molecular diversity, carbon skeletons and isomers
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
hydrocarbons
organic molecules made up of only carbon and hydrogen
hydrogen attach to carbon skeletons
not typically in living systems
properties of hydrocarbons
non-polar (due to long non-polar tails)
release large amounts of energy
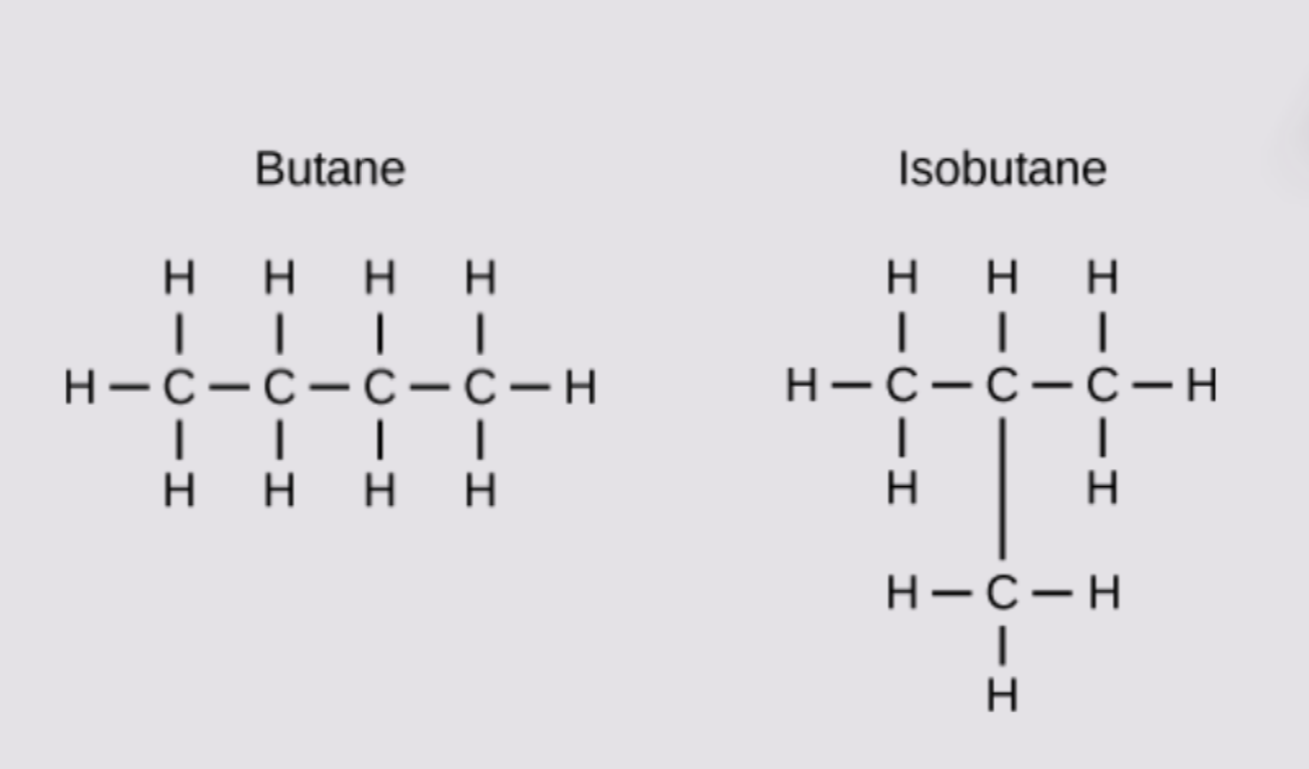
Isomers
compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formula
structural Isomers
same number of atoms but different in covalent arrangement of atoms
cis-trans Isomers
covalent bonds to the same atoms however the arrangements of cis isomers and trans isomers differ
infleibility because of double bonds
why can’t atoms freely rotate in cis-trans isomers?
the double bonds hold the atoms in place, preventing them from moving
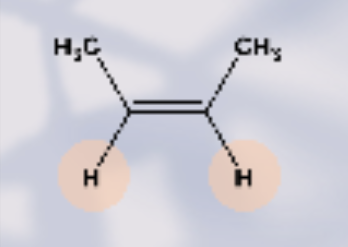
which type of isomer is this?
cis- H2 are parallel
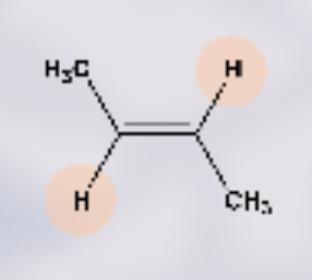
what type of isomer is this?
Trans- H2 are opposite to one another (bent shape double bond)
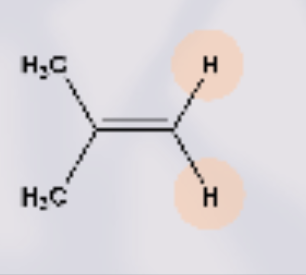
what type of isomer is this?
non- the H atoms are on top of one another
Enantiomers
isomers that mirror images of each other but differ in shape due to asymmetric carbon
asymetric carbon
a carbon attached to four different atoms/groups
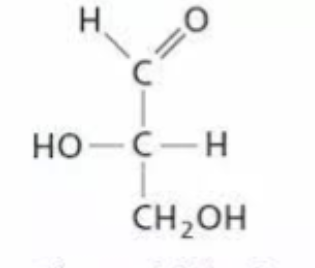
which glyceraldehyde is this
L-Glyceraldehyde - OH on LEFT side
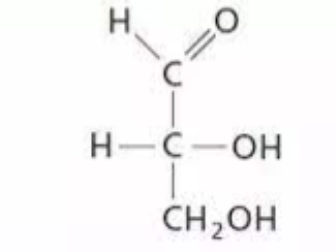
which glyceraldehyde is this
D-glyceraldehyde OH on the RIGHT side
importance of enantiomers
sometimes right vs left enantiomers don’t fit into the same spaces-could cause severe side effects such as with certain medication (one enatiomer can treat an illness while the other causes other problems)
one isomer is biologically active and binds to specific molecules in an organism
Functional Groups
atoms/groups of atoms attached to a molecule giving the molecule partificular chemical and physical properties
e: The presence of a carboxyl or hydroxyl group will make a molecule polar
Hydroxyl
chemical formula: ROH
Found in: carbs, lipids, melic acid →fruits
compound name: alcohol (ending in -ol)
example: ethanol
properties:
polar (electronegative O2)
hydrogen bond w/ water
dissolves compounds such as sugars

Carbonyl
names:
ketone (compound w/carbonyl skeleton within) RCOCR
sugars with ketone =ketoses
aldehyde(compound w/carbonyl skeleton at end) RCOH
sugars with aldehydes =aldoses
Found in: carbs (straight)

Carboxyl
Chemical Formula : RCOOH
properties:acts like an acid b/c of covalent bond of O2 and H2 (polar)/can donate H
Compound name: Carboxylic acid or organic acid
found in : proteins, lipids
example: Acetic acid gives vinegar sour taste

Amino
chemical name : RNH2
Properties: acts as a base - picks up H2 from surrounding solutions
compound name: amine
found in: proteins, lipids
ex: glycine

sulfhydryl
chemical name: -sH
Properties:
two sh can react to form cross-link (stabilize protein)
in hair maintains hair type (salon treatment breaks cross-link)
compound name: thiol
found in: proteins
e: cysteine

Phosphate
chemical formula: (-OPO3)²
found in: nucleic acids, lipids
properties:
-1 when inside chain of phosphates
-2 when at the end of chain of phosphates
helps molecule react w water and release energy
compound name : organic phosphate

Methyl
chemical formula : COOC
Properties:
affects the epression of genes when on DNA/bound to DNA
affects shape and function of se hormones
found in: lipids
compound name: Methylated compound

how does methyl group differ from the other six functional groups?
not reactive - a biological tag on molecules to help recognise them
why is sulfhydryl different from others?
it is hydrophobic
ATP
adenosine triphosphate → storing potential to react with water
one phosphate splits off when ATP reacts with water (becomes ADP)
→that reaction realise energy that is used by the cell
Ester
chemical formula: RCOOC
found in lipids and nucleic acids