Control and Regulation - Biology (Year 9)
1/53
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Homeostasis
Adrenal Glands (Adrenaline)
Axon
Axon Terminal
Brain stem
Cell body
Central Nervous Centre (CNS)
Connecting/Inter/Relay neuron
Dendrites
Effectors
Endocrine Glands
Glucagon
Glucose
Glycogen
Hormones
A checmical substance that acts as a messenger in the body. Hormones are transported around the body via the blood stream ad act on target cells.
Hypothalamus
Insulin
Liver
Motor Neurons
Myelin Sheath
Negative Feedback (Loop)
Nerve Impulse
Nerve cell
Neurotransmitter
Pancreas
Peripheral Nervous System
Positive Feedback (Loop)
Receptors
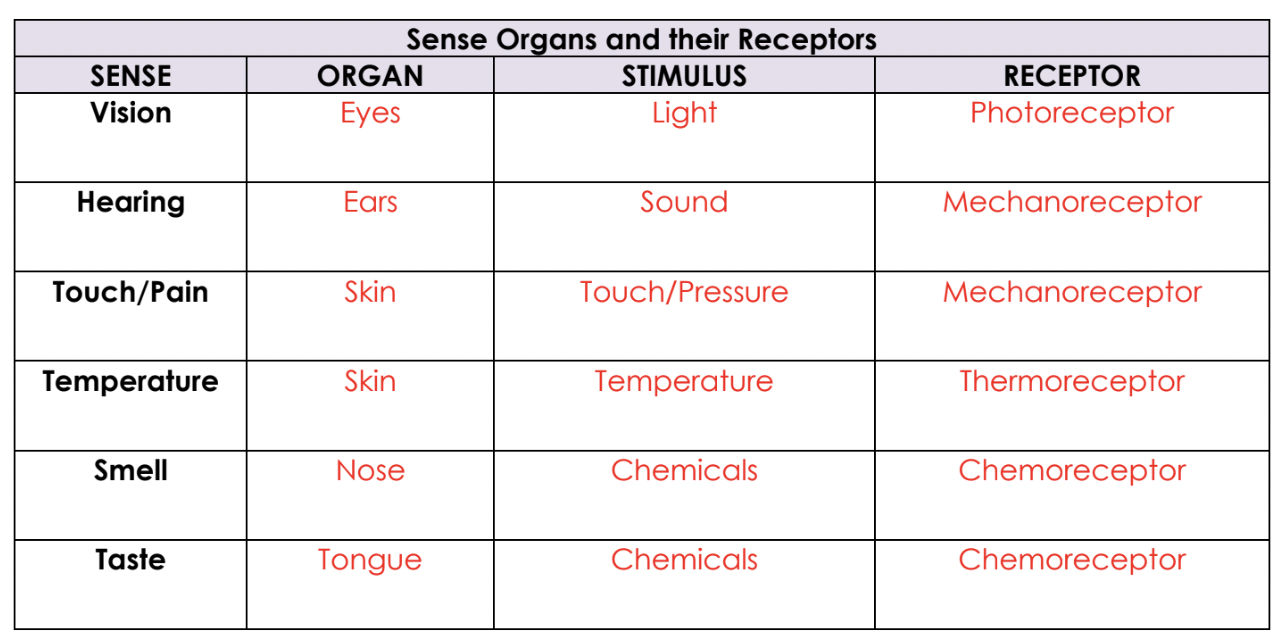
A receptor detects a stimulus.
Reflex action
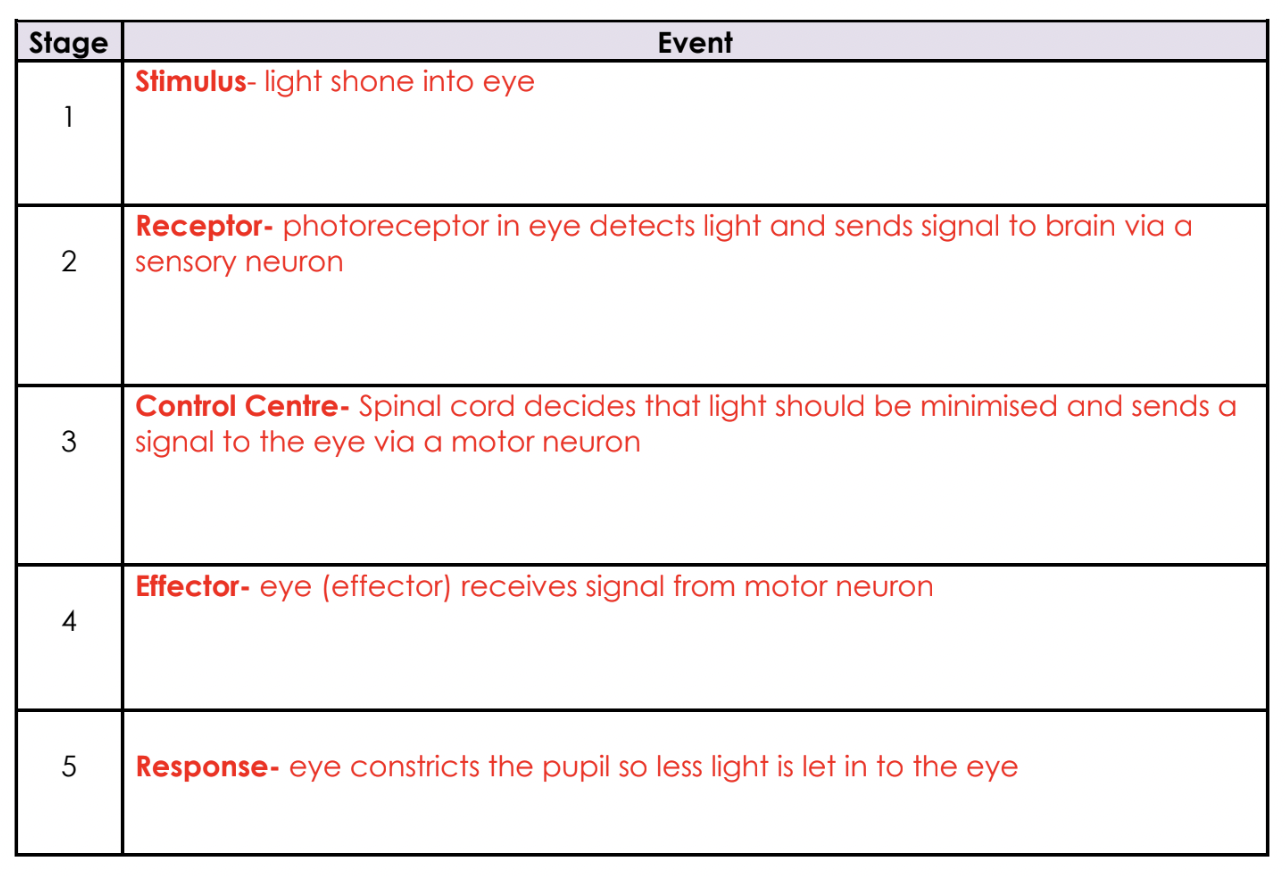
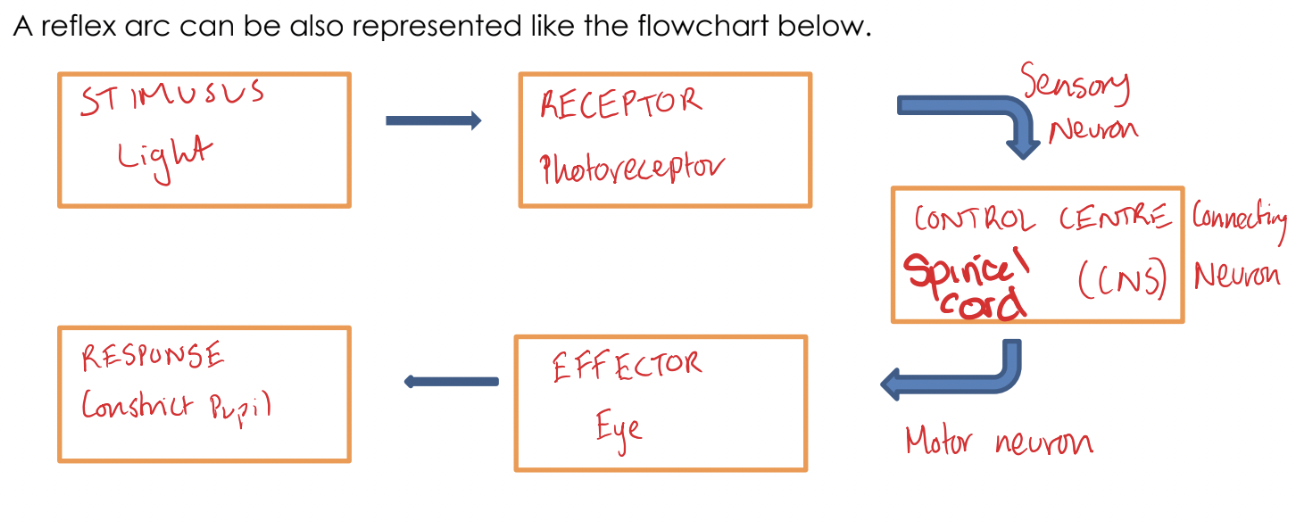
A reflex action is an extra-rapid response to a stimulus: the process involes the nervous system but bypasses the brain.
receptor detects a stimulus (change in environment)
sensory neuron is activated
signal is sent to connecting neuron in CNS (spinal cord)
motor neurons are activated and sends a signal to effector
effector produces a response
Reflex arc
Response
Sensory neurons
Spinal Cord
Stimulus
Synapse
Target cells
Vasoconstriction
Vasodilation
Piloerection
Sweating
Shivering
Temperature Regulation
Negative Feedback Loop
Blood Glucose Regulation
Negative Feedback Loop
Control Centre
Physiological Regulation
Behavioural Regulation
Target Cell
Fight or Flight
Node of Ranvier
Nucleus
Synapse
Neurotransmitter
Vesicles
Endocrine system