Lab 9: Neurology - Histologyn Brain Anatomy, and Radiology
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Cerebellum, and Brain Stem
What are the four parts of the brain?
cerebrum
largest region of the brain
longitudinal fissure
divides the cerebrum into left and right hemispheres
lateralization
specialization of function in one hemisphere of the cerebrum
gyrus
fold in the cerebral cortex
sulcus
shallow groove in the cerebral cortex
corpus callosum
white matter that connects the two cerebral hemispheres
gray matter
forms the outer convoluted surface of the cerebral hemispheres and the foliated surface of the cerebellum
white matter
lies deep in to the cerebral and cerebellar cortices
cortical gray matter
made of multipolar neuron cell bodies and attendant dendrites
pyrimidal cells
Located in the cerebral cortex; pyramid-shaped cells that conduct impulses down the brainstem into the spinal cord
1. molecular layer
2. outer granular layer
3. outer pyrimidal cell layer
4. inner granular layer
5. inner pyramindal and polymorphic layer
five basic layers of the cerebral cortex
1. molecular layer of cerebral cortex
contains mainly dendrites synapsing withcorical neuron axons.
2. outer granular layer
mostly made up of stellate eclls, axons, and dendrites.
3. outer pyramidial cell layer
mostly made up of pyramidal cells that increase in size as you move deeper into the layer.
4. inner granular layer
mostly made of densely packed stellate cells
5. inner pyramidal and polymorphic layer
mostly composed of large pyramidal cells in the more superficial portion of the layer and a wide variety of cell morphologies in the deepest parts of the layers.
thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus
three parts of the diencephalon
thalamus
relay station for incoming information, such as sensory information or integration inforation.
hypothalamus
autonomic control center, center for emotional response, body temperature regulation, regulation of food intake, regulation of water balance and thirst, regulation of sleep wake cycles, and control of the endocrine system functioning.
infundibulum
stalk of hypothalamic tissue that connects to the pituitary gland
epithalamus
where the pineal gland is located
melatonin
pineal gland secretes what?
suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
________________ of the hypothalamus controls the pineal gland
cerebellum
located dorsal to the pons and medulla oblongota
cerebellum
part of the brain that functions in coordination of complex movements.
1. molecular layer
2. purkinje layer
3. granular layer
layers of the cerebellum going from superficial to deep
basket cells and stellate cells
moleuclar layer of cerebellum is made up of
medulla oblongota, pons, and brain stem
three main parts of the brain stem
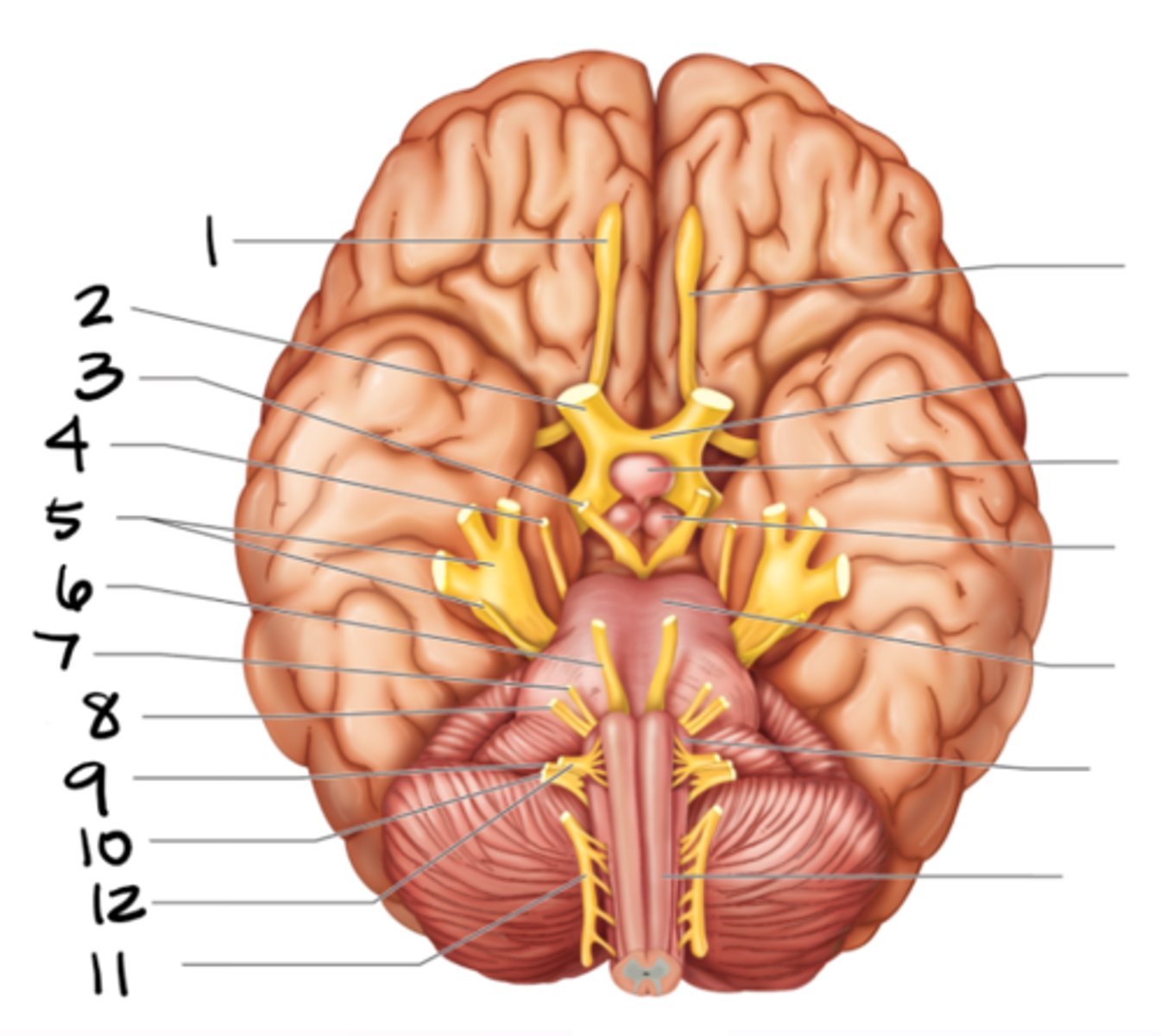
I. olfactory nerve
II. optic nerve
VIII. vestibulocochelar nerve
name the cranial nerves that are sensory only
III. oculomotor nerve
IV. trochlear nerve
VI. abducens nerve
XI. spinal accessory nerve
XII. hypoglossal nerve
name the cranial nerves that are motor only
V. trigeminal nerve
VII. facial nerve
IX. glossopharyngeal nerve
X. vagus nerve
name the cranial nerves that are both motor and sensory
I. olfactory nerve
II. optic nerve
III. oculomotor nerve
IV. trochlear nerve
V. trigeminal nerve
VI. abducens nerve
VII. facial nerve
VIII. vestibulocochlear nerve
IX. glossopharyngeal nerve
X. vagus nerve
XI. spinal accessory nerve
XII. hypoglossal nerve
all cranial nerves in order
Olfactory Nerve (I)
sensory, smell
Optic Nerve (II)
sensory, vision
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
motor, eye movement. four of six extrinsic muscles
Trochlear Nerve (IV)
motor, eye movement. one extrinsic muscle
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
both, largest of the cranial nerves. supplies sensory fibers ot the face and chewing muscles
Abducens Nerve (VI)
motor, lateral eye movement
Facial Nerve (VII)
both, facial expression and anterior 2/3 tongue
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII)
sensory, hearing and balance
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX)
both, taste and swallowing
Vagus Nerve (X)
both, only cranial nerve to extend beyond the head and neck
Spinal Accessory Nerve (XI)
motor, sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscle movement
Hypoglossal Nerve (XII)
motor, tongue movement
olfactory
#1
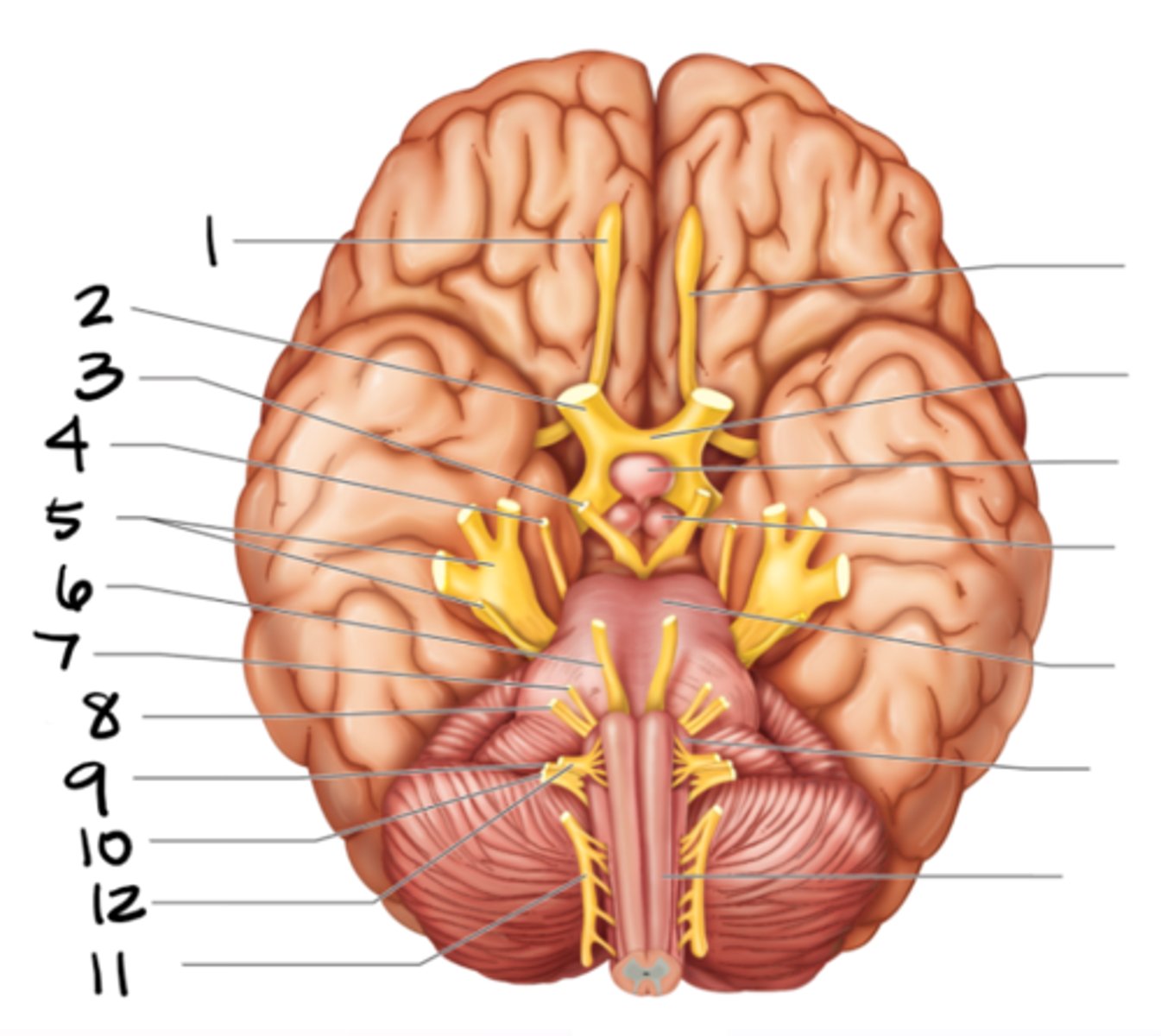
optic
#2
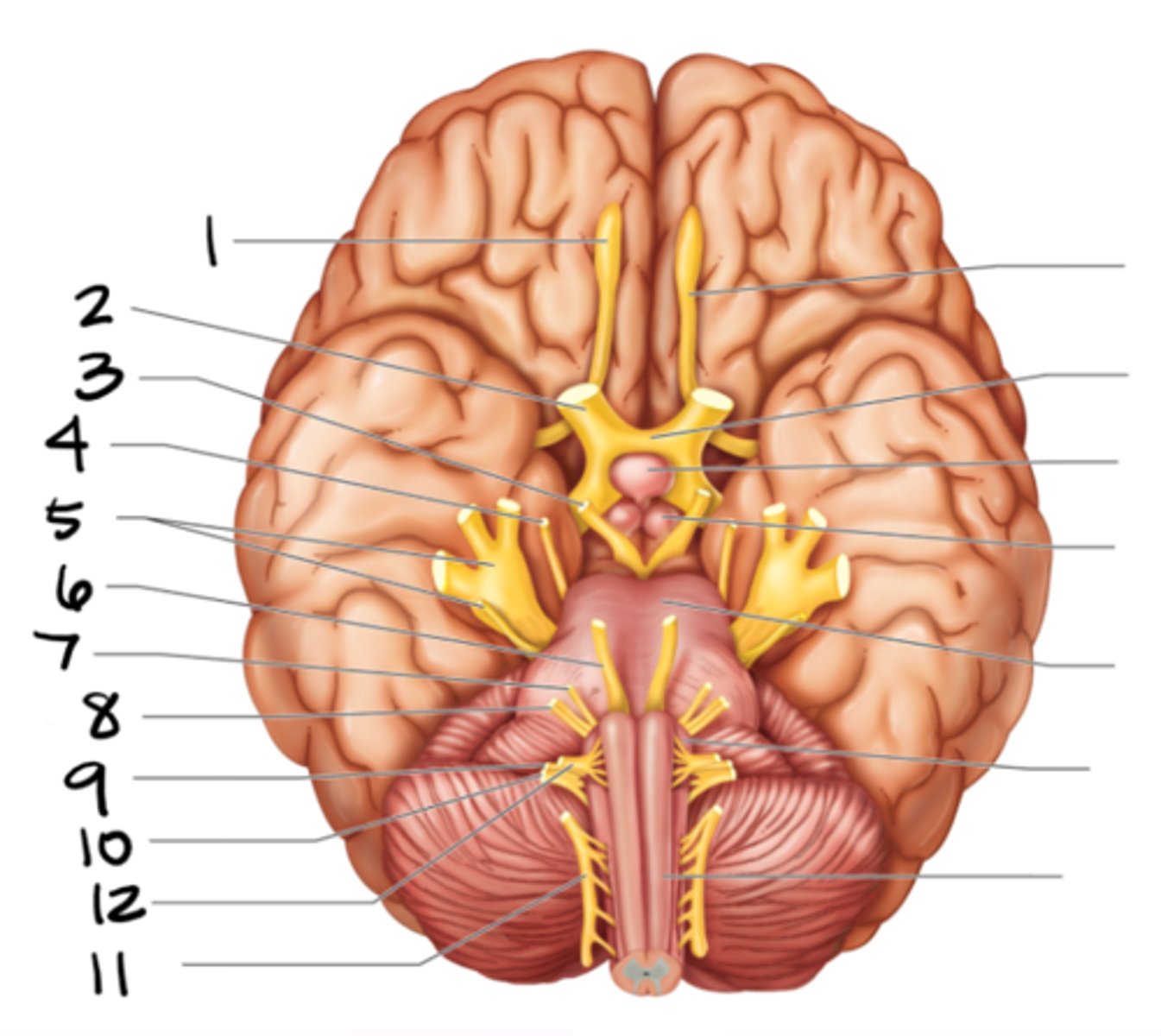
oculomotor
#3
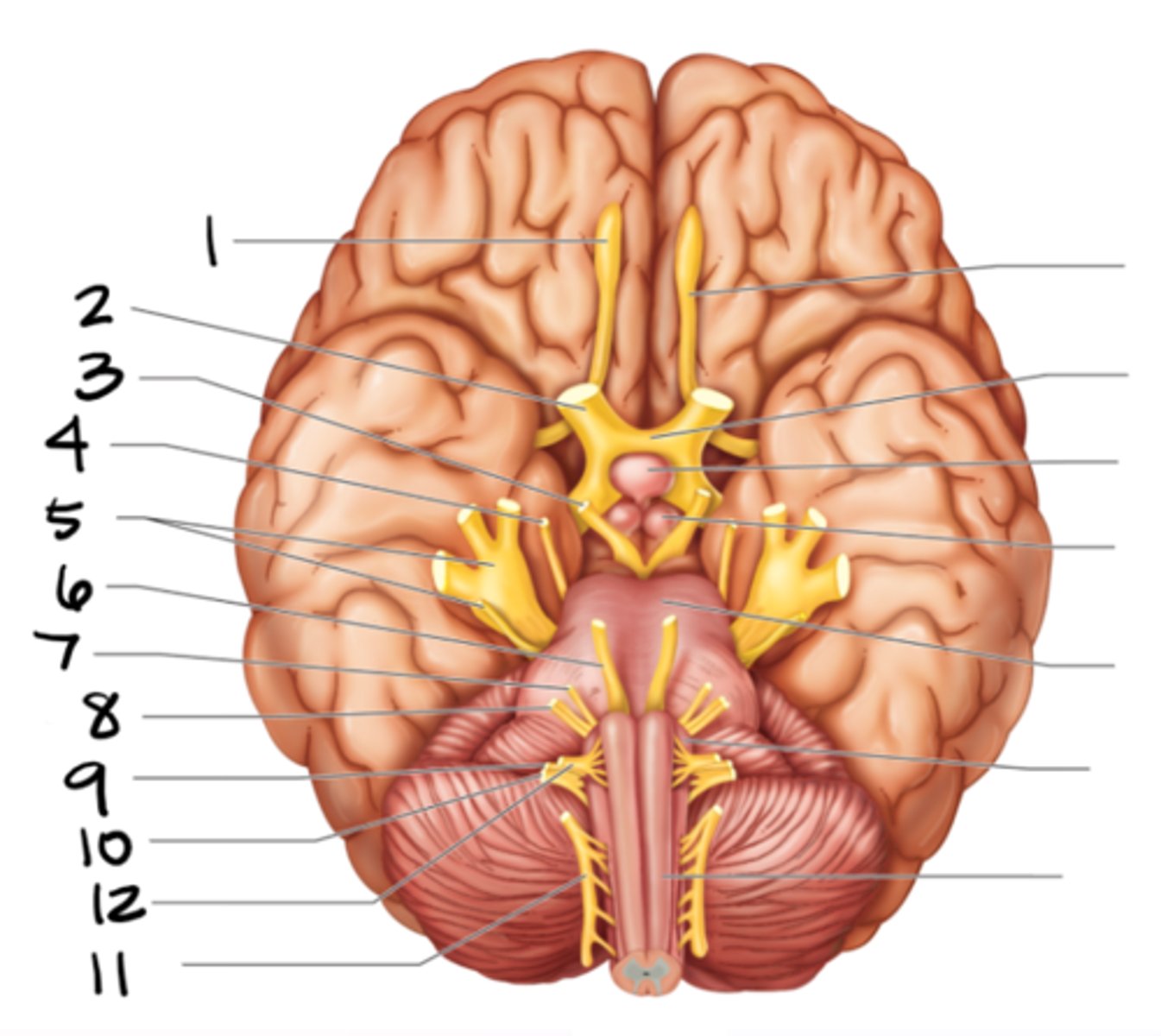
trochlear
#4
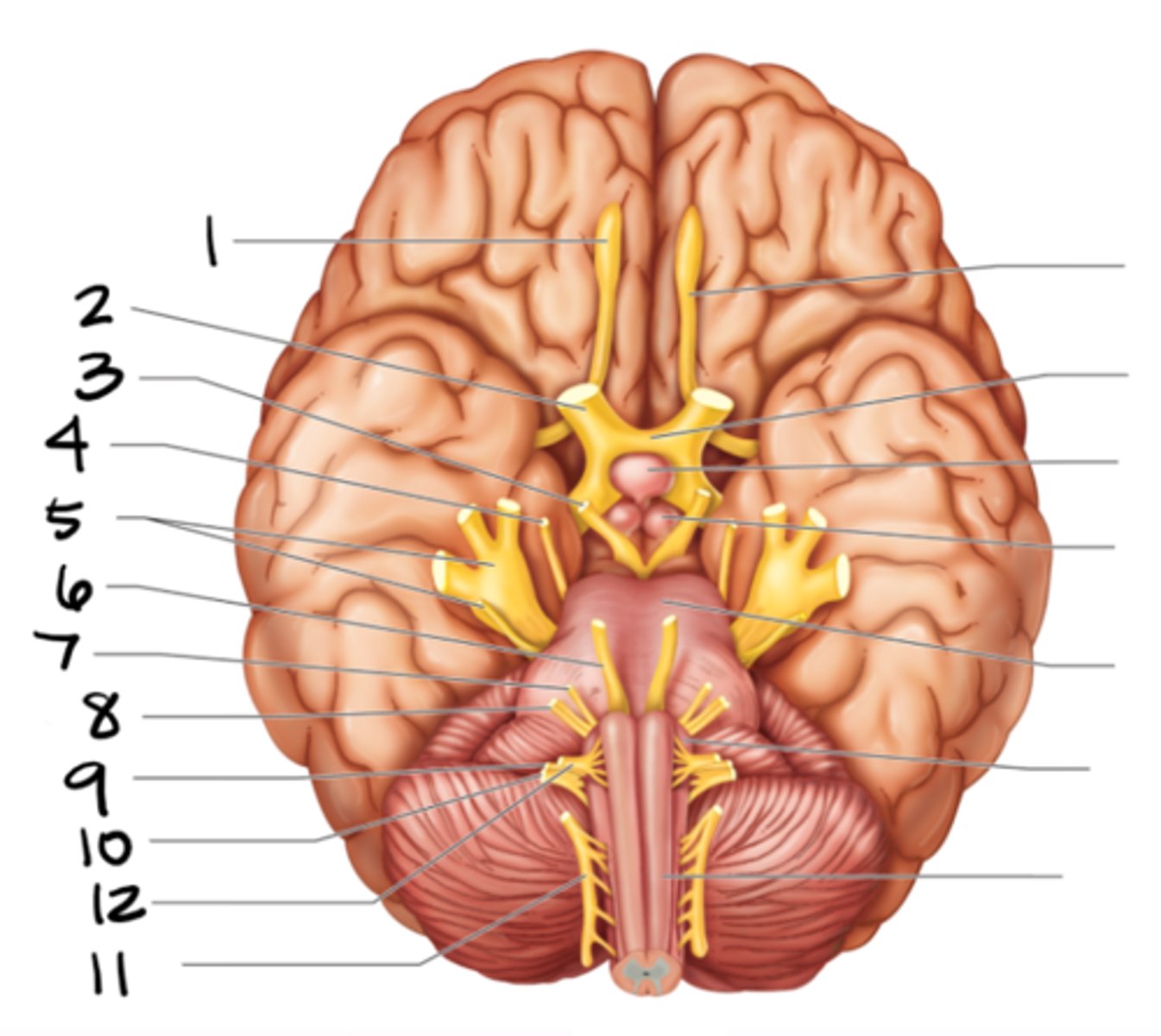
trigeminal
#5
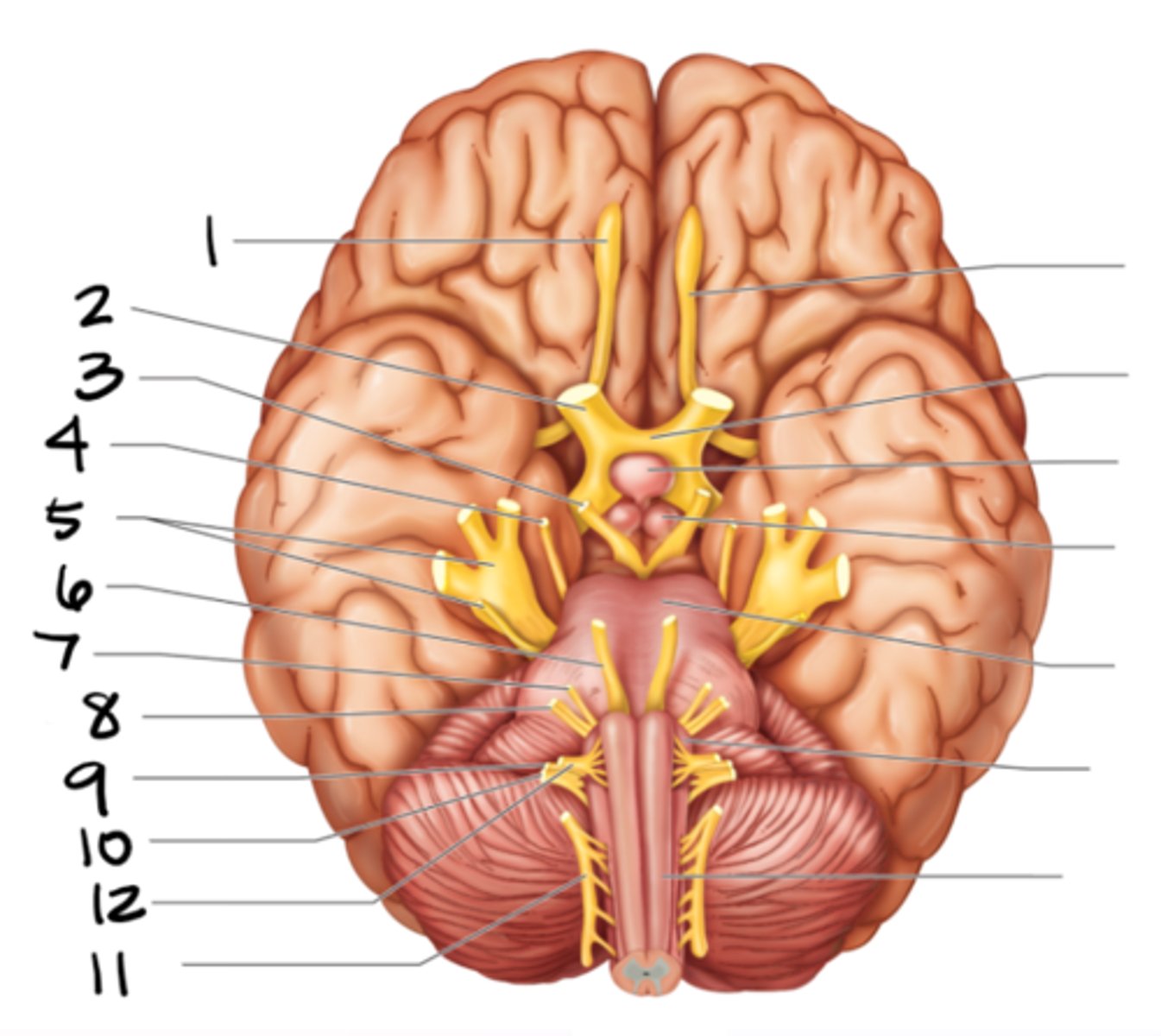
abducens
#6
facial
#7
vestibulocochlear
#8
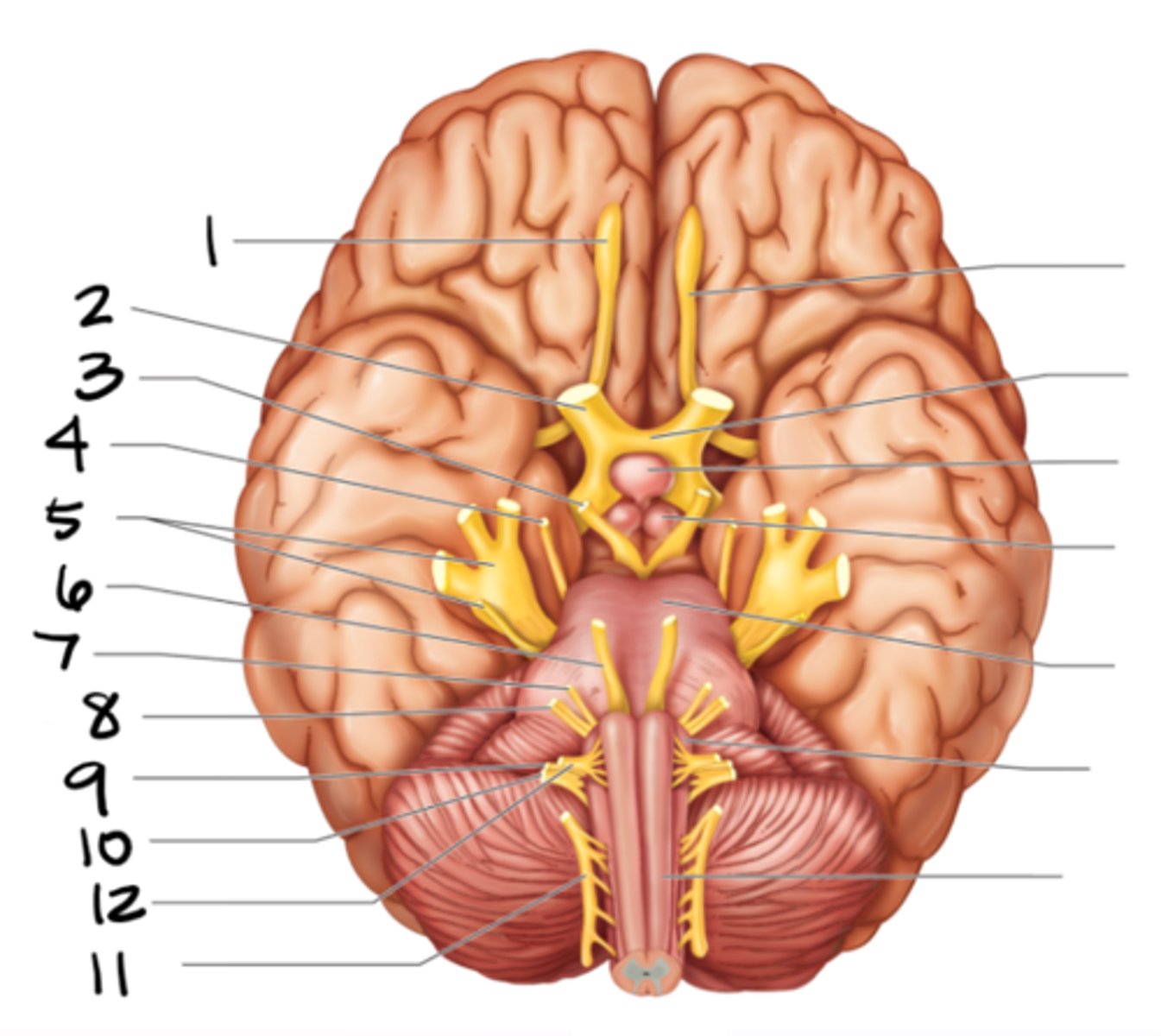
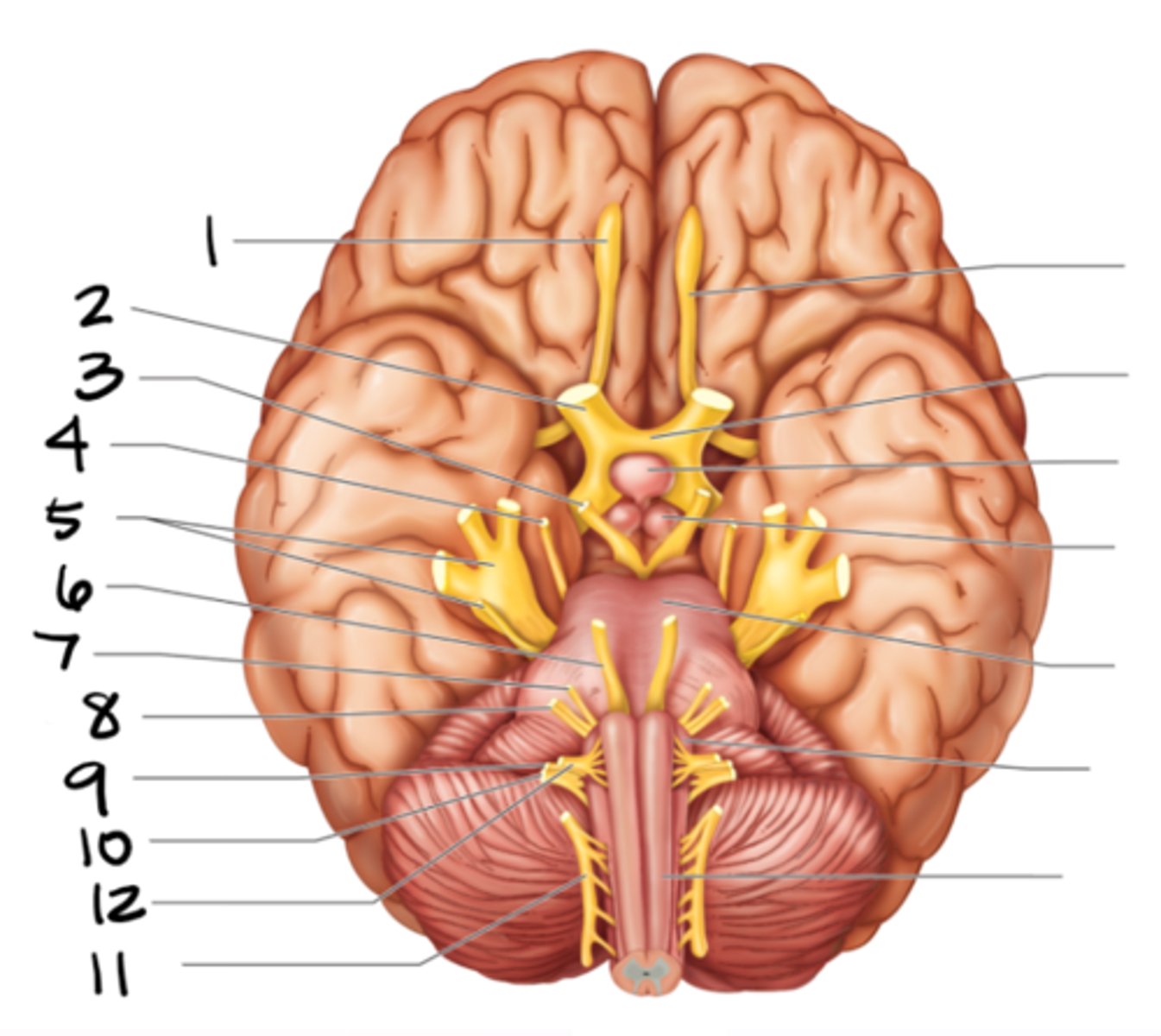
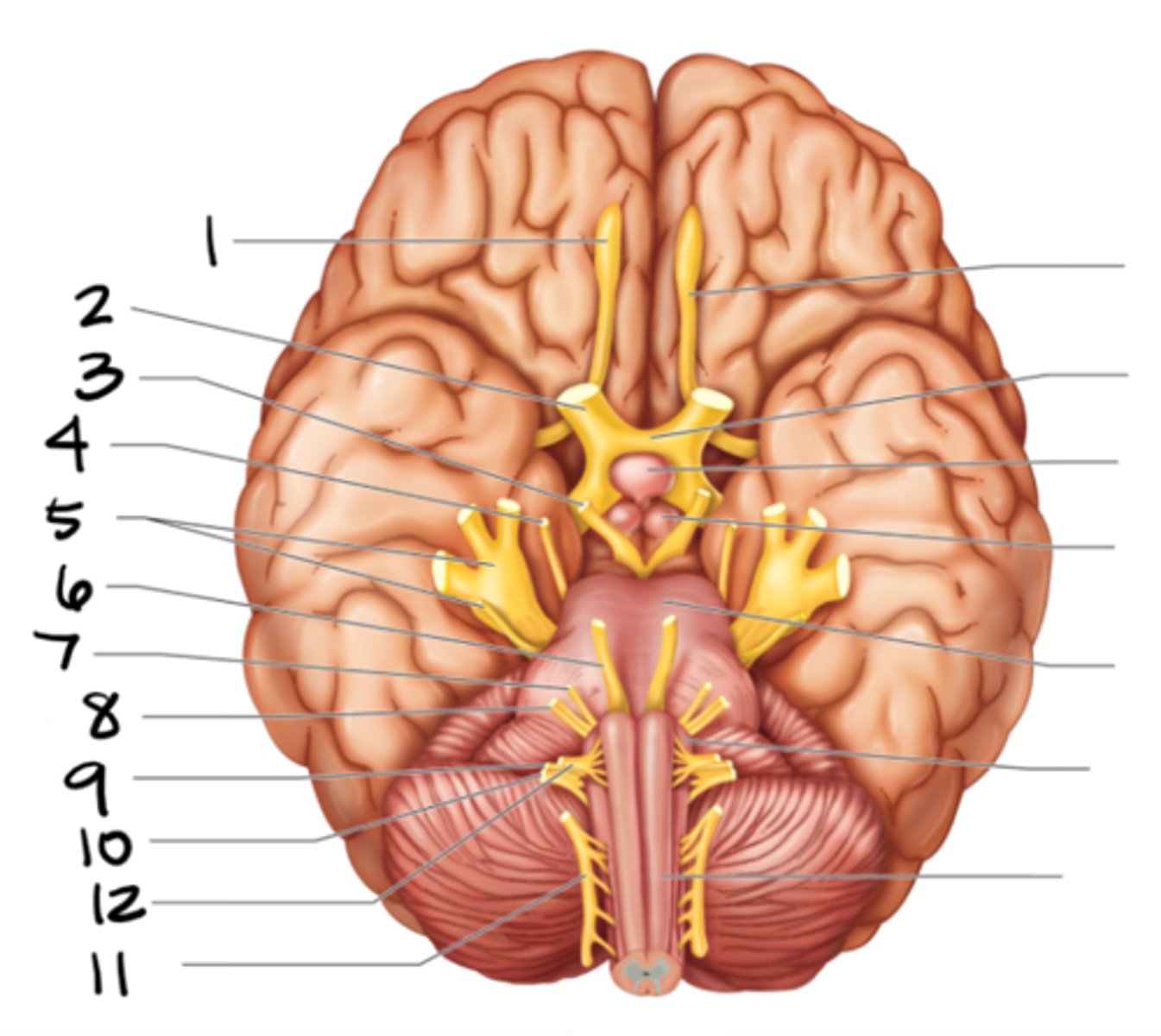
glossopharyngeal
#9
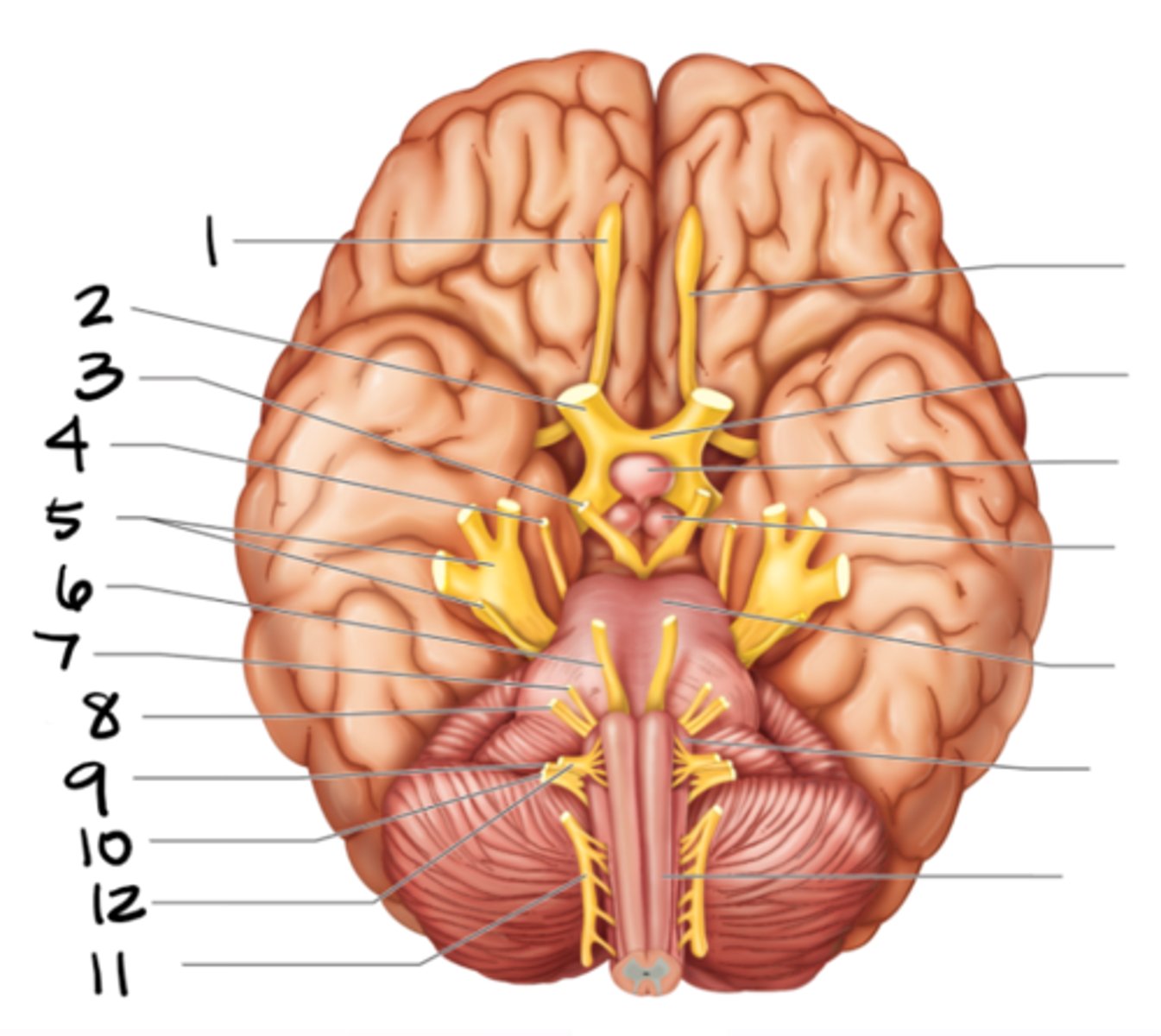
vagus
#10
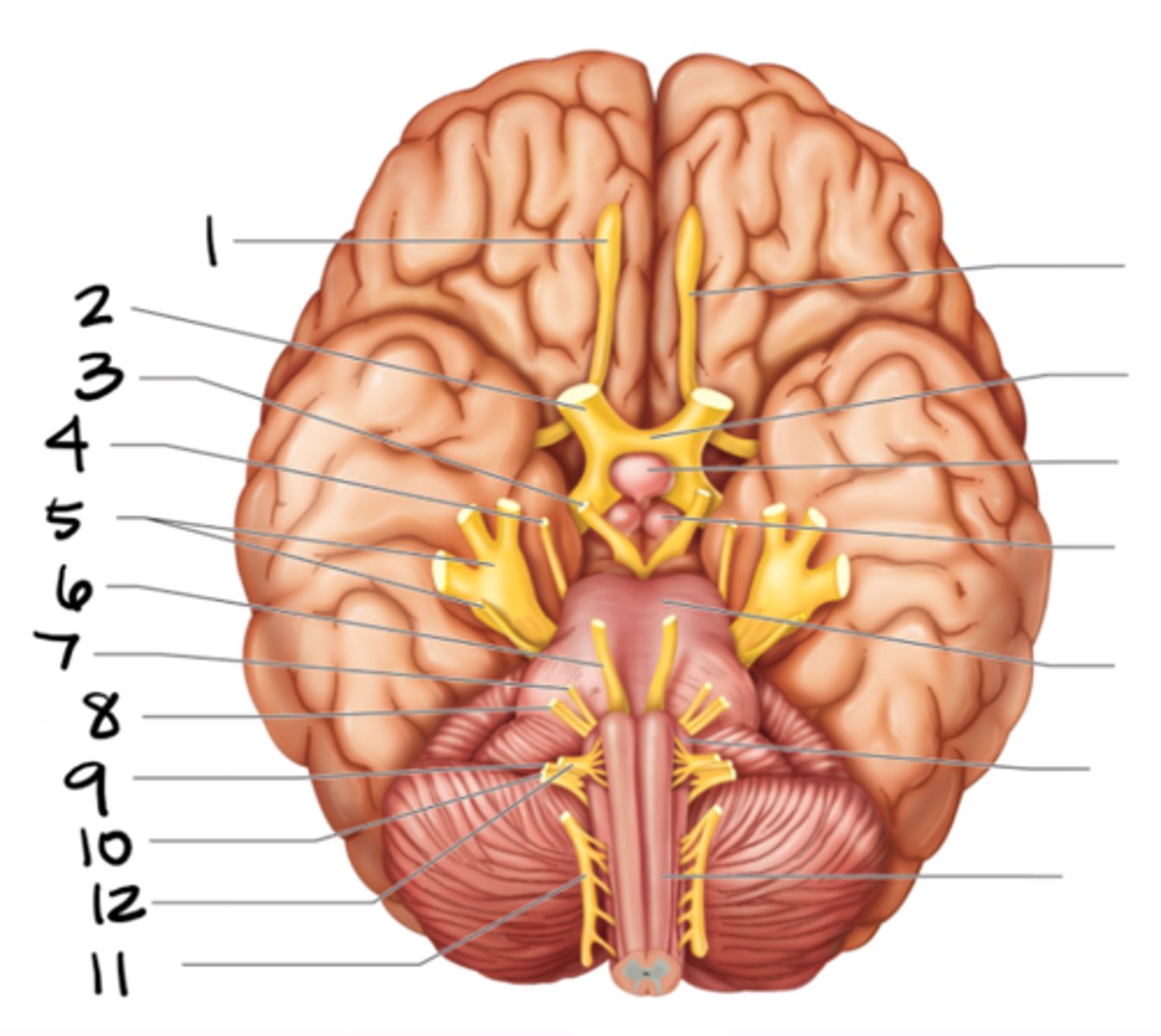
spinal accessory
#11
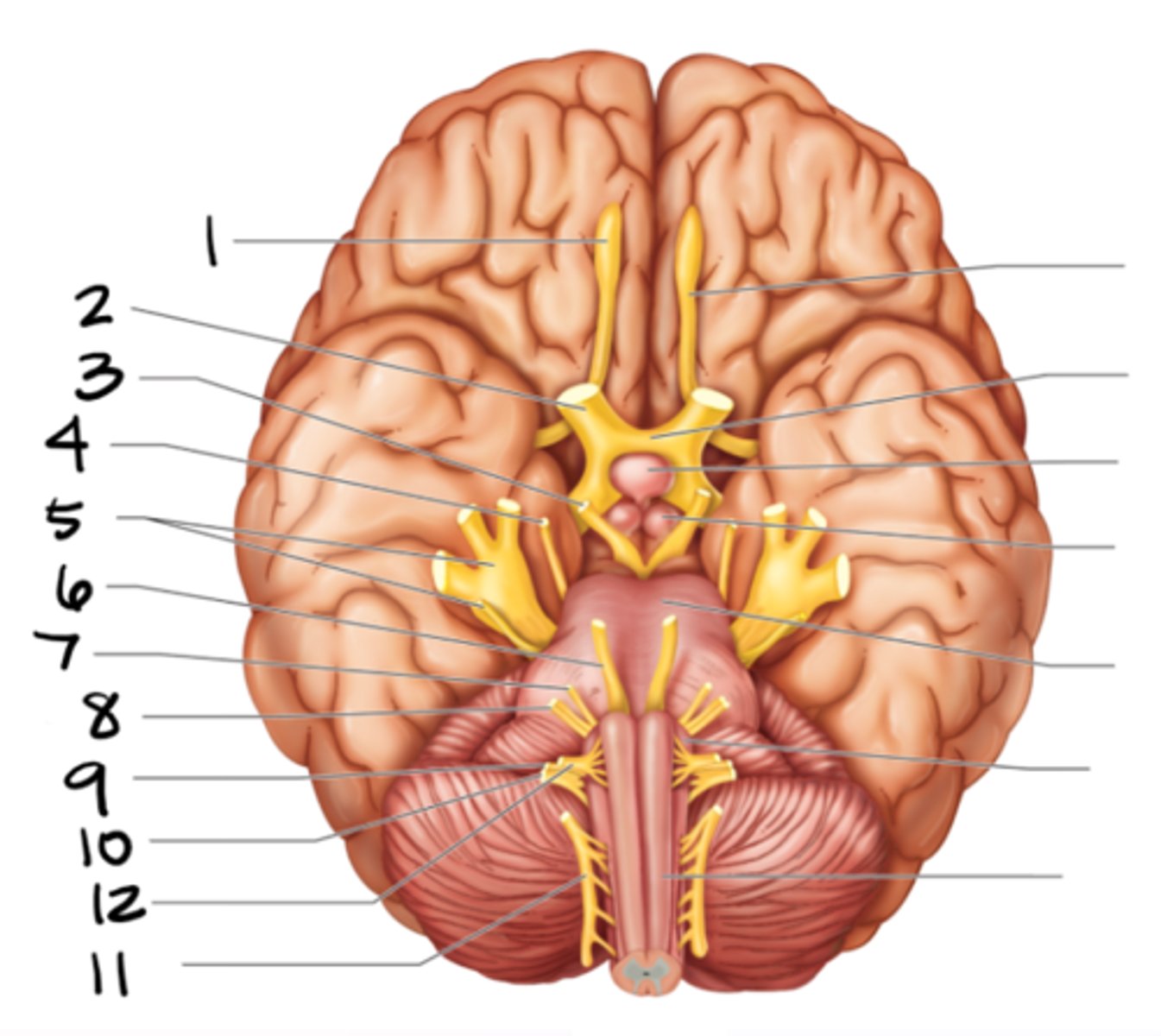
hypoglossal
#12
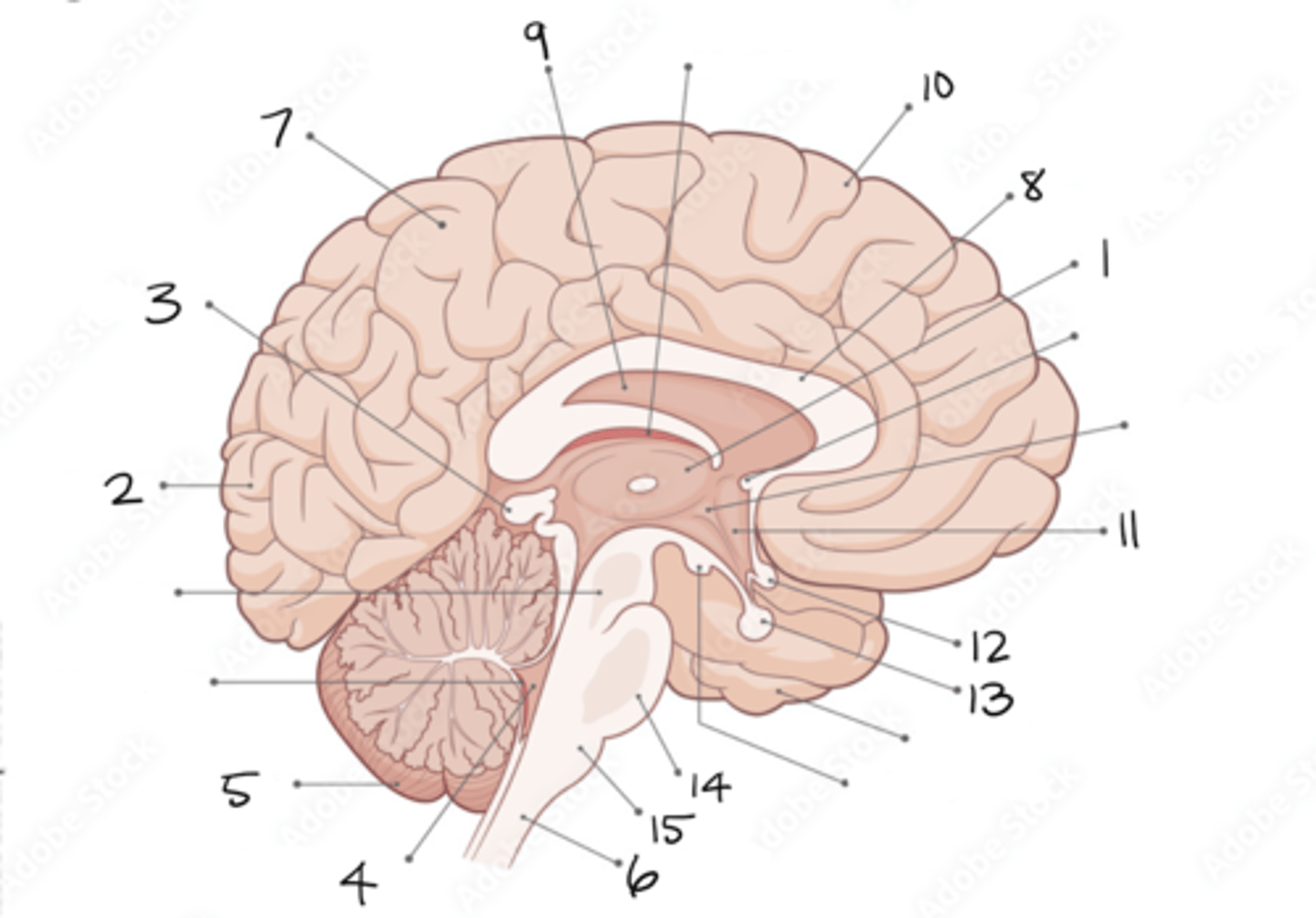
thalamus
1
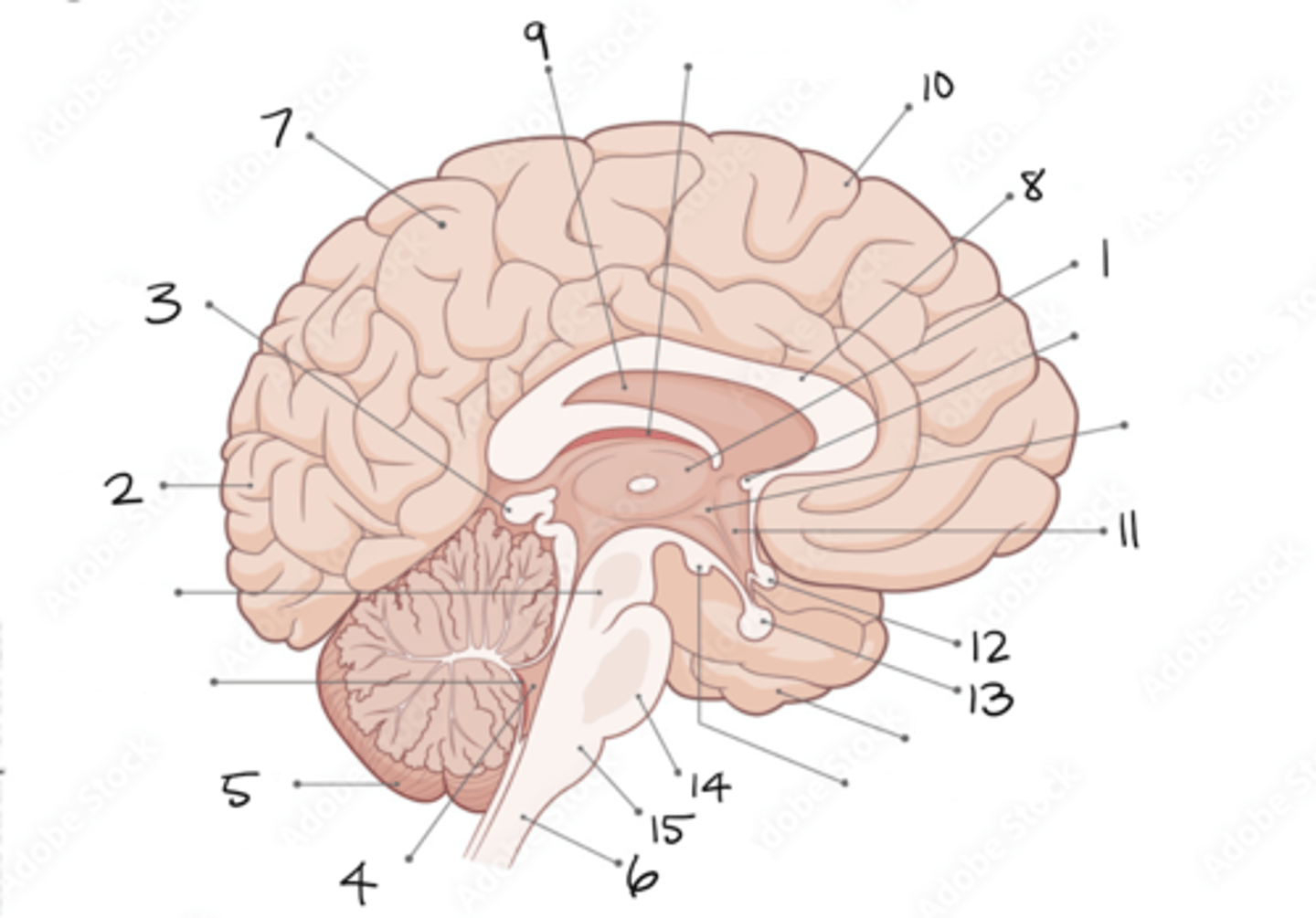
occipital lobe
2
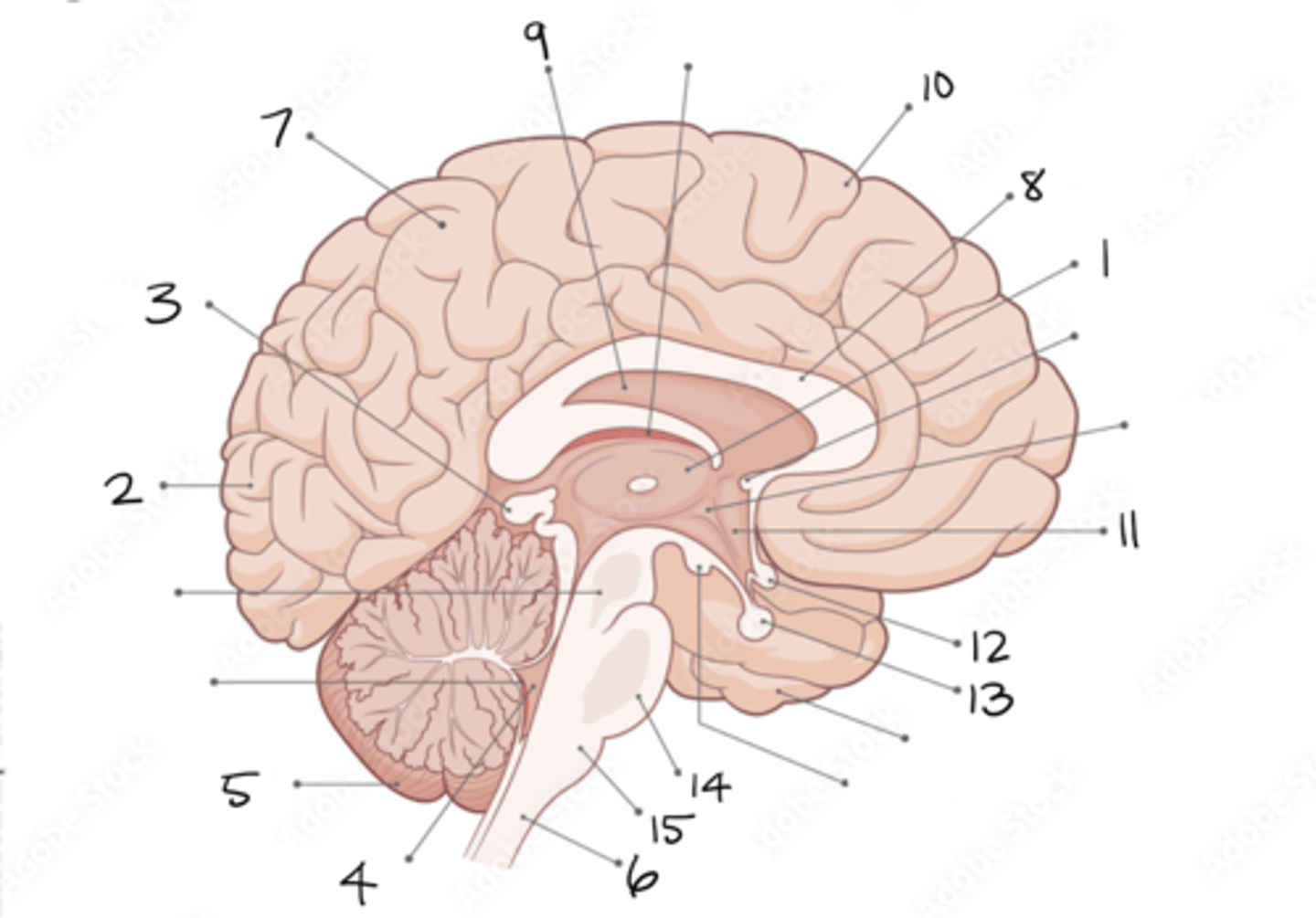
pineal gland
3
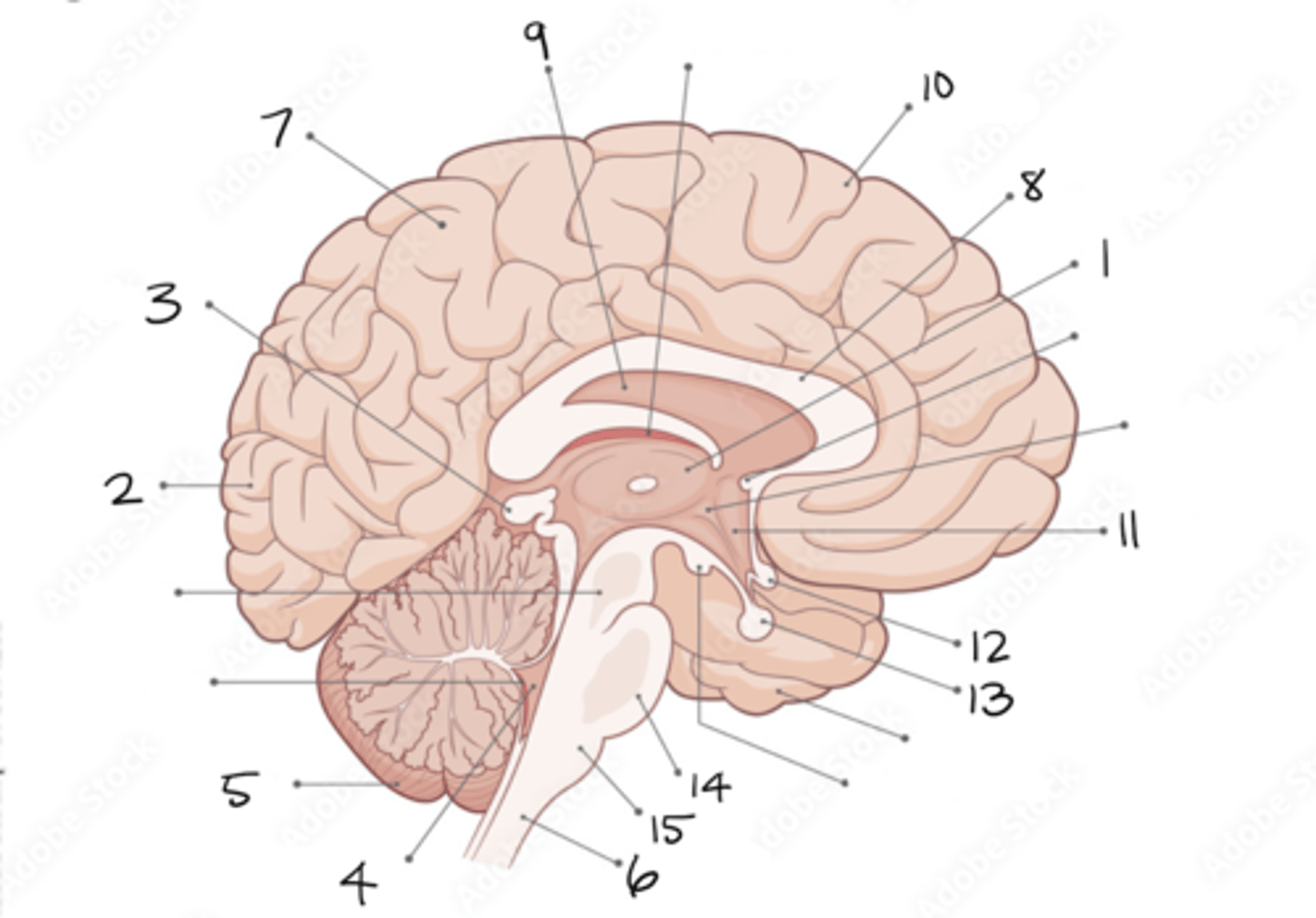
fourth ventricle
4
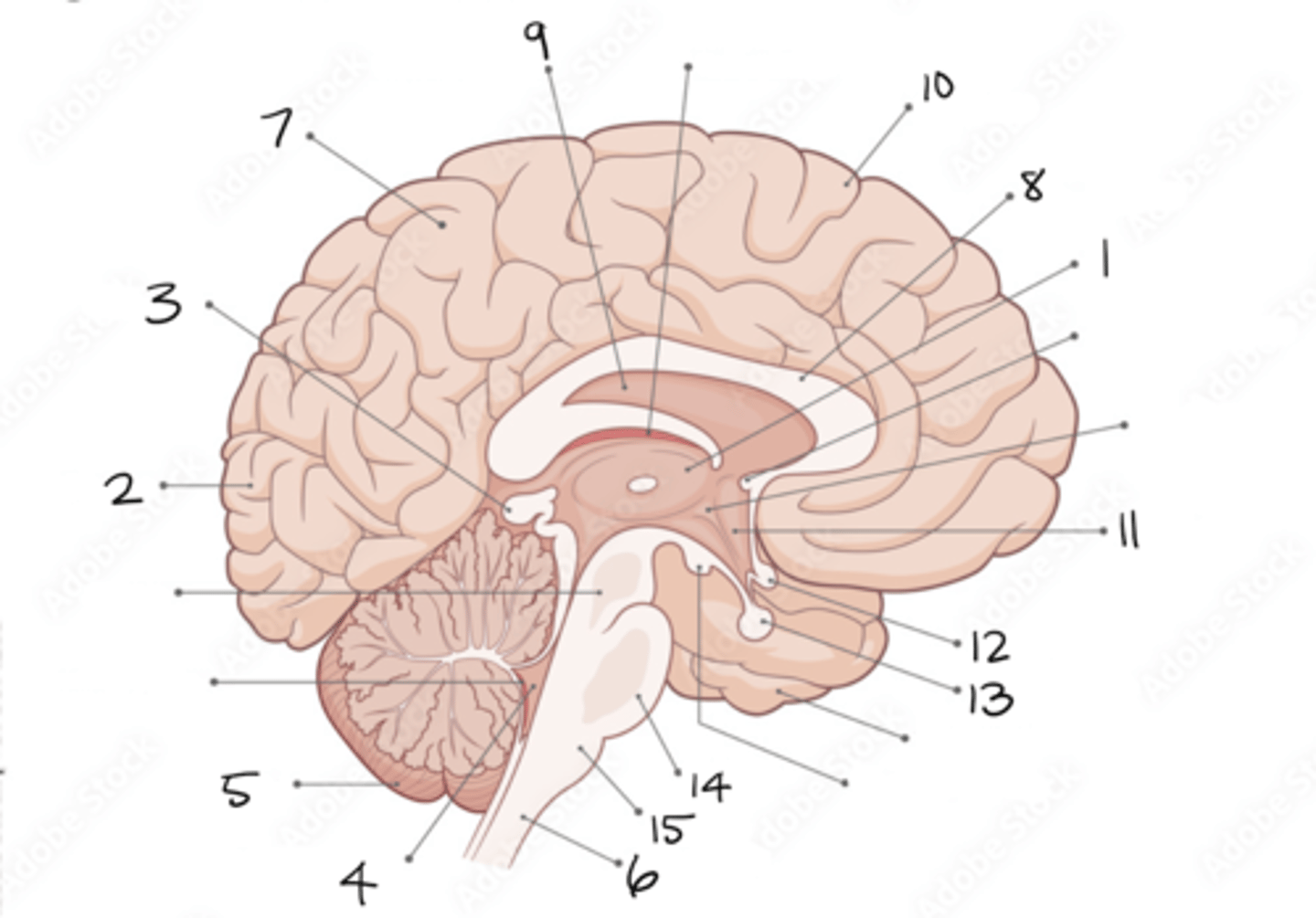
cerebellum
5
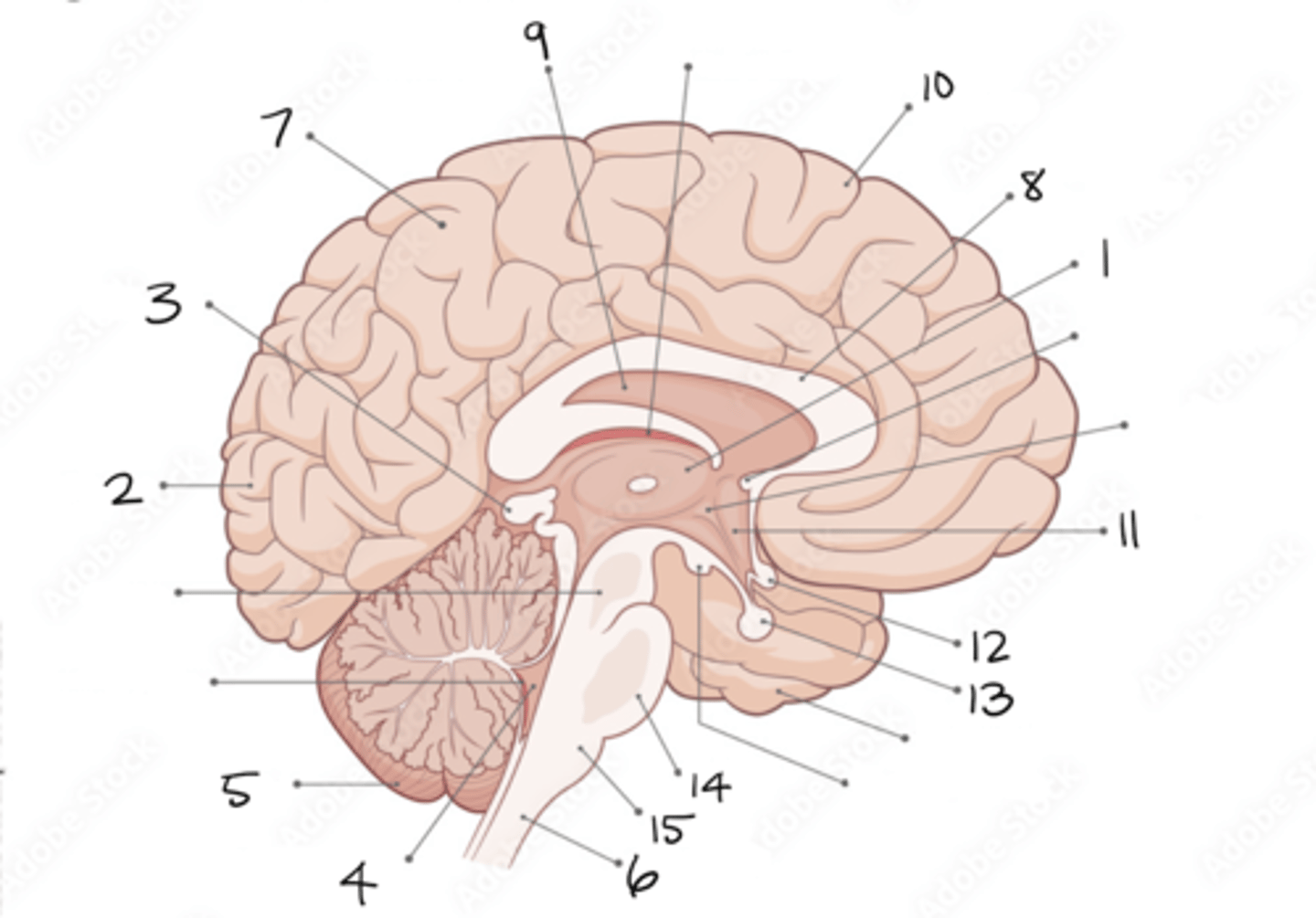
spinal cord
6
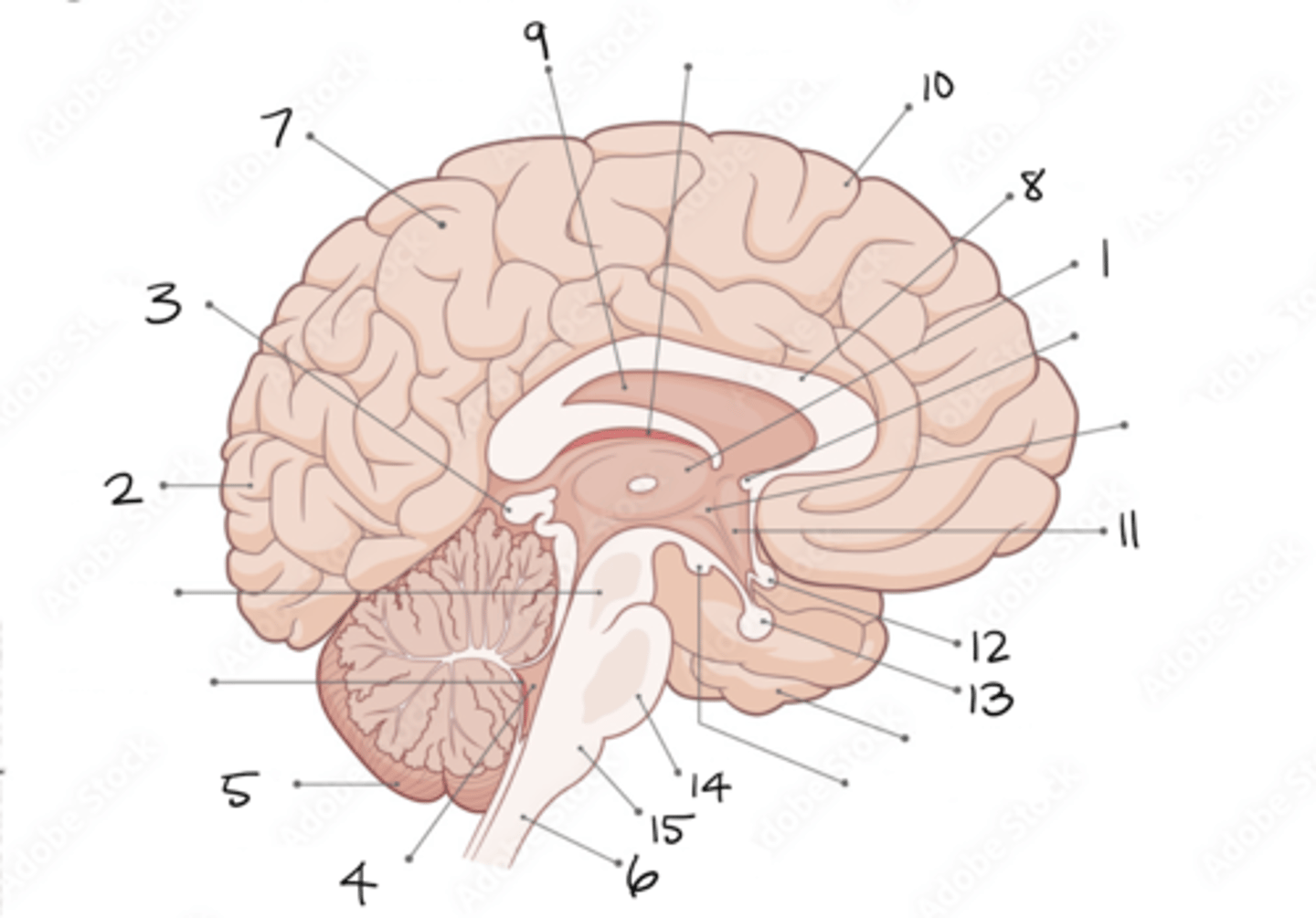
parietal lobe
7
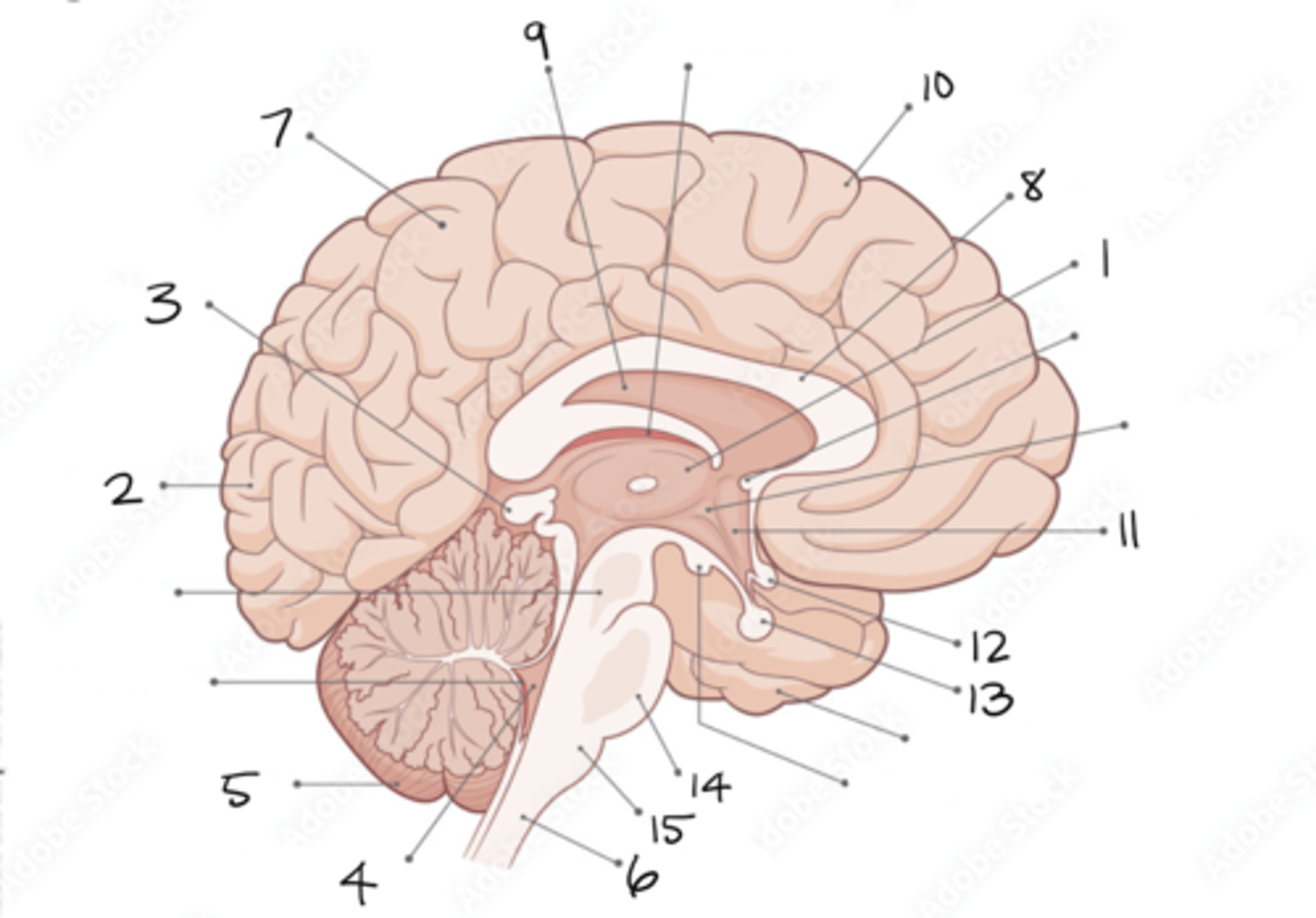
corpus callosum
8
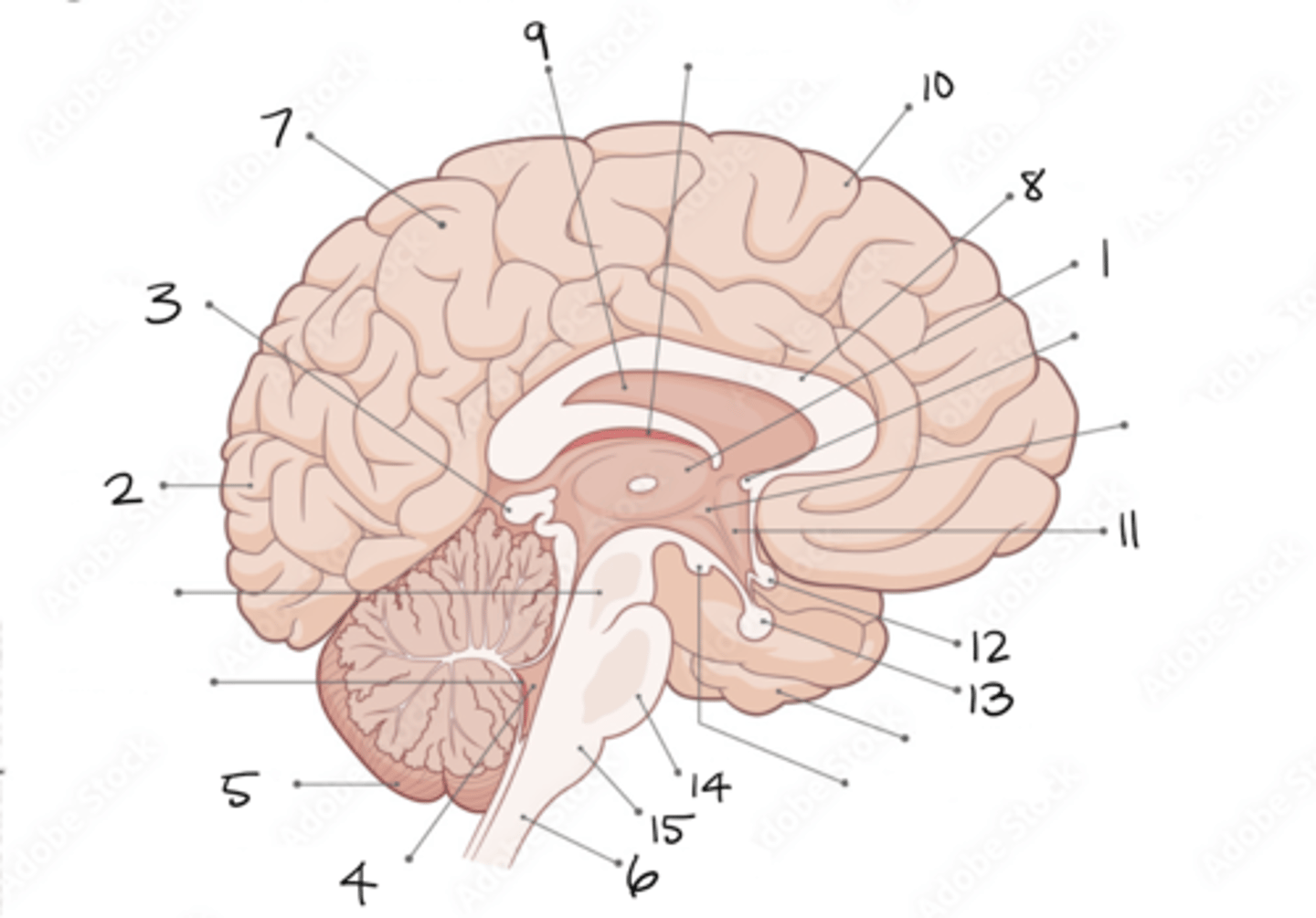
septum pellucidum
9
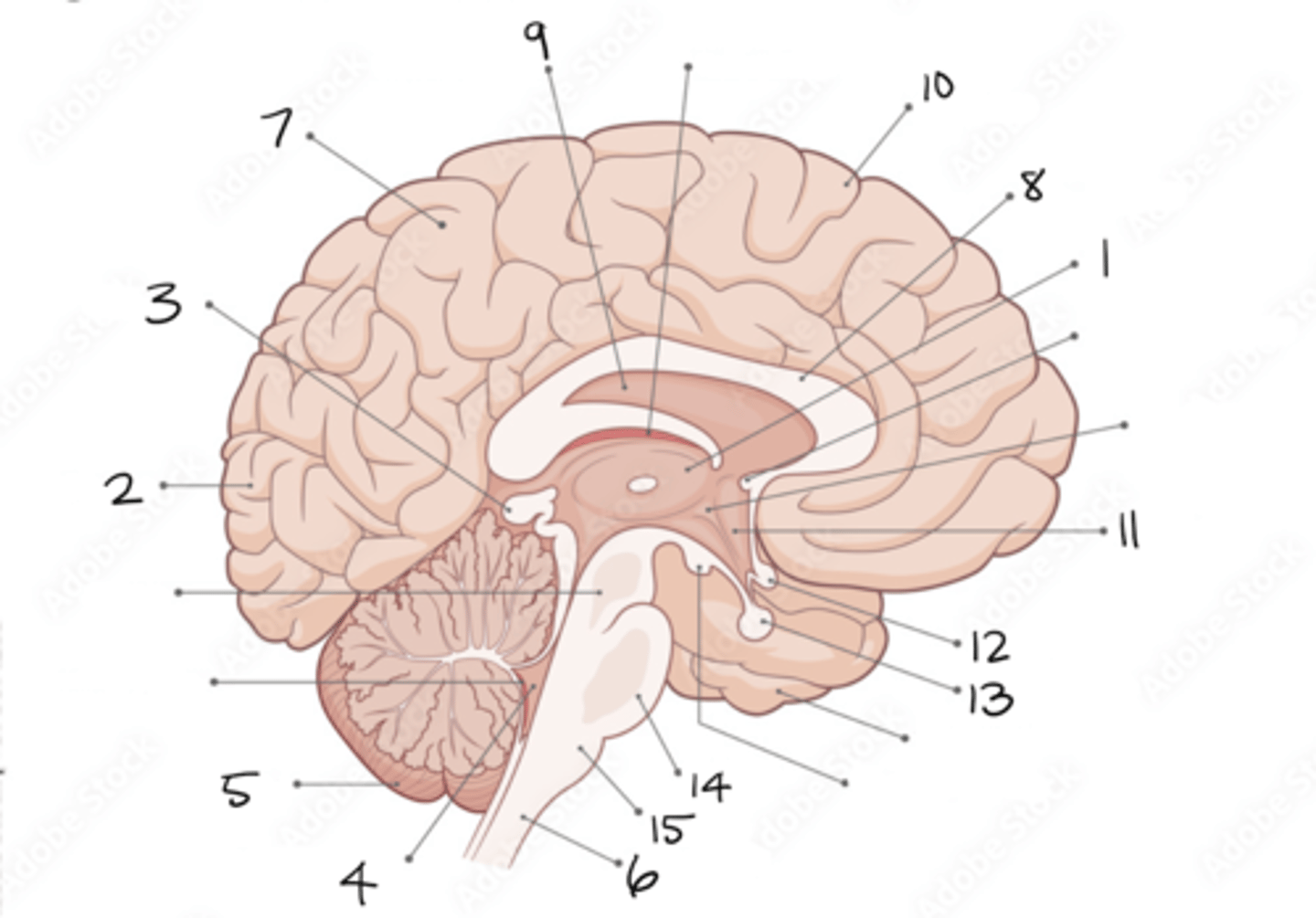
frontal lobe
10
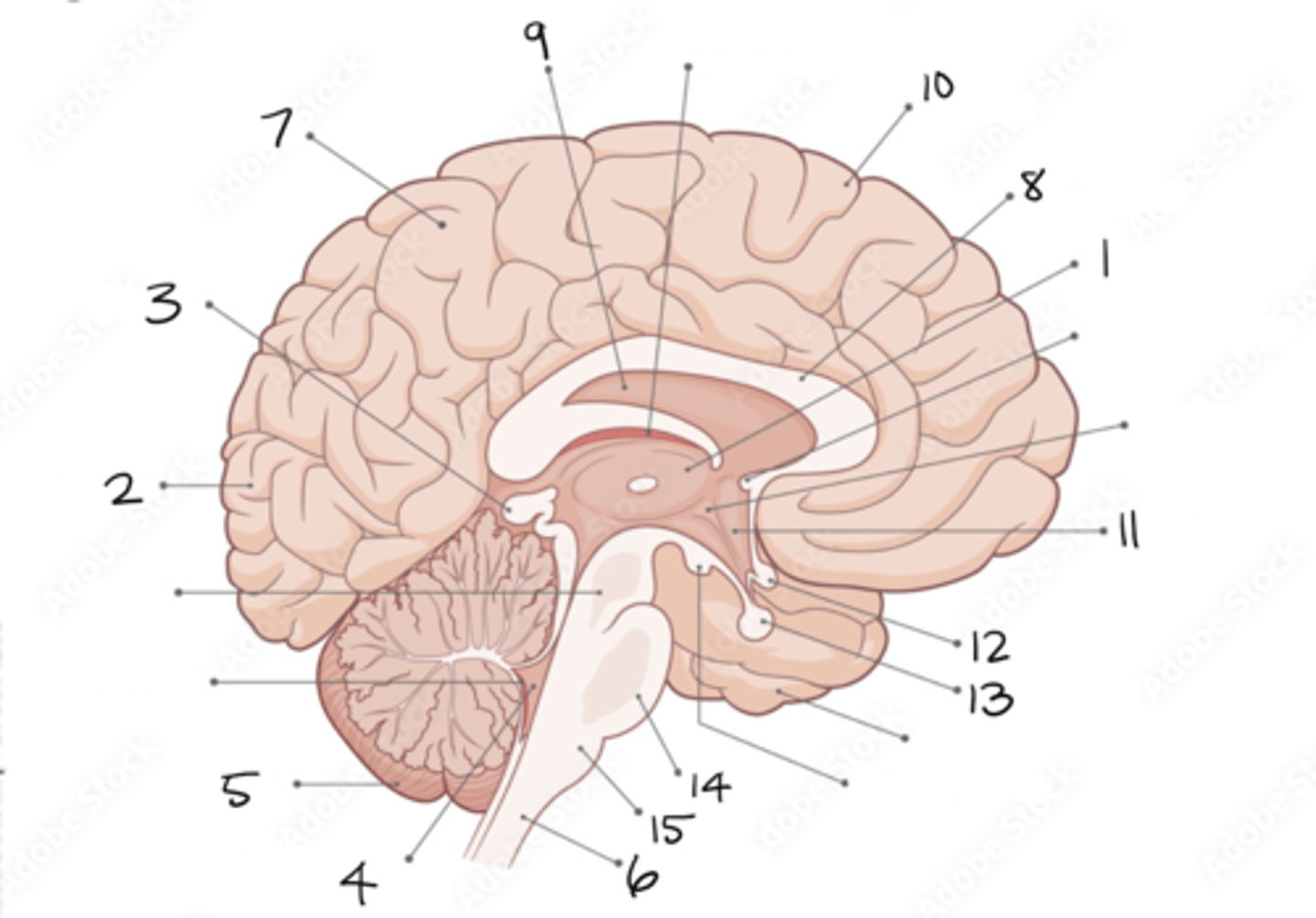
hypothalamus
11
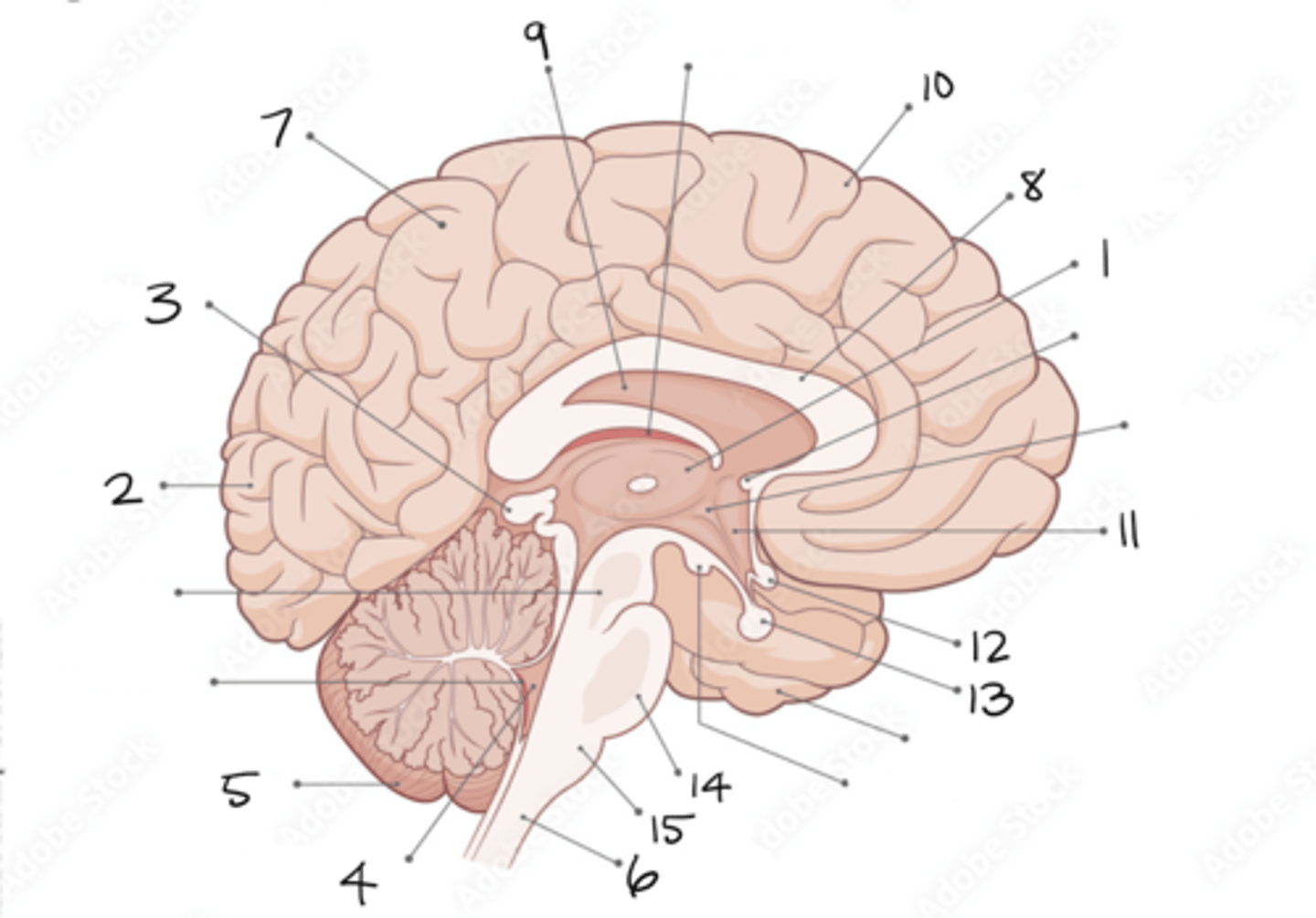
optic chiasm
12
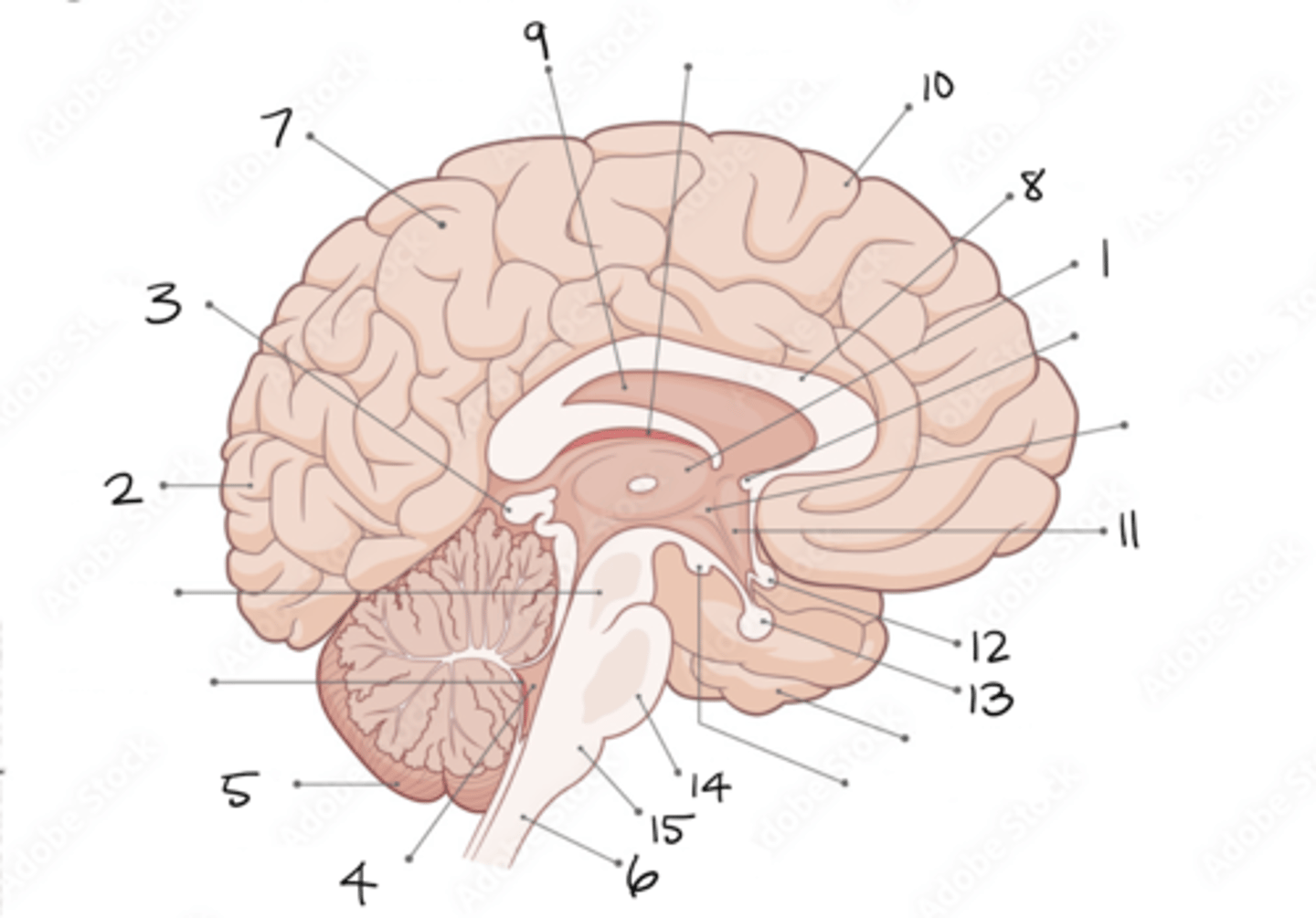
pituitary gland
13
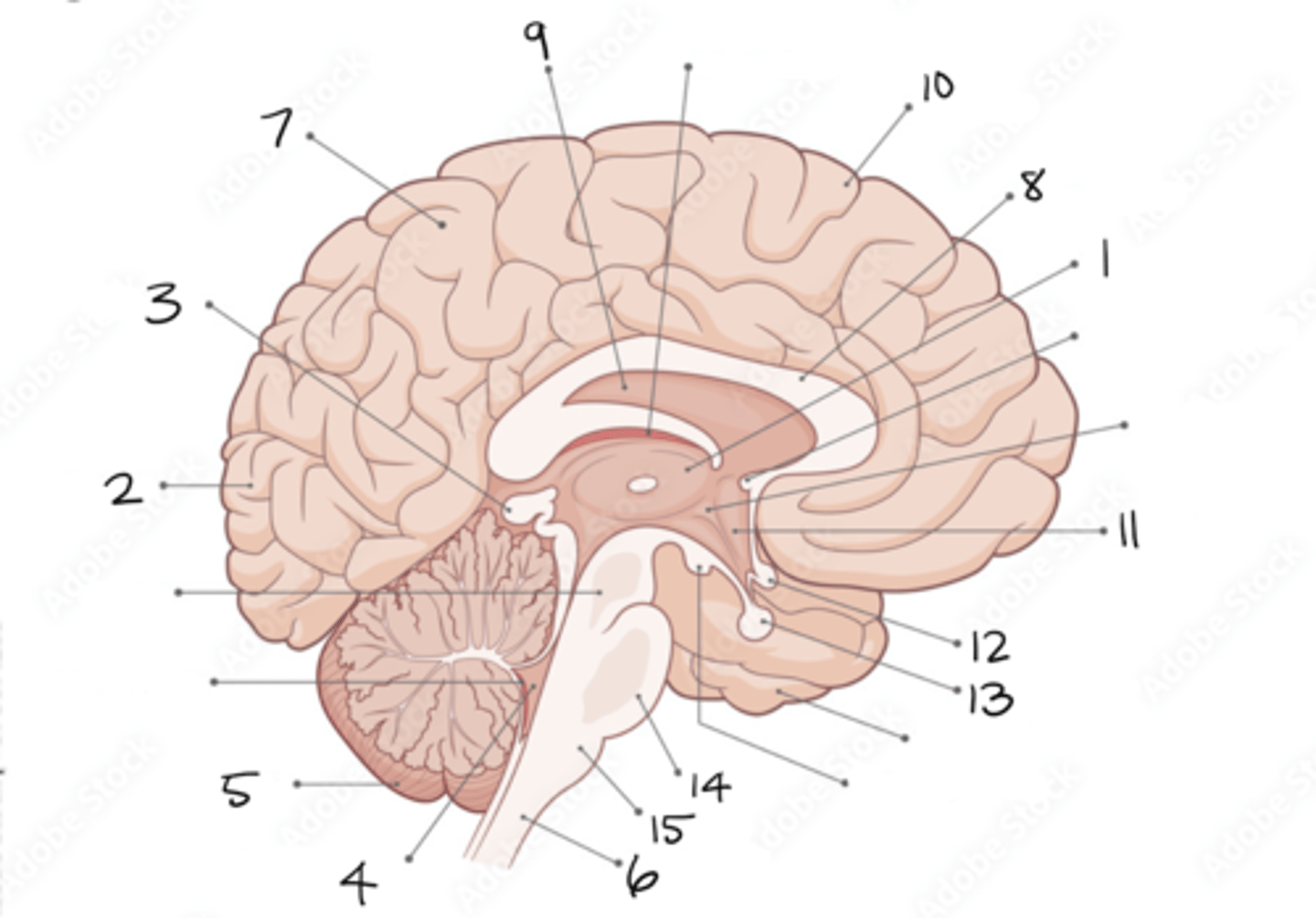
pons
14
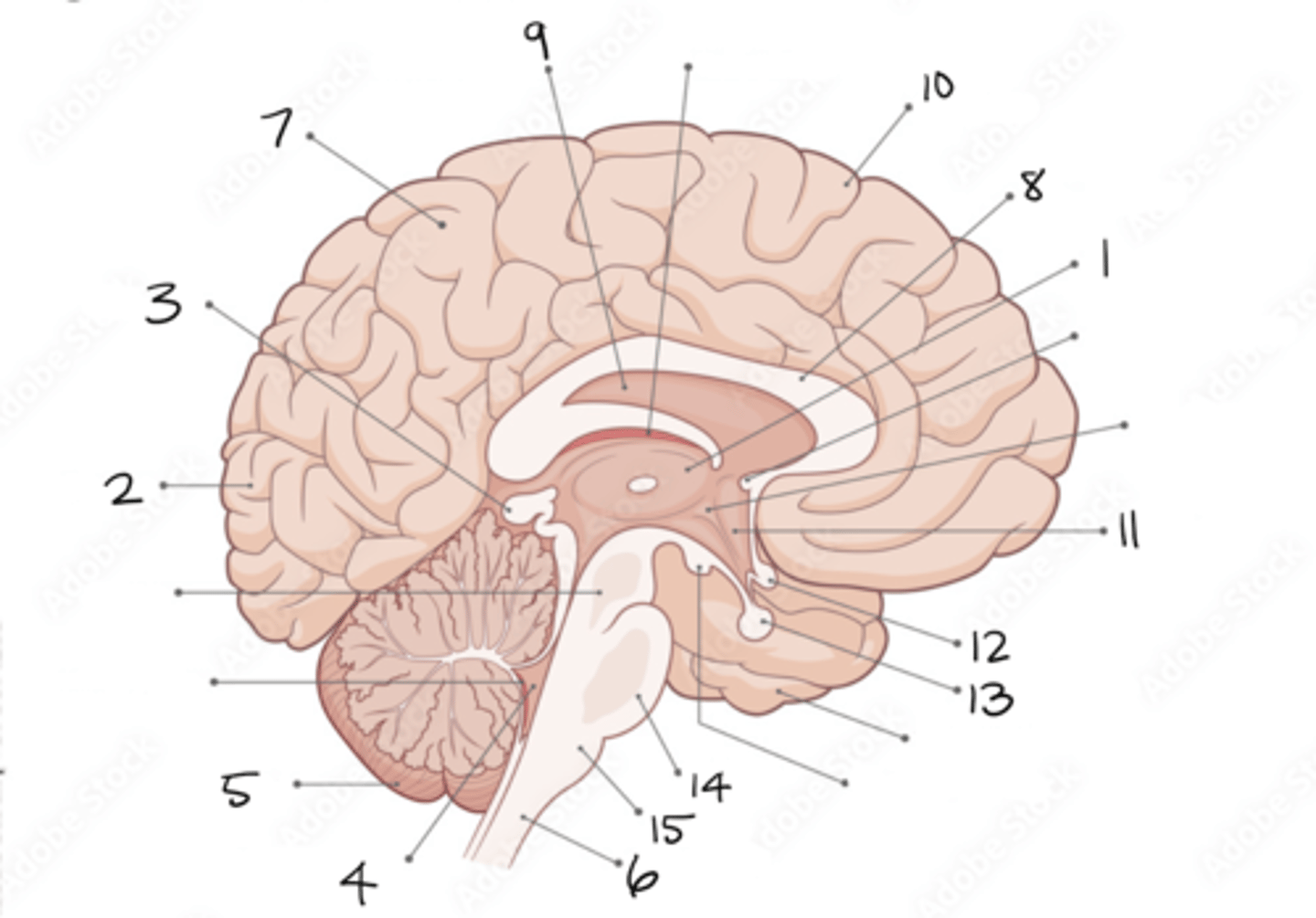
medulla oblongata
15