A&P1 Ch5 Tissues
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Epithelial Tissue (1)
Avascular [doesn’t have blood vessels]
Little matrix
Cells may show polarity
free apical space and has a basement membrane
Simple squamos Epithelial
Location: lungs, blood+lymphatic vessels
Function: diffusion, filtration,secretion, absorption
Simple Cuboidal Epithelial
Location: liver, kidney tubules, glands/ducts
Function: secretion, absorption, production+movement of mucus
Simple Columnar Epithelial
Location: glands, uterus, uterine tube, stomach intestine
Function: Secretion, absroption, movement [ciliated cells]
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelial
Location: nasal sinuses, trachea, bronchi
Function: synthesize + secrete mucus, moves mucus
[contain cilia]
Transitional Epithelial
Location: lining of the urinary bladder, ureters
Function: protection, allows stretching of the urinary bladder
Stratified Squamos Epithelial
Location: epidermis, oral cavity, esophagus, vagina
Function: resits abrasions, prevents infection, retards water loss
Connective Tissue (2)
abundant in matrix
specialized cells
composed of extracellular protein fibers + ground substance
Loose Connective Tissue
Areolar
Location:under epithelia
Function: cushions organs, holds + conveys tissue fluid
Adipose
White [yellow] fat: most abudant, white at birth and yellows with age.
Brown fat: found in axillae, neck and near kidneys
Reticular
Location: spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, bone marrow
Function: internal skeleton for soft organs
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Tendon [muscles to bones]
Ligaments [bones to bones]
collagen fibers run in parallel + tightly packed
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Location: dermis+sheath, around cartilage + bone
Function: provide strength + resists stress + stata against tearing
Hyaline Cartilage [connective tissue]
Location: Rib cage, trachea, bronchi, end of longs bones
Function: reduces friction at joints+ keeps air passages open
Most common cartilage
Elastic Cartilage [connective tissue]
Location: external ear, epiglottis
Function: maintains shape while allowing flexibility
Fibrocartilage [connective tissue]
Location: knee, jaw, between vertebrae [ where great pressure/stress is applied to joints]
Function: protects from wear and tear at weight-bearing
Spongy Bone [connective tissue]
Location: inside bones, end of bones
Function: reduce weight of bones. act as a shock absorber
Compact Bone [connective tissue]
Location: on periphery of bones
Function: supports + protects organs
Fluid Connective Tissue
Blood
Function: transport gases, nutrients, hormones, water, immunity
Muscle Tissue (3)
specialized for contraction
highly Vascular
Skeletal Muscle
multinucleated cells
Striated Voluntary muscle
Cannont divide
Location: attached to bones
Function: locomotion, facial expression
Cardiac Muscle
Striated INvoluntary muscle
intercalated disc
Cannot Divide
Location: walls of heart
Function: propels blood into circulation
Smooth Muscle
NON-Striated INvoluntary muscle
single nucleus
Can divide +regenerate
Location: wall of hollow organs[stomach, intestines]
Function: propels substances or baby along internal passageways
Nervous Tissue (4)
Conducts electrical impusles
conveys information from one area to another
Neurons
Transmit information
generate action potentials
Neuroglia
support neural tissue
help supply nutrients to neurons
Neural Anatomy
Cell Body
Dendrites
Axon [nerve fiber]
carries info to other neurons
muti,bi, uni polar
Dendrites + Axon = neuron processes
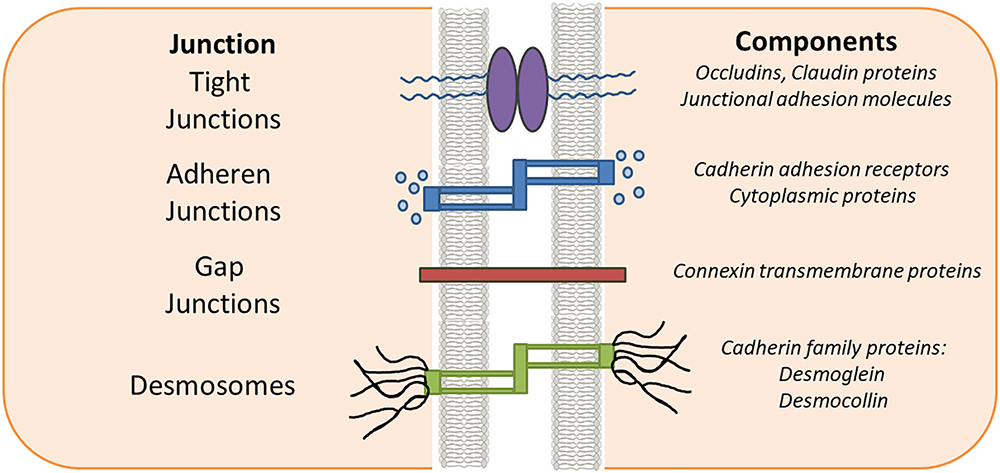
Tight Junction
2 cells are Tighly drawn together with Interlocking Proteins.
Prevents passage of substances between them
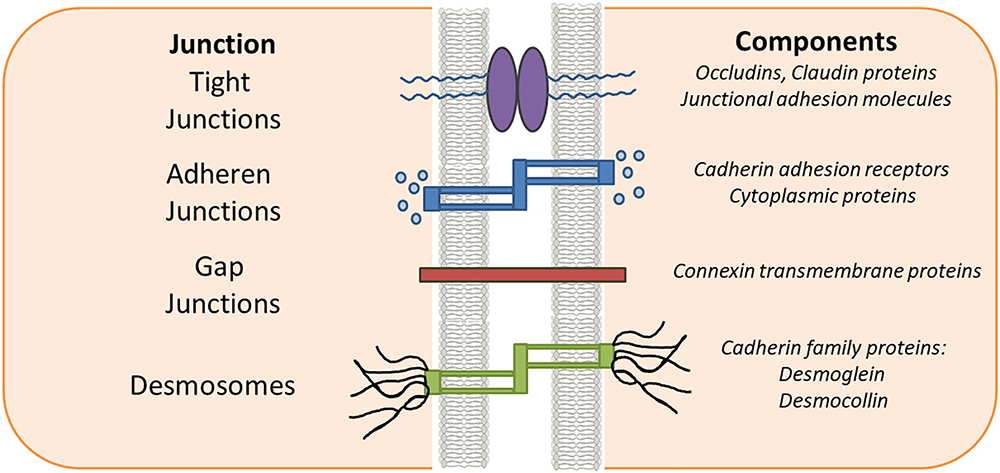
Desmosomes
strong “button like” or “belt like” protein attachments that are hard to break
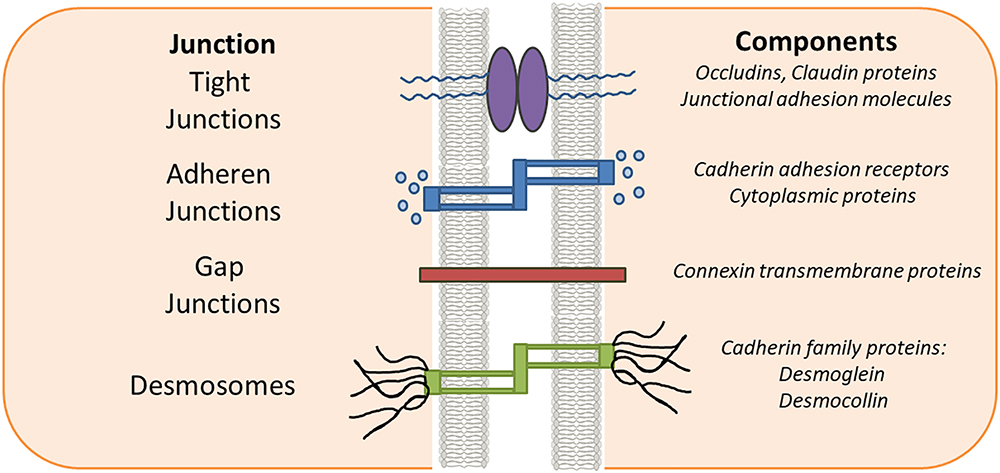
Gap Junctions
2 cells are tightly drawn with proteins that form channels between cells
allow ions + small moelcules to pass between cells
Tissue Growth Terms
Hyperplasia: cellular multiplication, not cellular enlargement
Hypertrophy: cellular enlargement, not cellular multiplication
Neoplasia: abnormal growth of new tissue, tumor
Atrophy: shrinkage of tissue due to age, disuse, disease
Necrosis: pathological tissue death, infection, trauma, hypoxia
Apoptosis: programmed cell deathGa
Exocrine Glands
secrete through ducts onto the body surface or into a cavity [sweat glands]
Endocrine Glands
release hormones into surrounding fluid [adrenal gland]
Merocrine [eccrine]
product released through exocytosis [sweat glands]
apocrine
involves the loss of both product and cytoplasm [milk glands]
holocrine
destroys the cell [sevaceous gland]