AP Biology: Animal Behavior
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/37
Last updated 1:27 AM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
Ethology
study of animal behavior

2
New cards
Behavior
what an animal does and how it does it
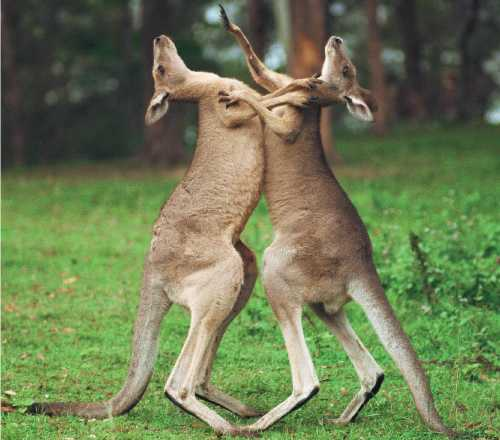

3
New cards
Instinct (Innate) Behavior
behaviors that are inherited

4
New cards
Kinesis
random movement of animal in relation to stimulus; the stimulus causes an alteration in rate or direction of activity or movement.
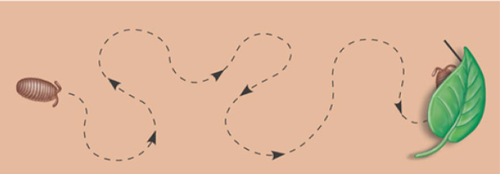
5
New cards
Fixed-action Patterns
sequence of unlearned acts that are unchangeable and usually continue until they are completed
6
New cards
Signal
stimulus that causes change in behavior
7
New cards
Learned Behaviors
Behaviors that are modified based on specific experiences
example: nest building
example: nest building

8
New cards
Habituation
loss of responsiveness to stimuli with little or no meaning; animal can ignore meaningless stimuli

9
New cards
Associative Learning
ability to connect one stimulus with another

10
New cards
Classical Conditioning
arbitrary stimulus associated with particular outcome
example: training a dog
example: training a dog
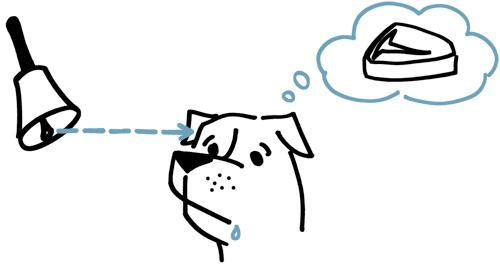
11
New cards
Operant Conditioning (trial and error)
when faced with two choices, an organism can learn to choose the option with the best reward.
example: students who study to improve their grades
example: students who study to improve their grades
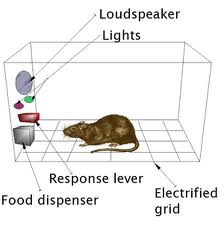
12
New cards
Cognition
process of knowing that involves awareness, reasoning, recollection, and judgement

13
New cards
Social Learning
learning by observing others

14
New cards
Altruism
engaging in behavior that doesn't help you, but helps rest of population (selfless)

15
New cards
Inclusive Fitness
total effect of producing offspring and helping relatives

16
New cards
Kin Selection
altruistic behavior that enhances reproductive success of relatives

17
New cards
Agonistic Behavior
threats, rituals, and combat; settles disputes over resources, asserting dominance
18
New cards
Foraging
food obtaining behavior

19
New cards
Sexual Selection
seeking and attracting mates/choosing and competing for males

20
New cards
Pheromones
Chemical signals

21
New cards
Suckling
A mammal is born knowing how to nurse.
example: pig suckling at birth
example: pig suckling at birth

22
New cards
Imprinting
Some baby bird species will follow the first moving object they see usually the mother.
example: ducks
example: ducks

23
New cards
Migration
organisms move from one place to another periodically, generally in response to temperature or food availability.
example: geese, monarch butterflies
example: geese, monarch butterflies

24
New cards
Hibernation
An organism goes dormant for a long period of time to escape cold temperatures
example: bears, chipmunks, frogs
example: bears, chipmunks, frogs

25
New cards
Estivation
An organism goes dormant for a long period of time to escape hot temperatures.
example: African bullfrog, fringe toed lizard, turtle
example: African bullfrog, fringe toed lizard, turtle

26
New cards
Positive Chemotaxis
An organism responds to a chemical by moving towards it.
example: male cockroach pheromones attract females
example: male cockroach pheromones attract females

27
New cards
Negative Chemotaxis
An organism responds to a chemical by moving away from it.
example: the smell of a skunk repels other animals
example: the smell of a skunk repels other animals

28
New cards
Positive Phototaxis
An organism responds to light by moving towards it.
example: moths to a light
example: moths to a light

29
New cards
Negative Phototaxis
An organism responds to light by moving away from it.
example: moles live underground
example: moles live underground

30
New cards
Mutualism
Both species benefit
example: bee and flowers
example: bee and flowers

31
New cards
Commensalism
One species benefits and the other is unaffected
example: whale and barnacle
example: whale and barnacle

32
New cards
Parasitism
one species benefits and the other is harmed
example: dog and flea
example: dog and flea

33
New cards
Intra-specific Competition
occurs among organisms of same species
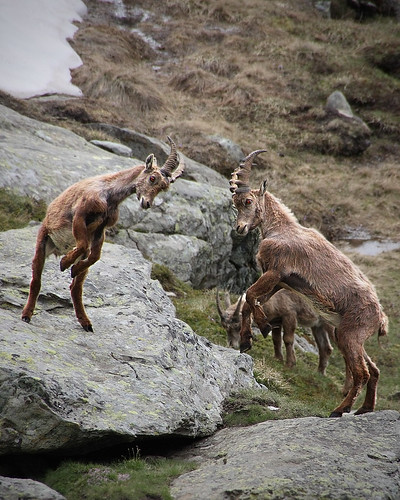

34
New cards
Inter-specific Competition
Occurs among organisms of different species
example: competition between hyenas and lions for a dead zebra
example: competition between hyenas and lions for a dead zebra

35
New cards
Resource Partitioning
Species consume slightly different foods or use other resources in slightly different ways
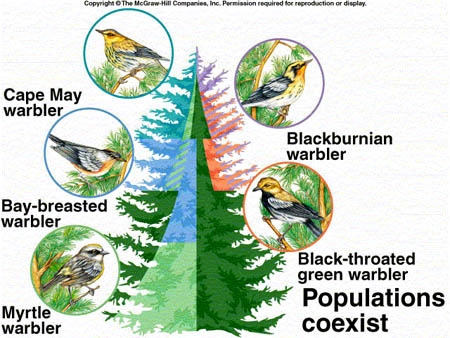
36
New cards
Aposematic Coloration
"stay away" color
example: black widow's red underbelly
example: black widow's red underbelly

37
New cards
Batesian Mimicry
Mimicking a poisonous organism's coloring

38
New cards
Disruptive Coloring
Obscures size/shape of an organisms body
example: zebras's stripes
example: zebras's stripes
