3.20-3.22 Total Internal Reflection
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
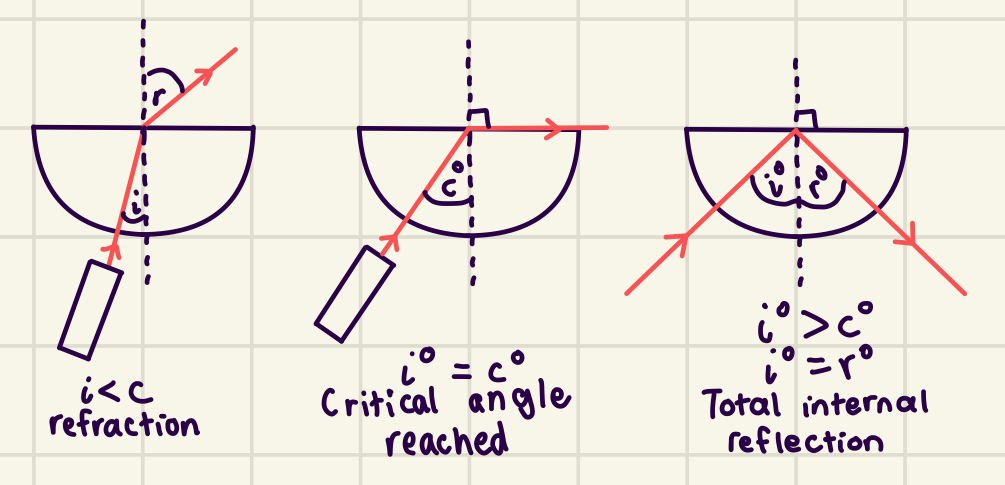
Critical angle
Angle of incidence that leads to the angle of refraction being equal to 90°, i.e. where the light beam is refracted along the boundary between the 2 media.
Total Internal Reflection
Angle of incidence (i°) > critical angle (c°)
Incident material’s density > second material’s density (light ray travels from material with ↑ density + ↑ refractive index to material with ↓ density + ↓ refractive index)
All (total) light reflected into/inside the incident medium instead of refracted outside into the second less dense material once it contacts the boundary between the 2 media
Critical angle equation
sin c = 1 / n
n = 1 / (sin c)
Proof of critical angle equation using Snell’s law
Snell’s law (the equation used when light is traveling from a medium with higher optical density to a medium with lower optical density):
n = (sin r) / (sin i)
critical angle is the angle of incidence where the angle of refraction = 90°
i = c
r = 90°
n = (sin 90) / (sin c)
sin 90 = 1
n = 1 / (sin c)
Larger refractive index’s effect
Larger refractive index → smaller sin c → smaller critical angle → more possible angles that are larger than critical angle → easier for incident angle to > critical angle → more likely for total internal reflection to occur
Smaller refractive index’s effect
Smaller refractive index → larger sin c → larger critical angle → less possible angles that are larger than critical angle → harder for incident angle to > critical angle → less likely for total internal reflection to occur
Optical fibre
Flexible thin glass or plastic fiber (thread/filament) through which light pulses can travel to transmit and carry information
Role of total internal reflection in optical fibres and their application
Each time light hits the optical fiber’s edge/boundary, it is totally internally reflected, which allows all light to stay inside the fiber as it travels downwards. Optical fibers can be used to transmit information for communications (i.e. telephone, internet, cable TV signals), endoscopes, lighting, and decorative lamps.
Endoscope
Medical instruments are composed of dense bundles of optical fibers. Endoscopes are inserted into the body to examine hollow organs (e.g. stomach). Total internal reflection within the endoscope’s optical fibers allows light from hollow organs to reach the doctor’s eyepiece so they can examine patients.
Prisms
Glass or transparent 3D object (usually triangularly shaped) that separates white light into its constituent colors by refraction. Used in optical equipment such as periscopes, binoculars, telescopes, cameras, safety reflectors for bicycles/cars, as well as posts marking the side or edge of roads.
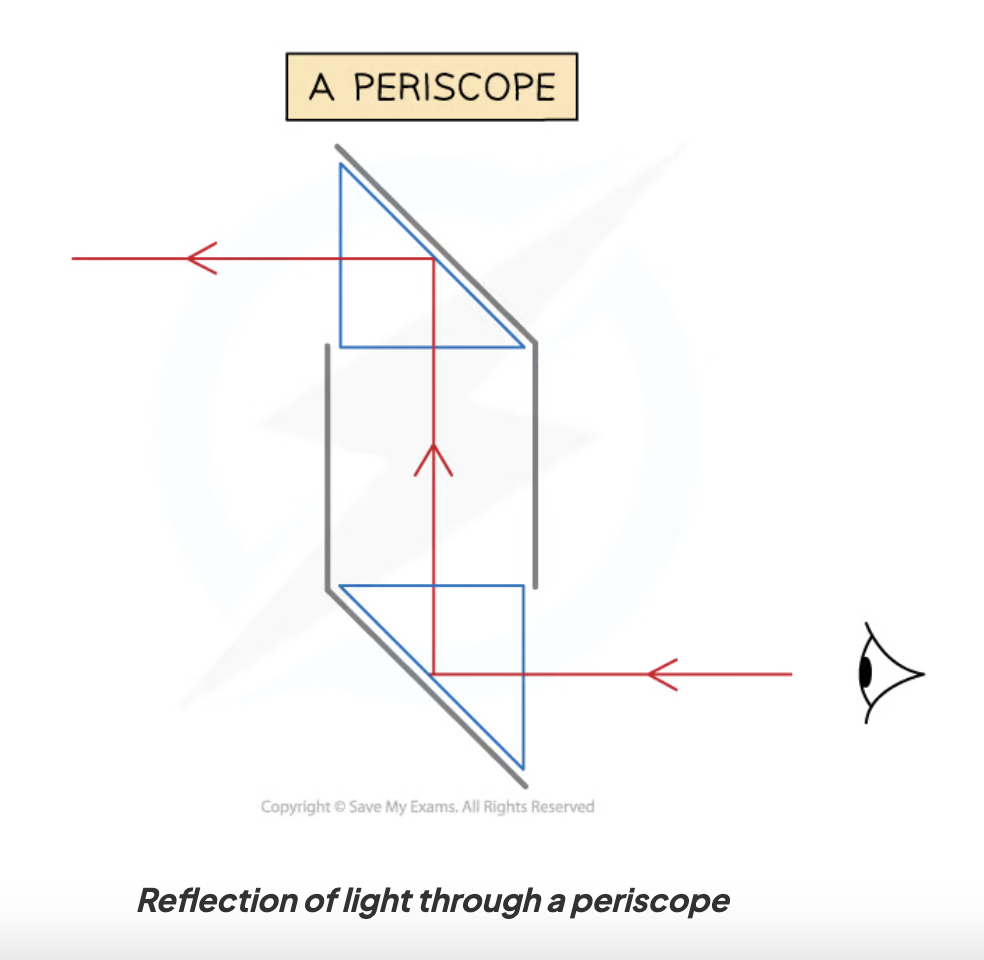
Periscope
Optical device that consists of 2 right-angled triangle prisms and can be used to see over tall objects
Single reflection occurs twice in periscopes to allow viewers to see the objects situated at higher altitudes
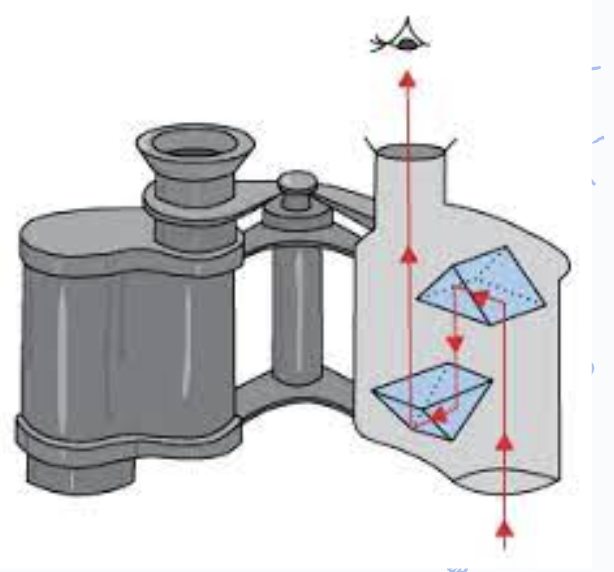
Binocular
Optical device that consists of 2 right-angled triangle prisms and can be used to see far away objects
Double reflection occurs twice in binoculars to allow viewers to see the objects at distant proximity
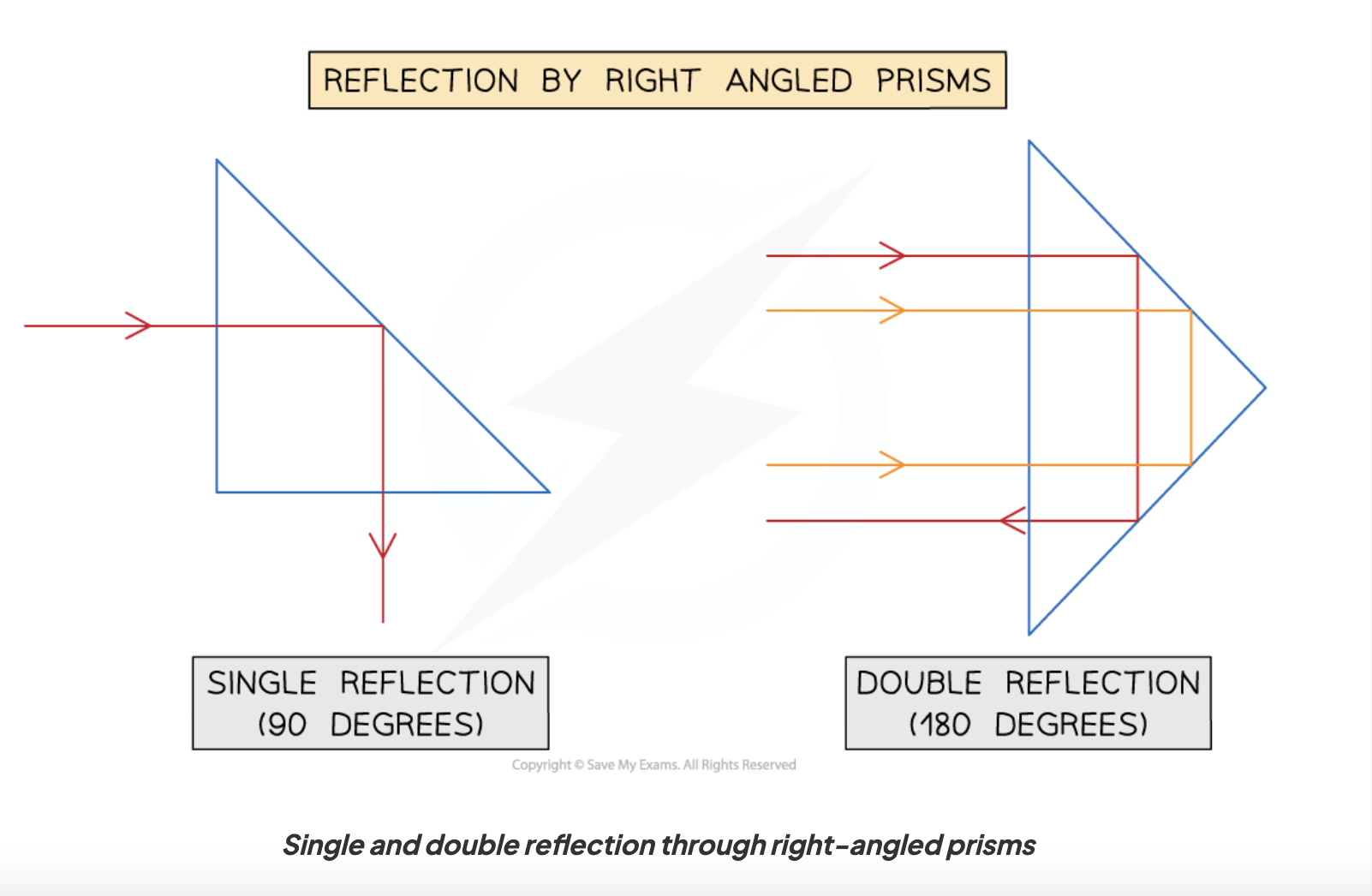
Reflection in right-angled prisms
Single reflection: reflection by 90 degrees
Double reflection: reflection by 90 degrees at 1 surface, then 90 degrees once more after contacting another surface → reflection by 180 degrees (90 + 90 = 180)
How to answer questions that ask for examples of how total internal reflection can be used:
State device that causes total internal reflection: right-angled prism or optical fibre?
Name device in which total internal reflection is used: periscope, binoculars, telescopes, cameras, communications, endoscopy, decorative lamps, and/or lighting