Drugs Used in the Treatment of Pain and Affecting the Musculoskeletal System: Part 2
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
◦Large and chemically diverse group of drugs with the following properties:
◦Analgesic
◦Antiinflammatory
◦Antipyretic
◦Aspirin-platelet inhibition
Properties all NSAIDs share:
◦Antipyretic
◦Analgesic
◦Antiinflammatory
◦NSAIDs are also used for the relief of:
◦Mild to moderate headaches
◦Myalgia
◦Neuralgia
◦Arthralgia
◦Alleviation of postoperative pain
◦Relief of the pain in arthritic disorders
◦Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), juvenile arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and osteoarthritis (OA)
◦Treatment of gout and hyperuricemia
ANYTHING CAUSING PAIN AND INFLAMMATION
◦Acetic Acid Derivatives
◦indomethacin (Indocin)
◦ketorolac (Toradol)
◦diclofenac sodium (Voltaren)
◦Cyclooxgenase-2 Inhibitors
◦celecoxib (Celebrex)
◦Enolic Acid Derivatives
◦meloxicam (Mobic)
◦Propionic Acid Derivatives
◦naproxen (Naprosyn, Aleve)
◦ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil, others)
◦Salicylates
◦aspirin
◦diflunisal (Dolobid)
NSAIDs: Mechanism of Action
◦Inhibition of the leukotriene pathway, the prostaglandin pathway, or both à blocking the chemical activity of cyclooxygenase (COX)
COX1/COX2 whats the difference
◦Cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1)
◦Maintains normal lining of the stomach (gastrointestinal mucosa)
◦Involved in kidney and platelet function
◦Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)
◦Present primarily at sites of inflammation
aspirin effects
◦Irreversible inhibitor of COX-1 receptors within the platelets à reduces formation of thromboxane A2 (substance that promotes platelet aggregation)
◦Other NSAIDs lack these antiplatelet effects
-why it causes stomach pain
-aspirin especially causes tinnitus
NSAID Contraindications
◦Known drug allergy
◦Clients with documented aspirin allergy must not receive NSAIDs
◦Conditions that place the client at risk for bleeding:
◦Vitamin K deficiency
◦Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)
NSAID INTERACTIONS
◦Serious interactions can occur when given with:
◦Anticoagulants and aspirin: increased risk of bleeding
◦Corticosteroids and other ulcerogenic drugs: increased risk of GI ulceration
◦Protein bound drugs such as warfarin, sulfonylureas, methotrexate
◦Diuretics
◦Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: NSAIDs block production of vasodilator/natriuretic prostaglandins; hyperkalemia, bradycardia à syncope
NSAIDs: FDA-Required Warnings (Black Box Warnings)
-cv risk
◦Increase risk for serious CV thrombotic events, myocardial infarction (MI), and stroke
◦Contraindicated in treatment of perioperative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery
-GI risk
◦Increased risk for serious GI adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines
◦Older adults are at greatest risk of serious GI events
NSAID ae
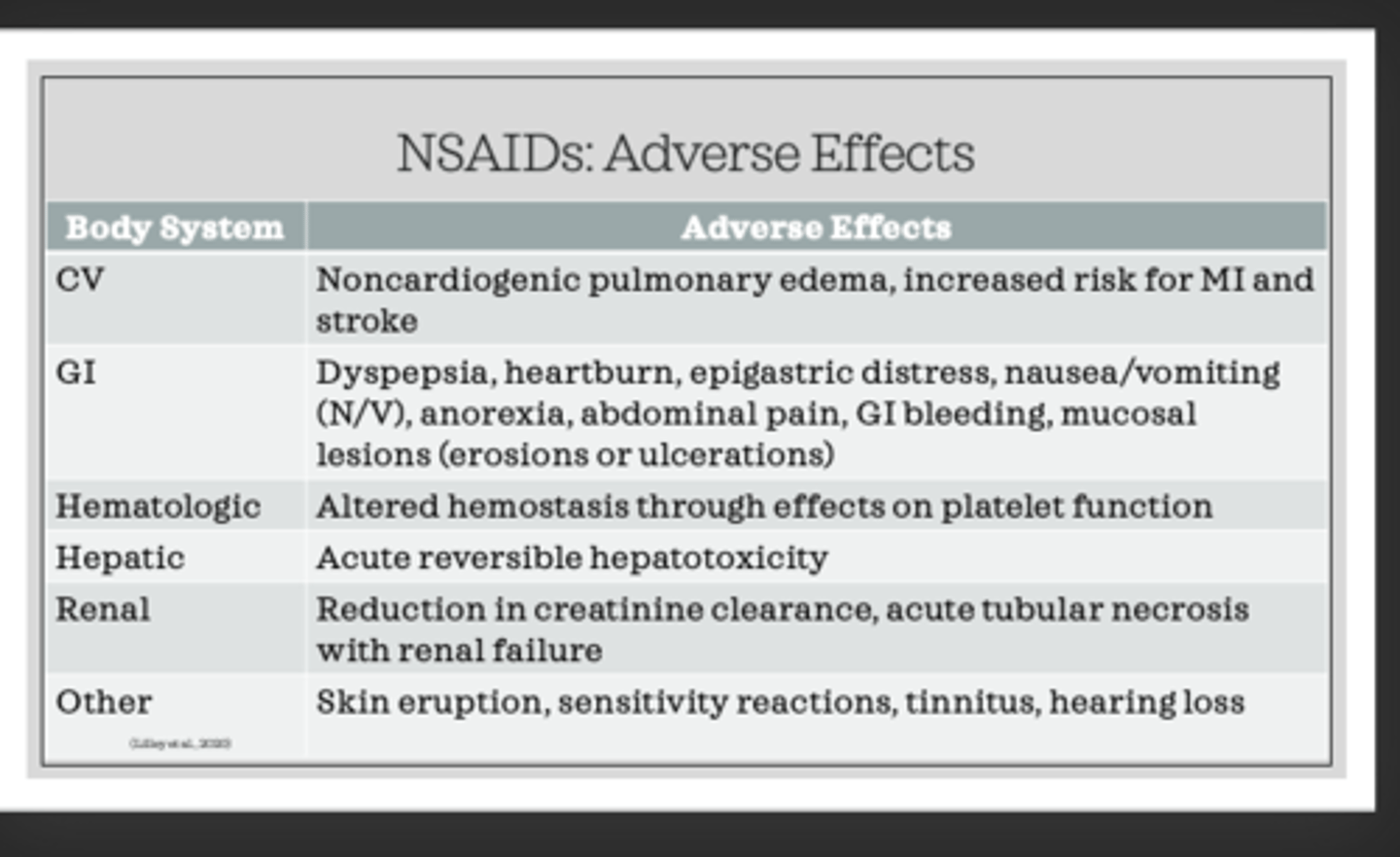
NSAIDs and Renal Function
◦Renal function depends partly on prostaglandins
◦Disruption of prostaglandin function by NSAIDs is sometimes strong enough to precipitate acute or chronic renal failure
◦Use of NSAIDs can compromise existing renal function
◦Renal toxicity can occur in clients with dehydration, heart failure, liver dysfunction, or use of diuretics or ACE inhibitors
Acetic Acid Derivatives: indomethacin (Indocin
◦Uses: RA, OA, acute bursitis or tendonitis, ankylosing spondylitis, acute gouty arthritis, and treatment of preterm labor
◦Promote closure of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), a heart defect that sometimes occurs in premature infants
◦Oral, rectal, intravenous (IV) use
Acetic Acid Derivatives: ketorolac (Toradol)
◦Some antiinflammatory activity
◦Used primarily for its powerful analgesic effects (comparable to narcotic drugs)
◦Indication: Short-term use (up to 5 days) to manage moderate to severe acute pain
◦Adverse effects: Renal impairment, edema, GI pain, dyspepsia, and nausea
COX-2 Inhibitors: celecoxib (Celebrex)
◦First and only remaining COX-2 inhibitor
◦Indicated: OA, RA, acute pain symptoms, ankylosing spondylitis, and primary dysmenorrhea
◦Adverse effects: Headache (HA), sinus irritation, diarrhea, fatigue, dizziness, lower extremity edema, and hypertension (HTN)
◦Little effect on platelet function
◦NOT to be used in clients with known sulfa allergy
◦nabumetone (Relafen)
•Better tolerated by GI system than other NSAIDs
•Used for OA and RA
◦meloxicam (Mobic)
◦piroxicam (Feldene)
•Used to treat OA, RA, and gouty arthritis
Propionic Acid Derivatives
◦ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil, others) more short term, every 2-4 hrs
◦naproxen (Naprosyn, Aleve): extended release q12 hrs or daily
◦Uses: Analgesic effects in the management of RA, OA, primary dysmenorrhea, gout, dental pain, musculoskeletal disorders, antipyretic actions(used in patients who catch fever with tylenol)
Salicylates
◦Inhibits platelet aggregation
◦Antithrombotic effect: Used in the treatment of MI and other thromboembolic disorders
-aspirin only given if you have an actual issue, NOT given if you are at RISK
salicylates indications
◦HA, neuralgia, myalgia, arthralgia
◦Pain syndromes as a result of inflammation: Arthritis, pleurisy, pericarditis
◦Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
◦Antipyretic action
Salicylate Toxicity
◦CV: Increased heart rate (HR)
◦Central nervous system (CNS): tinnitus, hearing loss, dimness of vision, HA, dizziness, mental confusion, lassitude, drowsiness
◦GI: N/V, diarrhea
◦Metabolic: sweating, thirst, hyperventilation, hypo- or hyperglycemia
-get blood level
Aspirin: Reye's Syndrome
◦Acute and potentially life-threatening condition involving progressive neurologic deficits that can lead to coma and may also involve liver damage
◦Triggered by viral illnesses such as influenza as well as by salicylate therapy itself in the presence of a viral illness
◦Survivors of this condition may or may not have permanent neurologic damage
◦Do not give to children and teenagers
aspirin allergy
-GI bleed but can give only if having an MI bc risk is outweighed by benefit
◦Do not give to children and teenagers
aspirin
GOUT
◦Gout: condition that results from inappropriate uric acid metabolism
◦Underexcretion of uric acid
◦Overproduction of uric acid
◦Uric acid crystals are deposited in tissues and joints, resulting in pain
◦Hyperuricemia
Antigout Agents: Indications
-ALLOPURINOL
-POBENACID
◦allopurinol (Zyloprim)
◦Prevents uric acid production
◦Prevents acute tumor lysis syndrome
◦probenecid
◦Inhibits the reabsorption of uric acid in the kidneys à increases the excretion of uric acid
◦Must have good renal function
◦colchicine
◦Reduces inflammatory response to the deposits of urate crystals in joint tissue
◦Used for short-term management or prevention of gout
◦For acute gout:
◦Initial dose of 0.6-1.2 mg, followed by 0.6 mg/hr until:
◦Pain is relieved
◦Severe nausea and diarrhea occur
◦Total of 6 mg has been administered
◦May cause short-term leukopenia and bleeding into the GI or urinary tracts
◦lesinurad (Zurampic)
◦Uric acid transporter inhibitors
◦Inhibits the transporter proteins involved in renal uric acid reabsorption resulting in lower serum uric acid levels and increase renal clearance of uric acid
◦Given in combination with xanthine oxidase inhibitor (allopurinol)
◦Teaching: Intake of at least 2 liters of fluid a day
Herbal Products: Glucosamine and Chondroitin
◦Used to treat the pain of OA
◦Adverse Effects
◦GI discomfort
◦Drowsiness, headache, skin reactions (glucosamine)
◦Drug Interactions
◦Enhances effects of warfarin (Coumadin)
◦May increase insulin resistance (glucosamine)
Nursing Considerations
◦Before beginning therapy, assess for conditions that may be contraindications to therapy, especially:
◦GI lesions or peptic ulcer disease (PUD)
◦Bleeding disorders
◦Assess for conditions that require cautious use
◦Perform laboratory studies as indicate:
◦Cardiac, renal, and liver function studies
◦Complete blood count (CBC)
◦Platelet count
Nursing Considerations (cont'd)
◦Perform a medication history to assess for potential drug interactions
◦Several serious drug interactions exist
◦Because these drugs generally cause GI distress, they are often better tolerated if taken with food, milk, or an antacid to avoid irritation
◦Explain to clients that therapeutic effects may not be seen for 3 to 4 weeks
◦Educate clients about the various adverse effects of NSAIDs, and inform them to notify their prescriber if these effects become severe or if bleeding or GI pain occurs
◦Inform clients to watch closely for the occurrence of any unusual bleeding
◦Advise clients that enteric-coated tablets should not be crushed or chewed
◦Monitor for therapeutic effects, which vary according to the condition being treated
◦Decrease in swelling, pain, stiffness, and tenderness of a joint or muscle area
◦Categories: for osteoporosis
◦Bisphosphonates
◦Selective estrogen receptor modifiers (SERMs)
◦Hormone Replacement
-must have caLCIUM AND VIT D
Bisphosphonates MOA and examples
alendronate
◦risedronate (Actonel)
◦zoledronic acid (Zometa, Reclast)
◦Work by inhibiting osteoclast-mediated bone resorption = indirectly enhances bone mineral density = preventing bone loss
◦Can reverse lost bone mass and reduce fracture risk
Bisphosphonates: Contraindications & Cautions
-hypocalcemia
-Inability to sit or stand upright for at least 30 minutes after taking the medication
-older adults at risk for femoral fractures, can happen without trauma and happen even during medication regime
-use with cautions in breast feeding
Bisphosphonates: Adverse Effects
-GI irritation (drink full glass of water)
-blurred vision
-eye pain
-occular inflammation
-osteonecrosis of the jaw (see dentist prior to taking)
-bone pain/joint pain (take analgesic)
Bisphosphonates can be given IV
monitor pt especially if they have kidney issues have high risk for toxicity
-check phosphorus levels (will be low due to decreased bone resorption ocurring none being released during bone resorption)
Bisphosphonates: Nursing Considerations
◦Ensure that clients have no esophageal abnormalities and can remain upright or in a sitting position for 30 minutes after the dose
◦Instruct clients to take medication upon rising in the morning, with a full glass of water, and 30 minutes before eating.
◦Emphasize that clients must sit upright for at least 30 minutes after taking the medication
-long half life: if the patient misses a dose it will not affect them badly
-taken daily or once a week
-monitor bone density every 8-12 months
-check calcium in blood(9-10.5)
alendronates decreased resorption with
-iron
-mag
-antacids
-orange juice
-caffeine
-wait two hours after given to have any of these
expected effects
=increased bone density
-no fractures
-increased calcium
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modifiers (SERMs) MOA and ex
◦Stimulate estrogen receptors on bone and increase bone density
◦Examples
◦raloxifene (Evista)
◦tamoxifen (Nolvadex)
◦Indications
◦Prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
◦Stimulate estrogen receptors on bone and increase bone density
serm contraindications
◦Venous thromboembolic disorder or history
◦Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
◦Pulmonary embolus (PE)
◦Retinal vein thrombosis
nursing consideration SERM
Nursing Considerations: Instruct clients that the medication will need to be discontinued 72 hours before and during any prolonged immobility (such as surgery or a long trip)
-STOP 10 mins every hour to prevent DVT
-if gonna have surgery as well
SERM AE
◦Hot flashes
◦Leg cramps
◦Increase risk of venous thromboembolism
Hormone Replacement: Calcitonin. moa AND indications
◦Indications: Treatment of osteoporosis
◦Mechanism of Action: Directly inhibits osteoclastic bone resorption
-give additional
-given IM, SC, iontranasal
calcitonin contraindication
-allergic to fish protein and salmon
nasal prep used for
patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis
-inspect nares for ulceration bc can cause nasal drynness
AE
hypocalcemia
dry nose
-decreased lithium levels
flushing
N/D
Hormone Replacement: Teriparatide (Forteo)
◦Mechanism of action: Stimulates bone formation
◦Contraindications: Known drug allergy
AE
◦Chest pain
◦Dizziness
◦Hypercalcemia
◦Nausea
◦Arthralgia