Introduction to anatomy and physiology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Sagittal
divides the body. Right to the left
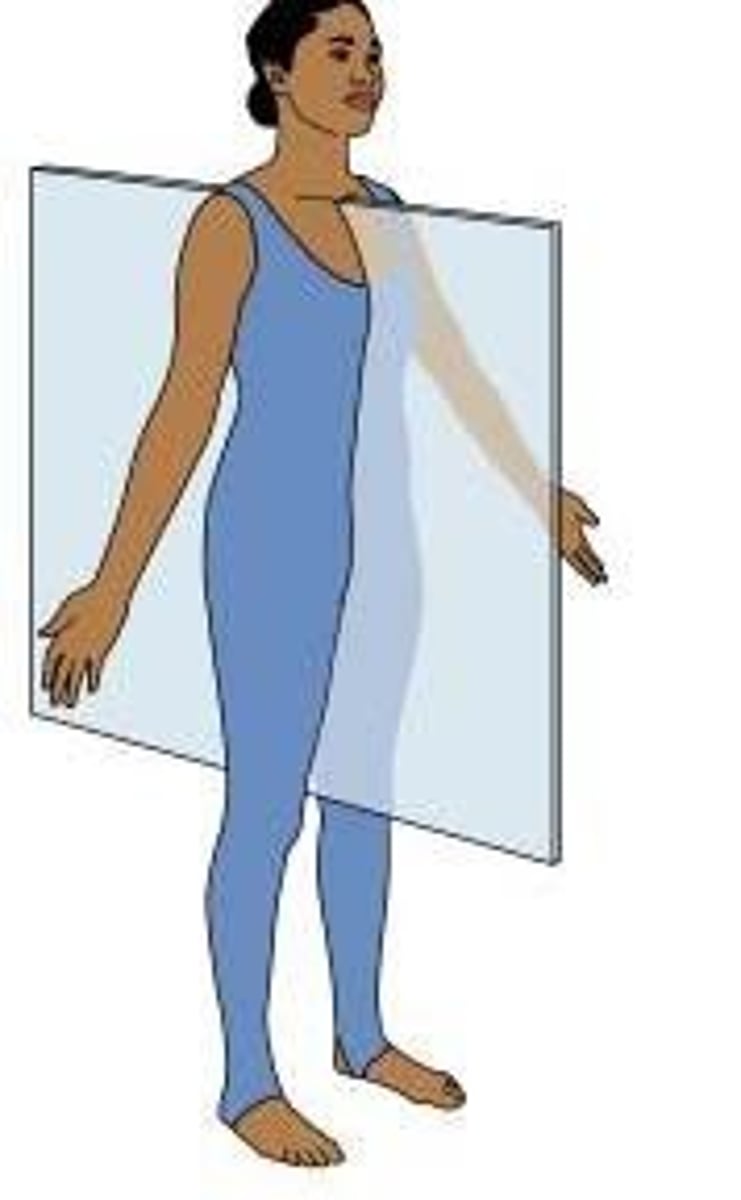
Coronal or Frontal
divides the body into anterior and posterior portions
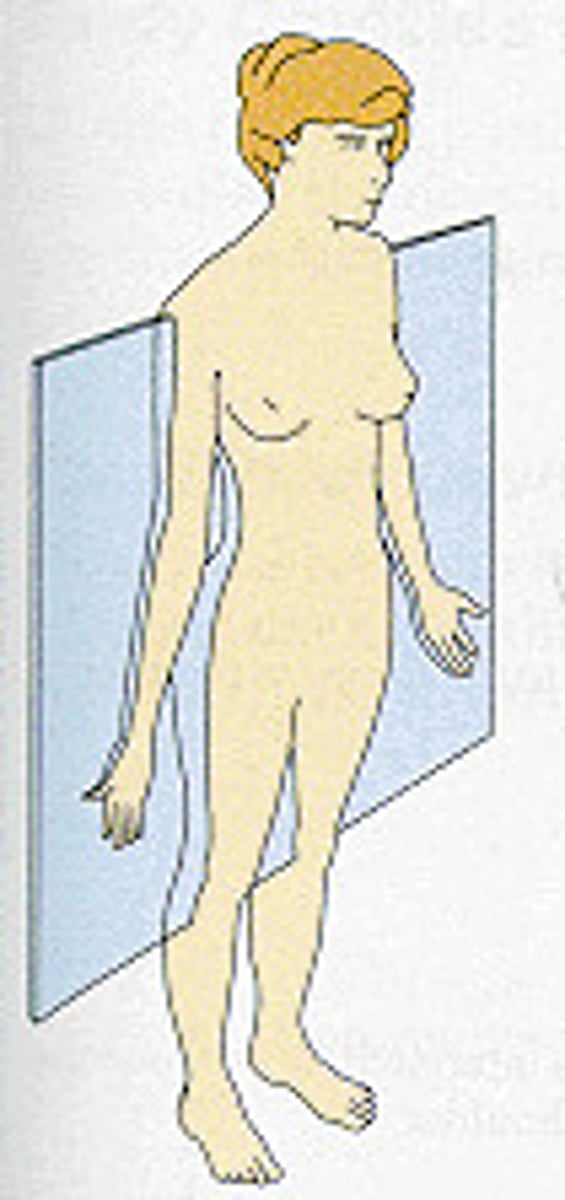
Transverse
Divides body into upper and lower parts
What structure divides the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity?
Diaphragm
What is the space/cavity located within the thoracic cavity and between the lungs that contains the heart, trachea, esophagus, and great vessels
Mediastinum
Anterior
front of the body (ventral)
Posterior
behind the body
Ventral
front side of the body/belly
dorsal
pertaining to the back
superior
Higher on the body, nearer to the head
inferior
Lower on the body, farther from the head
central mediastinum contains
Heart
peripheral
outside of center
deep
Away from the body surface; more internal
cephalic (cranial)
head
caudal
pertaining to the tail
distal
farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
medial
Toward the midline of the body
When elements come together they form
molecule
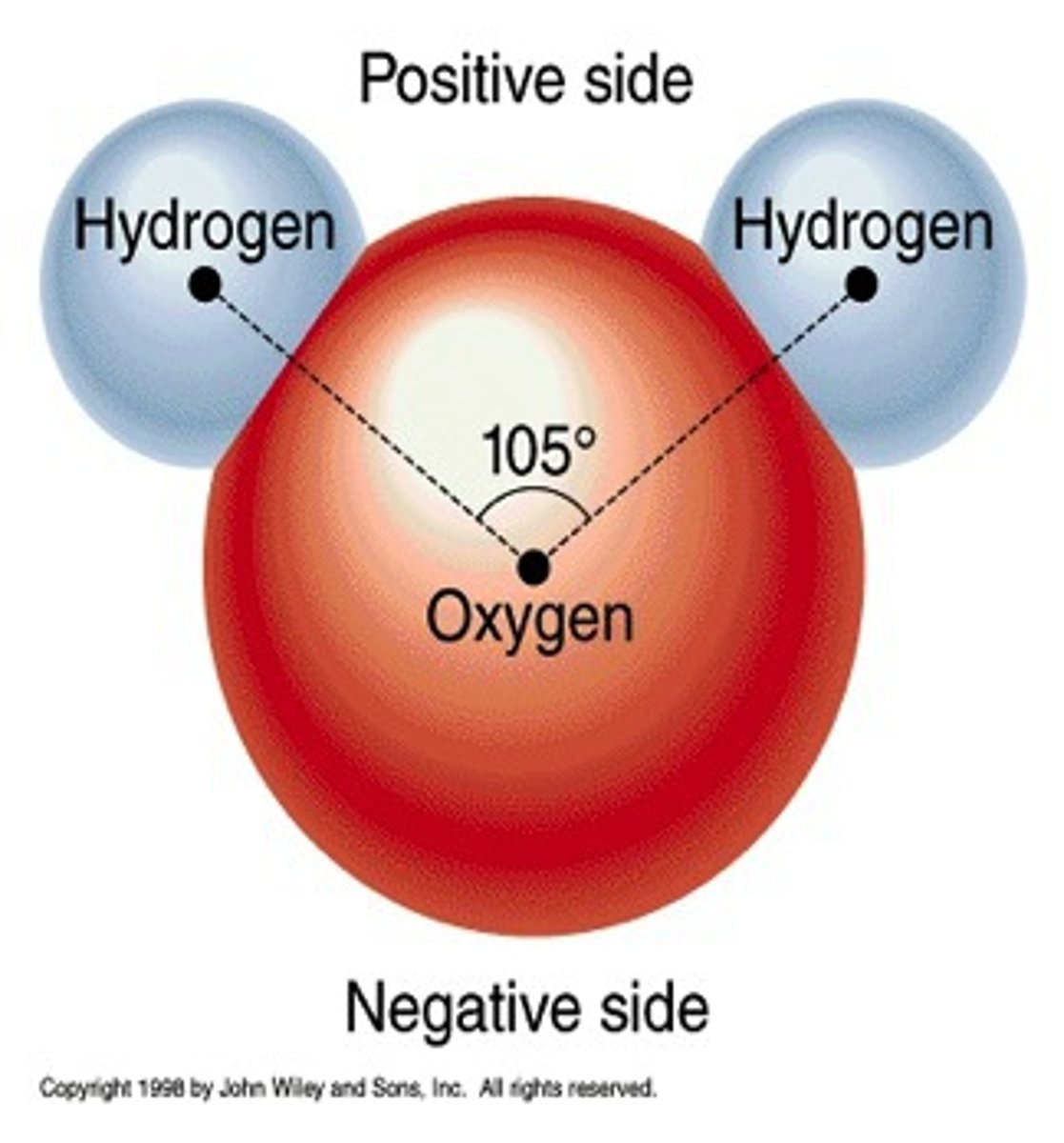
When the molecules come together they form
when two or more cells come together they form
tissue
4 tissue types in the body
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nervous Tissue
When two or more tissues come together they form
organ
when two or more organs come together they form
organ system
When all parts are functioning together it is called an
organism
The cell is surrounded by a medium known as
extracellular fluid or interstitial fluid.
Endocrine
Release secretions directly into the blood/ ducts less. Inside of the body
What body systems have organs that are all lined with mucous membranes
Respiratory, Digestive, Urinary, Reproductive
Visceral
Closest to the organ
parietal
it covers the cavities
Cardiac
pertaining to the heart
Define Homeostasis
maintenance of a stable internal environment
Negative feedback loop
A feedback loop that causes a system to change in the opposite direction from which it is moving
Positive feedback loop
feedback loop that causes a system to change further in the same direction
Reproduction
Formation of new cells for replacement or regeneration of old/ injured cells/ formation of a new person
Why is excretion necessary for homeostasis
To removing waste of digestion and metabolism
Integumentary
pertaining to the covering of the body
Blood
Carry oxygen and nutrients
Respiration
Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between external environment and cells/cellular respiration
Digestion
The talking in of useful substances ,breaking them down useful substances include; carbohydrates, protein,fats,vitamins,minerals,water.
Cardiovascular
Pumps blood to the tissue
Respiratory
gas exchange
Define anatomical position?
1. Standing upright
2. Facing forward
3. Arms down by your side
4. Palms facing forward
Extracellular fluid
Fluid outside of the cell
The function of the nervous tissue is
neurons transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors (muscles and glands); supporting cells support and protect neurons
abdominal pelvic cavity membrane
parietal peritoneum
visceral pleural membrane
covers the lungs
peritoneal cavity
abdominal cavity
axial region
Head, neck, and trunk
Forms the main vertical axis of the body
negative feedback example
body temperature regulation
positive feedback example
childbirth and blood clotting