regulation of body fluids (#17)
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
🍂
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
homeostasis
process by which an organism maintains a stable internal environment despite external changes;
involves osmoregulation, excretion, & thermoregulation
osmoregulation
regulation of water & solute levels in the body to maintain a constant balance;
essential for preventing dehydration or overhydration, especially in varying environmental conditions
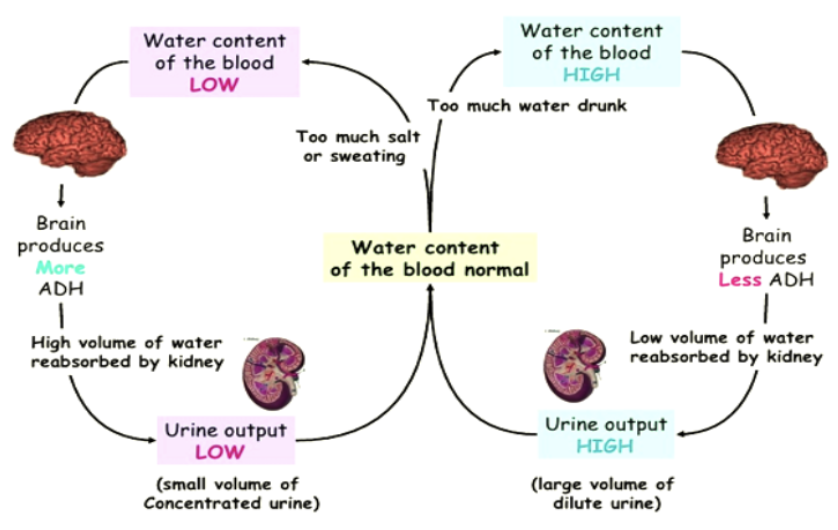
hypothalamus
UNDER OSMOREGULATION:
detects changes in blood water levels and signals the release of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) from the pituitary gland
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
UNDER OSMOREGULATION:
the hypothalamus detects changes in this which increases water reabsorption in the kidneys, leading to concentrated urine when water is scarce, or decreased levels when water is abundant, producing diluted urine
hypoosmotic
UNDER OSMOREGULATION:
refers to area of water with low solute concentration
hyperosmotic
UNDER OSMOREGULATION:
refers to water with high solute concentration
hypoosmotic to hyperosmotic
in osmoregulation, water moves from _____ areas to _____ areas via osmosis
osmoconformers
UNDER OSMOREGULATION:
relating to animal adaptations, these animals match their internal osmotic pressure with the environment
ex. most marine invertebrates like jellyfish
osmoregulators
UNDER OSMOREGULATION:
relating to animal adaptations, these animals actively control internal osmotic pressure
ex. freshwater fish & mammals
excretion
removal of metabolic wastes, such as nitrogenous compounds, from the body to maintain chemical balance
excretion
Without ______, toxic substances like ammonia or urea would accumulate and harm the organism.
Filtration
4 PROCESSES OF EXCRETION:
Blood is filtered in the glomerulus, separating waste from essential substances;
a mass of capiliaries
Reabsorption
4 PROCESSES OF EXCRETION:
Vital nutrients like glucose and water are returned to the bloodstream in the nephron
Secretion
4 PROCESSES OF EXCRETION:
Additional waste products are added to the filtrate
Excretion
4 PROCESSES OF EXCRETION:
Urine containing urea, water, and salts is expelled from the body
Ammonia
UNDER EXCRETION (NITROGENOUS WASTE):
Requires large amounts of water to excrete
ex. in fish
Urea
UNDER EXCRETION (NITROGENOUS WASTE):
Less toxic and water-intensive
ex. in mammals like humans
Uric Acid
UNDER EXCRETION (NITROGENOUS WASTE):
Excreted as a paste, conserving water
ex. in birds & reptiles
ADH
UNDER EXCRETION (KEY HORMONES):
Enhances water reabsorption in the kidneys
Aldosterone
UNDER EXCRETION (KEY HORMONES):
Promotes sodium retention, indirectly increasing water reabsorption
thermoregulation
maintenance of a stable internal body temperature regardless of external changes;
ensures optimal enzyme activity and cellular functions by preventing overheating or excessive cooling
MECHANISMS OF HEAT TRANSFER:
Direct heat transfer
ex. sitting on a cold surface
Convection
MECHANISMS OF HEAT TRANSFER:
Heat transfer through air or water
ex. wind blowing over skin
Radiation
MECHANISMS OF HEAT TRANSFER:
Heat transfer without direct contact
ex. warmth from the sun
Evaporation
MECHANISMS OF HEAT TRANSFER:
Cooling through the transformation of liquid to gas
ex. sweating
Endotherms
THERMOREGULATION IN ANIMALS:
refers to animals who generate heat internally to maintain a constant temperature
ex. humans, birds
Ectotherms
THERMOREGULATION IN ANIMALS:
refers to animals who rely on external sources for body heat
ex. reptiles like lizards
sweating, panting, & vasodilation
these adaptations to heat stress help release heat;
ex. dogs pant to cool themselves on hot days
vasodilation
widening of blood vessels due to the relaxation of the blood vessel's muscular walls;
enhance blood flow to areas of the body lacking oxygen or nutrients, reducing blood pressure
vascoconstriction, shivering, & brown fat thermogenesis
these adaptations to cold stress help retain or generate heat;
ex. polar bears rely on a thick layer of fat & fur to insulate against the cold
vascoconstriction
narrowing (constriction) of blood vessels by small muscles in their walls;
blood flow is blocked
brown fat thermogenesis
when brown fat burns, it creates heat without shivering;
breaks down blood sugar (glucose) and fat molecules to create heat and help maintain body temperature
torpor
UNDER THERMOREGULATION:
state of reduced metabolic activity to conserve energy during extreme conditions
hibernation
TYPES OF TORPOR:
long-term torpor during winter
ex. bears
aestivation
TYPES OF TORPOR:
long-term dormancy during dry or hot conditions
ex. some amphibians
daily torpor
TYPES OF TORPOR:
short-term energy conservation
ex. hummingbirds at night
concentrated urine
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) increases water reabsorption in the kidneys, leading to ______ urine when water is scarce.
diluted urine
As a result of not responding to the ADH signal, there is decreased levels of water reabsorption, leading to _____ urine when water is abundant.
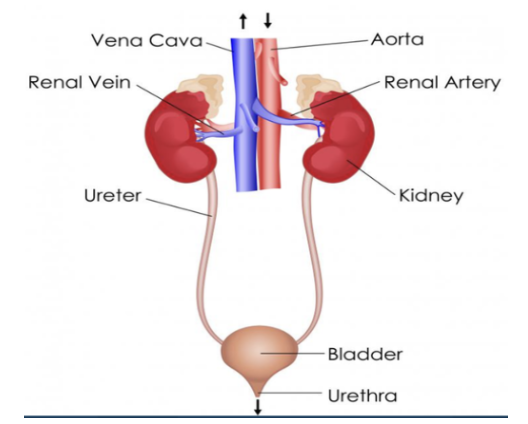
kidneys
body organs which filter blood to remove waste and regulate water and ion levels, forming urine stored in the bladder and expelled through the urethra
maintain electrolyte balance in the body
what is the primary function of osmoregulation?
glomerulus
in the filtration process of urine, where is blood filtered?
nephron
in the reabsorption process, vital nutrients like glucose & water are returned to the bloodstream in the _____?;
functional unit
liver
EXCRETORY SYSTEM:
this organ converts toxic nitrogen waste (ammonia) to less toxic urea.
renal arteries
EXCRETORY SYSTEM:
these carry urea to kidneys
renal veins
EXCRETORY SYSTEM:
the filtered blood collectively exits the kidney through these;
after, wastes proceed to a collecting duct at each nephron
ureters
EXCRETORY SYSTEM:
tubes that exit the kidney & store urine in the bladder, where it waits to be excreted
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
Lungs, skin, large intestine, rectum, anus, & liver are all part of the excretory system.