plasmids and gel electrophoresis - biotechnlogy
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
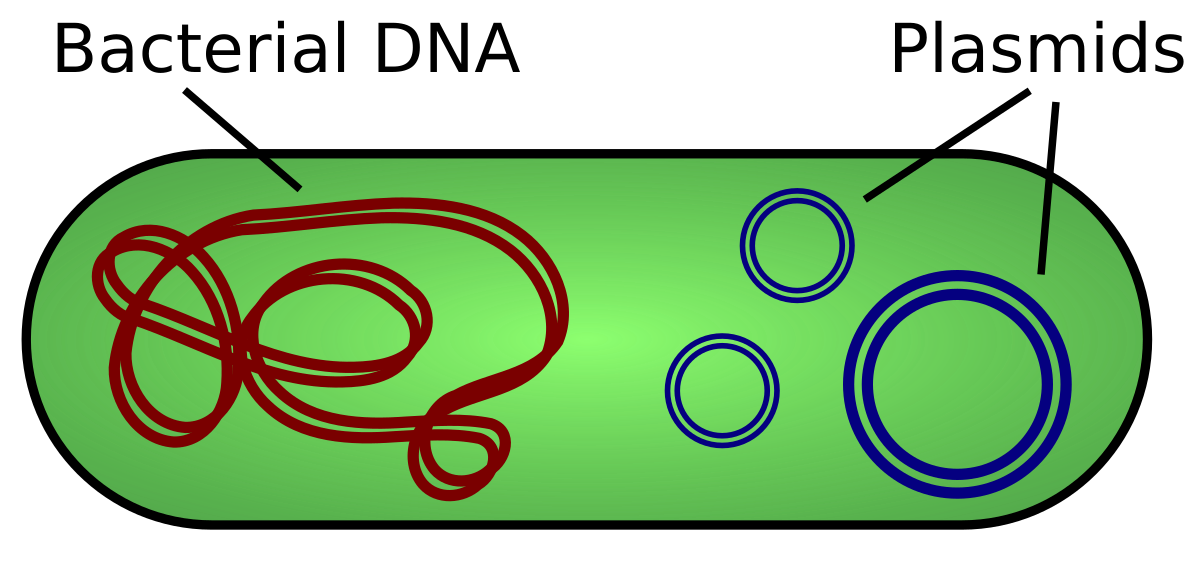
What are plasmids?
circular extrachromosomal DNA
Naturally occurring
Replicate independently
Small, stable, easy to manipulate
Found in microbes like bacteria
What do plasmids carry?
genes for metabolic activities
Genes are advantageous for host bacterium
I.e. resistance to antibiotics, heavy metals, bacteriophages
Plasmids and cloning
plasmids are cloning vectors
Must have Ori: origin of replication
many have gene for antibiotic resistance

What process allows the study of a specific gene?
transformation
plasmid DNA is cut open: blunt or sticky ends
complimentary gene fragment is inserted of gene of interest
DNA ligase joins fragments together, forming recombinant DNA
plasmid is forced into cell via transformation
allows plasmid to independently replicate
allows one to gain enough material to examine
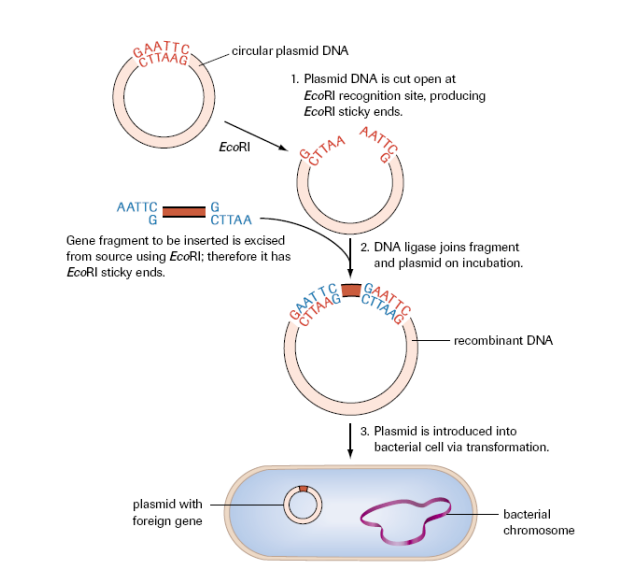
transformation
introducing DNA into a bacterium from another source
occurs when cell takes up and expresses new genetic materia
new trait observed
what new traits can be observed from transformation?
antibiotic resistance
frost, pest, or drought resistance
green fluorescence
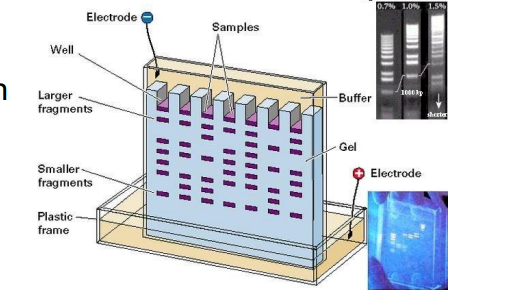
gel electrophoresis
used to separate DNA fragments based on size; amount of nucleotides
a gel with wells is soaked in a solution in a chamber between two electrodes
side with wells is negatively charged
small DNA fragments move farther and faster to positive side due to less nucleotides
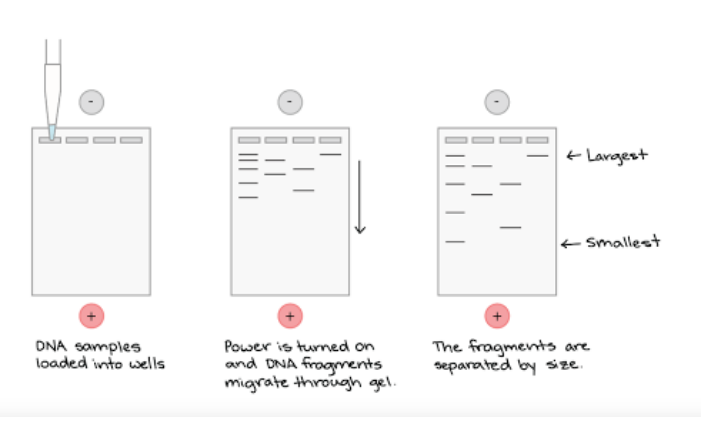
process of gel electrophoresis
wells are loaded with samples using pipette
gel is placed in buffer solution in a chamber with to electrodes
positive electron opposite to wells
DNA’s negative charge due to phosphate causes it to be attracted to positive side
smaller fragments travel faster and farther
larger fragments travel slower
how is gel electrophoresis measured?
size of fragments measured using a molecular marker → like a guide+
tells us size of unknown fragments
allows comparison of fragment sizes from diff sources

applications of gel electrophoresis
forensic: thumbprints leave unique dna sequence, can identify based on dna
paternity tests: matching child and possible fathers
medical: diagnosing genetic diseases or infections