Biology Chapter 1-2 Themes & Concepts in Biology
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 1: The Study of Life
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
What is Biology?
The study of living organisms, divided into many specialized fields that cover their morphology, physiology, anatomy, behavior, origin, and distribution.
“Bio” Greek word Bios
Living organisms share key characteristics that define life and differentiate them from non-living entities
Properties that define life
Order, response to stimuli, reproduction, growth, development, adaptation/evolution
Are viruses alive?
Yes, viruses are alive
Molecules
Building blocks of life, including proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids
Cells
Basic unit of life, where metabolic processes and function occurs
Organisms
An individual living plant animal or single-celled life form. Don’t forget that bacteria and archaea are organisms composed of a single cell.
Ecosystems
Communities of organisms interacting with each other and their physical environment
How many domains in diversity of life?
3 domains
Prokaryotes entail:
Eubacteria and Archaea
Eukaryotes entail:
Only Eukaryotes
Kingdoms
In each domain life is further divided into groups that highlight unique characteristics and functions in ecosystems
Evolutionary Relationships
The evolutionary tree illustrates the relationships between organisms, showing how species have evolved and diversified over time
Process of Science
Ask a question form a hypothesis, conduct and experiment, analyze results
What does Biology primarily study?
Living organisms and their interactions from molecular structure and function of cells, to evolution growth, and distribution of organisms along with their complex relationships within ecosystems and environments
Eukarya
the domain that includes all multicellular organisms (and some single celled too)
What falls under Eukarya domain?
Plants, fungi, protists
Order as a property of life
Reflects how living organisms maintain structured complexity
Insulin
Peptide hormone essential for regulating blood glucose levels enabling cells to absorb and use sugar for energy, and maintaining metabolic balance in the body
Structure of Atoms
Smallest unit of matter and cannot be subdivided into smaller substances. They interact for form molecules
Chemistry
Study of interactions between atoms and molecules
How many essential elements are needed for an organism to live and reproduce?
20-25% of the 92 naturally occurring elements
What elements comprise of 96% of living matter?
Hydrogen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen
Electrons
Negatively charged particles
Protons
Positively charged particles
Neutrons
Uncharged particles
What subatomic particle make up the nucleus?
Protons and neutrons
Where to electrons move around?
In orbit around the nucleus/ “shells”
Isotope
Atoms with different number of neutrons
Energy
Capacity to cause change
Potential energy
Energy that matter has because of its location or structure
Electron shell
An electron’s state of potential energy called energy level
Electron Configuration
Electrons are arranged in electron shells, each corresponding to a different energy level
Energy levels based on shells
First/lowest shell has the lowest energy level, highest energy level in the highest shell
Valence
Number of missing or extra electrons in the outermost shell
Why do molecules hold together?
the valence electrons of the combining atoms form attractive forces, called chemical bonds, between the atomic nuclei
What influences the reactivity of an atom?
The number of electrons in the outer valence shell
Shell 1
Holds 2 electrons
Shell 2
Holds 8 electrons
Shell 3
Holds 8 electrons as well
Compounds
Molecule that contains two or more kinds of atoms
Ionic bonds
Attraction between ions of the opposite charge and are charged atoms that have gained or lost electrons
Cations
Atoms that lose electrons and become positively charged
Anions
Atoms that gain electrons and become negatively charged ions
Covalent bonds
When two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons and are stronger and more common in organisms than ionic bonds
Hydrogen bonds
Form when a hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded to an O or N atoms is attracted to another N or O atom in another molecule
Intermolecular force
Force that is weaker than covalent and ionic bonds
Van der Waals interactions
When transiently positive and negative regions of molecules attract each other. They are weak bonds but allow geckos to stick on walls.
Chemical reactions
Involves the making or breaking of bonds between atoms and a change in chemical energy occurs during this reaction
Endergonic
reactions that absorb energy
exergonic
Reactions that release energy
Synthesis reactions
When atoms, ions, or molecules combine to form new, larger molecules
Anabolism
Synthesis of molecules in a cell
Decomposition reaction
when a molecule is split into smaller molecules, ions or atoms
Catabolism
decomposition reactions in a cell
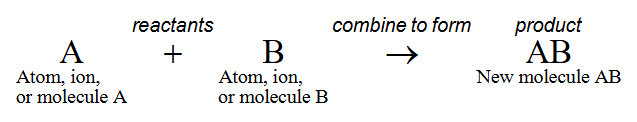
Synthesis Reaction

Decomposition Reaction
Exchange reaction
Part synthesis and part decomposition
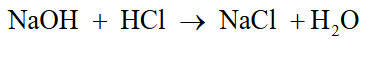
Exchange reaction
Water
Polar molecule, powerful solvent, temperature moderation, cohesive behavior, density
Properties of water that make it essential for life
It is inorganic polar molecule that has an unequal distribution of charges
What happens too an ionic compounds when dissolved in water?
each ion is surrounded by a sphere of water molecules
Acids
Substances that dissociate into one or more hydrogen ions and one or more negative ions
Bases
Substances that dissociate into one or more hydroxide ions and one or more positive ions
Concentration of H+
expressed as pH
What pH do most organisms grow best between?
pH 6.5 and 8.5