Plants + Culture Prelim 1
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
4 important uses of plants?
1) Oxygen 2) Medicine 3) Materials (wood, fiber, paper) 4) Food
Approximate number of plant species on Earth?
200,000+
Approximate number of plant species in the Ocean?
8,600
How old is Earth?
4.5 billion years
How far away from the sun is Earth?
3 planets
By the end of what time period did the first photosynthesizing organisms emerge?
Archean
The first organisms were called…
Archaea
Where were archaea found?
Deep-sea hydrothermal vents
What are stromatolites?
Layers of lime-secreting cyanobacteria and trapped sediment.
What is the current Earth eon?
Phanerozoic era
What does eon mean?
An indefinite and very long period of time.
What 2 events characterized the paleozoic era?
1) Explosion in animal life 2) World’s largest mass extinction
What plant species arise during the Ordovician period?
Bryophytes: mosses, hornworts, liverworts
The Devonian period s characterized by…
The diversification of vascular plants; development of roots, leaves, seeds, wood, etc.
During what time period did Pangea take place?
Carboniferous
What plants took over in Permian era"?
Gymnosperm
What plant group took over during the Cretaceous era?
During what era did flowering plants, dicots, and monocots appear?
Cretaceous
Which plant species were the most dominant in most paleoecosystems?
Angiosperms
What are primary producers?
Organisms that are able to create their own food.
What process do plants use to create their own food?
Photosynthesis
What organelles allow plants to carry out photosynthesis?
Chloroplasts
What does photosynthesis produce?
Sugar and O2
How are plants modular?
Their growth is dependent on the repeated production of modules; stems, leaves, roots
How do plants disperse?
Through pollination and attracting dispersers.
Algae are not plants because…
They lack plant structures and don’t have a vascular system.
What are the four algae groups?
Glaucophytes, rhodophytes (red), chlorophytes (green), charophytes
What are the groups of land plants?
Liverworts, hornworts, mosses, ferns, gymnosperms, angiosperms
What is the main ancestor of land plants?
Green algae, chlorophytes
What are the 3 plant lifespans?
Annual, biennial, perennial
What is the life span of annual plant?
Complete growth over one growing season and then die.
What is the life span of biennial plants?
2 growing seasons.
What occurs during the 2 growing seasons of a biennial plant?
1st: Roots, stems, and leaves
2nd: Flowers, fruits, and seeds
What is the life of a perennial plant?
2+ years; annual growth, death, and regrowth
What characterizes herbaceous plants?
Soft, green stems
What characterizes woody plants?
Hard, woody stems
What are the 3 habits of woody plants?
1) shrub 2) vine 3) tree
What is shoot system of plant composed of?
Stem and leaves
What is the root system composed of?
roots
What are the vegetative organs of plants?
Stem, root, and leaf
What are the reproductive organs of plants?
Flower, fruit, seed
What is the function of the stem?
Support, transports, length
What is a node on a stem?
The place where one or more develops
What is the internode on a stem?
The space between two nodes
What are the 3 underground stems?
1) Rhizome 2) Tuber 3) Bulb
Function of underground stems?
Allow plant to survive unfavorable conditions and food storage
Characteristics of rhizomes and examples?
Distinct nodes and internodes, ex. ginger
Characteristics of tuber and examples?
Short and starchy, ex. potato
Characteristics of bulb and examples?
Short with fleshy leaves and layers, ex. onion
Function of sub-aerial stems?
Vegetative reproduction; a clone grows from portion of original plant
What are the 3 sub-aerial stems
1) Runner 2) Stolon 3) Sucker
Function of roots?
Absorption of water, anchor plant to the ground
What is the main root of a plant seedling called that can bear lateral roots?
The tap root.
What is the parenchyma?
Tissue composed of cells that do photosynthesis and store nutrients.
What is the function of leaves?
Main site of photosynthesis
What are the 3 types of leaf arrangement?
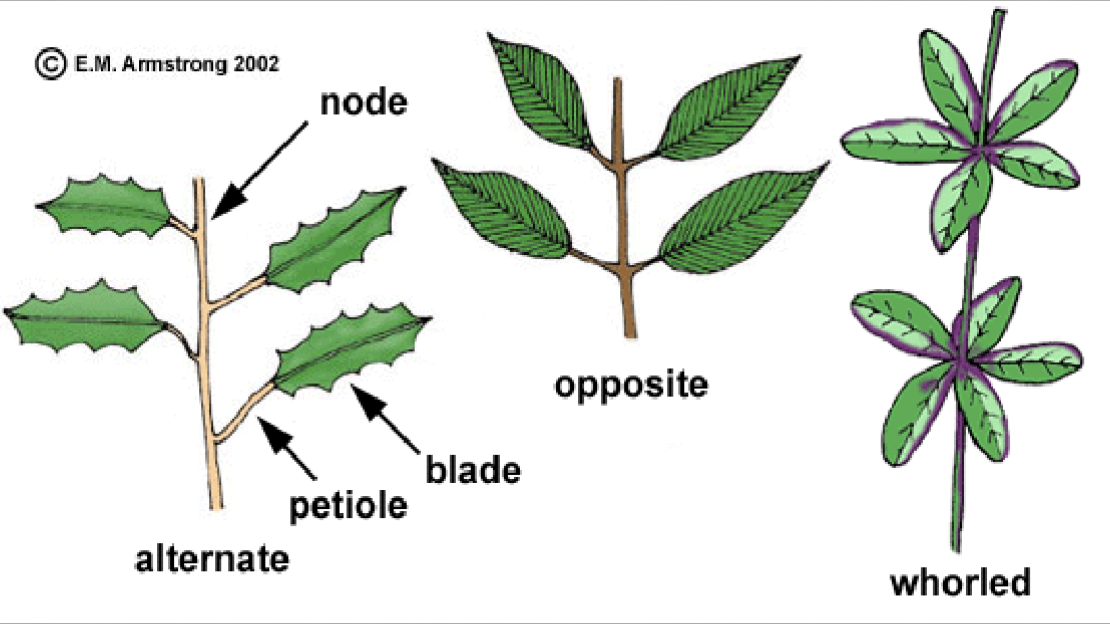
1) Alternate 2) Opposite 3) Whorled
What are the 2 types of leafs?
1) Simple 2) Compound
Function of flower?
Reproductive part of the plant
What is the male part of a flower?
The stamen (consists of long filament and anther, which produces pollen)
What is the female part of a flower?
The pistil (consists of long stye, stigma at the top, and ovary)
What is the flower attached to the plant by?
A pedicle
What are the 3 ovary positions?
1) Hypogyny 2) Epigyny 3) Perigyny

What does the ovary of a plant contain and what is their function?
Contains ovules which contain eggs that after fertilization become cells.
What is a fruit?
A ripened ovary
What is a seed?
A fertilized ovule
What is the body of a fruit called?
The pericarp
What are the layers of the pericarp called?
1) Exocarp (skin) 2) Mesocarp (meat) 3) Endocarp (portion surrounding the seed)
What is parthenocarpy?
The development of fruit without fertilization
What are parthenocarpic fruits?
Fruits that are seedless
Examples of parthenocarpic fruits?
Bananas and pineapples
What are the 2 categories of dry fruits?
1) Dehiscent 2) Indehiscent
What is a dehiscent fruit?
A fruit that splits opens to release its seeds (ex. peas, string beans)
What is a indehiscent fruit?
Fruits that don’t open to release their seeds (ex. nuts)
What are the 2 types of fleshy fruits?
1) Drupe 2) Berry
What are the 3 categories of berries?
1) Pepo 2) Pome 3) Hesperidium
What is an aggregate fruits?
Fruits derived from a cluster of ovaries in one flower
What is a multiple fruit?
A fruit derived from a group of flowers.
What are the two categories of ripening fruits?
1) Climateric fruits 2) Non-climateric fruits
What are climateriic fruits?
Fruits that continue to ripen after being harvested
What are non-climateric fruits?
Fruits that don’t continue to ripen after being picked
What do seeds contain?
An endosperm that provides nutrients for a developing plant
What is the seed coat called?
The testa