principles of imaging: production of xrays
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
xrays are a form of
electromagnetic radiation
electromagnetic waves low frequency vs high frequency
long wavelength vs short wave length
conditions required for xray production
source of electrons (filament)
accelerate electrons (high voltage)
decelerate electrons (target)
all occurs in a vacuum
production of xrays occurs when
fast moving electrons are suddenly decelerated by interaction with target material
production of xrays occurs within _________ of target surface
.25 to .5 mm
energy=
amount=
quality
quantity
incident electrons
what is coming from cathode and hitting out anode
"the incident"
xray photons
after they hit the harget
anode is made up of
tungsen
kinetic energy of incident electrons
99% is converted to heat
1% is used for the production of xray
xray energy is directly proportional to the...
kinestic energy of the incident electrons
heat production (the 99%)
-electrons interact with outer shell electron of target atoms
-outer shell electrons raised to a higher energy level
-electrons drop back to relaxed state
-transition accompanied by infrared radiation
two types of target interactions produce xray photons
diagnositc radiation production (1%)
bremsstrahlung
characteristic
diagnositc radiation production (1%)
-electrons give up energy to target atoms
-type of interaction depends on kinetic energy of incoming electron and binding energy of electron shells
bremsstrahlung is the german word for
braking or slowing
bremsstrahlung interactions make up
80-90% of the primary beam
in bremsstrahlung interactions high speed electron passes near the _______
nucleus
in bremsstrahlung interactions the ________ charge of the nucleus ______ the electron from the ______________
positive charge
deflects
original path of travel
electrostatic force
power of force field
brems radiation
-incident electron slowed by force field of nucleus
-incident electron continues in a different direction with reduced energy (can cause numerous interactions)
brems reaction is the
loss of kinetic energy given off as an xray photon
energy of brems radiation depends on
-the energy of incident electron
-the charge of the nucleus
-the proximity of the incident electron to the nucleus
interactions further from the nucleus equals
lower energy brems
interaction closer to the nucleus equals
higher energy brems
averag beam energy equals
30-40% of kVp selected
incident electron may lose _________ of its kinetic energy in an interaction with the nucleus
any amount
when 70 kVp is set on the control panel
-produce kinectic energy up to 70 kVp
-electrons may use some, none or all kinetic energy
-brems xrays produced my have energies up to 70 kVp
kVp selected vs kEv
kVp the peak energy selected
kEv energy can only go up to kVp
in brems radiation the energies are
unpredictable
-may range from very low levels to peak kV
-very low energies are absorbed within the tube
in brems radiation incident electrons may have ______ interactions before it _____ all its energy
multiple
loses
in brems radiation a ________________ beam contains a variety of energies
heterogenous/ polyenergetic
characteristic radiation
-10-20% of primary beam
-incoming electron ejects inner shell (k shell)
-leaves vacancy in inner orbital shell
-characteristic xrays are emitted when an outer shell electron fills an inner shell void
characteristic radiation/ cascade effect
xrays are emitted here
the energies are predictable (we know the energy of K shell)
tungsten atom
atomic number 74
110 neutrons
74 electrons
electron shell of tungsten
K= 2 electrons
L= 8 electrons
M= 18 electrons
N= 32 electrons
O= 12 electrons
P= 2 electrons
tungsten binding energies
-emitted radiation is characteristic of the target element
-binding energies of specific element have distinct values
K shell
number of electrons 2
keV 69.5
tungstem electron transition
-xray energy equals difference in binding energies of the orbital electrons involved
-electrons dropping into K shell may be from any shell (not always subsequent)
in tungstem electron transition, the ______ out the electron comes out to "drop" into vacancy, the _______ the characteristic radiation produced
further
greater
in characteristic radiation only ______ interactions contribute to the _______ beam
K shell
useful
lower energies ______ the tube
exit
characteristic radiation SUMMARY
-incident electron must have enough energy to knock an inner shell electron from orbit
-interaction will only occur at 69.5 keV (70 kVp) and above
-the ejection of the innershell orbital electron creates a temporary hole
-an outer shell electron moves in to fill the void
-outer shell electron moves into fill the void
-outser shell electron drops to inner shell and xray is emitted
-energy= to the difference in binding energy of the shells involved
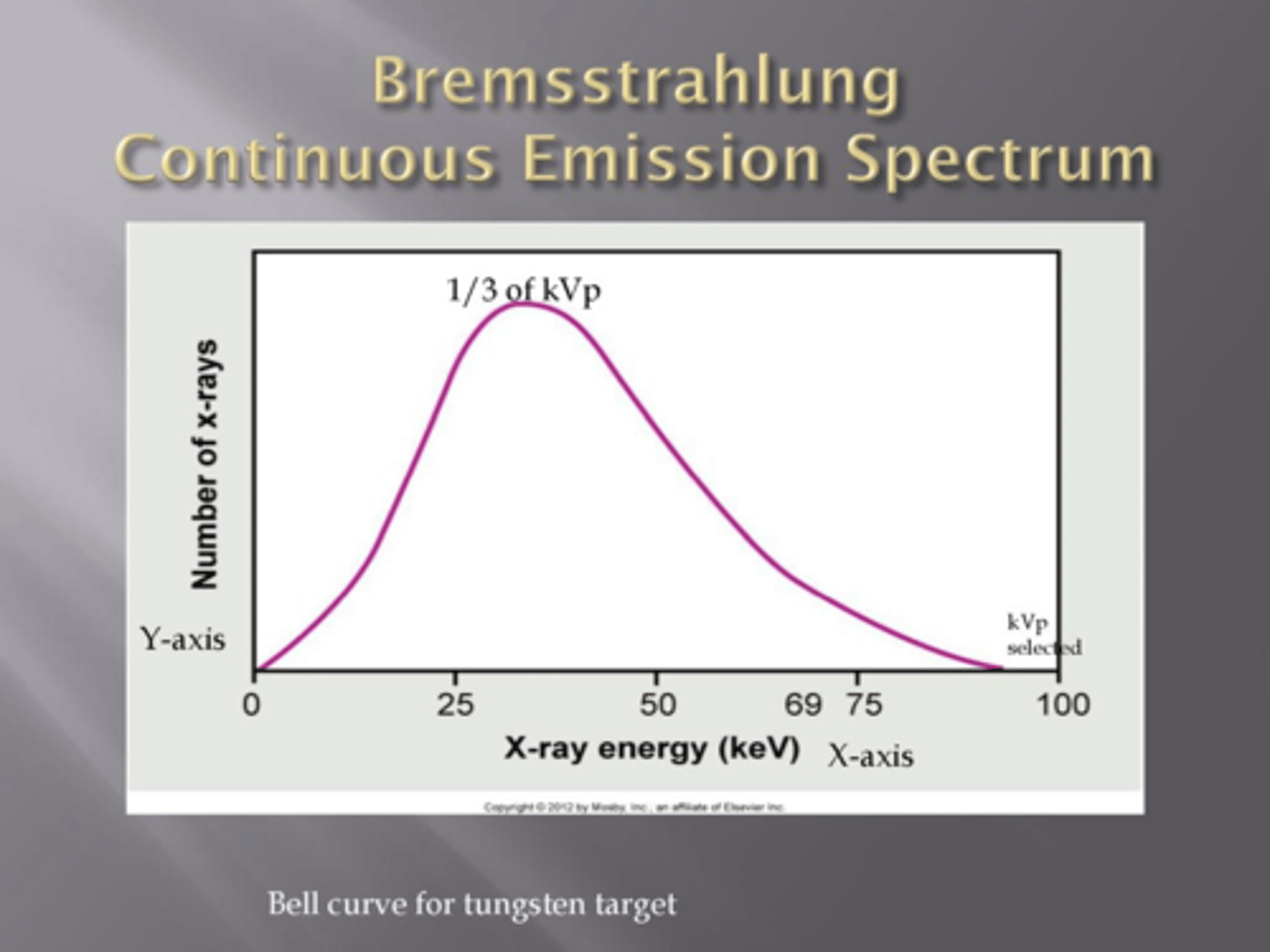
emission spectrum graphically represents xray beam (brems and characteristic)
energies emitted in the beam at a particular kVp setting
brems emission spectrum
-plot of the number of xrays emitted per energy level
-heterogenous beam contains broad spectrum of energies
-kEv is calculated from peak (30-40% of peak)
characteristic emission spectrum
-characteristic energies are predictable
-energies emitted through k shell interactions (57, 66, 68, 69)
-L shell interactions will be absorbed (will not contribute to the image)
-anything below 70 wont contribute
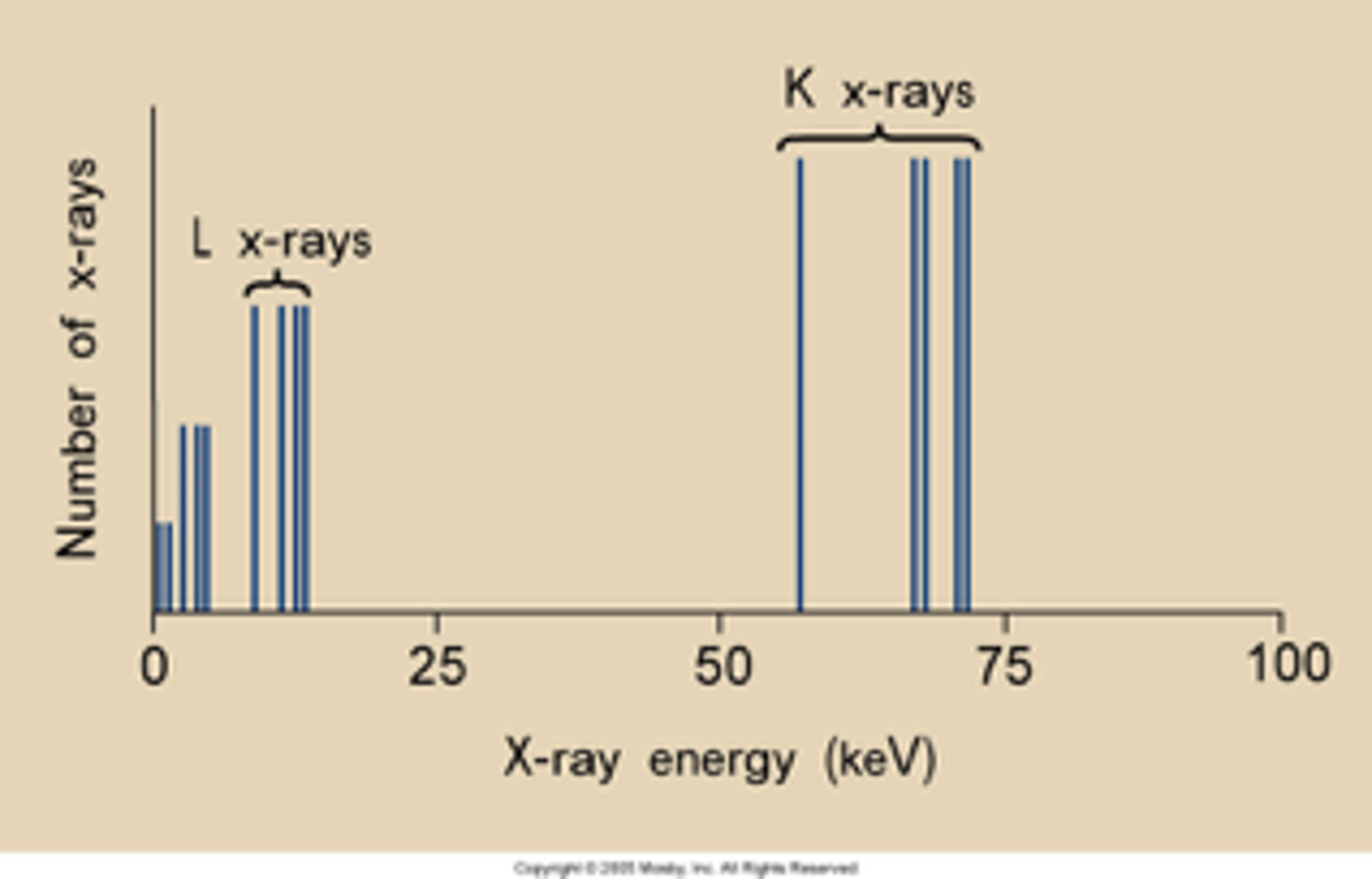
xray production emission spectrum: characteristic
xrays emitted at 70 kVp and above (69.5)
produces specific discrete xray energies
represented by spike
xray production emission spectrum: brems
xrays emitted over entire spectrum of beam
area under curve
emission spectrum summary:
most photons produced by ________ target interactions within the diagnotic range
bremsstrahlung
above 70 kVp approximately ______ of the beam consists of characteristic xrays
10-20%
average energy beam (keV)=
30-40% of set kVp
factors affecting the spectrum
mAs
kVp
filtration
generator type- voltage waveform
generator type- voltage waveform
single
3 phase 6 pulse
3 phase 12 pulse
high frequency
mAs determines the:
number of electrons that boil off during thermonic emission, number of xray photons in beam, and beam quanity
mAs and amplitude are:
directly proportional
mAs and exposure are:
directly proportional
mAs is doubled, exposed doubled
kVp determines the:
quality (energy) of beam
kVp: affects penetrability/ quality
affects the quantity of photons, but NOT in a directly proportional manner
-kVp effects quantity but not proportionally
change in kVp affects:
both the amplitude and postion of the spectrum
-curve shifts to the right
-amplitude increases
filteration
xray beams through materials as exiting xray tube and housing
higher filtration = decreased quantity= increased average energy
increased generator efficiency
-increased average photon energy
-increased number of photons in beam and/ or amplitude of spectrum