BIOLOGY Finals Reviewer
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Evolution
Can be defined by Darwin’s phrase descent with modification
1795: Hutton
he proposed the principle of gradualism
1798: Malthus
He published his “Essay on the Principle of Population”. (Species can produce more offspring than the environment can support. Variations of the population.)
1809: Lamarck
He published his hypothesis of evolution.
1812: Cuvier
Publishes his extensive studies of vertebrate.
1830: Lyell
Published the Principles of Geology.
1831-36: Darwin
He traveled around the world on HMS Beagle
1844: Darwin
He writes his essay on descent with modification.
1858: Wallace
While studying species in the Malay Archipelago, he sends his hypothesis of natural selection.
1859
When On The Origin of Species is published by Charles Darwin
Aristotle
He proposed the Scala Naturae
Sc/ala Natur/ae
The scale by which species are ordered by how perfect they are
Paleontology
Study of fossils (Helped to lay the groundwork for Darwin’s ideas)
Largely developed by Georges Cuvier
Fossils
Remains or traces of organisms from the past, usually found in sedimentary rock, which appears in layers or strata
Natural Variation
Competition
Survival of the fittest
Organisms change over time
Four Steps of Natural Selection
Natural Variation
This naturally exists in nature (1st Step in Natural Selection)
Competition
Organisms struggle for survival: more organisms are produced than the environment can support
Survival of the fittest
Only the best adapted survives. Adaptations are important
Organisms change over time
Organisms change but they have a common descent — they have a common ancestors
Adaptations
Inherited characteristics. Increase an individual’s chance of survival and reproduction.
Directional
Stabilizing
Disruptive
Types of Natural Selection
Directional
A shift in the frequency of a trait in a particular direction
E.g. Horse Racing: Breeders pick horses that can run the fastest
Directional
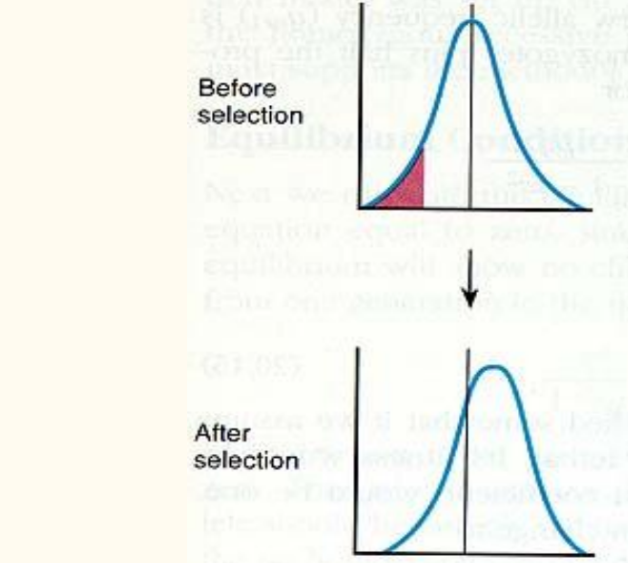
Stabilizing
Selects for average phenotypes and against extreme pheno.
E.g. Common in stable and unchanging environments
Stabilizing
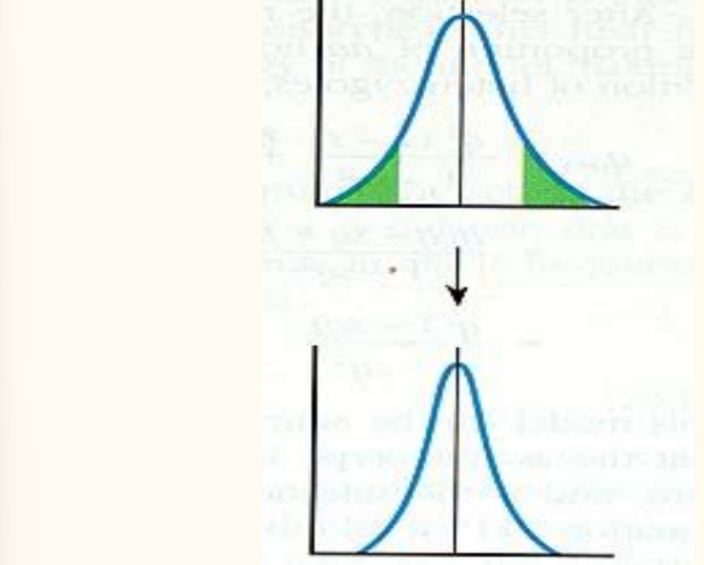
Disruptive
Selects for extreme phenotypes and against average phenotypes for being subjected to predation.
Disruptive
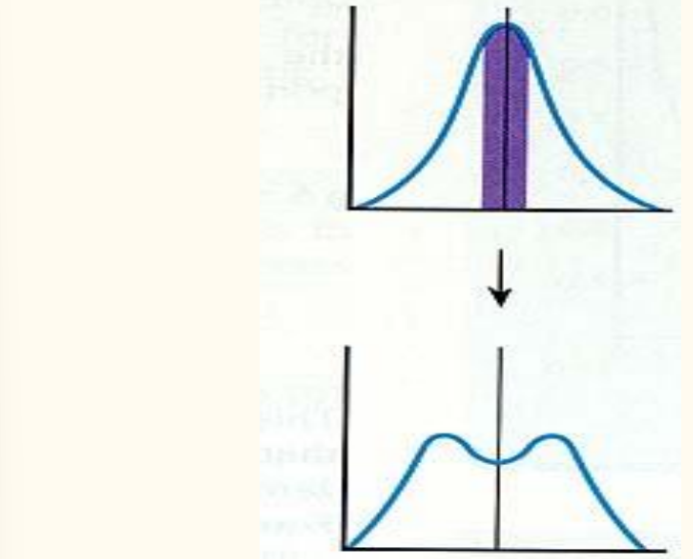
Artificial Selection
Humans select variations we find useful (domestic animals and crops)
Natural Selection
environment is the selective force. Only those organisms that are well adapted will survive in the wild.
Sexual selection
The species select which variations are useful (opposite of artificial selection).
Catastrophism
Speculation that each boundary between strata represents a catastrophe
James Hutton and Charles Lyell
They Perceived that changes in the Earth’s surface can result from slow continuous actions still operating today
Uniformitarianism
States that the mechanisms of change are constant overtime.
Lamarckism
Species evolve through use and disuse of body parts and the inheritance of acquired characteristics
adaption
Darwin perceived ______ to the environment and the origin of new species as closely related processes.
Natural selection
a process which individuals with favorable inherited traits are more likely to survive and reproduce
The Unity of Life
The diversity of life
The match between organisms and their environment
The origin of species
Descent with Modification
Summarized Darwin’s perception of the unity of life. Refers to the view that all organisms are related through descent from an ancestor that lived in the remote past (same ancestor)
Members of a population often vary in their inherited traits
Observation #1 of Natural Selection
All species can produce more offspring than the environment can support, and many of these offspring fail to survive and reproduce
Observation #2 of Natural Selection
Individuals whose inherited traits give them a higher probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment tend to leave more offspring than other individuals
inference #1 of natural selection
This unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to the accumulation of favorable traits in the population over generations
Inference #2
Homology
Similarity resulting from common ancestry
Homologous Structure
Are anatomical resemblances that represent variations on a structural theme present in a common ancestor
Vestigial Structures
Are remnants of features that served important functions in the organism’s ancestors
Evolutionary Trees
Hypotheses about the relationships among different groups
Convergent evolution
Is the evolution of similar, or analogous, features in distantly related groups.
Analogous traits
Traits that arise when groups independently adapt to similar environments in similar ways
Biogeography
The geographic distribution of species, provides evidence of evolution
Endemic species
species that are not found anywhere else in the world
Epithelial
Connective
Muscular
Nervous
Types of Tissues in Animals
Epithelial Tissue
A sheet of cells that protects the body’s sensitive systems
Connective tissue
Most abundant tissue in the anima body. Connects, binds, supports, and separates other tissues and organs.
Muscular tissue
skeletal muscle (usually attached to skeleton, voluntary), smooth muscle (covering walls of organs, involuntary), cardiac muscle (only covering the walls of the heart, involuntary)
Dermal
Vascular
Ground
Three parts of the tissue system for plants
Nervous Tissue
Transmit electrochemical signals
Stimulates muscle contraction
Affects emotions, memory, and reasoning
Cell Body
Axon
2 Main parts of the Neuron
Epidermis
The dermal tissue in nonwoody plants
Cuticle
Waxy coating that helps prevent water loss from the epidermis (plants)
Periderm
Protective tissues in woody plants
Trichomes
Outgrowths of the shoot epidermis and can help with insect defense. (hair like structures)
Vascular tissue system
Carries out transport of materials between roots and shoots
Xylem
Conveys water and dissolved minerals upward from roots into the shoots.
Phloem
Transports organic nutrients from where they are made to where they are needed
s.t.e.l.e
The vascular tissue of a stem or root is collectively called the ____
central vascular cylinder
the stele of the root in angiosperms
vascular bundles
the stele of stems and leaves
Pith
The Ground tissue internal to the vascular tissue
cortex
ground tissue external to the vascular tissue
Stem Cell
A cell that can differentiate into different kinds of cells.
Parenchyma
Collenchyma
Sclerenchyma
Major types of plant cells
Parenchyma Cells
retain the ability to divide and differentiate (stem cell in plants)
Collenchyma cells
Grouped in strands and help support young parts of the plant shoot
Sclerenchyma Cells
Rigid because of thick secondary walls strengthened with lignin.
Sclereids
Fibers
Two types of Sclerenchyma cells
Sclereids
Are short and irregular in shape (type of sclerenchyma cell)
Fibers
Long and slender and arranged in threads (type of sclerenchyma cell)
tracheids
vessel elements
Water-conducting cells of the xylem
Angiosperm flowers
Can attract pollinators using visual cues and volatile chemicals. Can reproduce sexually and asexually through symbiotic relationships.
Sexual Reproduction
Creation of an offspring by fusion of a sperm and egg to form a zygote (animals)
Asexual reproduction
Creation of offspring without the fusion of egg and sperm clones. Many invertebrates reproduce asexually by fission.
Sporophytes
Diploid - produce spores by meiosis and these spores grow into haploid. Dominant generation
Gametophytes
produce haploid gametes by mitosis. fertilzation of gametes produces a zygote sporophyte cell
Flowers, Double Fertilization, Fruits
Three F’s of angiosperm life
Stamen: Anther, Filament
Male reproductive system in flowers
Carpel: Stigma, Style, Ovary
Female reproductive system
Inflorescences
Clusters of flowers
Pollination
Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma
External Fertilization
Eggs shed by the female are fertilized by sperm in the external environment
internal fertilization
Sperm deposited in or near the female reproductive tract. Provides greater protective of embryos and more parental care
Amniote eggs
the embryos of some land animals develop in ____ with protective layers
Fruit
Develops from the ovary and protects the enclosed seed. Aids in seed dispersal through wind or by animals.
Species are at risk of extinction
Disadvantage of asexual reproduction
Ovaries
Female Gonads in animals
Mammary glands
Not part of the female gonads but important in mammalian reproduction