Lecture 3: The lean start-up method
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Describe why early market engagement is important for startups
Early market engagement is crucial for start-ups to: Validate Product-Market Fit: Understand whether the product solves a real customer problem.
Identify Pain Points: Gain insights into customer preferences, challenges, and willingness to pay.
Reduce Risks: Avoid costly missteps by testing assumptions and iterating based on real-world feedback.
Explain Boo.com
Boo.com, an online fashion retailer, failed to engage with the market early. Their lack of early market engagement resulted in several critical missteps that ultimately led to their failure:
Overestimating Customer Readiness
Expensive and Overly Ambitious Rollout
Misunderstanding Customer Preferences
Explain Overestimating Customer Readiness in the Boo.com case
Boo.com misjudged their audience's technical capabilities. At the time of their launch, only 1% of potential customers had high-speed internet, making their website's sophisticated design slow and inaccessible to most users.
Furthermore, the website excluded Mac users, excluding a segment of the market.
What could Boo.com do to prevent Overestimating Customer Readiness
If Boo.com had conducted early market engagement, they would have identified these limitations, such as the lack of widespread high-speed internet—a critical complementary asset—and adjusted their product accordingly.
Explain Expensive and Overly Ambitious Rollout in the Boo.com case
Instead of starting small and iterating, Boo.com launched simultaneously in multiple markets, having high operational costs for a product that had not been validated.
What could Boo.com do to prevent Expensive and Overly Ambitious Rollout
It is key to start with a minimal viable product (MVP), focusing on basic functionality and testing customer reception before scaling.
Explain Misunderstanding Customer Preferences in the Boo.com case
Boo.com failed to test customer reactions to elements of their product, such as "Miss Boo," their virtual shopping assistant, which customers found irritating, but was their key selling point to investors.
What could Boo.com do to prevent Misunderstanding Customer Preferences
Through iterative engagement with users, they could have gathered feedback on these features, and pivot to better meet customer needs.
In general what could Boo.com could have done differently
Start small with a functional MVP, testing core features to gather feedback and improve iteratively.
Conduct surveys or interviews to understand customer needs, technical readiness, and preferences.
Test the product in a single market to identify potential flaws before scaling.
Explain the product development approach of Netscape Navigator/Myo
The product development approaches of Netscape Navigator and Myo reflect iterative, user-centric strategies that align with the Lean Start-Up (LSU) method, emphasizing rapid prototyping, customer engagement, and efficient resource use.
Both Netscape and Myo adopted iterative processes to develop their products: Frequent Prototyping User-Centric Development Risk Mitigation
Explain Frequent Prototyping in the development approach of Netscape Navigator/Myo
Netscape released multiple beta versions, while Myo progressed from low-cost prototypes to high-fidelity versions. These iterations allowed both companies to test assumptions and refine their products incrementally based on user feedback.
Explain User-Centric Development in the development approach of Netscape Navigator/Myo
By actively engaging customers during development, Netscape identified market needs and usability issues, while Myo validated core functionality and adjusted features to align with user expectations.
Explain Risk Mitigation in the development approach of Netscape Navigator/Myo
Netscape minimized wasted effort by overlapping development phases, and Myo postponed significant capital expenses to preserve value and reduce financial risks.
Explain the reasons why the Netscape and Myo's strategies closely align with the Lean Start-up method
Agile Development: LSU advocates for iterative and incremental development, eliminating wasted resources. Netscape and Myo followed this approach by continuously testing and refining their products.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP): Both companies embraced the MVP concept—developing basic versions of their products to validate ideas before full-scale deployment.
Customer Feedback: Early and frequent engagement with users allowed both companies to adapt their offerings to real-world needs, reducing uncertainty and improving market alignment.
Value Preservation: both Netscape and Myo adhered to LSU's principle of minimizing financial risk while maximizing learning.
What are the 3 key principles of the LSU method
Build, measure, learn
The Lean Start-Up (LSU) method emphasizes a hypothesis-driven, customer-focused, and iterative approach to product development. It enables entrepreneurs to minimize risks, optimize resources, and adapt quickly to market feedback. Its process revolves around three key principles: Build, Measure, and Learn.
Explain Build as a key principle of the LSU method
Entrepreneurs begin with a series of hypotheses or assumptions about their product, customers, and market.
The goal is to develop a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to test these hypotheses as quickly and cost-effectively as possible.
The MVP allows for early experimentation, reducing wasted time and resources by focusing only on what's essential for learning.
What is a minimum viable product (MVP)
A simplified version of the product with essential features (prototype)
Explain Measure as a key principle of the LSU method
Once the MVP is introduced to the market, entrepreneurs gather data on customer responses to validate (or invalidate) their assumptions.
The data collected doesn't need to be perfect; it needs to be "good enough" to enable actionable insights. Testing must happen quickly to ensure the product evolves in real time with market needs.
Methods such as analogs/antilogs, interviews, and controlled experiments are used to measure outcomes and refine strategies.
Explain Learn as a key principle of the LSU method
Entrepreneurs use the feedback and evidence gathered during the measurement phase to refine or pivot the product.
Access to expertise, such as through accelerators or mentors, is crucial for interpreting feedback effectively and making informed decisions for future iterations.
Why do some entrepreneurs prefer stealth mode instead of the LSU method?
Fear of Criticism: Entrepreneurs may be uncomfortable showcasing an underdeveloped product and wish to avoid negative feedback or confrontation during the early stages.
Concern About Idea Theft: Entrepreneurs often worry that revealing their product prematurely might enable competitors to replicate or improve upon their idea, especially in highly competitive industries.
What are the mechanisms to seek evidence
analogs/antilogs, interviews, and experiments
Explain analogs/antilogs as a mechanism to seek evidence
Analogs/antilogs are evidence of something that has worked/failed elsewhere, transposed to another context.
By studying analogs and antilogs, entrepreneurs can identify patterns, adapt proven strategies, and avoid repeating past mistakes.
Competition, for instance, is not a threat but a source of evidence. Markets with competitors often indicate demand, while a lack of competition might signal potential issues with market feasibility
What is an example of analogs/antilogs
Airbnb's Use of Analog and Antilog
Analog:When Airbnb was pitching its business model to early investors, it cited eBay as an analog.
Why?: eBay had successfully built a marketplace that connected buyers and sellers, proving that trust could be established between strangers for online transactions. Airbnb used this example to argue that a similar marketplace could work for homeowners and travelers.
Antilog:At the same time, Airbnb highlighted Craigslist as an antilog.
Why?: While Craigslist allowed people to list rental properties, it lacked a secure payment system, customer service, and trust-building mechanisms (e.g., verified profiles and reviews). Airbnb positioned itself as solving these issues, creating a safer and more reliable platform.
Explain Interviews as a mechanism to seek evidence
Interviews involve engaging directly with potential customers or users to gather qualitative insights into their problems, preferences, and needs.
What are important things to remember when doing interviews
Preparation: Segment customers and create personas to ensure a targeted approach. Plan questions carefully, focusing on what you want to learn.
Ask open-ended questions and focus on understanding the problem first before discussing solutions. For example, ask, "What challenges do you face in this area?" instead of "Would you use this product?"
Active Listening: Avoid trying to sell the idea during interviews; the goal is to learn, not to pitch. For example: In the movie The Wolf of Wall Street, a salesperson asks someone to "sell me this pen." The lesson here is to avoid focusing on the product itself and instead ask about the customer's needs, such as whether they're looking for a pen.
Explain Experiments as a mechanism to seek evidence
Experiments involve testing assumptions through prototypes and hands-on trials to observe real-world responses and validate ideas quickly and cost-effectively.
Prototyping techniques are for example rough sketches, simple applications or mock-ups.If experiments reveal flaws in the initial assumptions, entrepreneurs should pivot by iterating the design or exploring alternative approaches.
What is an example of experiments
A start-up developing an intelligent pillbox for elderly users began by creating a foam prototype. This low-cost prototype allowed users to test shapes and suggest functionalities, ensuring the product met their needs before further investment.
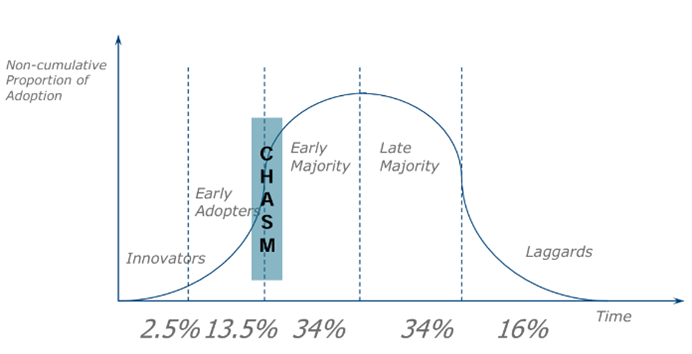
What is crossing the chasm
Early adopters are excited by innovation and willing to experiment, but the mainstream market demands a well-defined product that solves a clear problem. Many entrepreneurs struggle to navigate this shift, known as "crossing the chasm."
Explain how the LSU-method is related to the concept Crossing the Chasm
The LSU framework addresses this challenge by employing the Build-Measure-Learn (BML) cycle, which enables rapid validation of hypotheses, iterative improvements, and data-driven pivots. The method's focus on frequent iterations ensures that startups adapt their offerings to market needs, making it easier to transition from early adopters to the mainstream.
Explain how the LSU-method is related to the concept of firm value creation over time
LSU allows startups to increase firm value in a short timeframe without requiring massive investment. Additionally, by the time external funding is necessary, startups have greater bargaining power due to demonstrated traction.
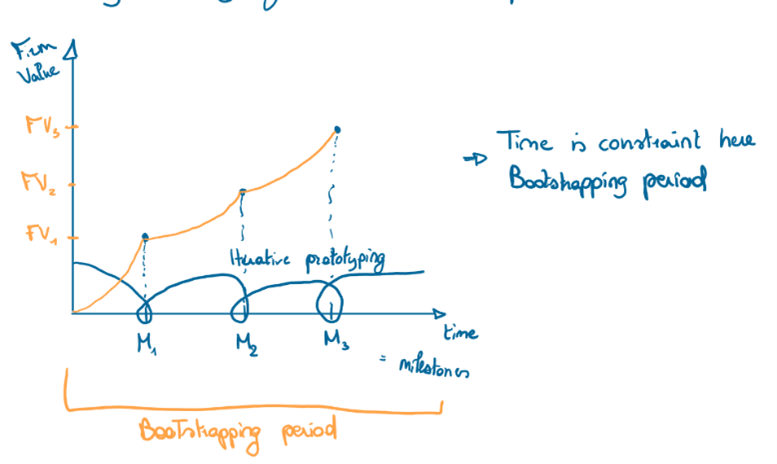
What is the boundary for the LSU process
The boundary of this process is the bootstrapping period, typically 14-18 months, when entrepreneurs rely on their own resources and savings. By effectively managing this period, startups can delay raising external investment until they have maximized their value and negotiating position.