Lab 16: Gestation and Contraception
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
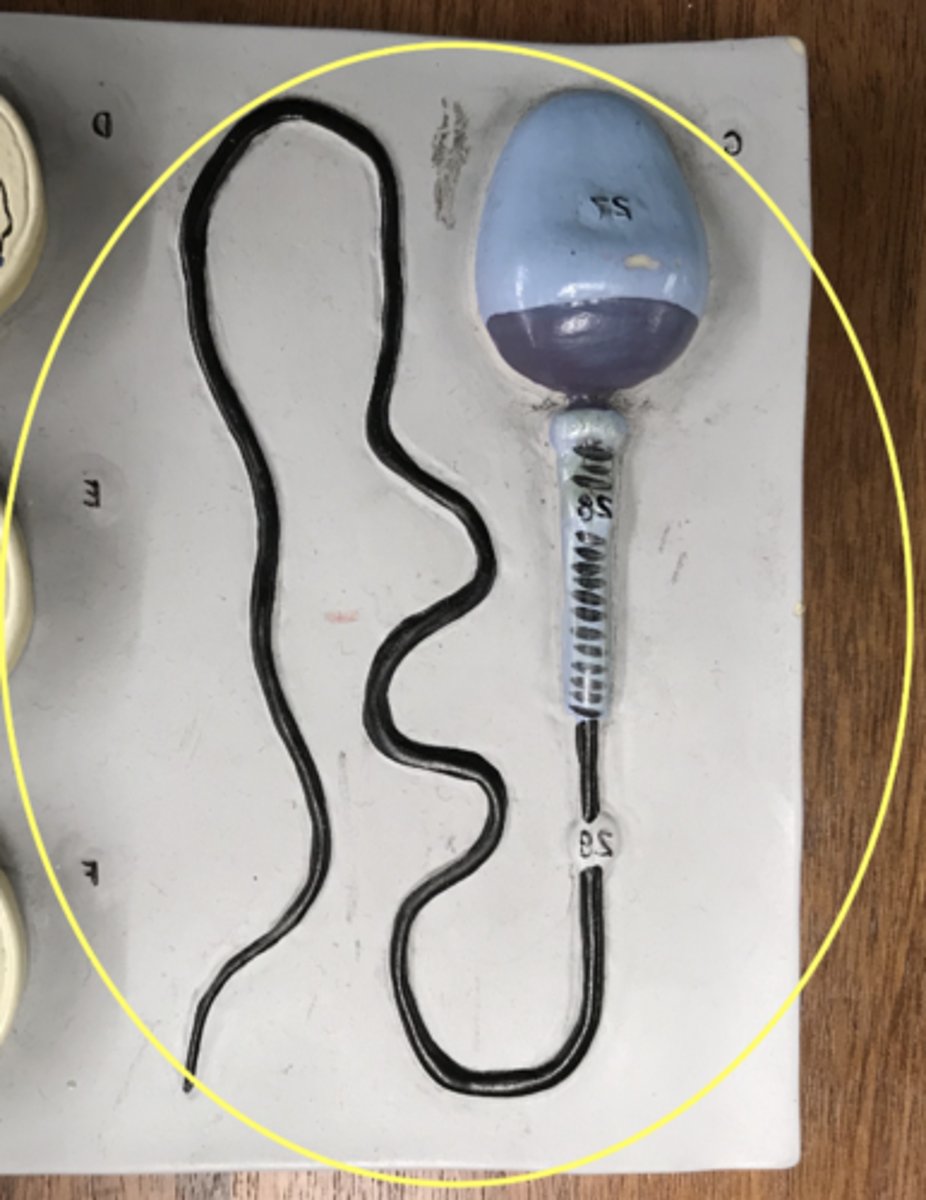
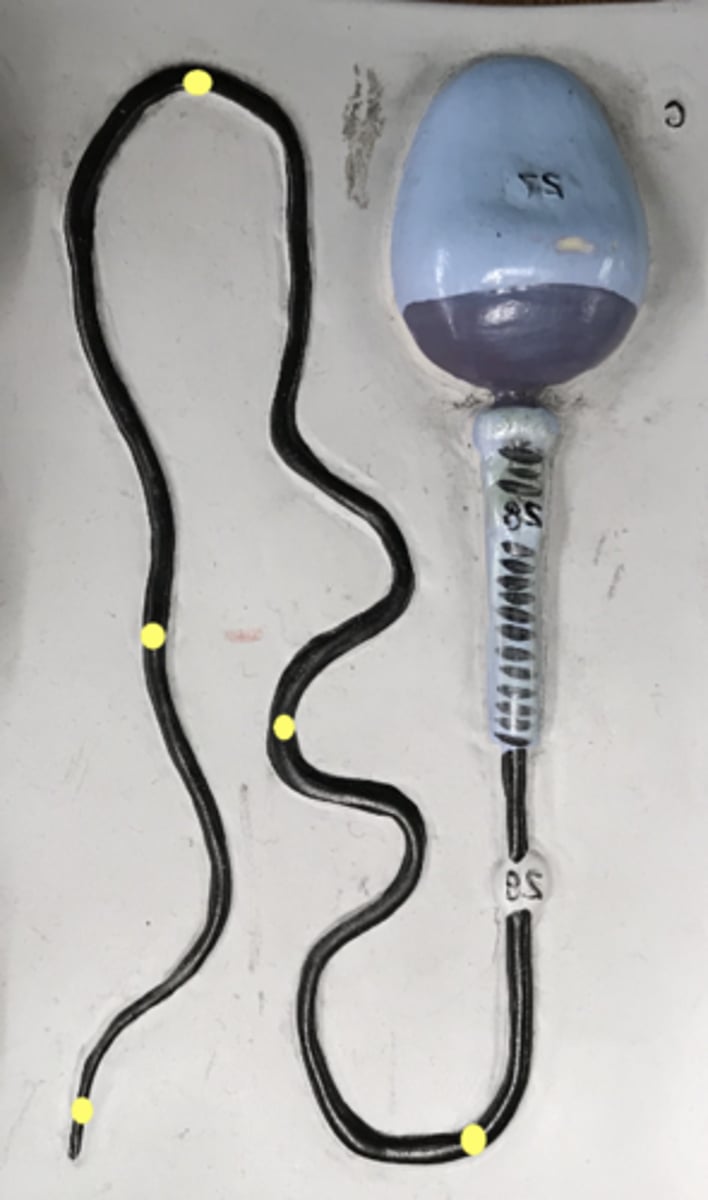
Sperm
male gamete
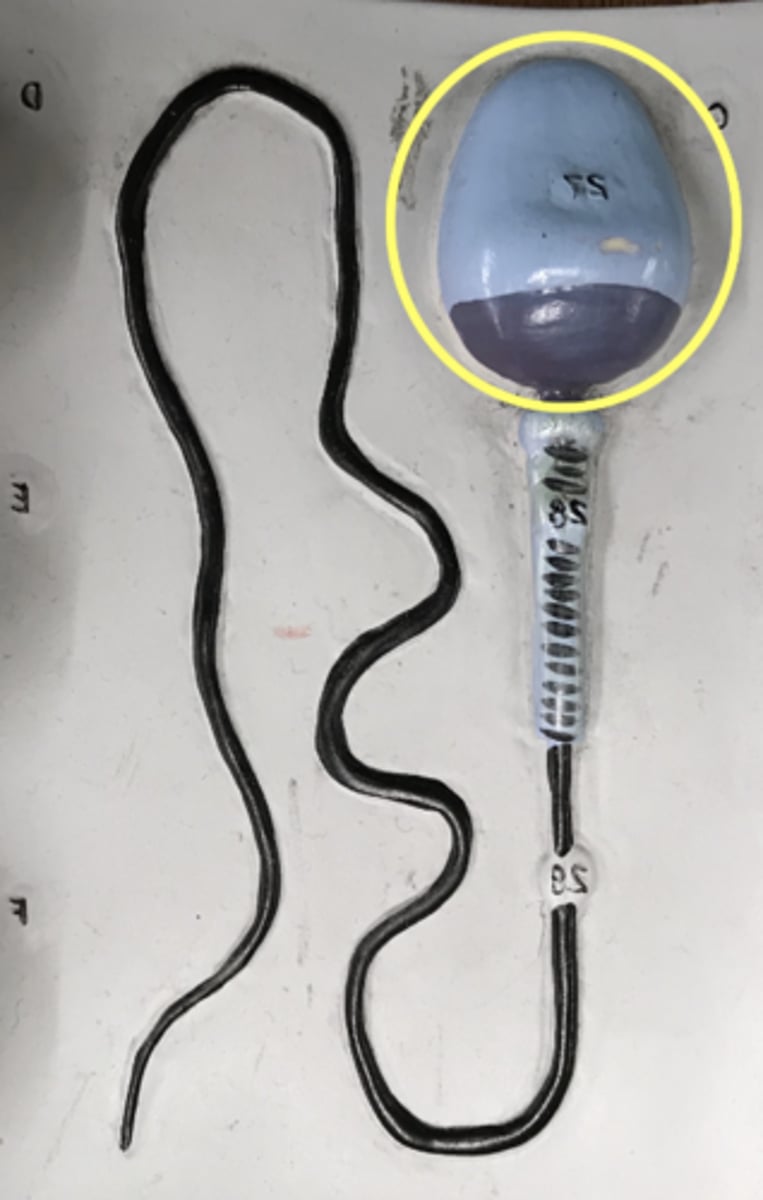
Head of sperm
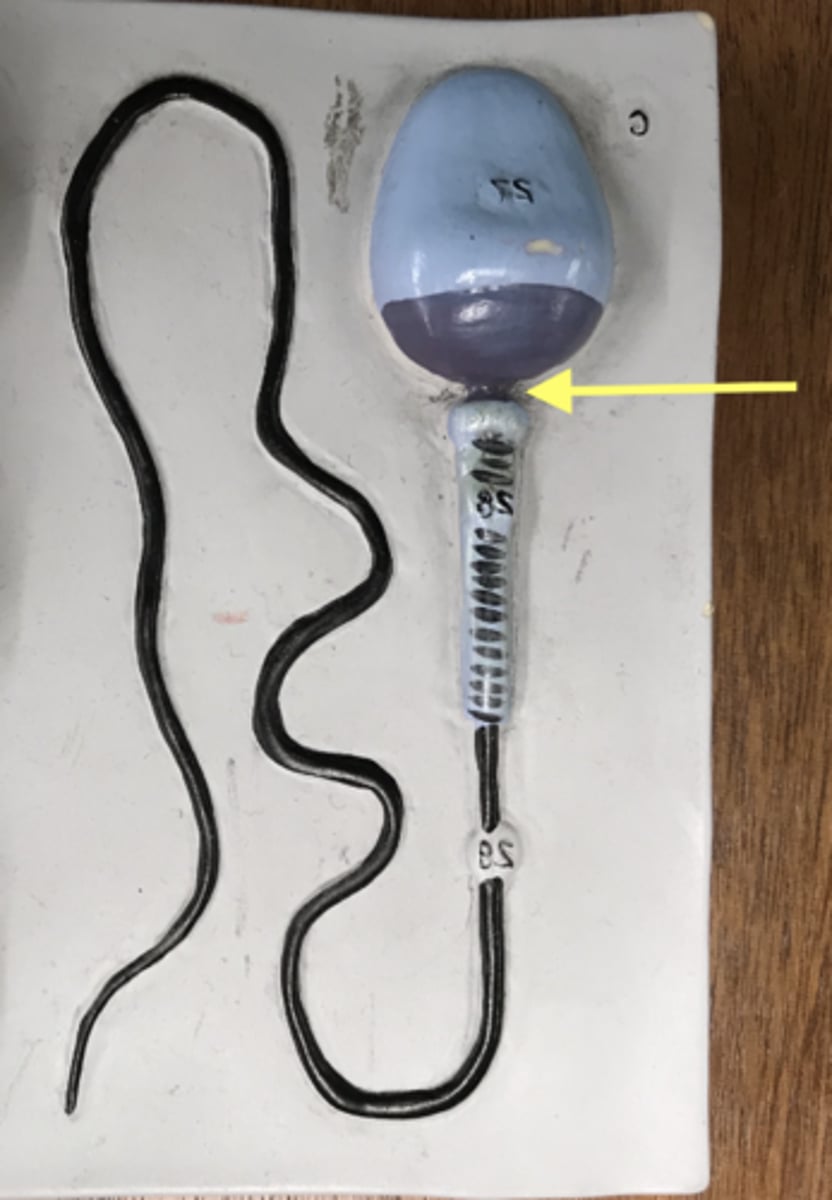
name this region

Neck of sperm
Name this region
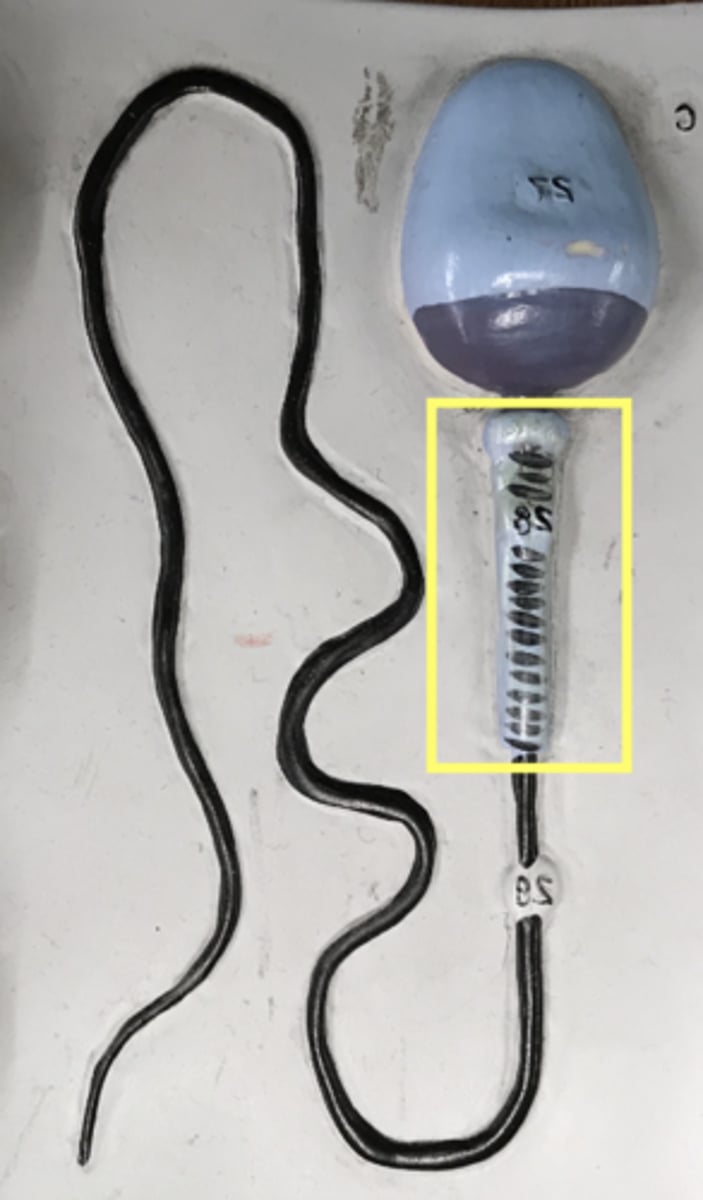
Middle piece of sperm
name this region

Tail of Sperm
name this region

Oocyte
Female gamete
Secondary oocyte
Once in the uterine tube after fertilization. Secondary oocyte is what becomes fertilized.
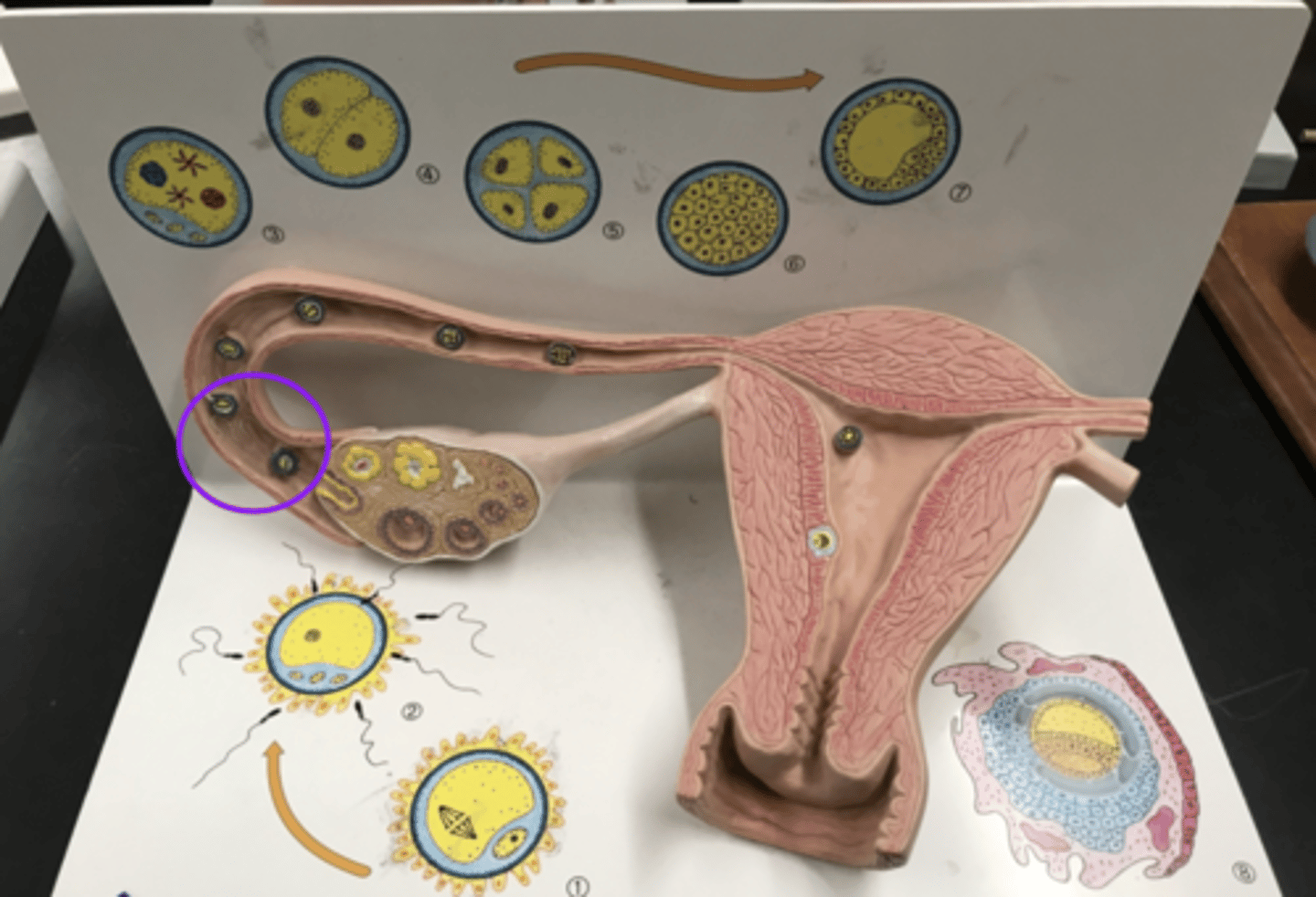
Corona radiata
Layer of cells that surrounds the oocyte when it is ovulated that protect the egg
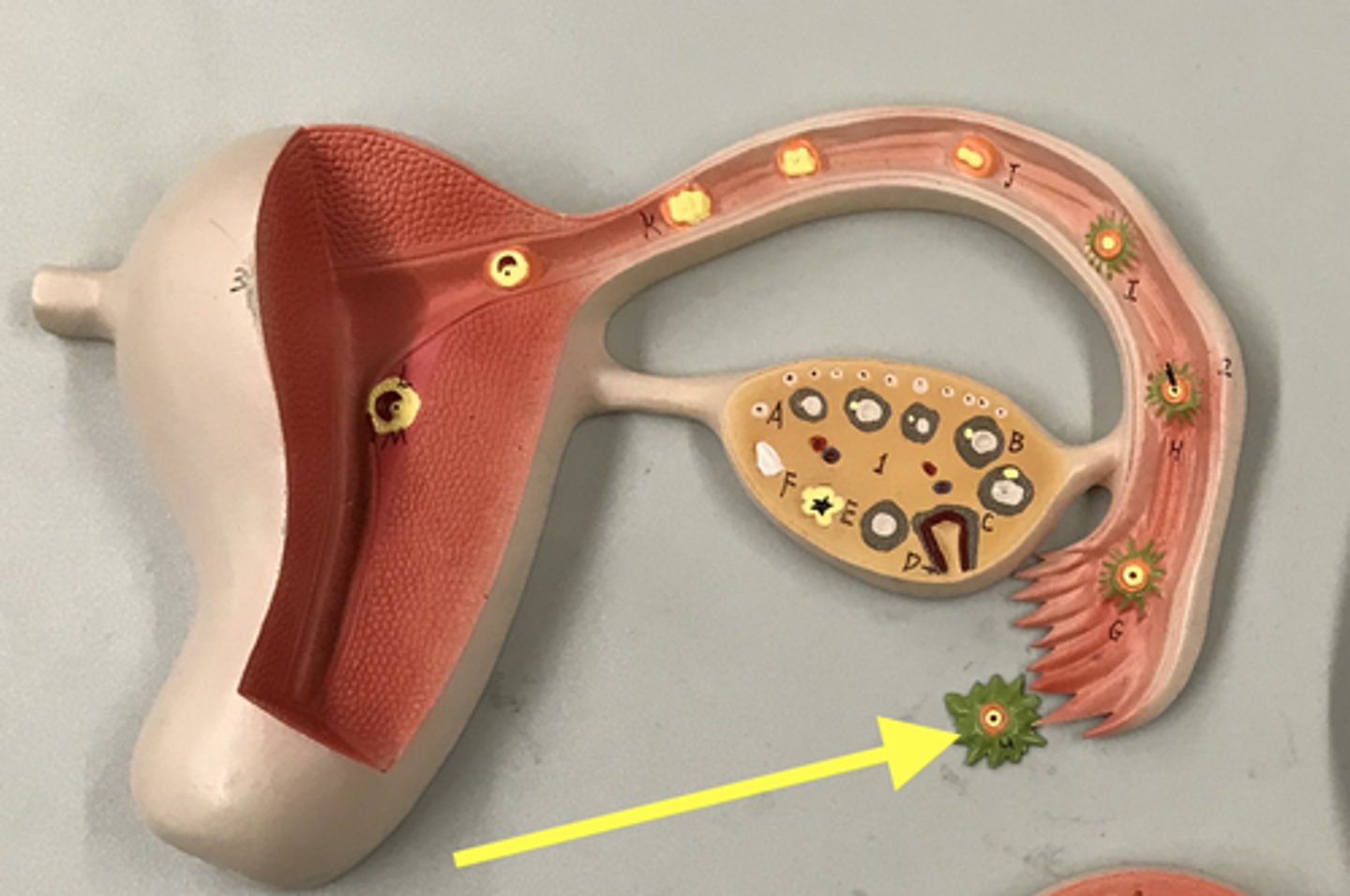
Corpus luteum
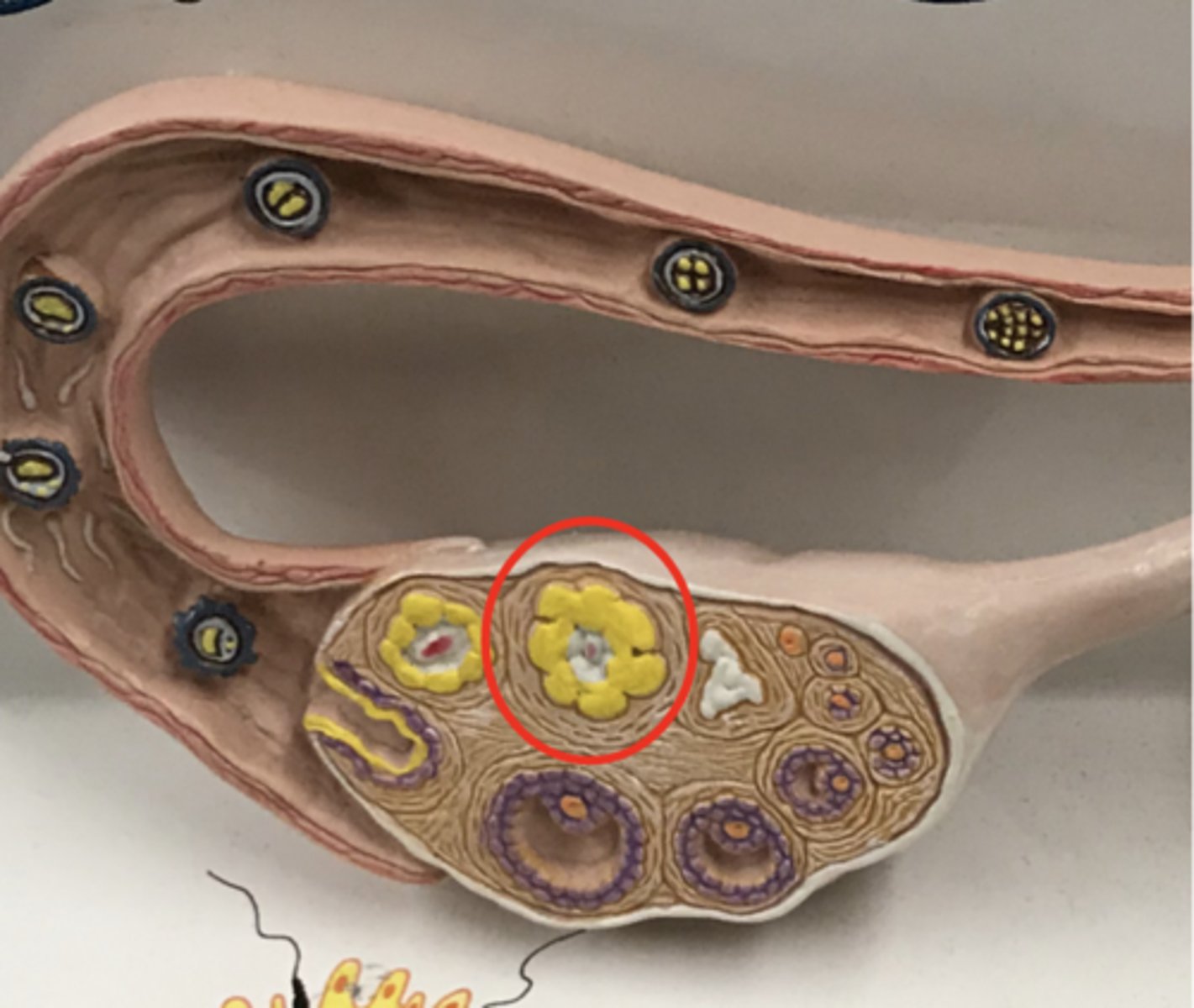
Blastomere
2, 4, 8 cell stages
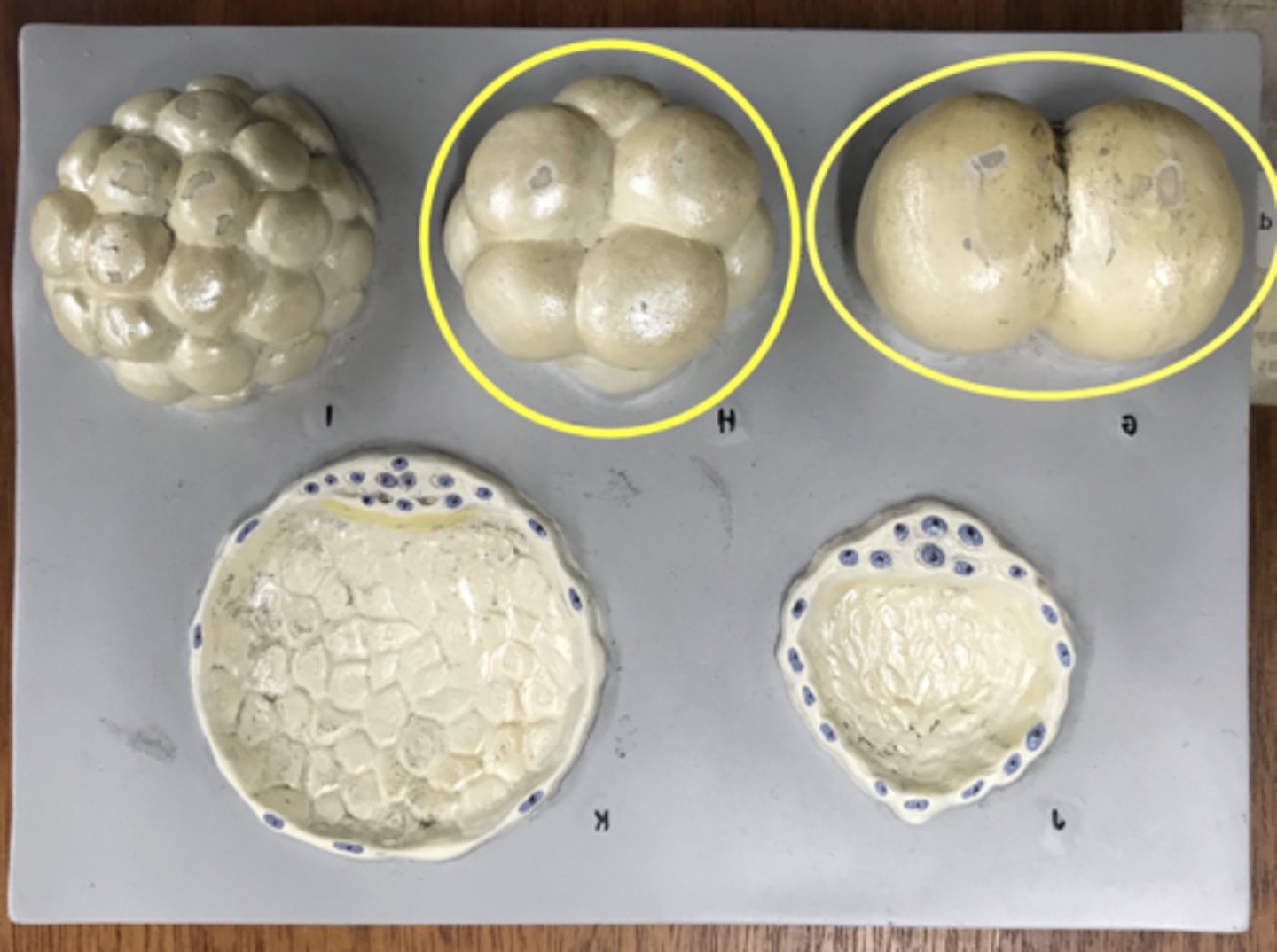

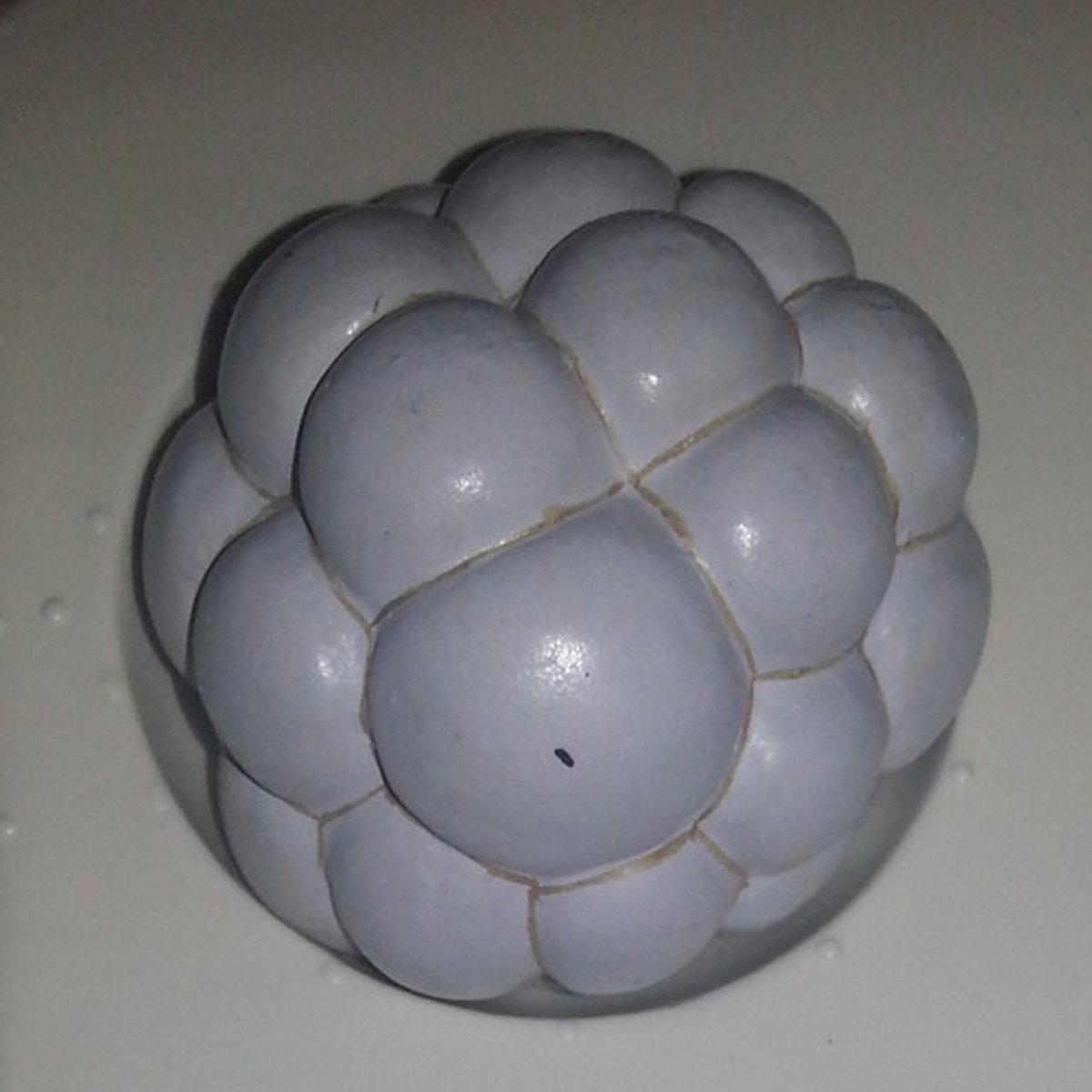
Morula
When the cell begins to differentiate
16 or more cells

Blastocyst
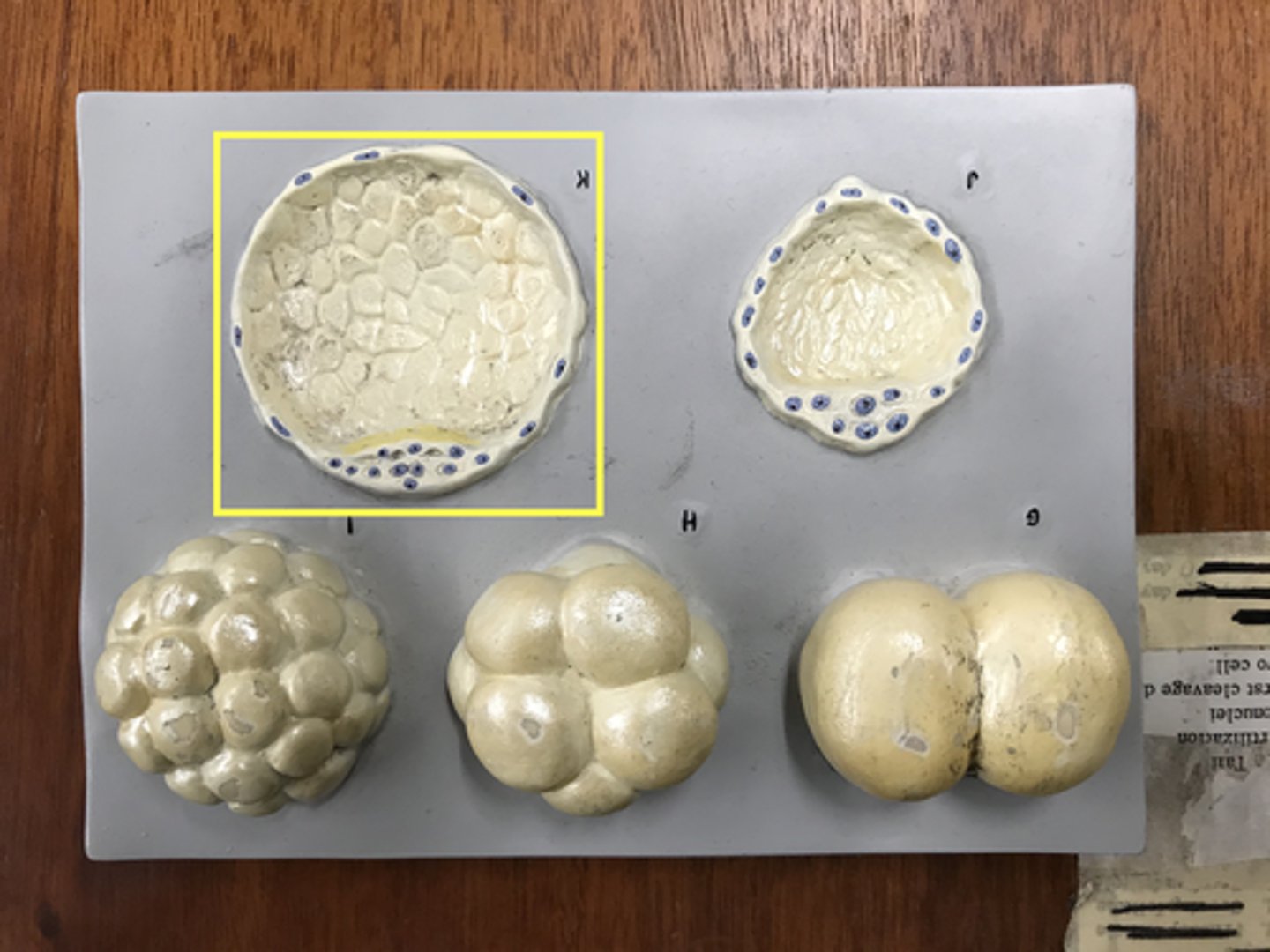

Blastocoele
The space or cavity inside the blastocyst
Name this SPACE
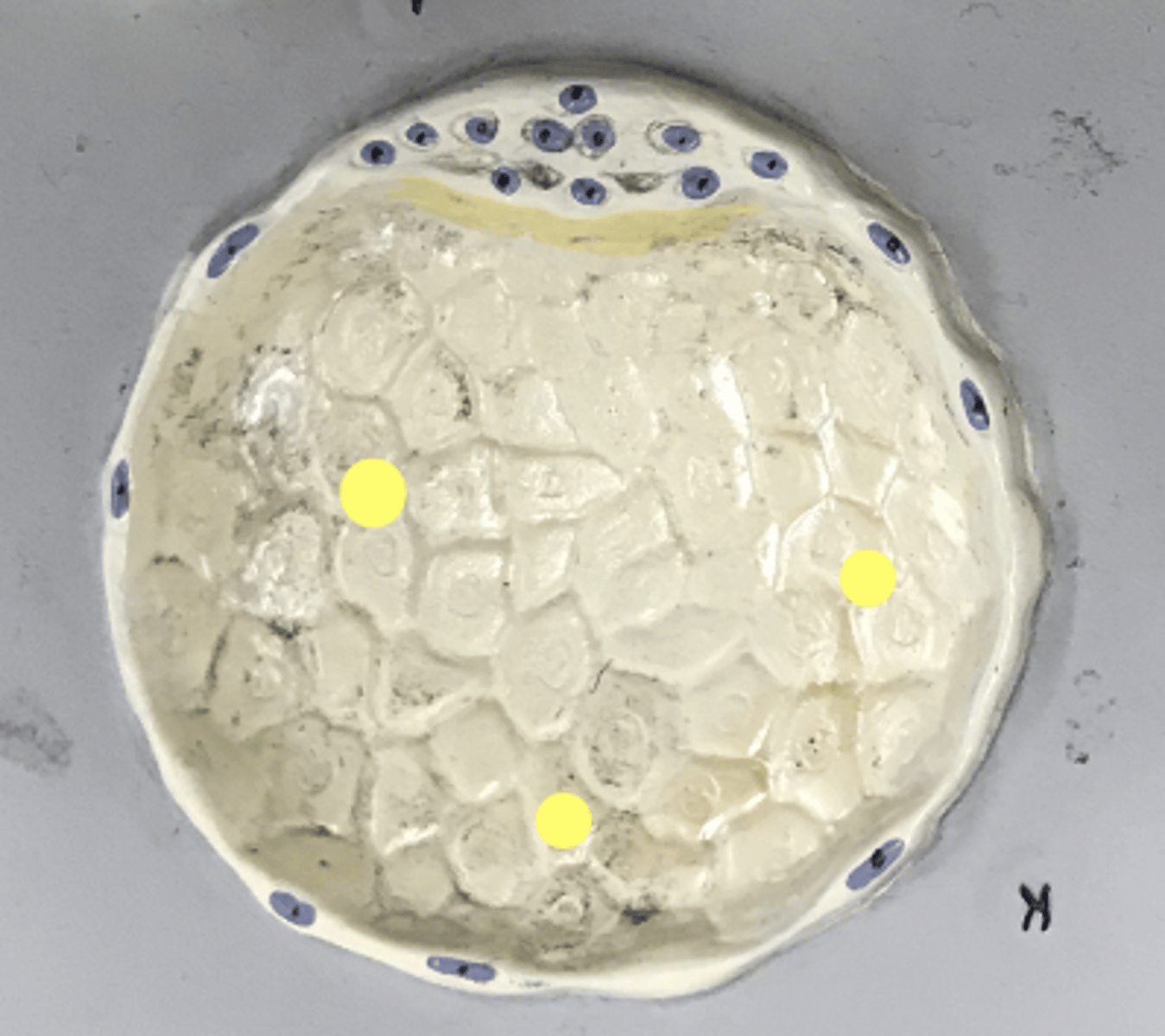
Trophoblast
- Outer layer of the blastocyst
- One single layer thick outer layer
- will become the placenta
Name this LAYER

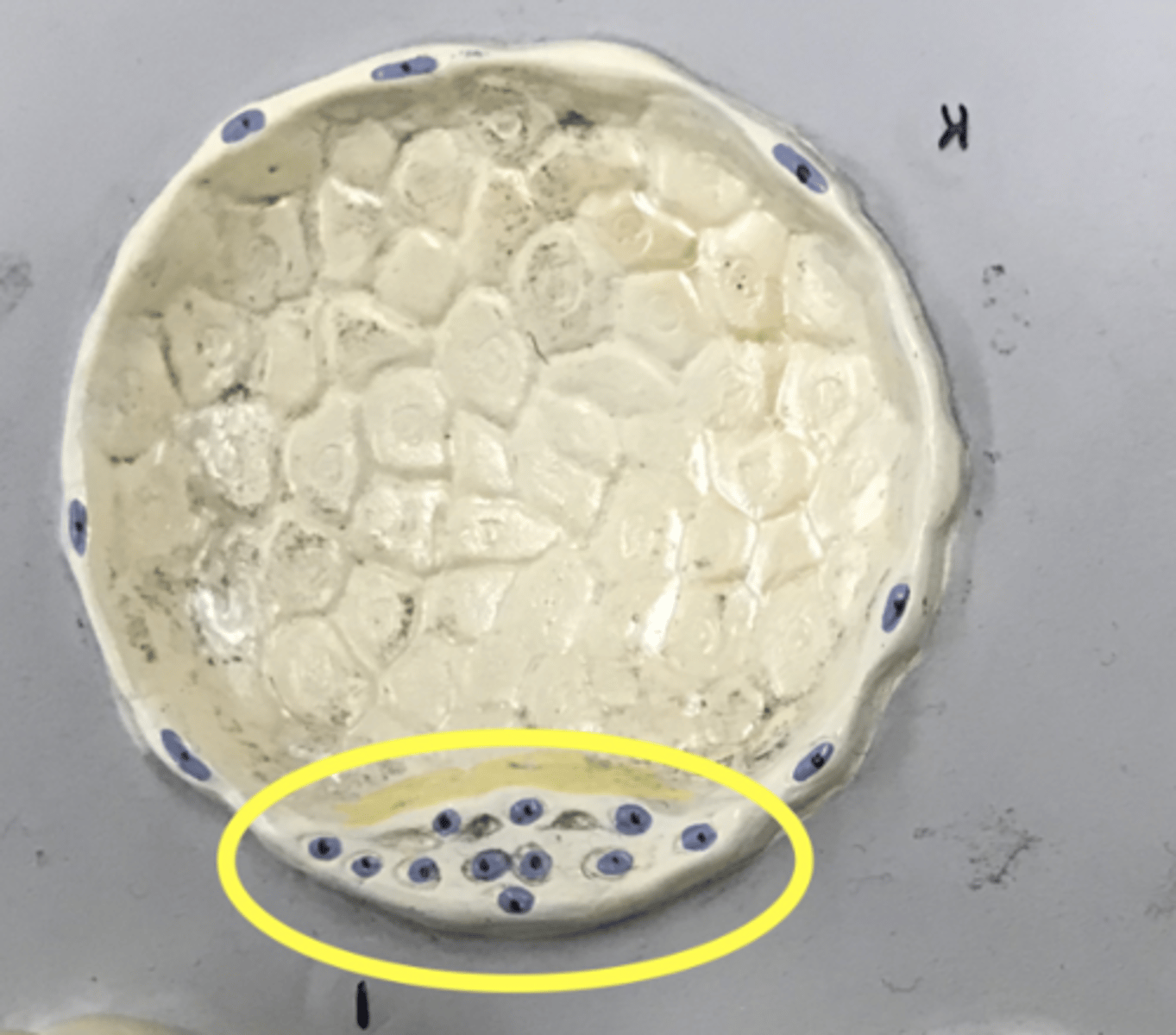
Inner cell mass
Cells on the inside of the blastocyst
- Will become the fetus
First trimester
The first 13 weeks after the last menstrual period
12 weeks
- Rudimentary organ systems have formed
- Fetus is about 3 inches long
- Fetus weighs about 0.5 lbs
Second trimester
Weeks 14-26 after the last menstrual period
16-20 weeks
Fetal movements become perceptible around..........
25 weeks
- Fetus is about 9 inches long
-Fetus weighs about 1.4 lbs
-Eyelids open
Third trimester
Weeks 27-40 after the last menstrual period
38 weeks
- Average weight is about 7 lbs
- Average length is about 14 inches
Pre-term baby
Refers to babies born prior to 37 weeks gestation
Term baby
Refers to babies born between 37-40 weeks gestation
Post-term baby
Refers to babies born at greater than 40 weeks gestation
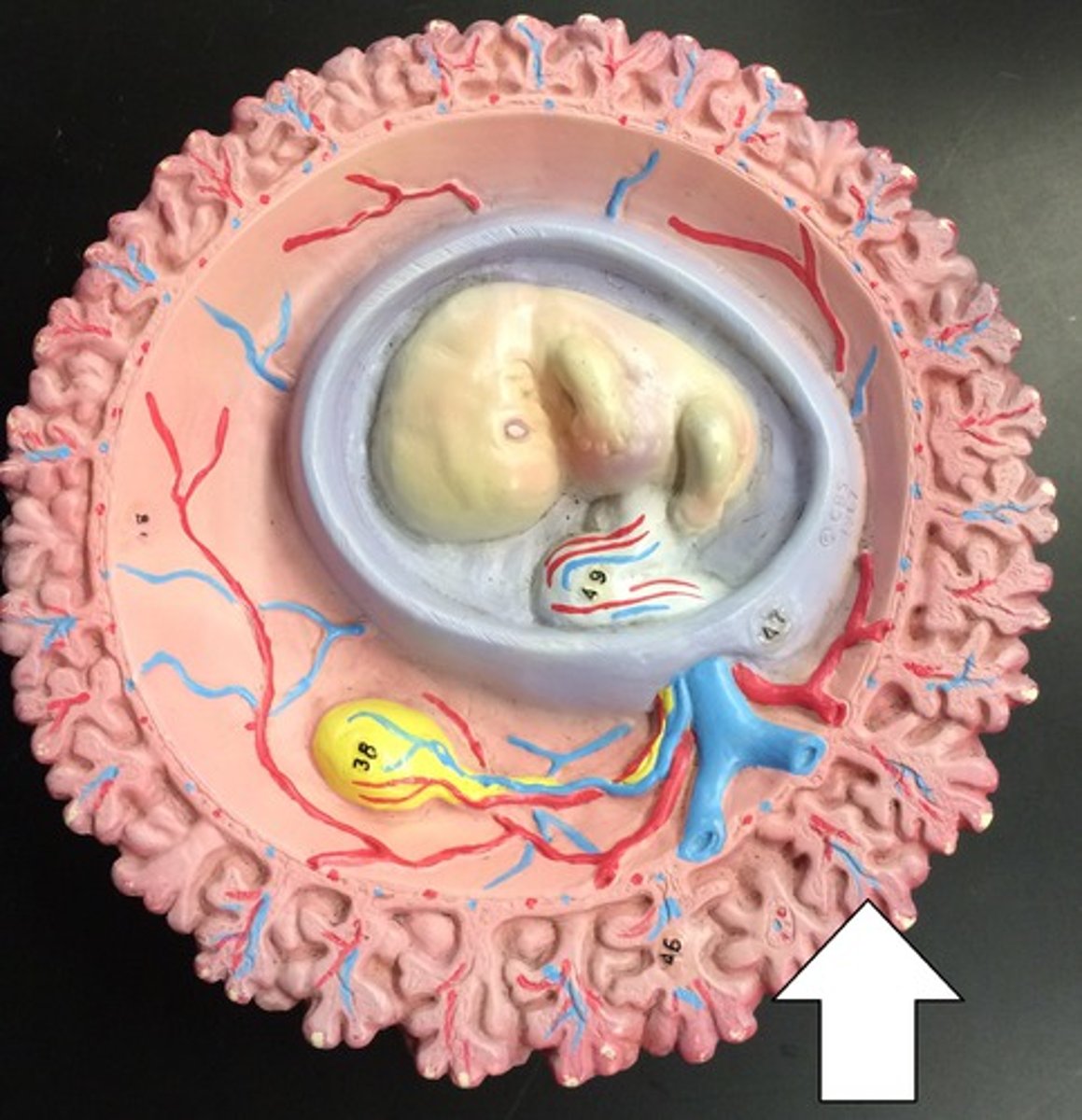
Yolk sac
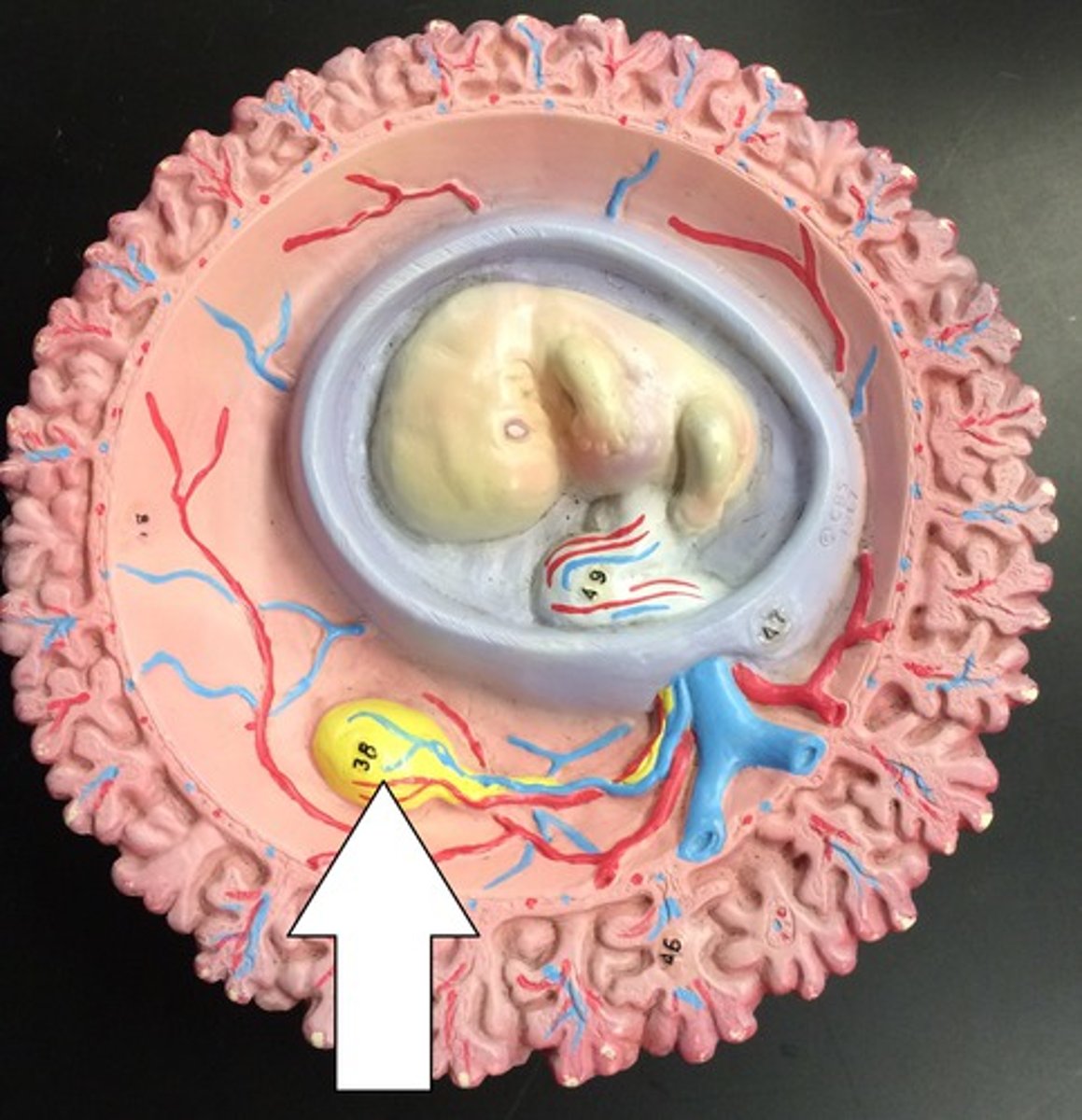
Placenta
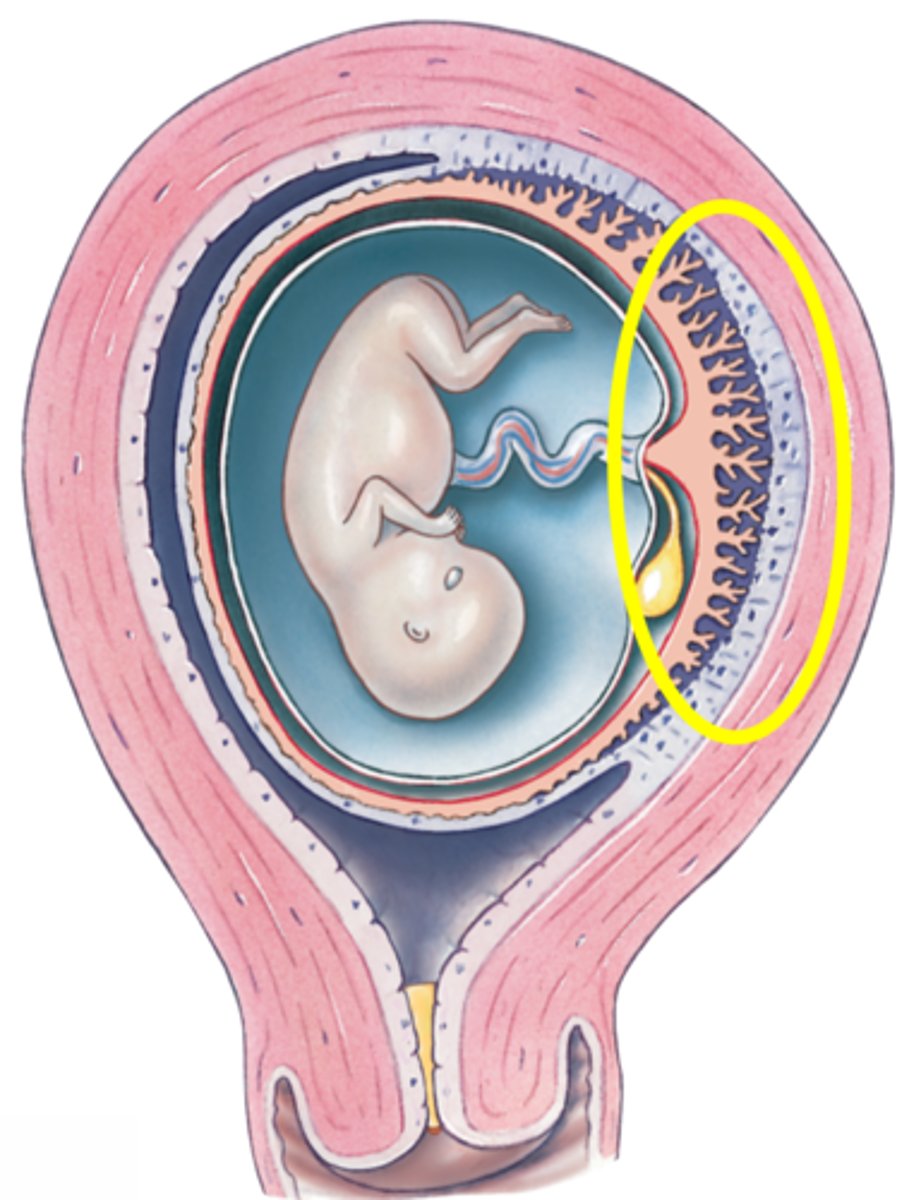
Umbilical cord
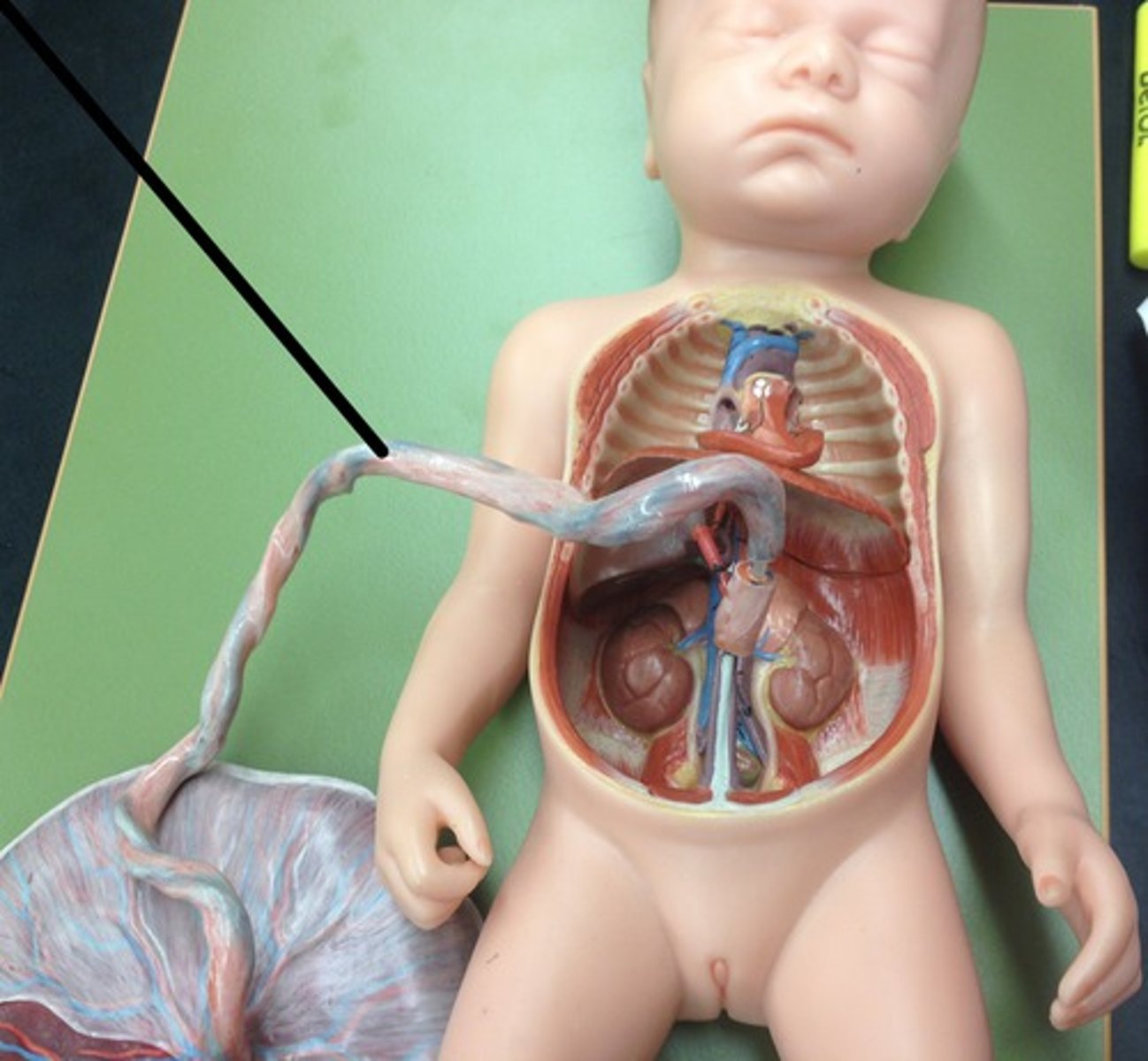
Umbilical arteries (2)
carry deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta
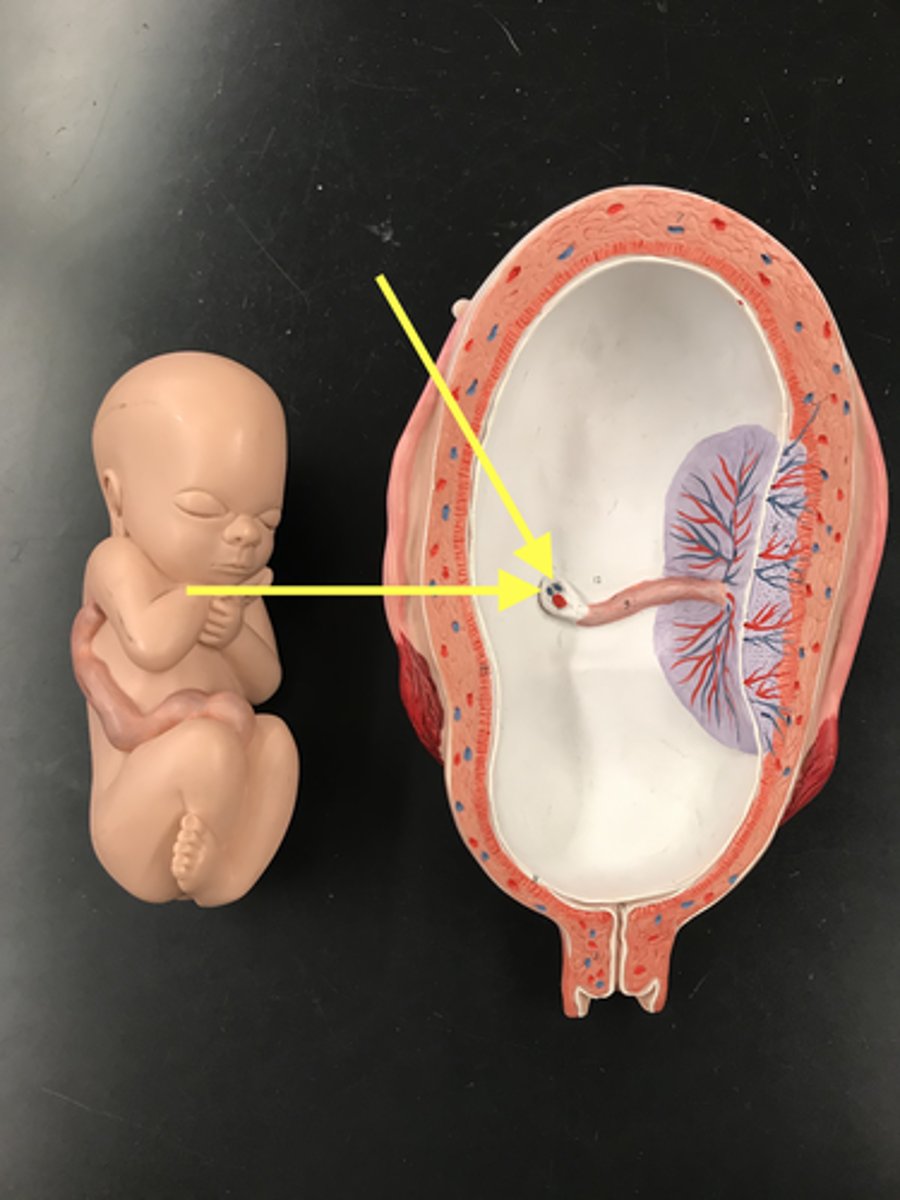
Umbilical vein (1)
delivers oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus
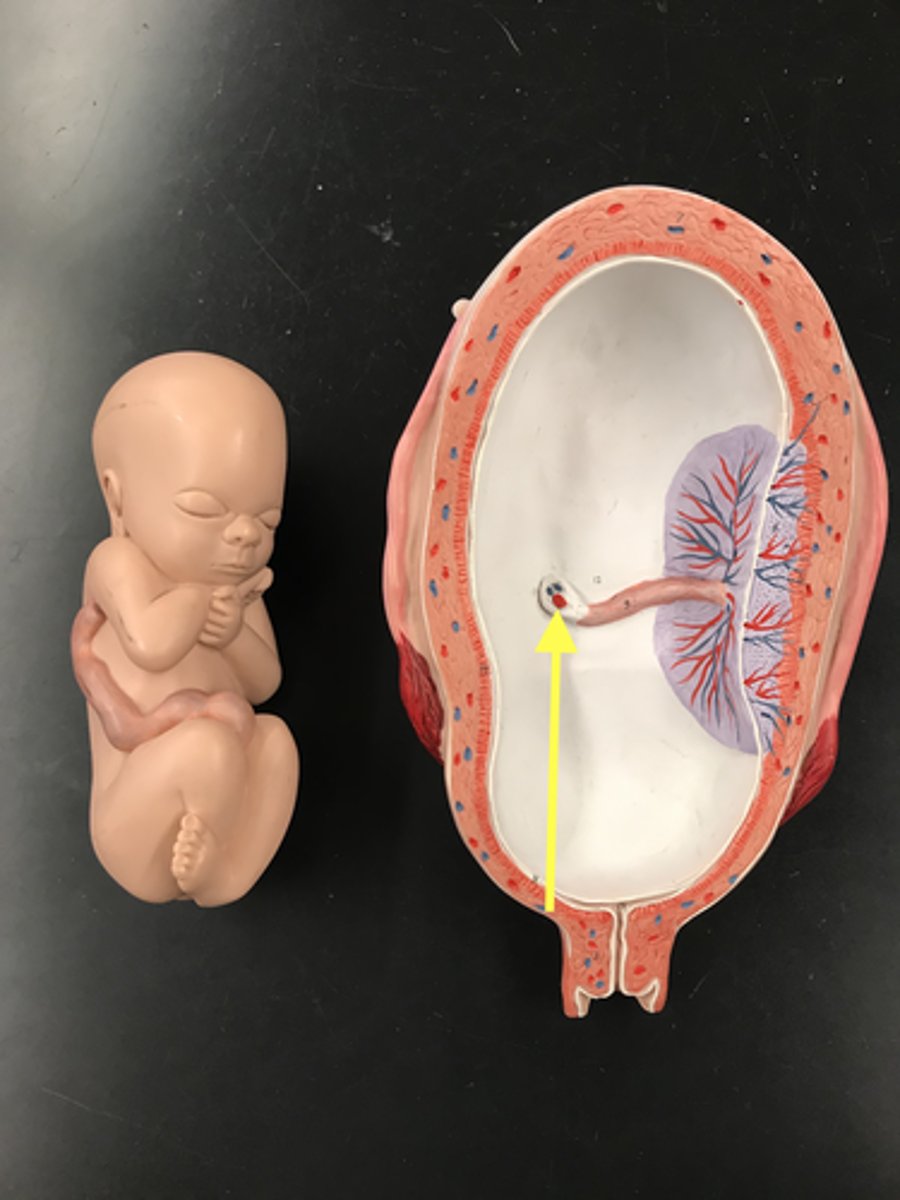
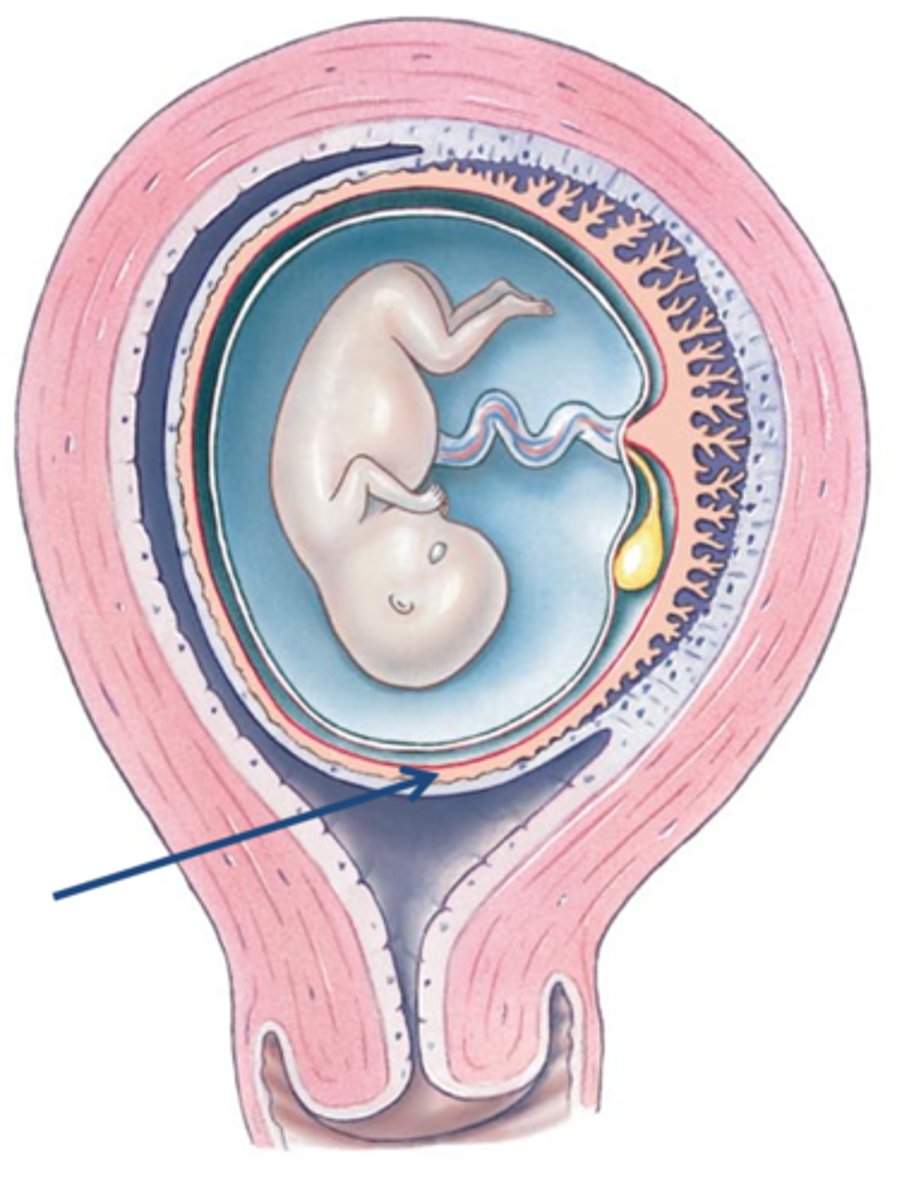
Amniotic cavity
name this SPACE

Amnion
name this LAYER
(white)
Chorion
name this LAYER
Chorionic villi
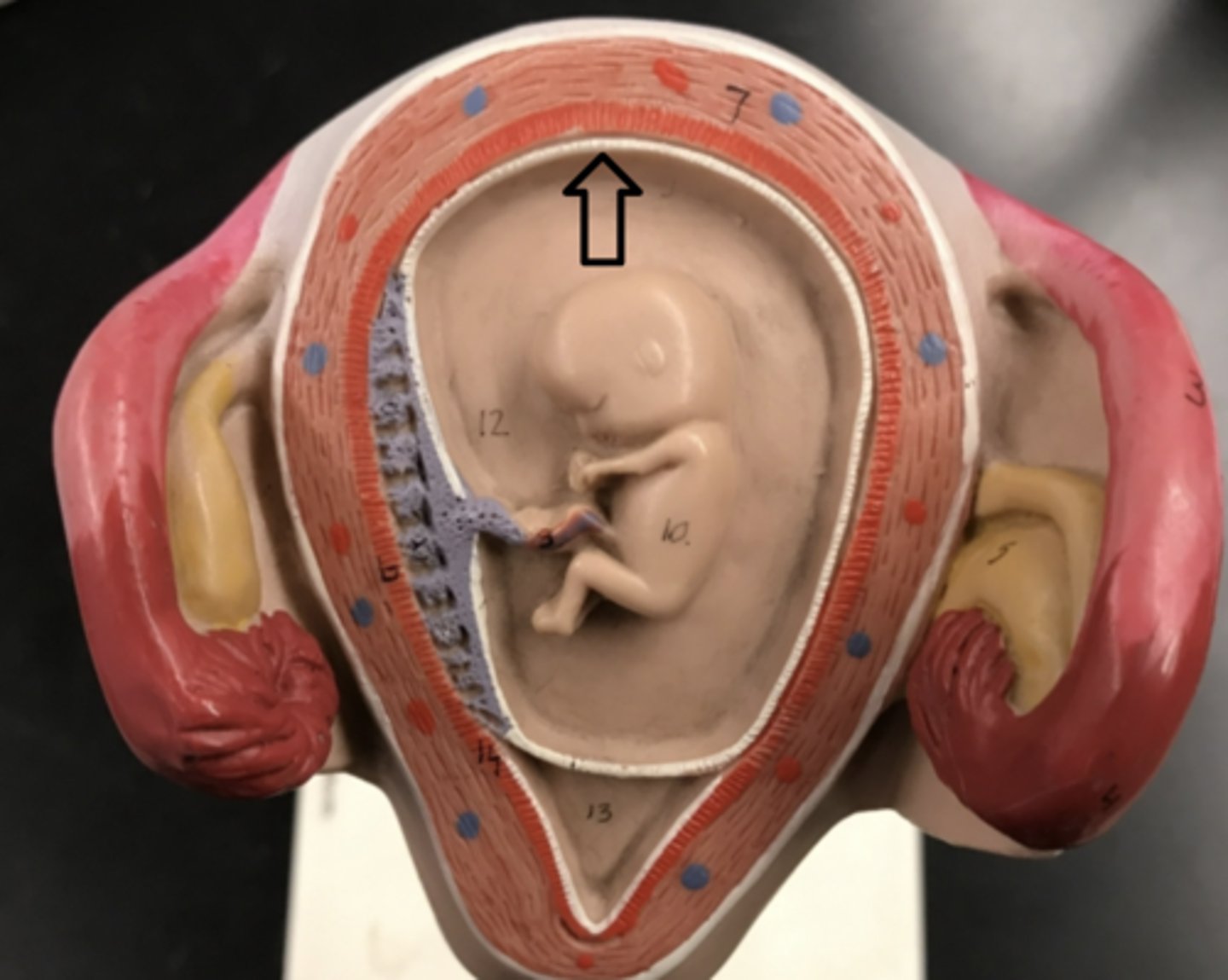
Decidua capsularis
Only touches the baby
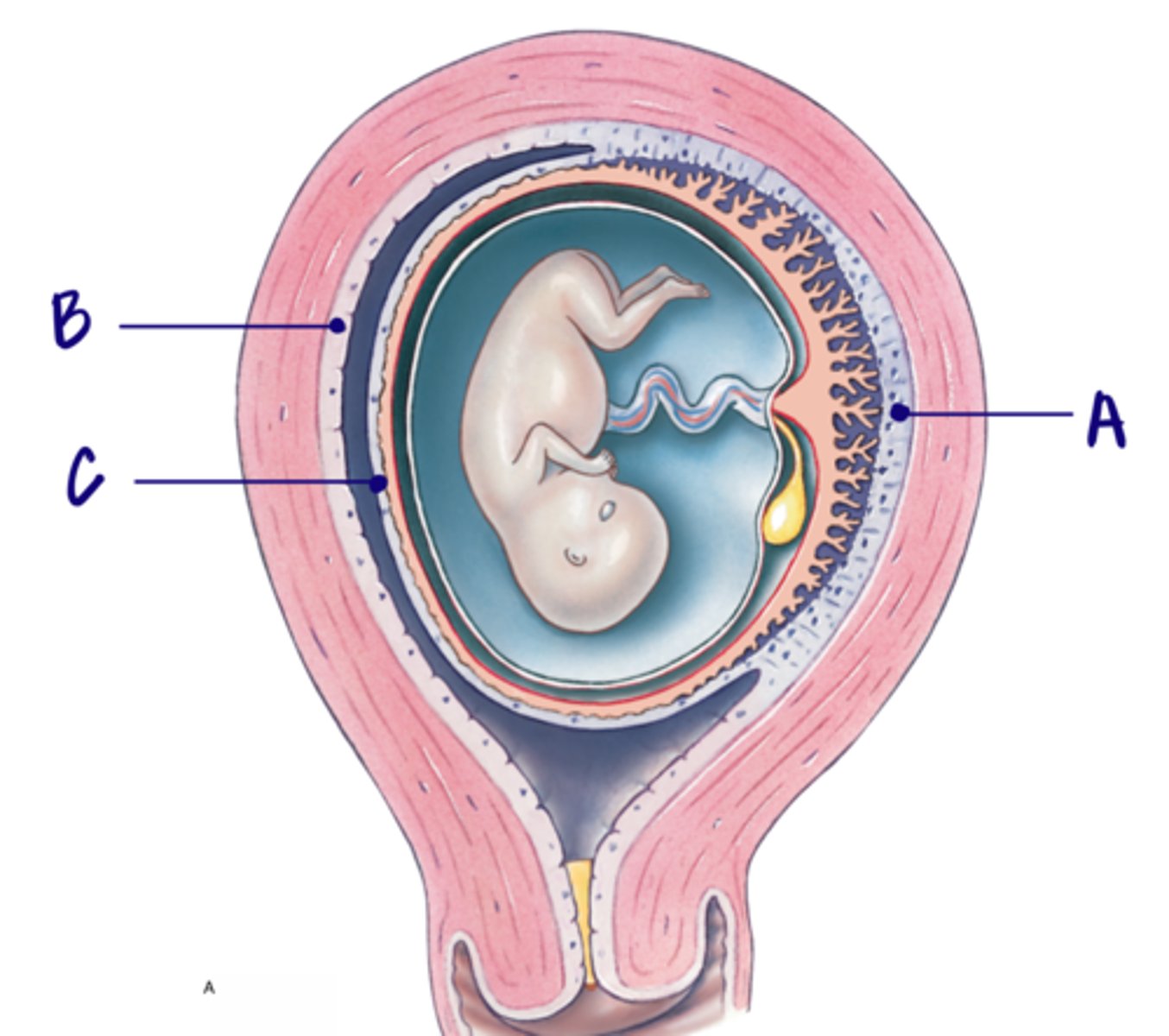
C
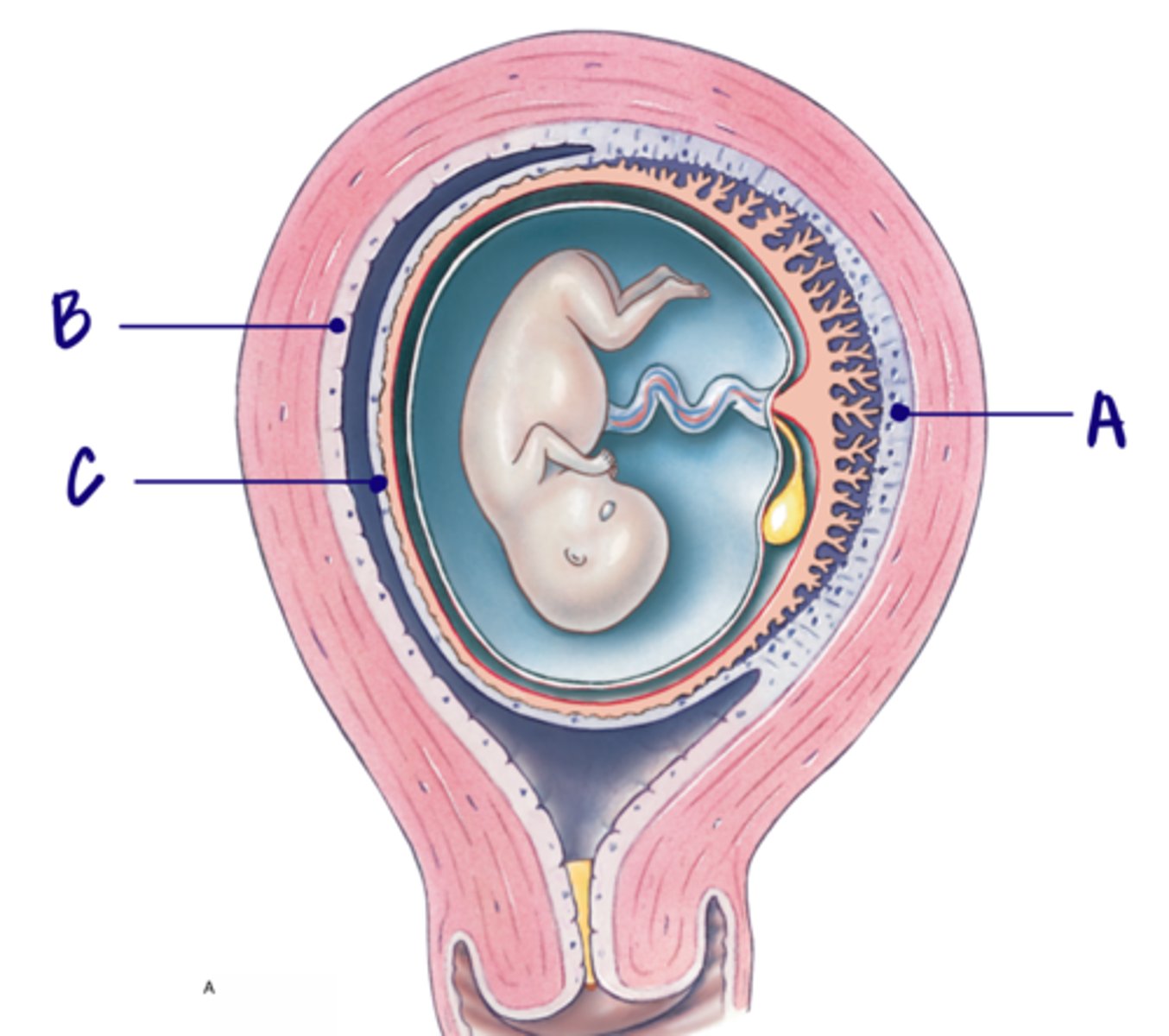
Decidua parietalis
Only touches the mother
B
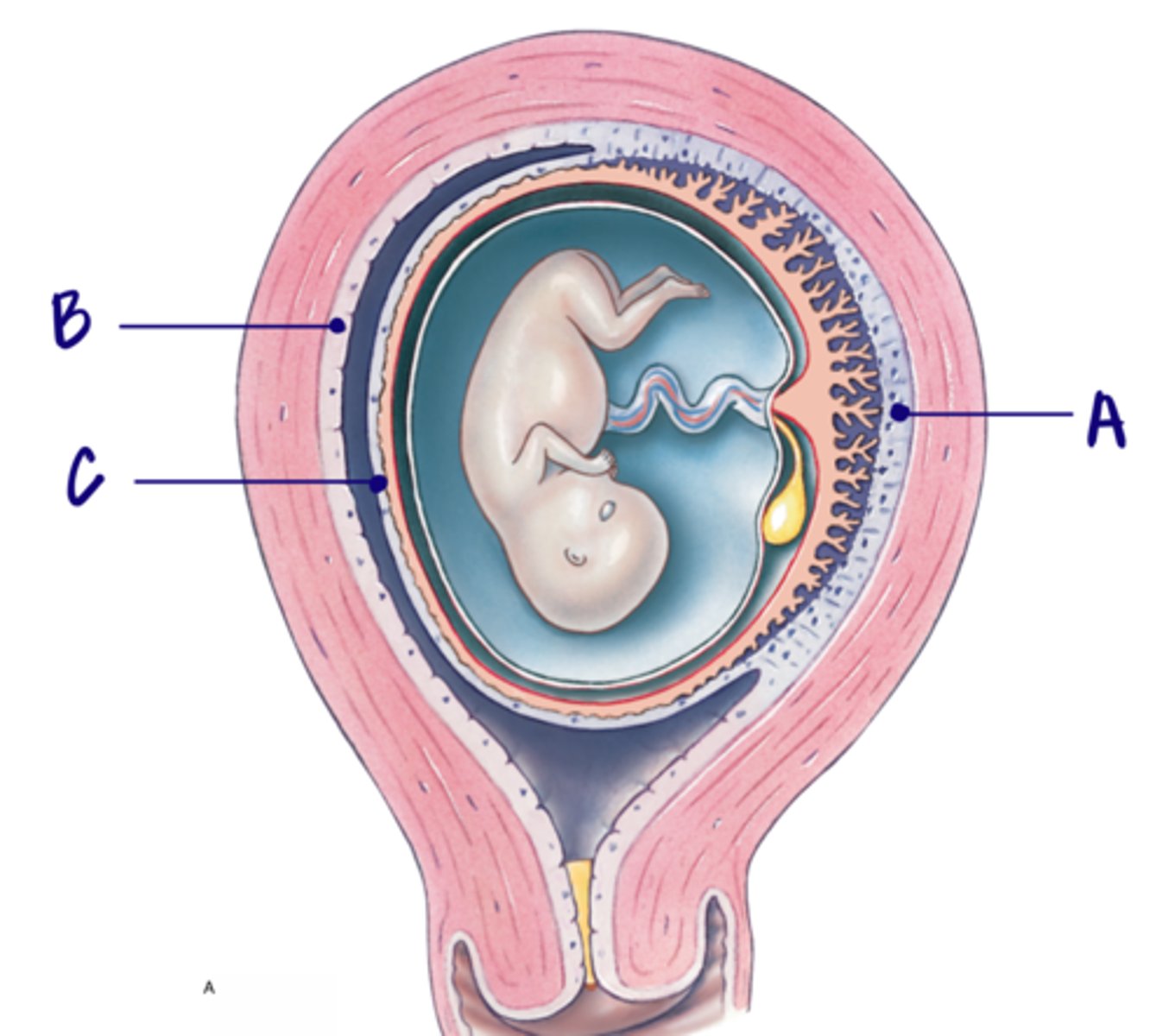
Decidua basalis
Touches both the baby and the mother
A
Male condom
Lamb skin condoms do not protect against infections
-Non-hormonal
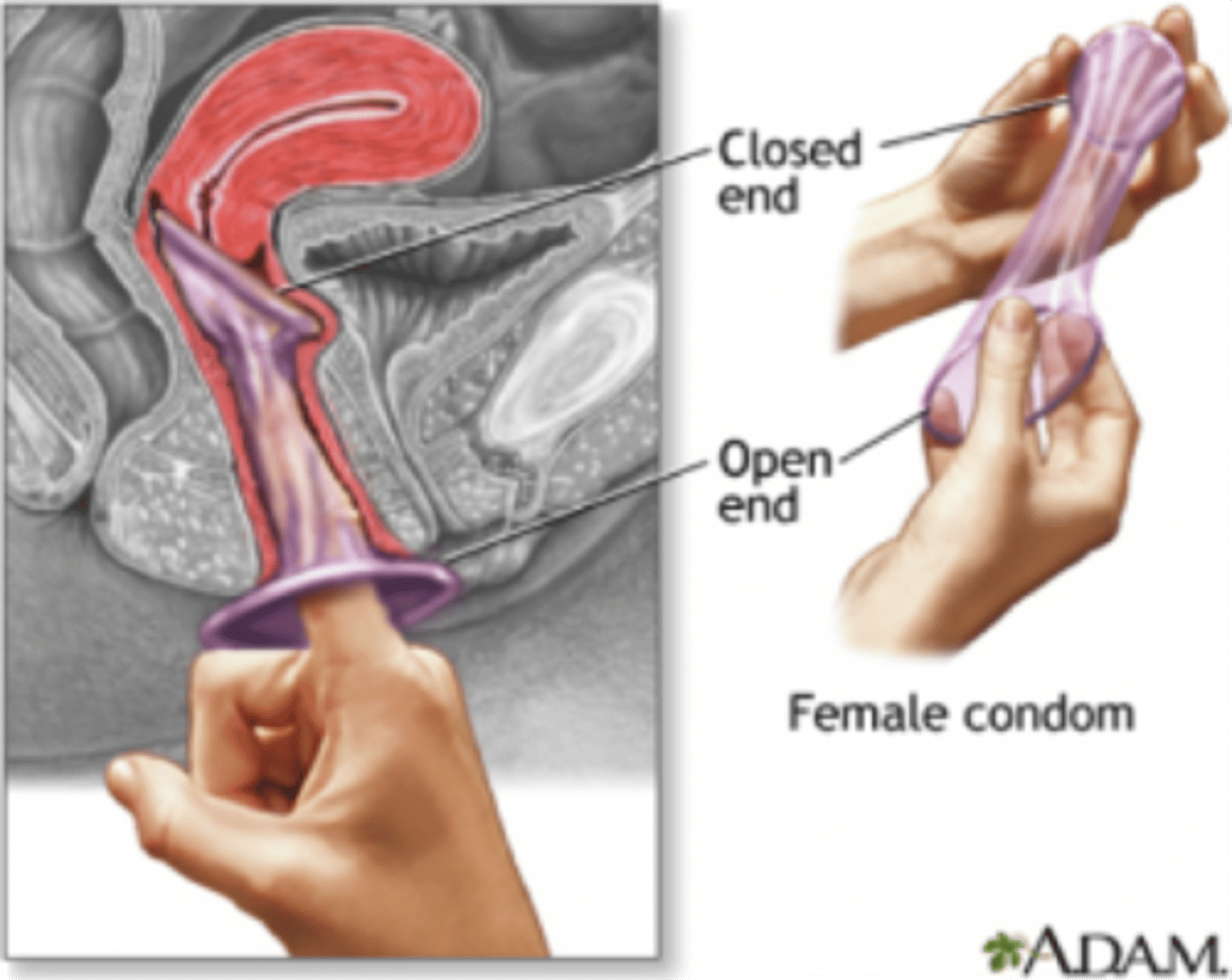
Female condom
Has a closed end and open end
-Non-hormonal
Diaphragm
Bigger and looks like a bowl
-Non-hormonal
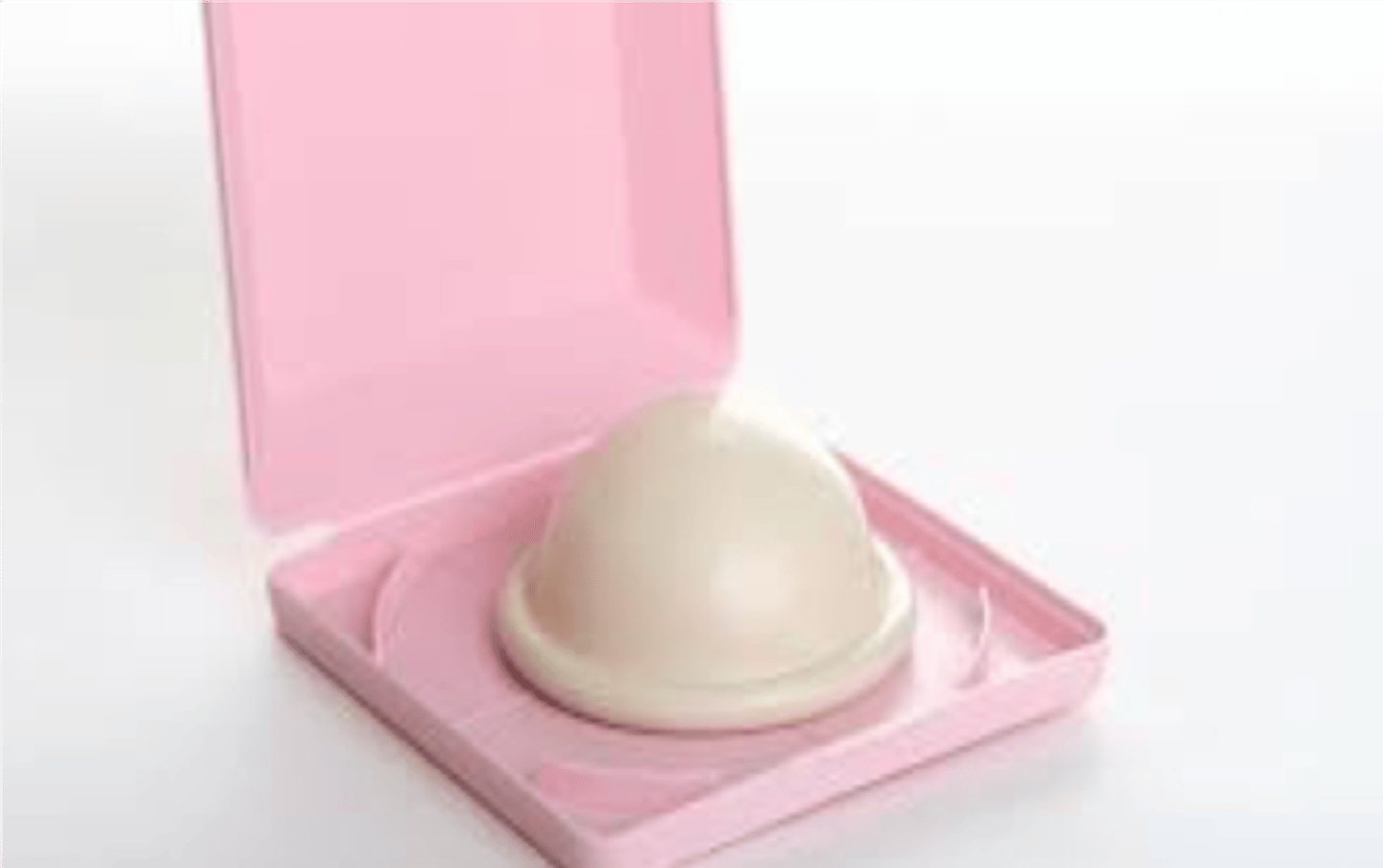

Cervical cap
Smaller and looks like a bottle top
-Non-hormonal
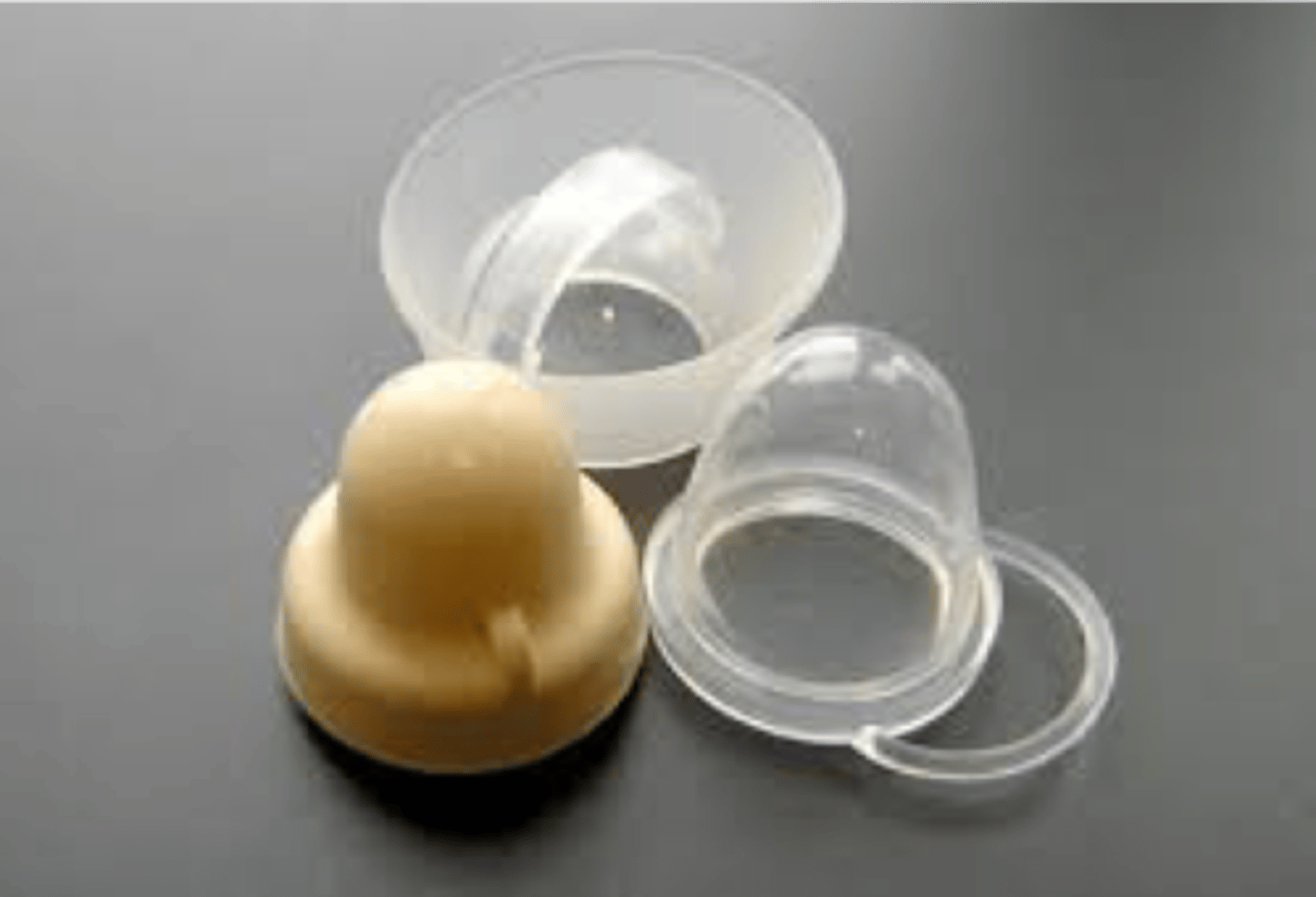

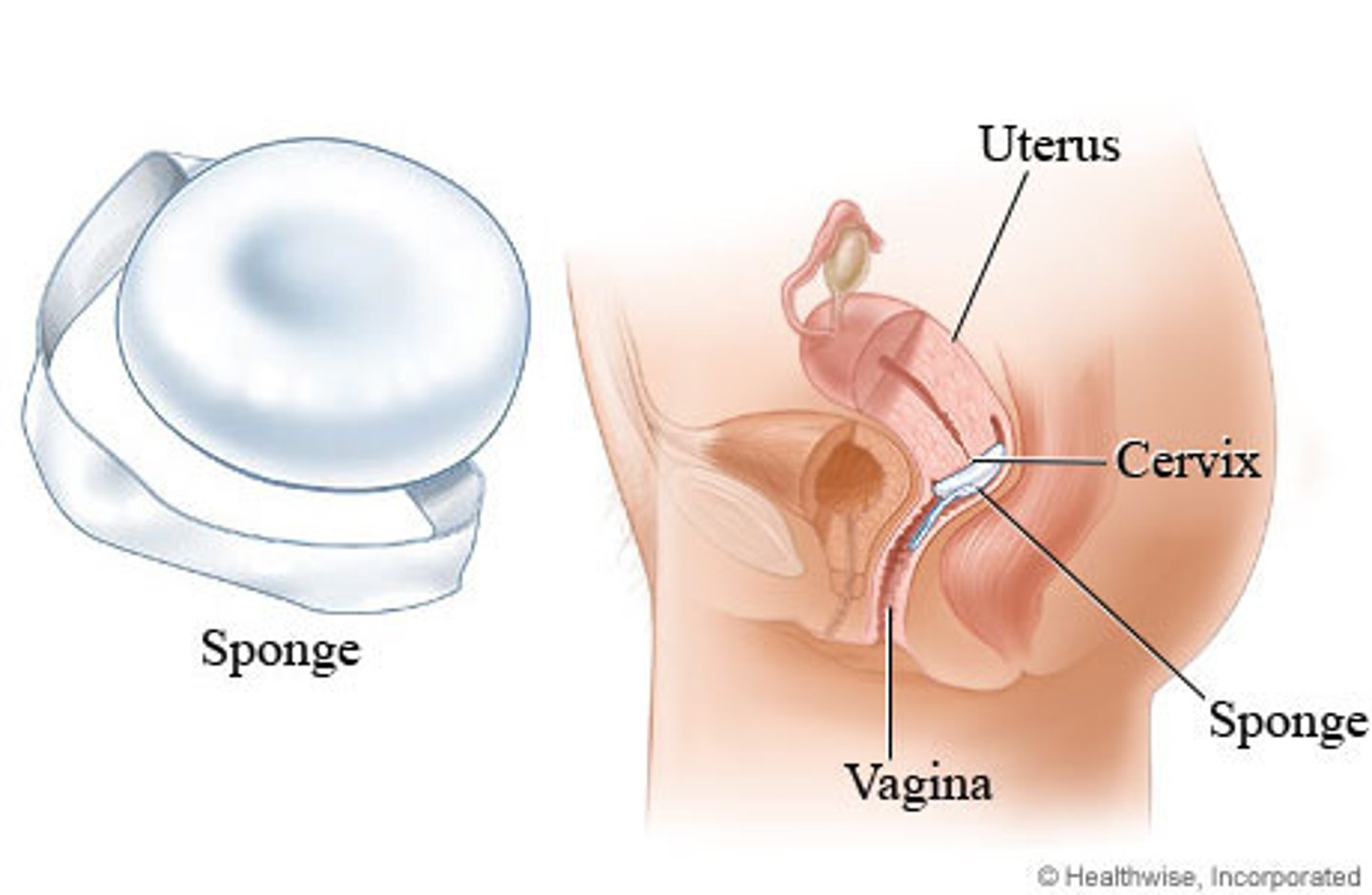
Sponge contraception
A sponge structure similar to cervical cap
-Non-hormonal
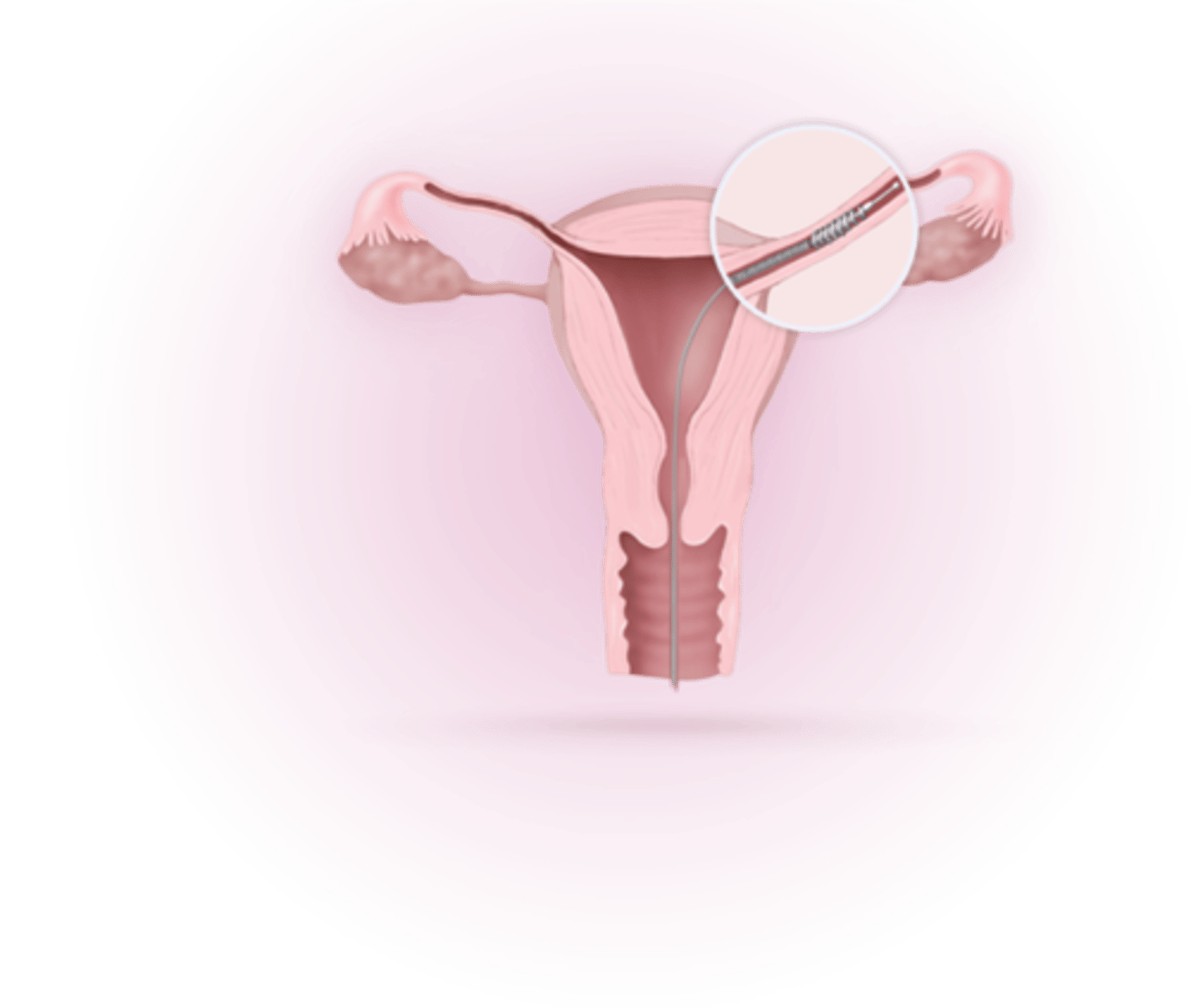
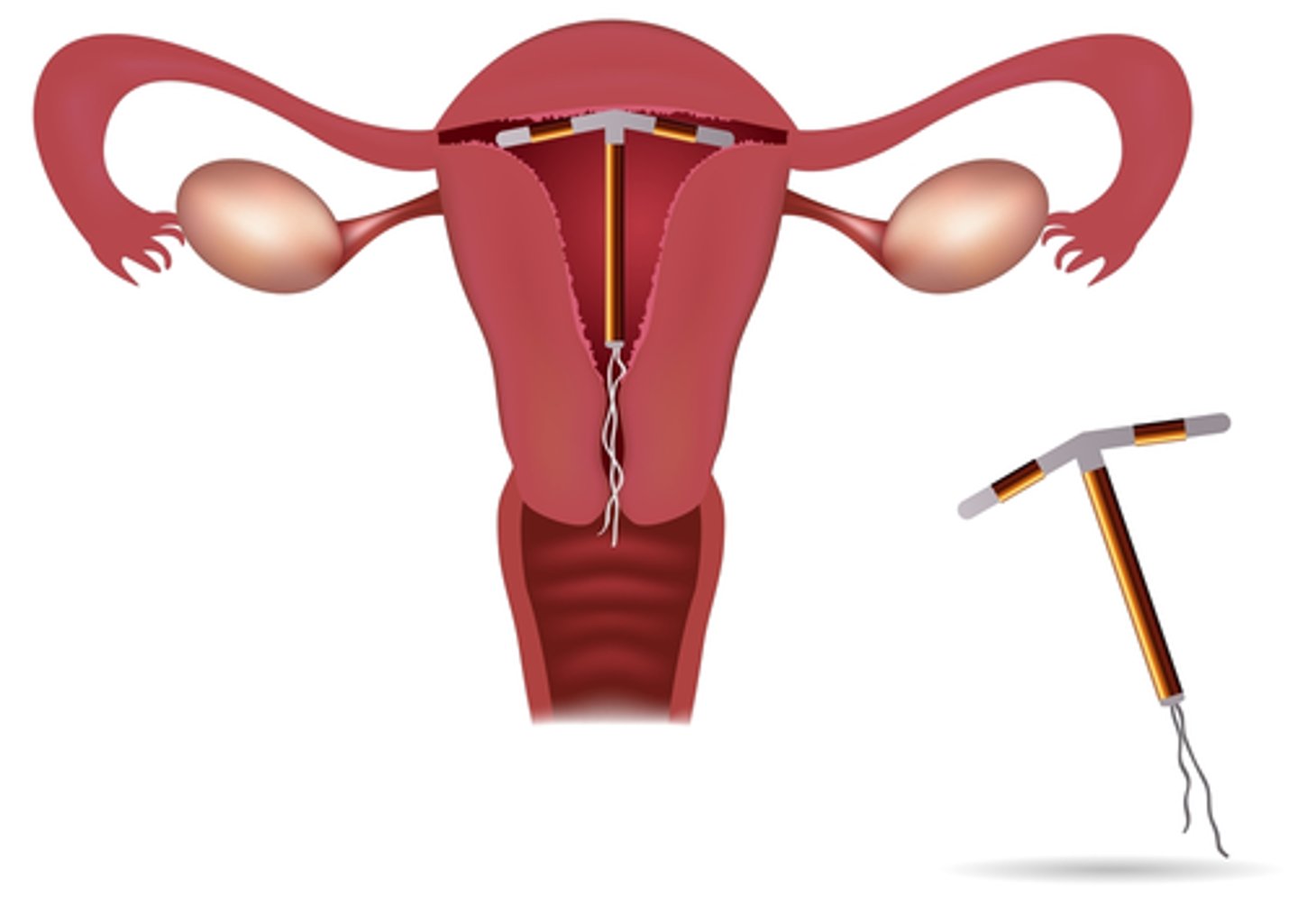
Non-hormonal Intrauterine device (IUD)
Placed in the uterus by a physician prevents egg and sperm from fusing
-Non-hormonal
Spermicide
Condoms and diaphragms are often full with it
-Non-hormonal

oral contraceptives
the "pill"
-Hormonal
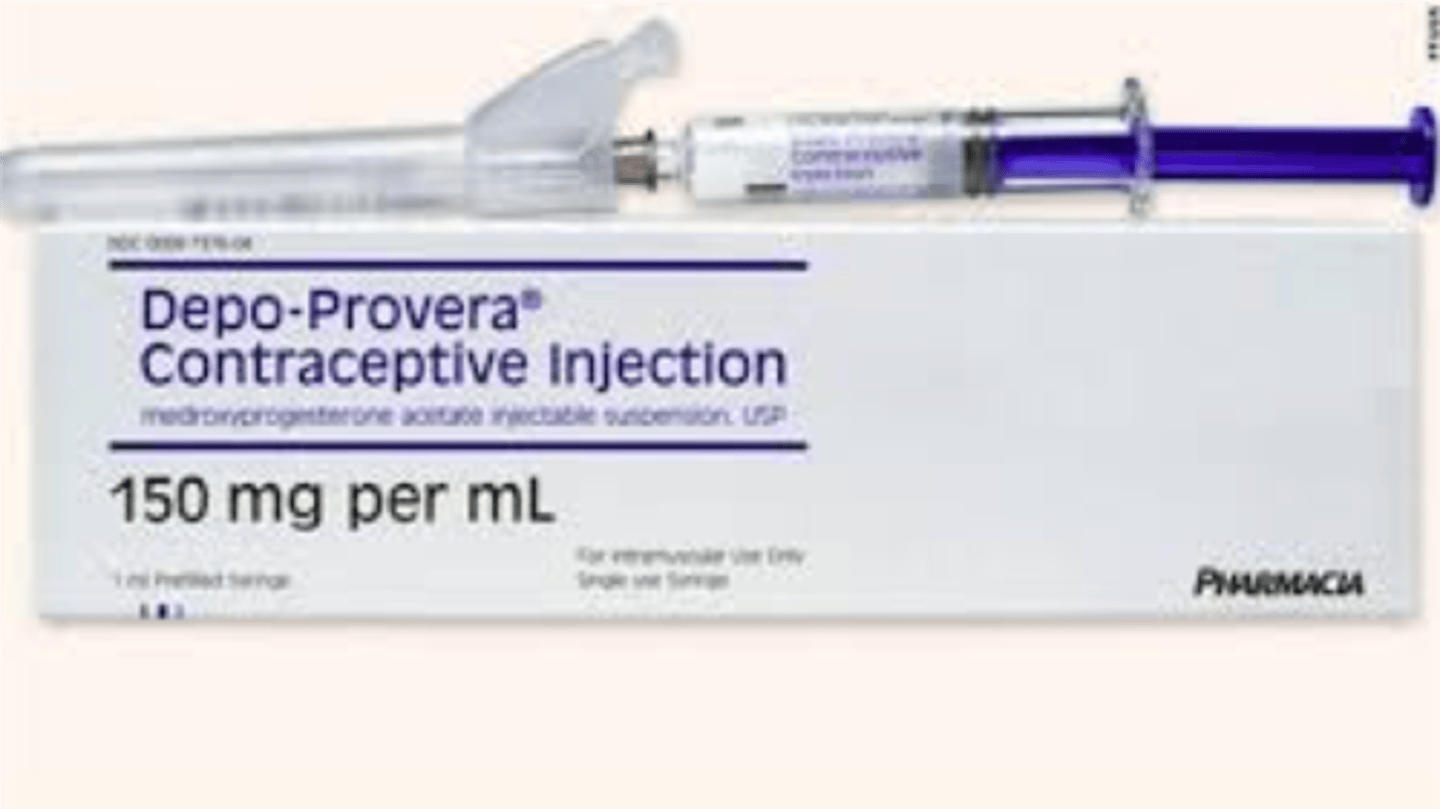
Injection
Depo-pavera
-Hormonal
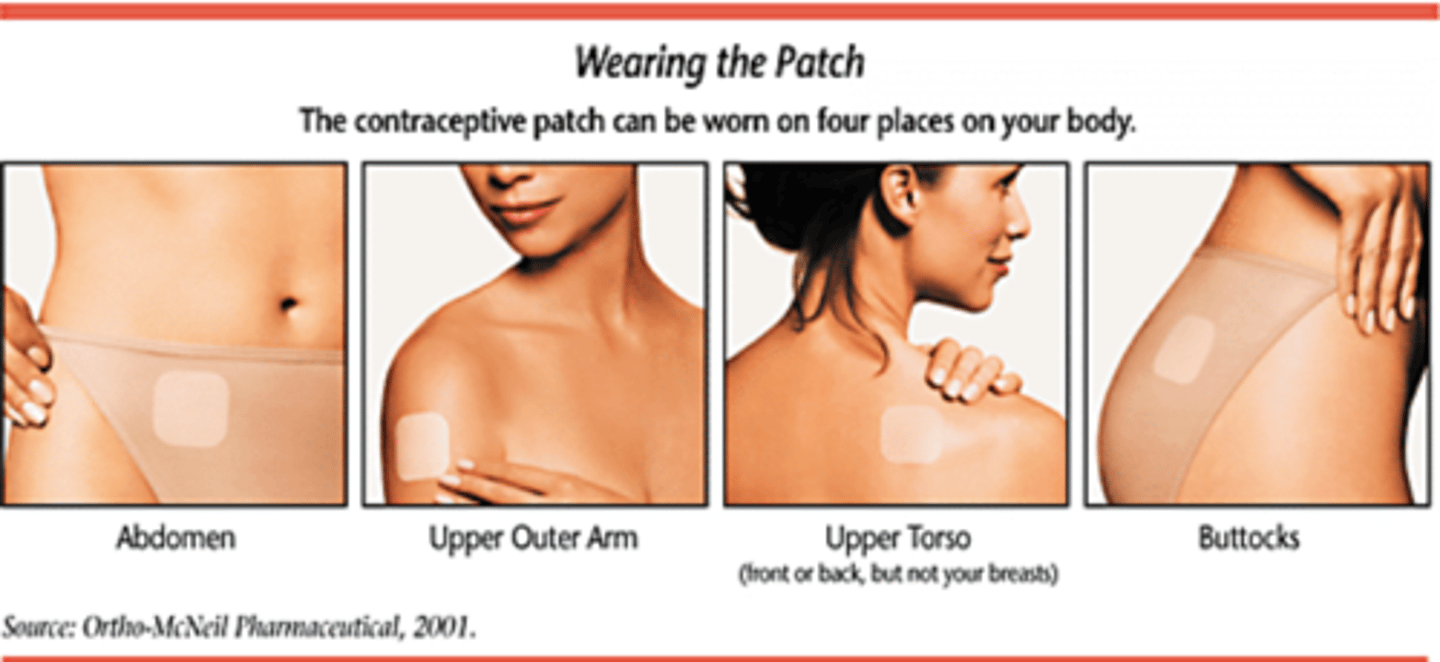
Patch
-Hormonal
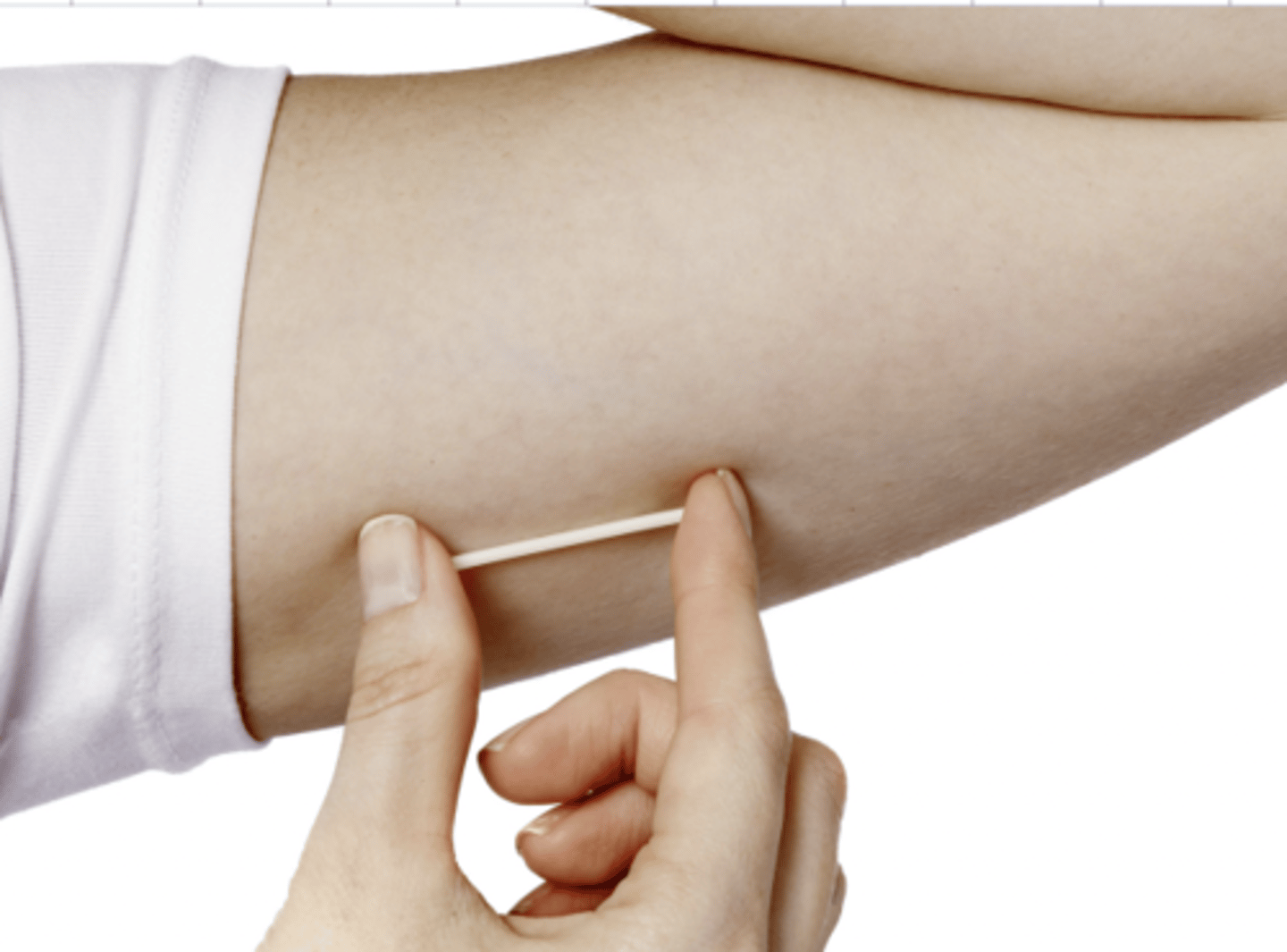
Progestin implant
in the arm
-Hormonal
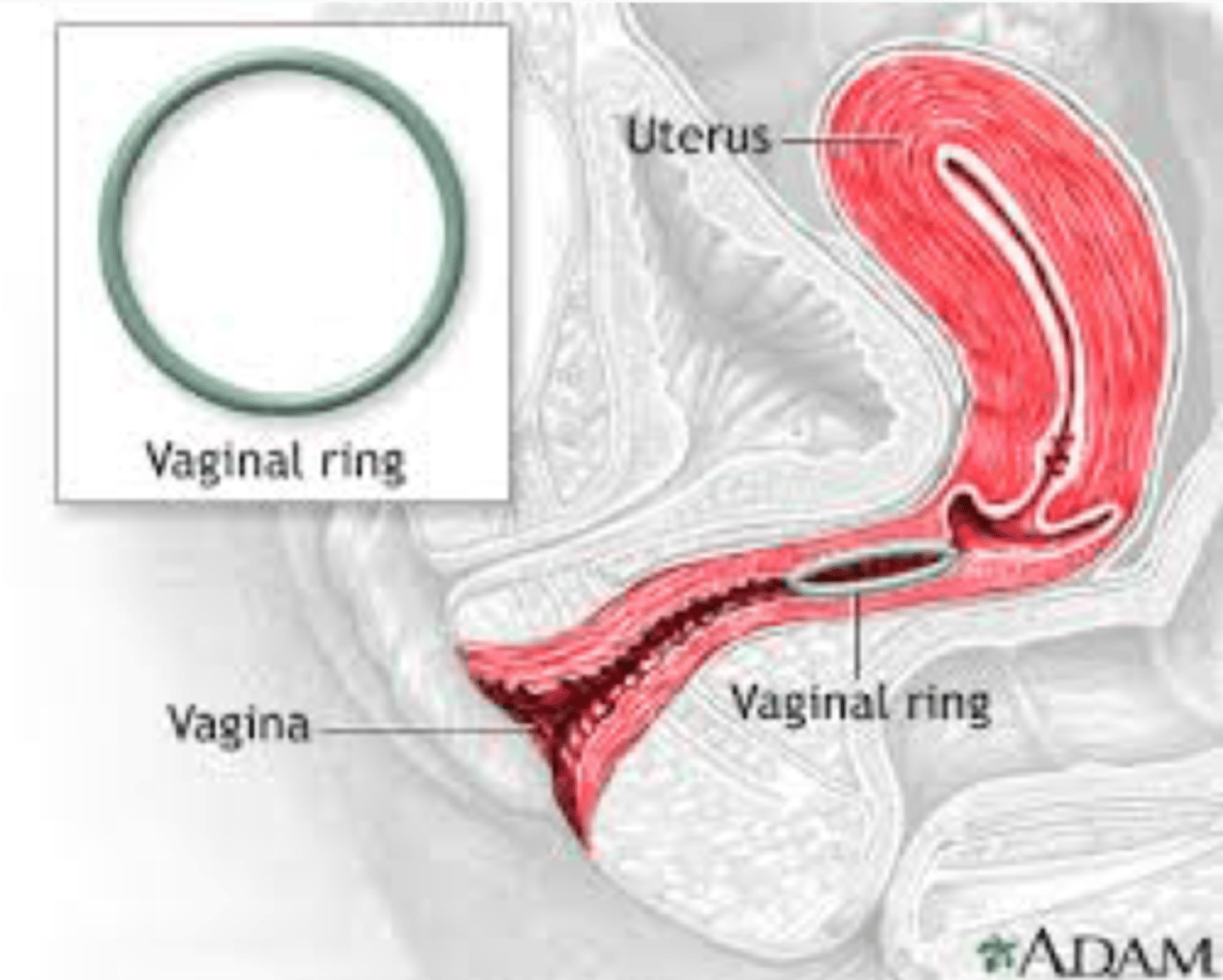
Vaginal ring
ring that releases hormones
-Hormonal
Intrauterine device (hormonal)
IUD that ejects hormones
-Hormonal

Vasectomy
surgical procedure that removes all or part of the deferens deferns that prevents sperm to travel through the urethra
-Permanent method
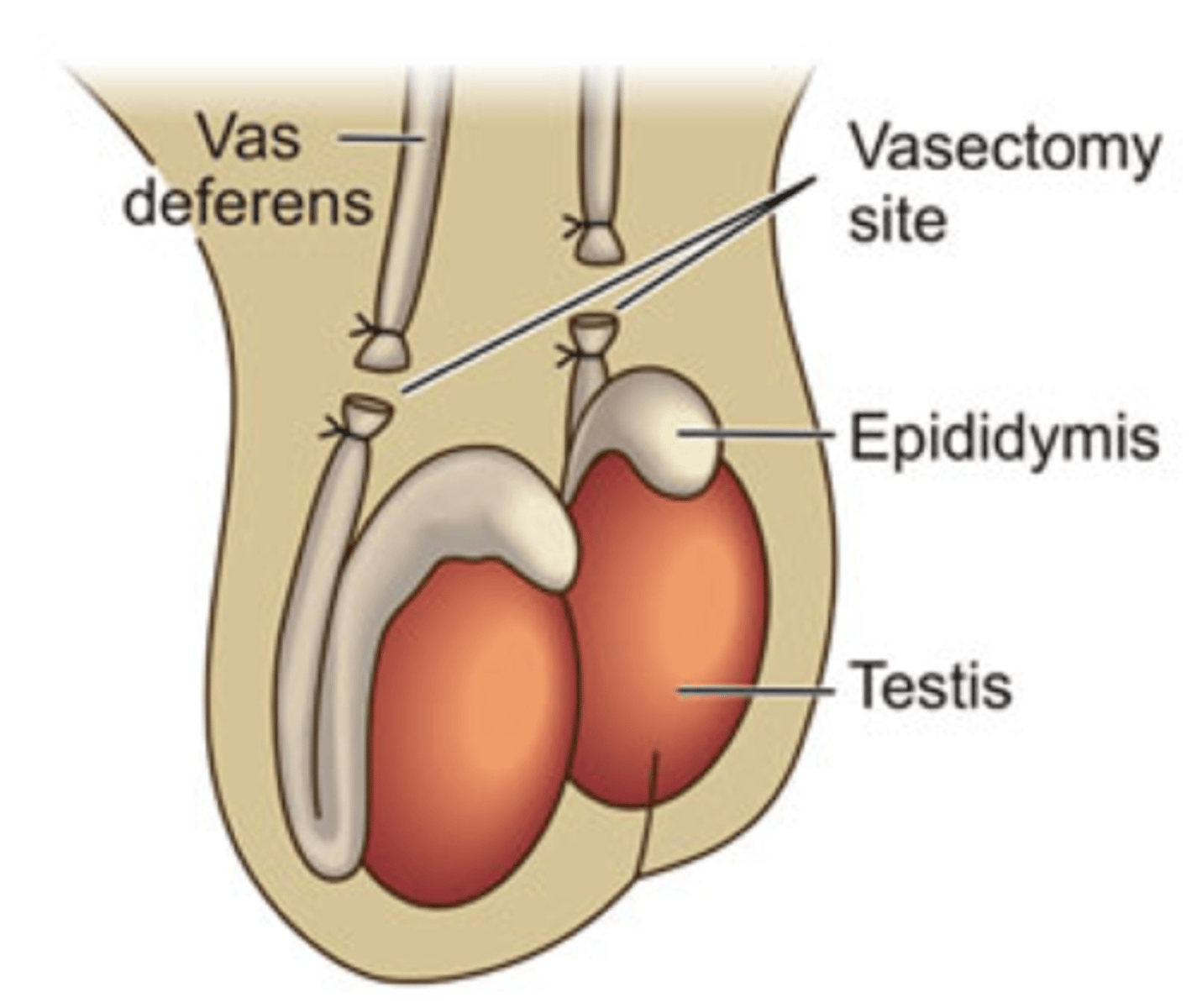
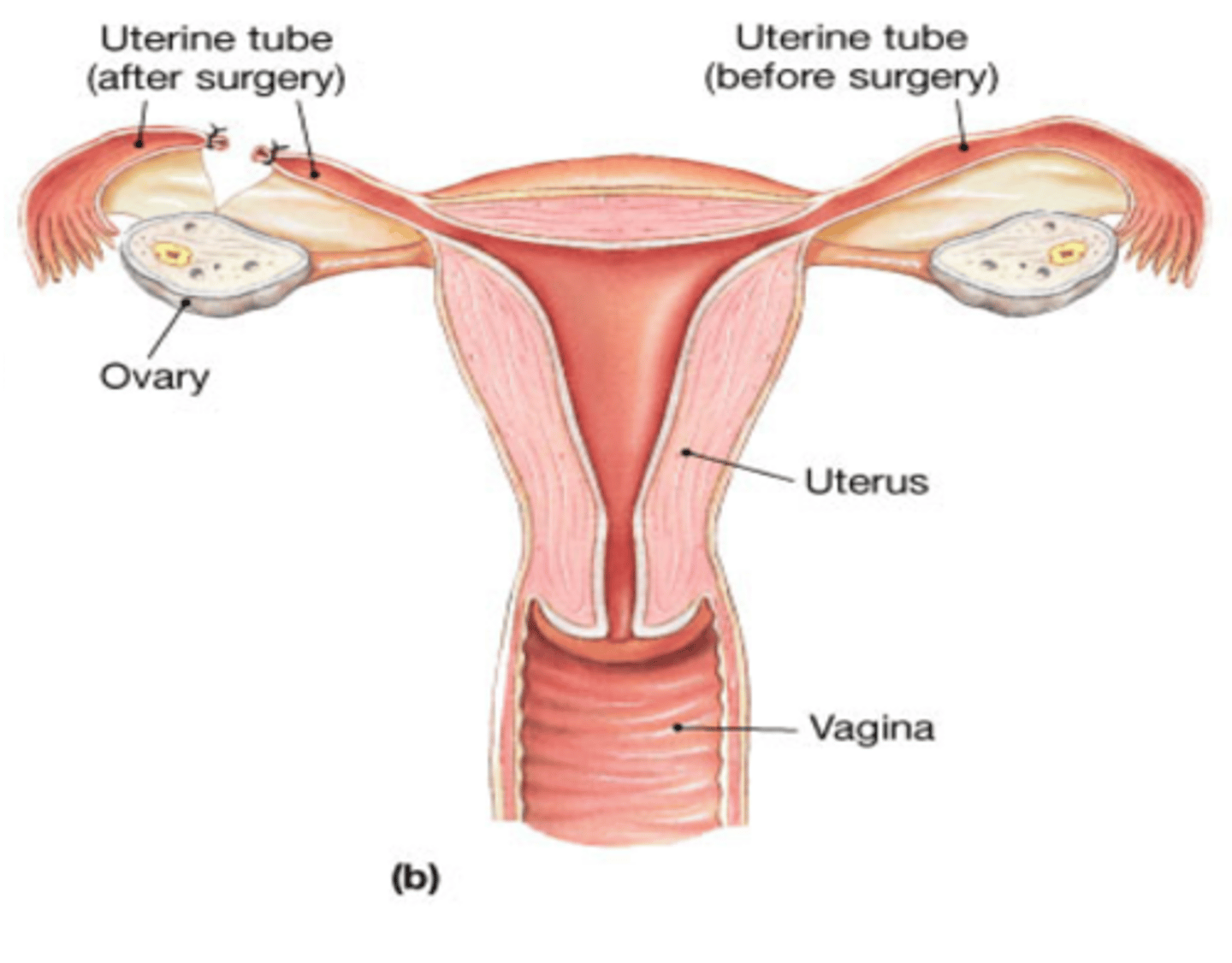
Tubal ligation
blocking or cutting of the fallopian tubes to prevent fertilization from occurring
-Permanent method
intra-uterine tube coil placement
Results in the coil producing scar tissue in the uterine tubes that prevents the release of eggs
-Permanent method