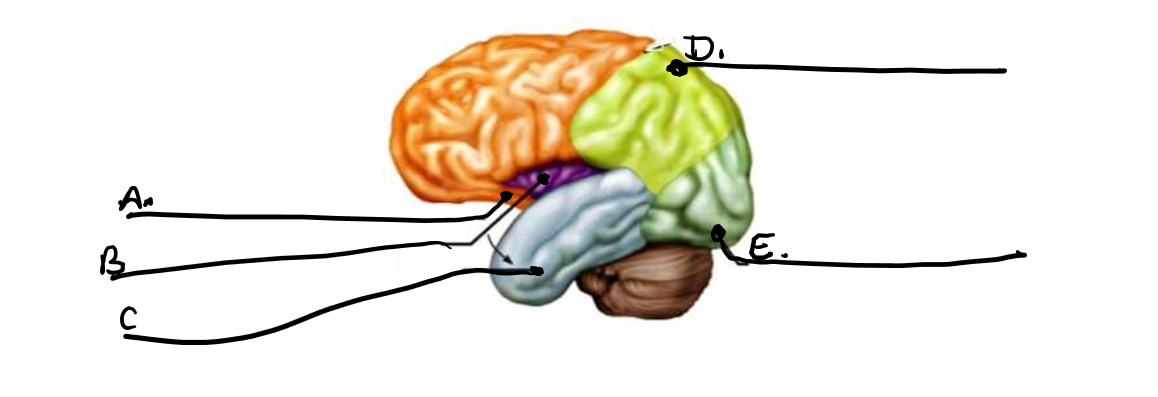
what is b
insula
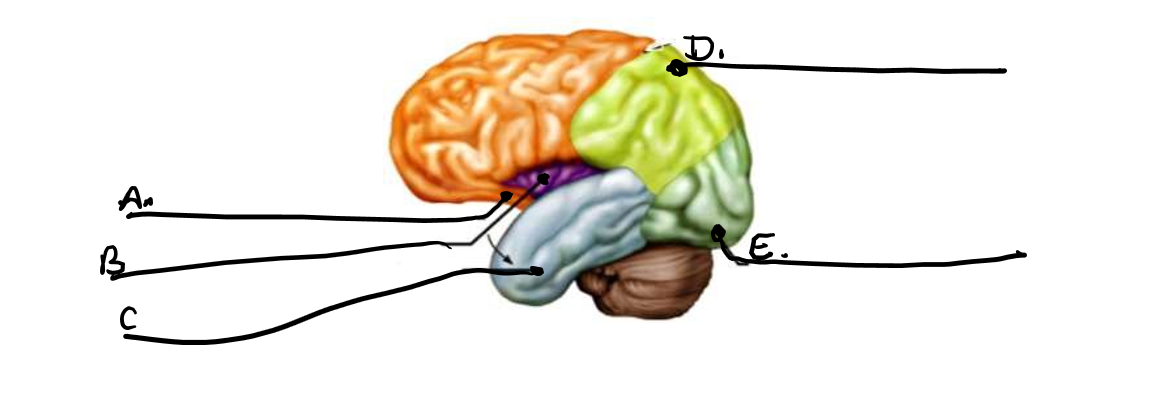
what is c
temporal lobe
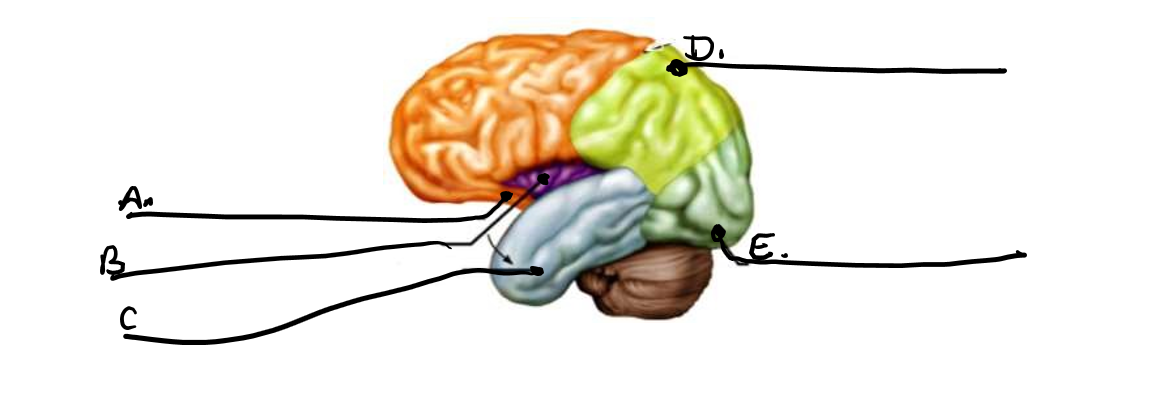
what is d
parietal lobe
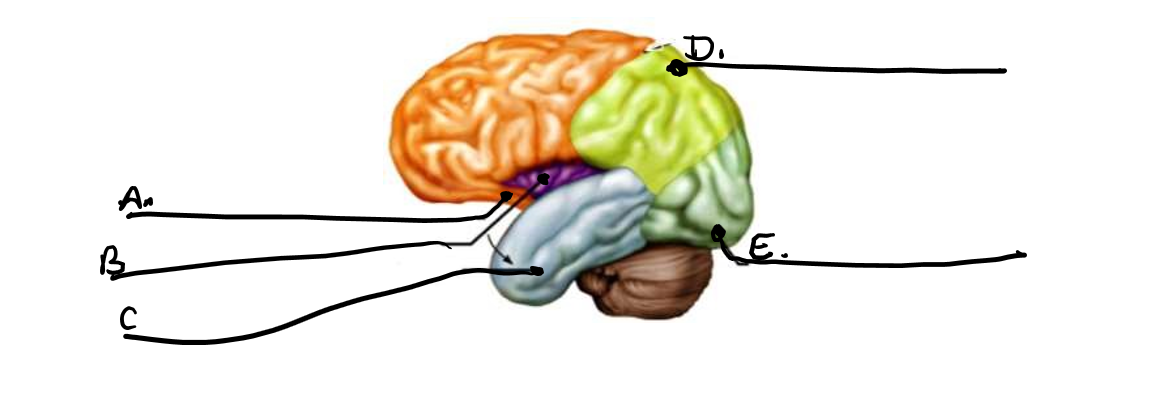
what is e
occipital lobe
interprets sensory information and depth perception of body parts
helps maintain posture
coordination of skeletal muscle
cerebellum
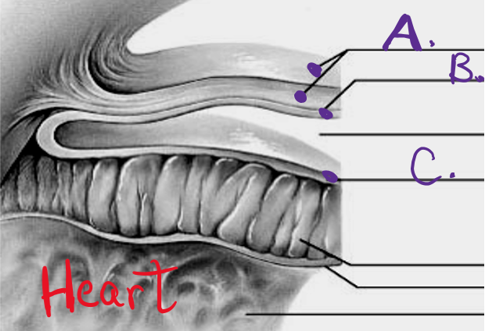
what is a
epicardium
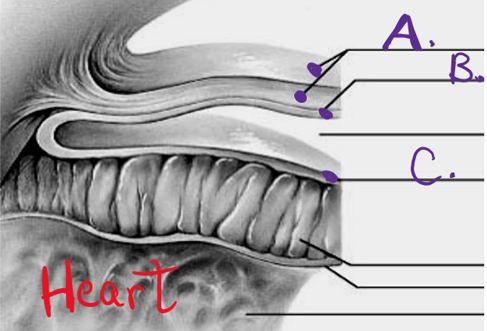
what is b
myocardium
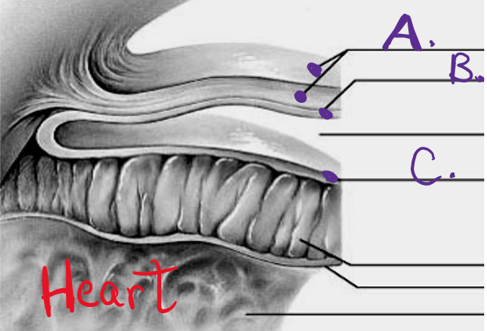
what is c
endocardium
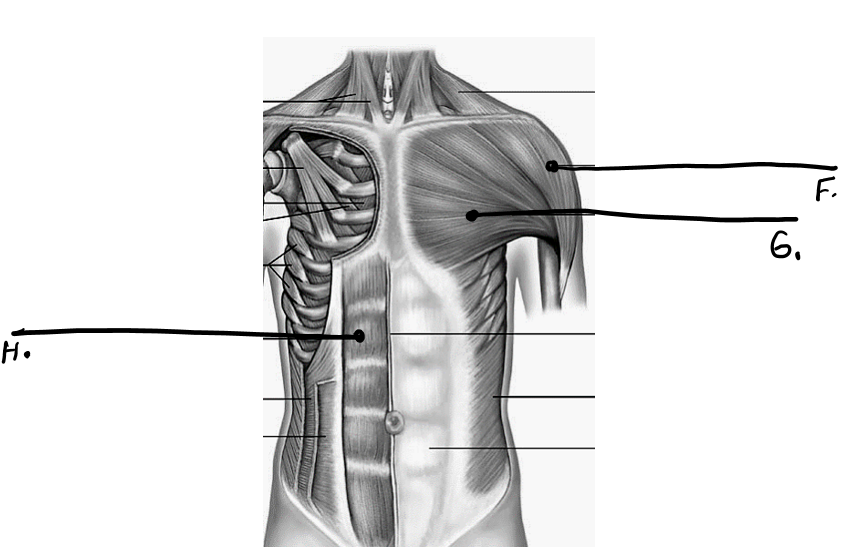
what is h
rectus abdominus
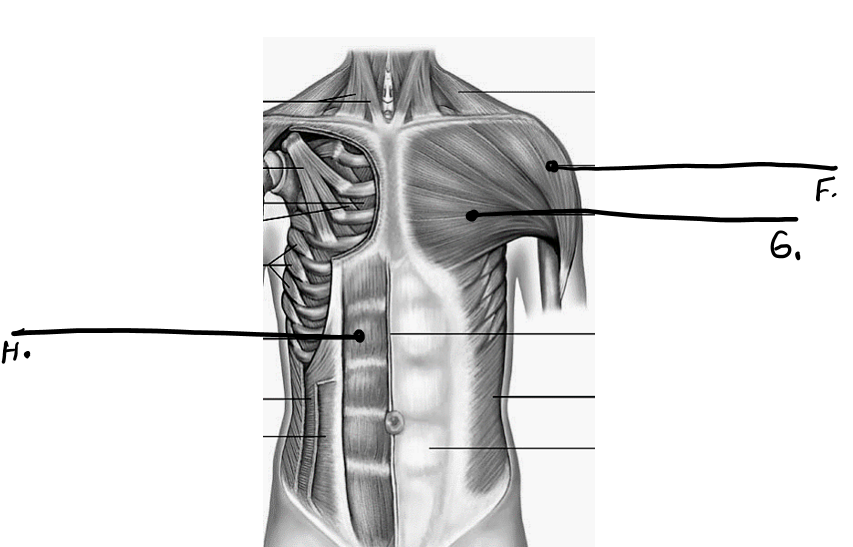
what is g
pectoralis major
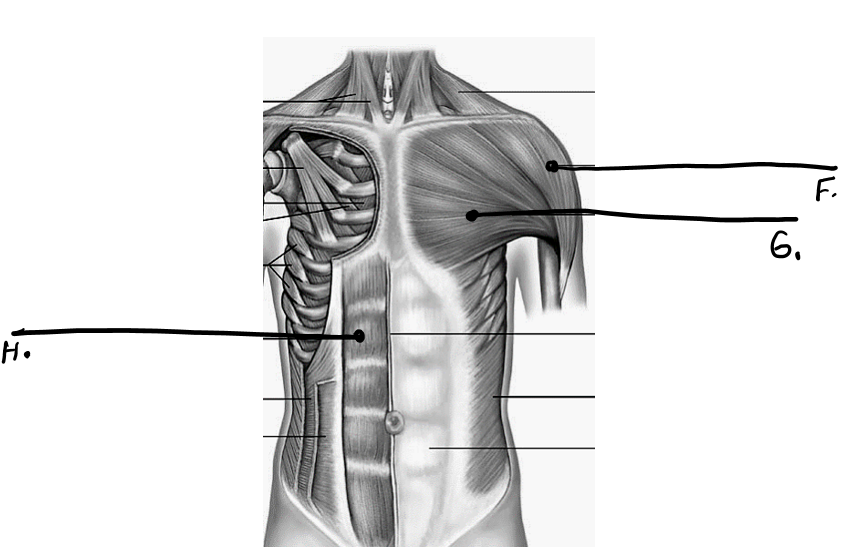
what is f
deltoid
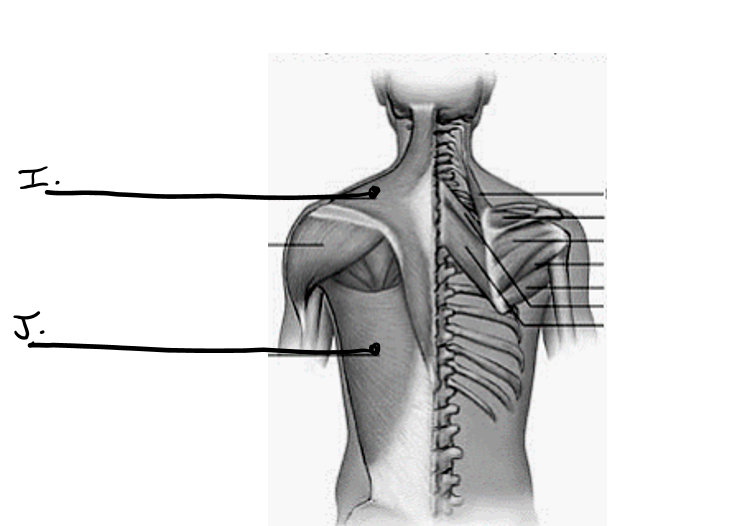
what is i
trapezius
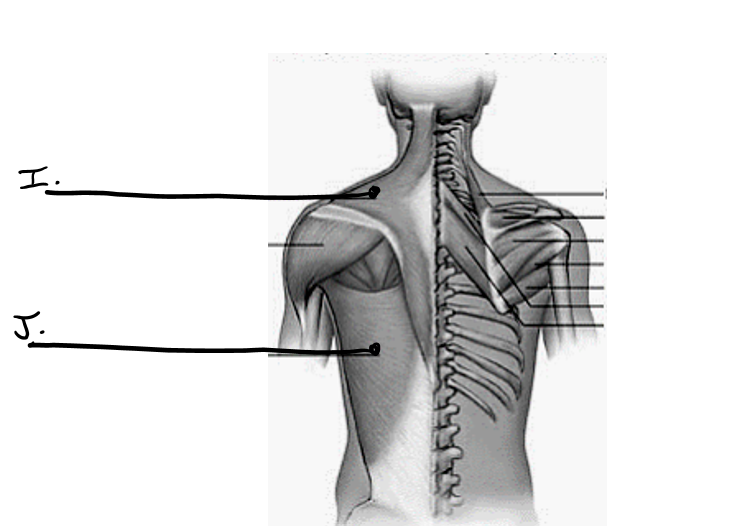
what is j
latissimus dorsi
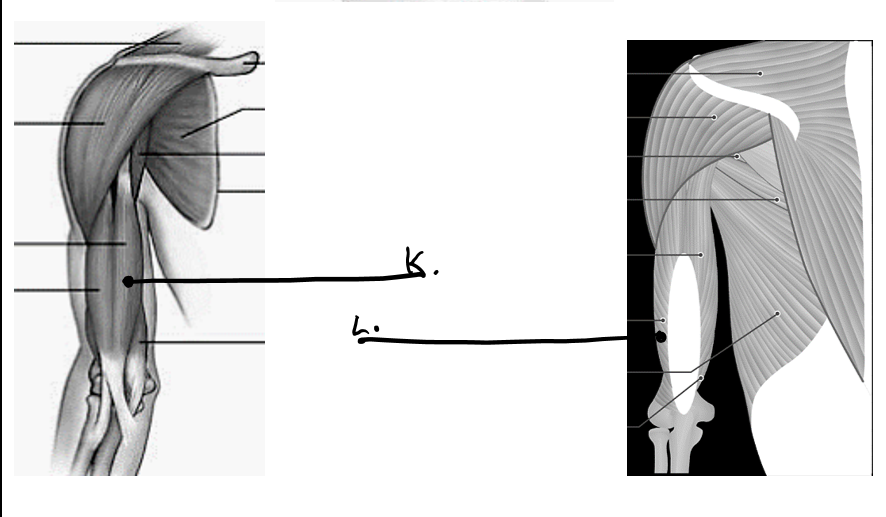
what is k
bicep
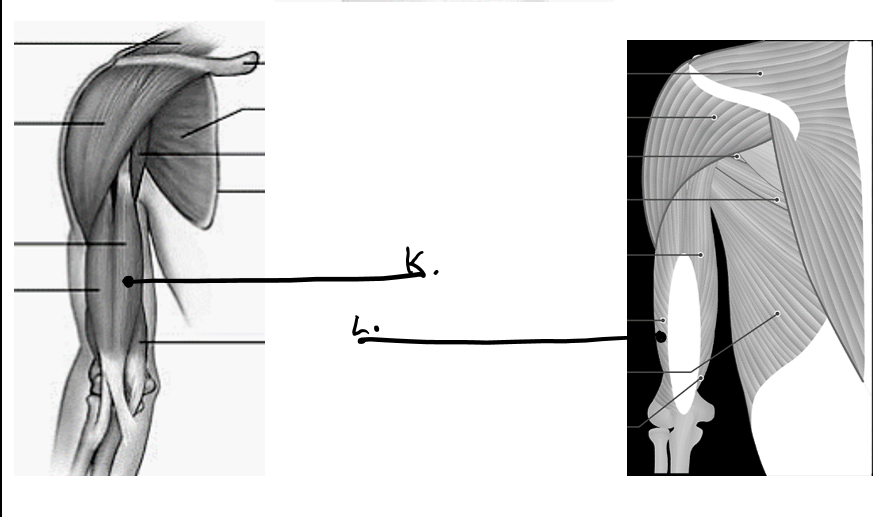
what is l
tricep
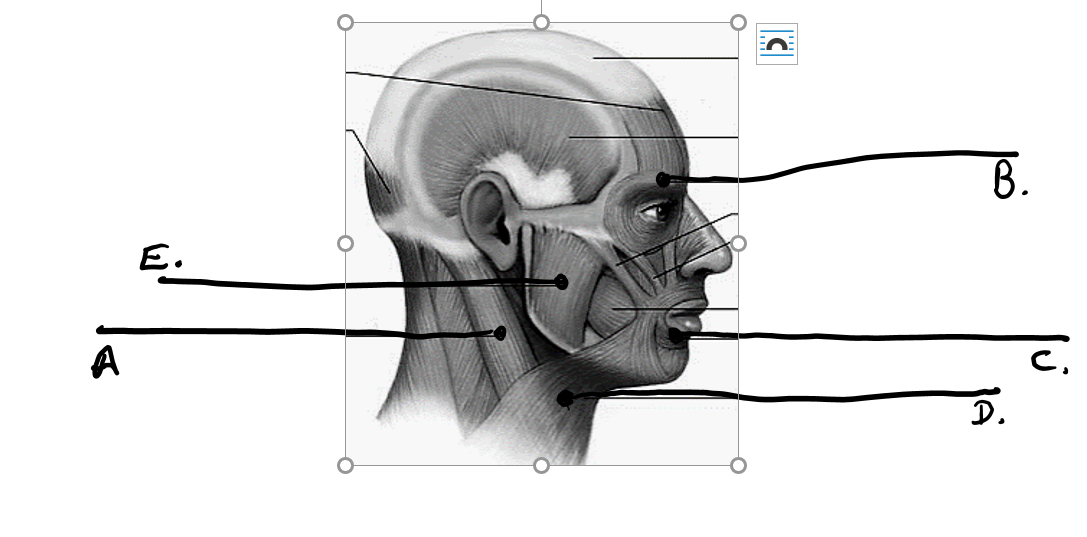
what is a
sternocleidomastoid
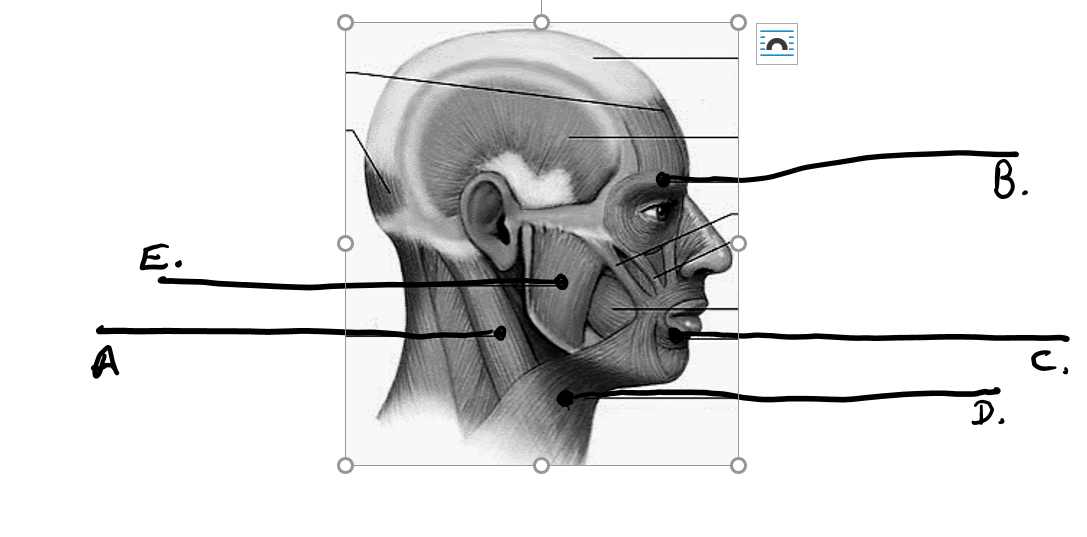
what is b
orbicularis oculi
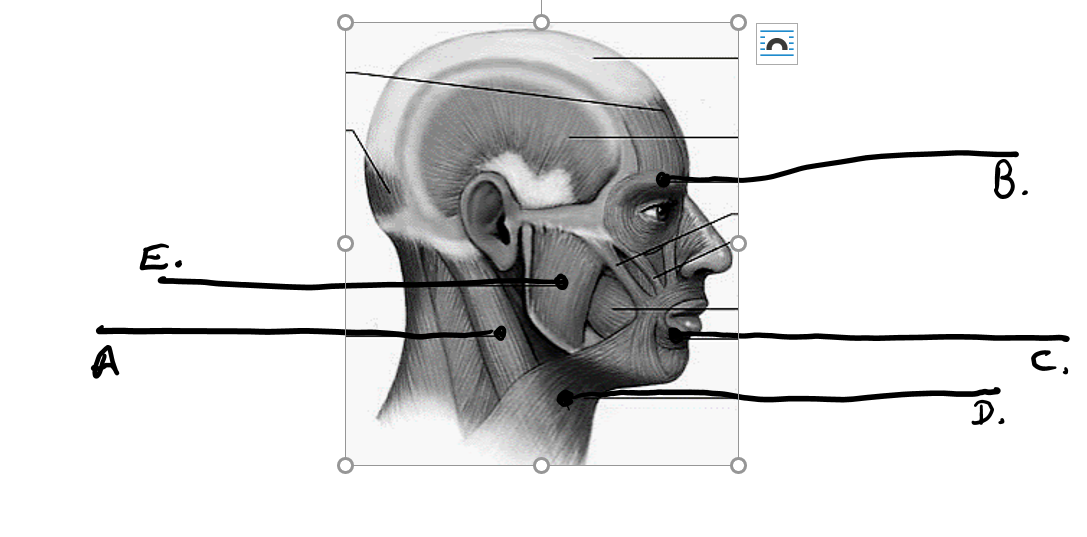
what is c
orbicularis oris
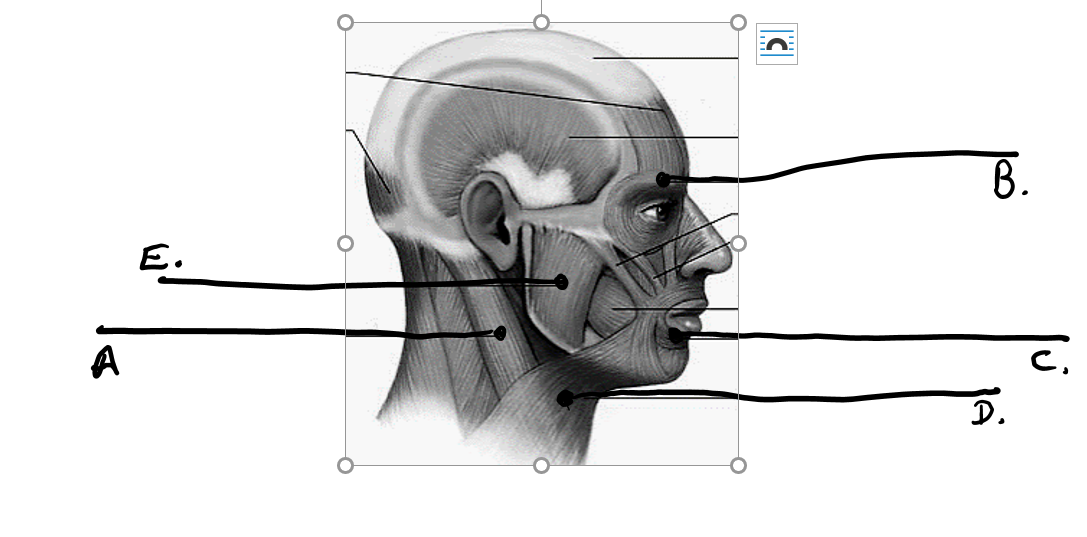
what is d
platysma
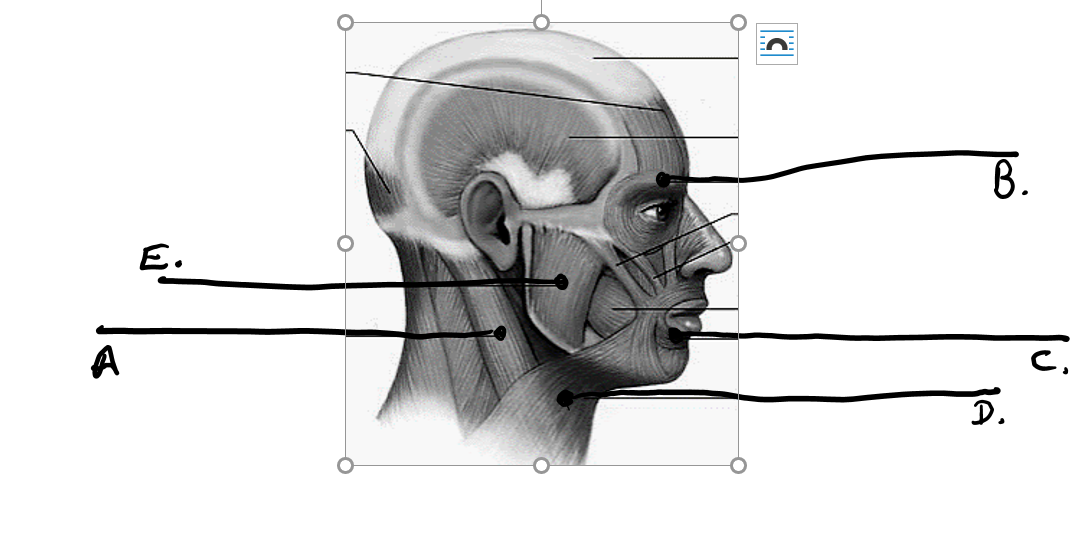
what is e
masseter
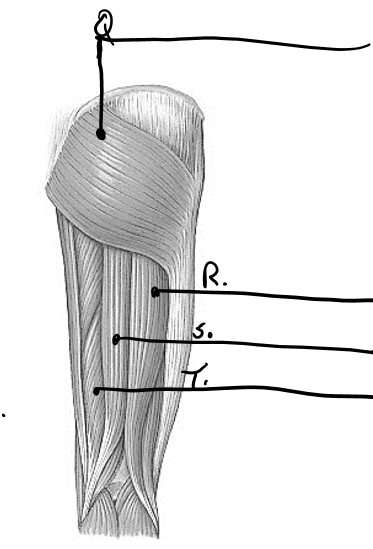
what is q
gluteus maximus
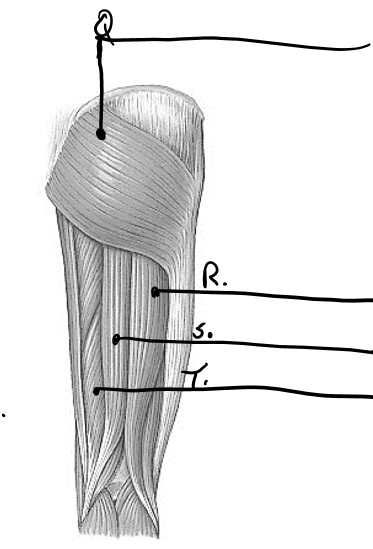
what is r
biceps femoris
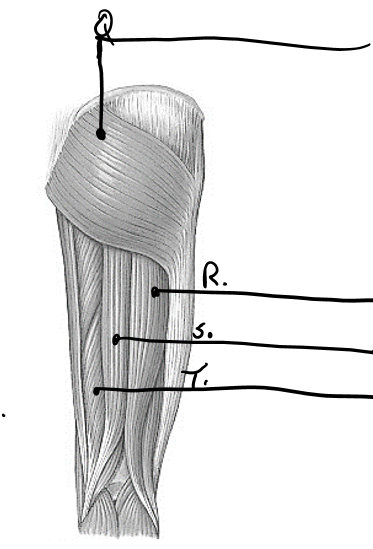
what is s
semitendinosus
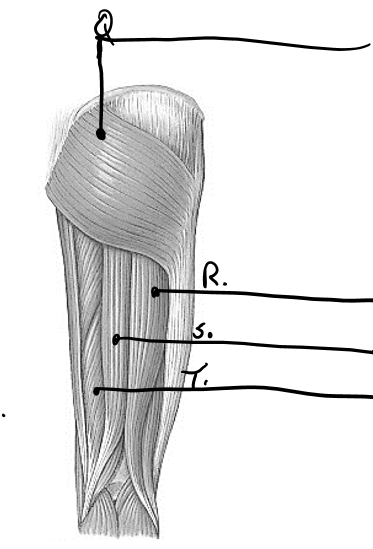
what is t
semimembranosus
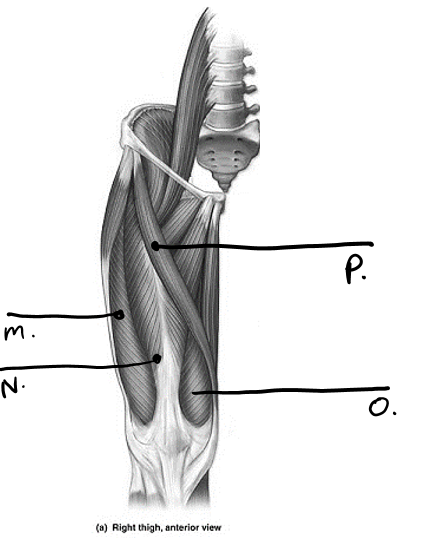
what is p
sartorius
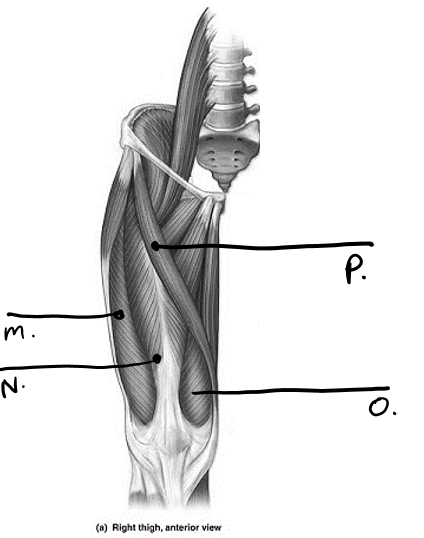
what is n
rectus femoris
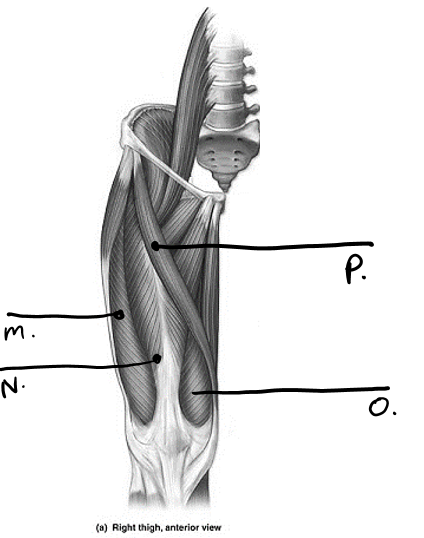
what is m
vastus lateralis
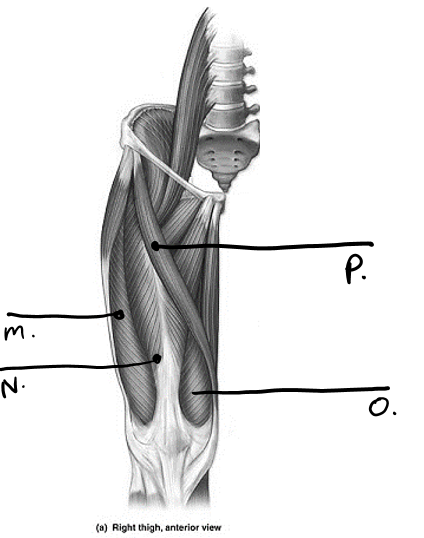
what is o
vastus medialis