Biology Midterm 2 L15-L19
1/86
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Plants vs fungi vs animals
Plants - cell walls, autotrophy (carbon source), phototrophy (energy source)
Fungi - cell walls, heterotrophy, chemotrophy, absorption
Animals - mobile cells, heterotrophy, chemotrophy, ingestion
Fungi
Yeasts, molds, mushrooms
Cell walls made of chitin
Opisthokont: "posterior flagellum" - most current specieis lack flagella
Make hyphae: single-cell thick tubes
Extend into environment --> secrete digestive enzymes --> absorb nutrients
Mycelium: dense network of hyphae
Spores --> colonize new environments
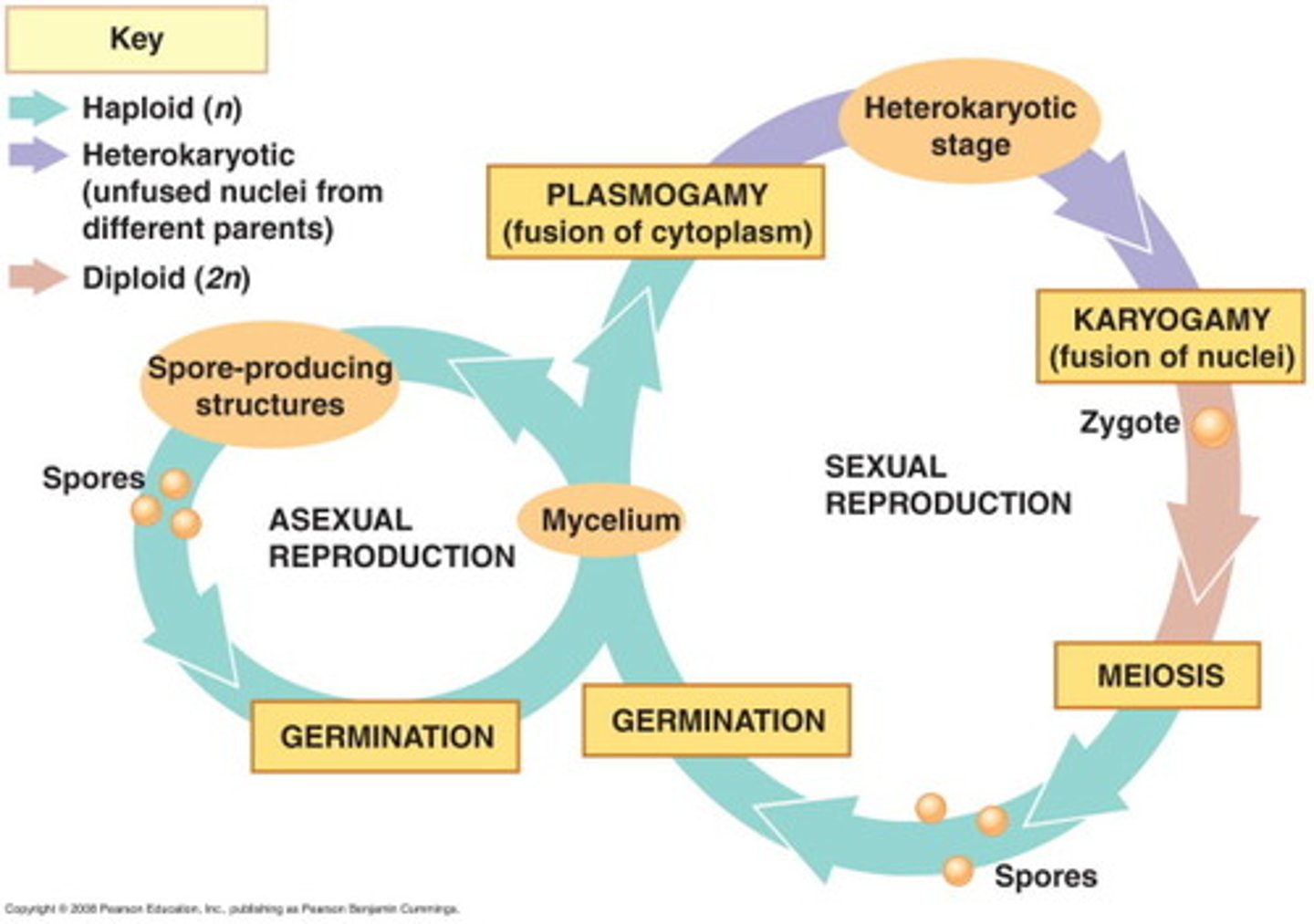
Asexual reproduction
Dominated by haploid gametophyte
Heterokaryote
When 2 mycelia fuse
2 separate genomes sharing an organism
Not diploid
--> genetic diversity
Fungi reproduction
Lichens
Link fungi and plants --> mutalism
Sheet that grows hyphae around algae cells
Photosynthetic
Embryophyta
Plants
Shared ancestral characteristics: photosynthetic, cell walls
Plant zygotes form dependent embryos
Alternation of generations: multicellular diploids and multicellular haploids
Plant phylogeny
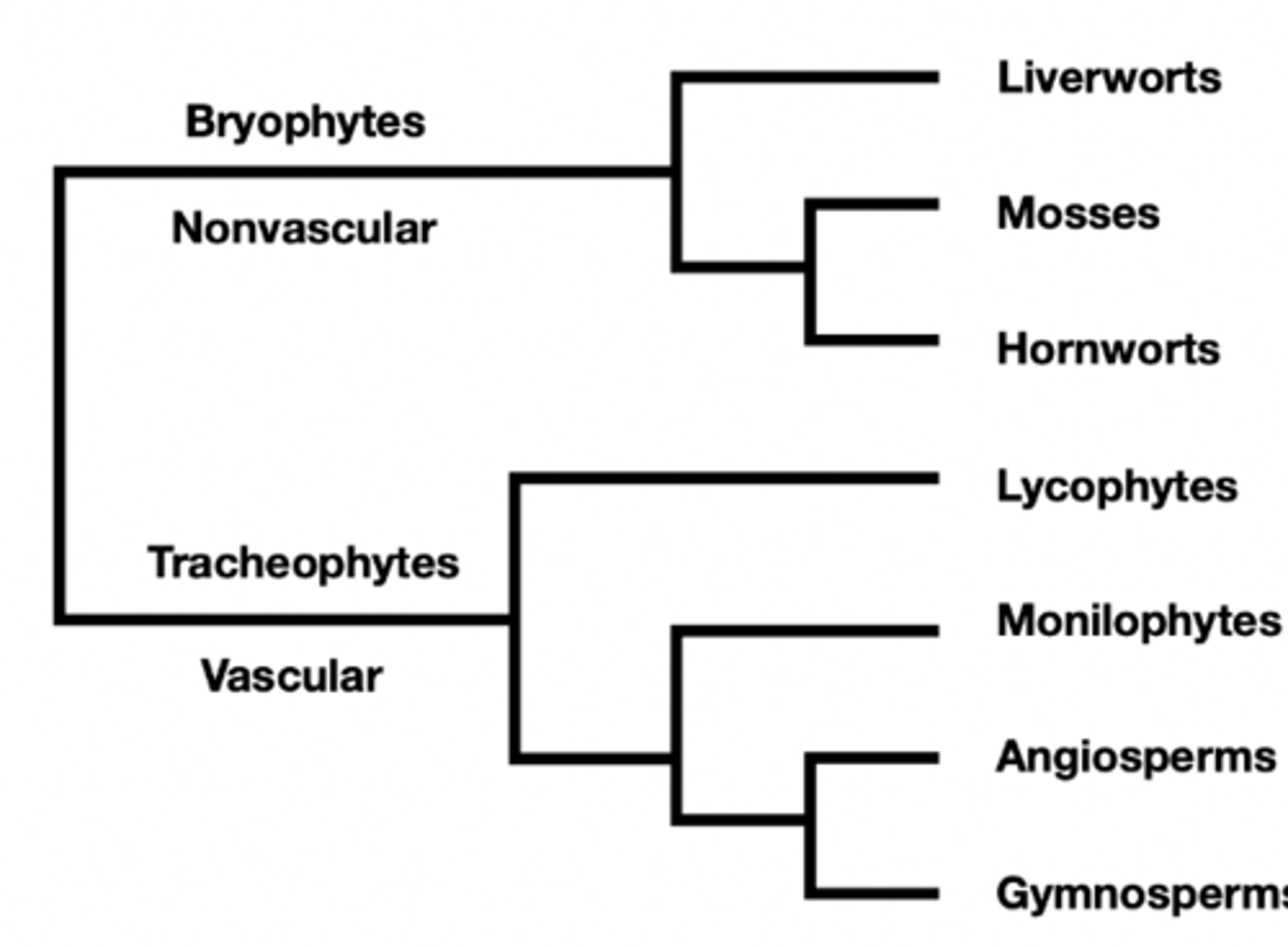
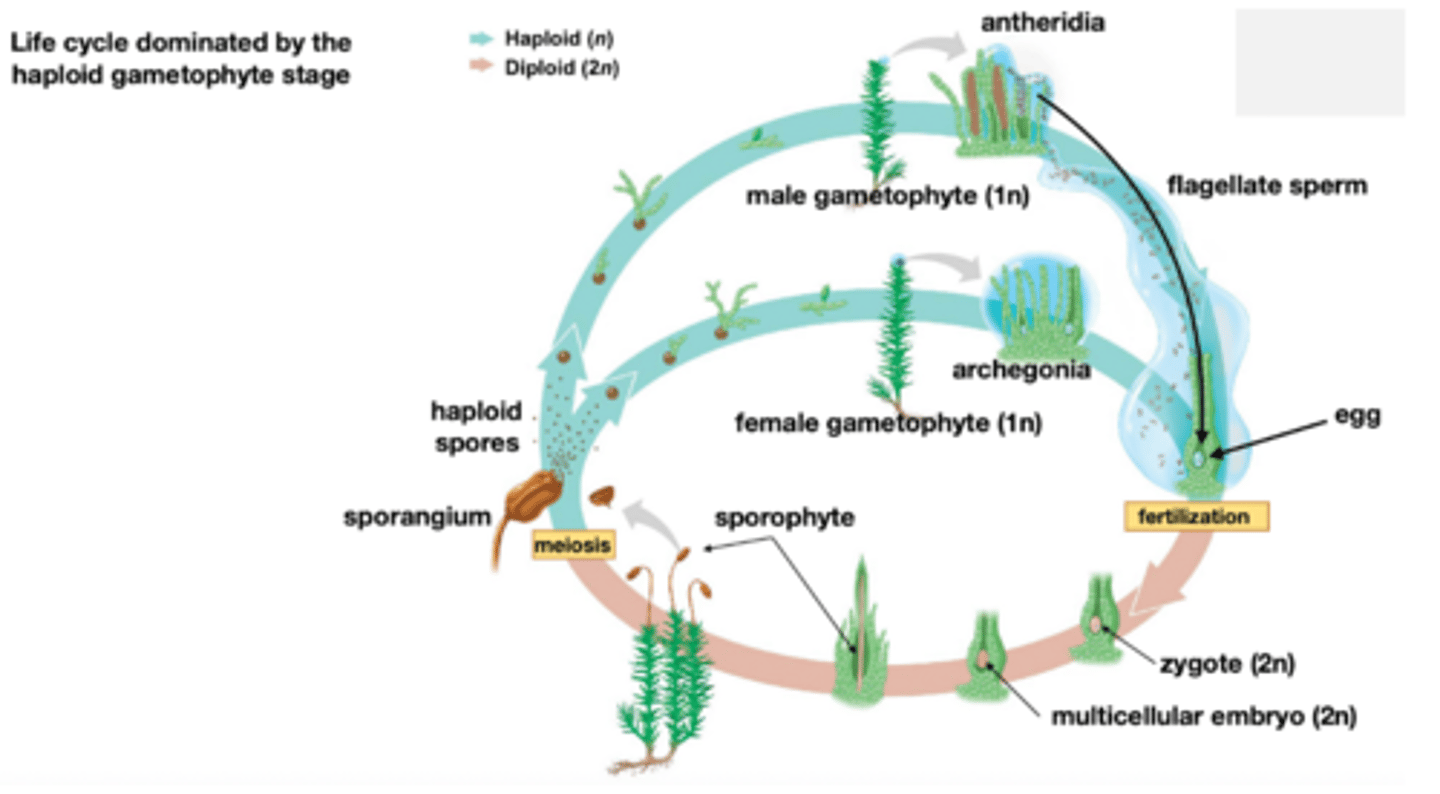
Bryophytes
Nonvascular
Independent gametophyte (1n) --> main macroscopic plant
Dependent sporophyte (2n) --> smaller organism dependent on haploid
Tracheophytes
Vascular
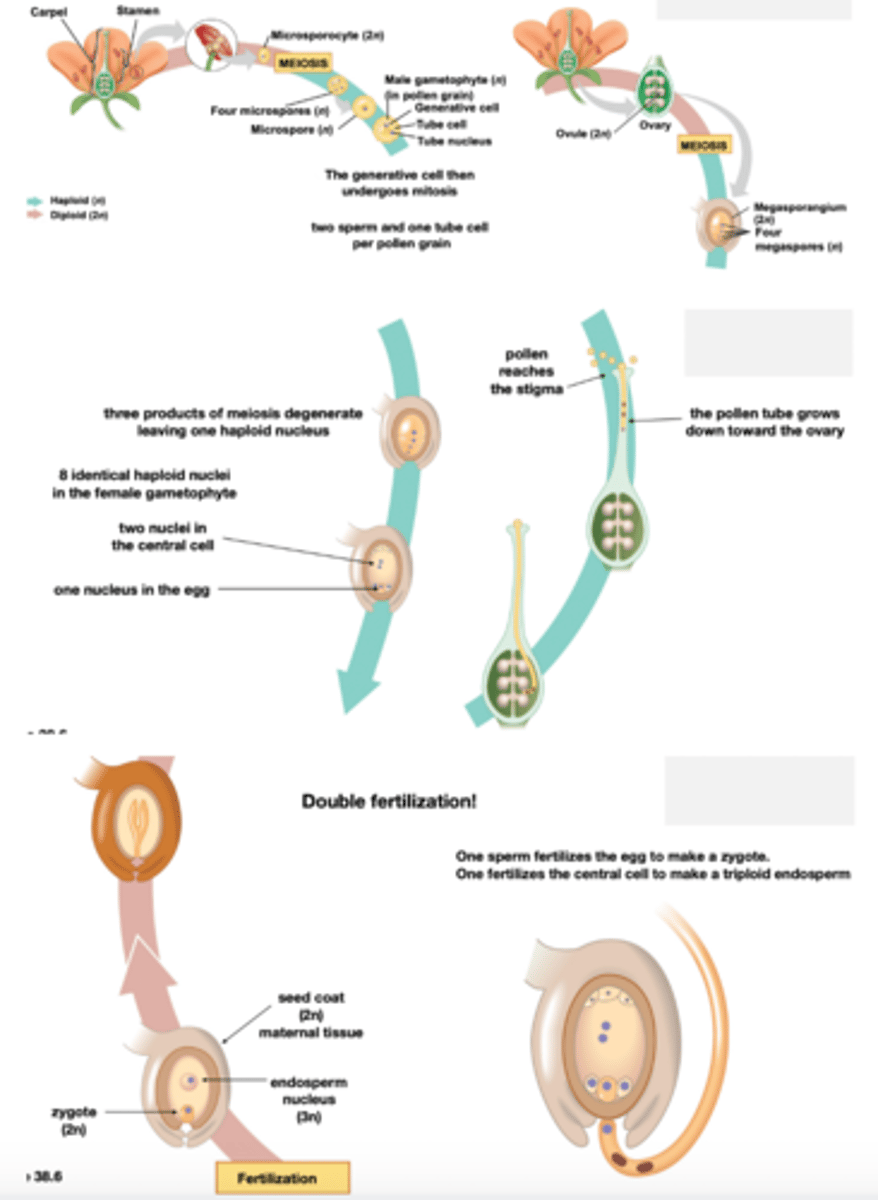
Gymno and angiosperms: dependent gametophyte, independent sporophyte
Lyco and monilophytes:
independent gametophyte; independent sporophyte
Sporangium
Diploid structure where meiosis occurs
Makes haploid spores
Plant life cycle general

Bryophytes life cycle
Tracheophytes seeds life cycle
Tracheophytes seedless life cycle
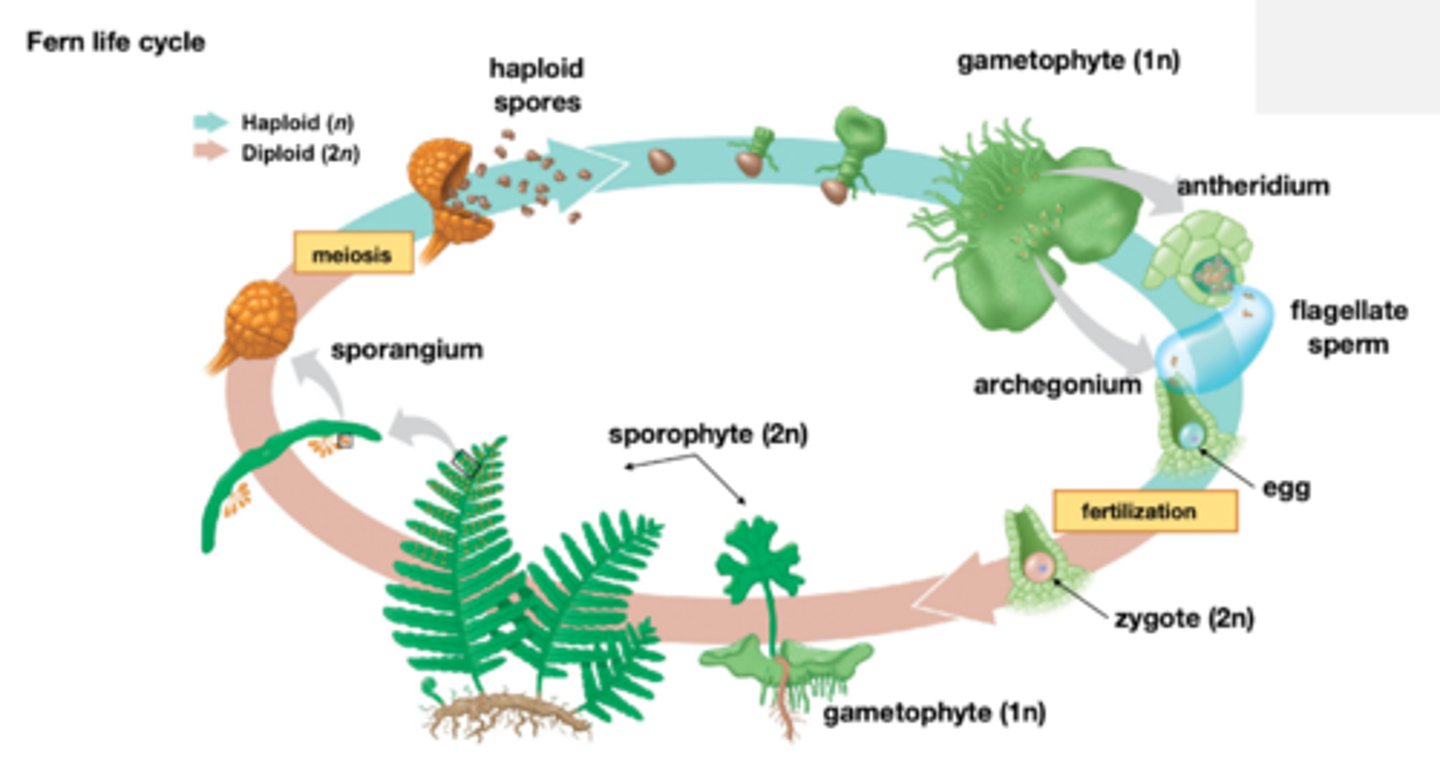
Tracheophytes vasculature
Xylem - dead, lignified vessels pull water
Phloem - live cells move sugars
Angiosperms monocot
Rice, corn, oil palm, sugarcane, wheat
Embryos --> 1 cotyledon
Leaf venation is parallel
Stems --> vascular tissue scattered
Angiosperm eudicot
Potatoes, cassava, soybean, sweet potatoes
Embryos --> 2 cotyledon
Leaf venation is netlike
Stems --> vascular tissue arranged in ring
Ovule
Gymnosperms exposed seeds
Climate is influenced by
Temperature, precipitation, sunlight, wind
Seasons result from
Earth's permanent tilt on its axis
Equinox
Length of night = length of day
Solar radiation varies with
Latitude
Global air circulation and precipitation
Tropics experience LEAST seasonal variation + GREATEST annual input in solar radiation
Closer to equator --> more moist
Closer to poles --> more dry
Air circulation = rising/sinking air precipiation + dry air and wind patterns
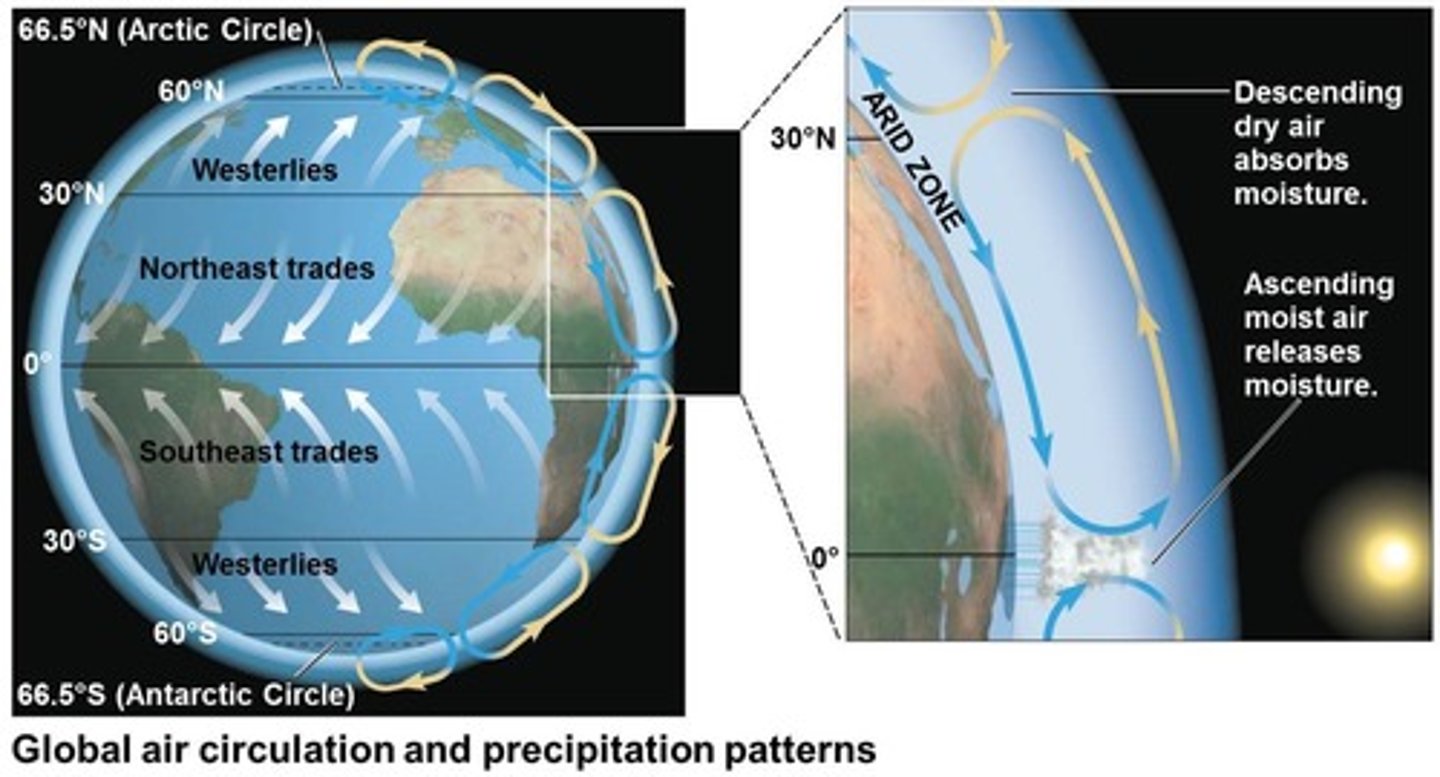
Coriolis effect
The Earth's rotation deflects the surface flow of air
Land near equator is moving faster than poles
Cooling trade winds flow
From east to west
Westerlies flow
From west to east
ITCZ
Where northeasterly and southeasterly trade winds meet
Not stationary; migrates toward region with warmest surface temperature
High amount of precipitation
Hadley cells
Circulation cells that surround equator
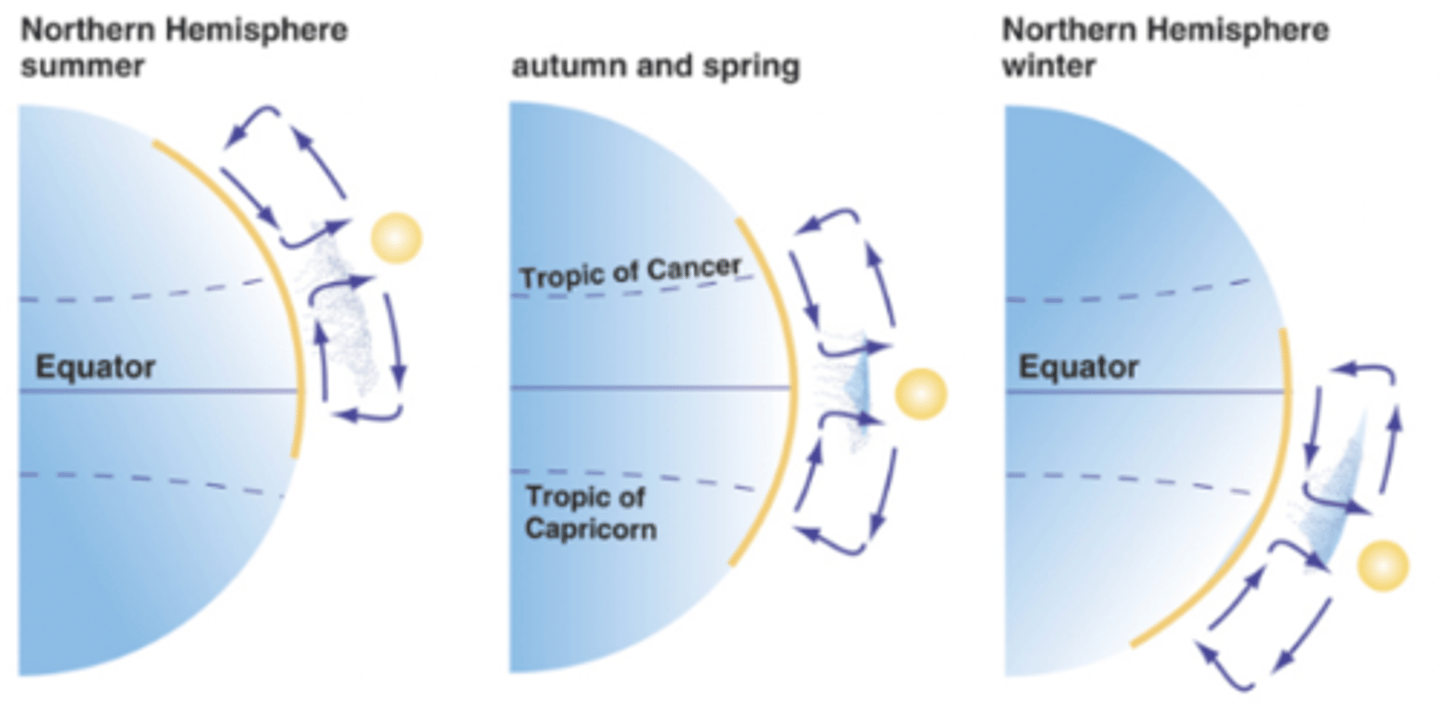
Ocean currents are created by
Winds, planet rotation, unequal heat of surface waters, locations and shapes of continents
Gyres
Formed as warm water moves away from the equator
Each ocean dominated by 2 gyres
Water moves clockwise in northern hemisphere
Water moves counter-clockwise in southern hemisphere
Ocean currents influence coastal climate
Specific heat is lower on land
Day --> land warms faster than ocean --> warm air rises and moves to the sea
Night --> land cools quicker --> warm air from sea comes in --> offshore breeze
Topography
Influences rainfall
Orographic lifting --> warm, moist encounters windward side of mountain --> air flows upward --> releases precipitation
Leeward side: dryer air descends --> warms --> rain shadow
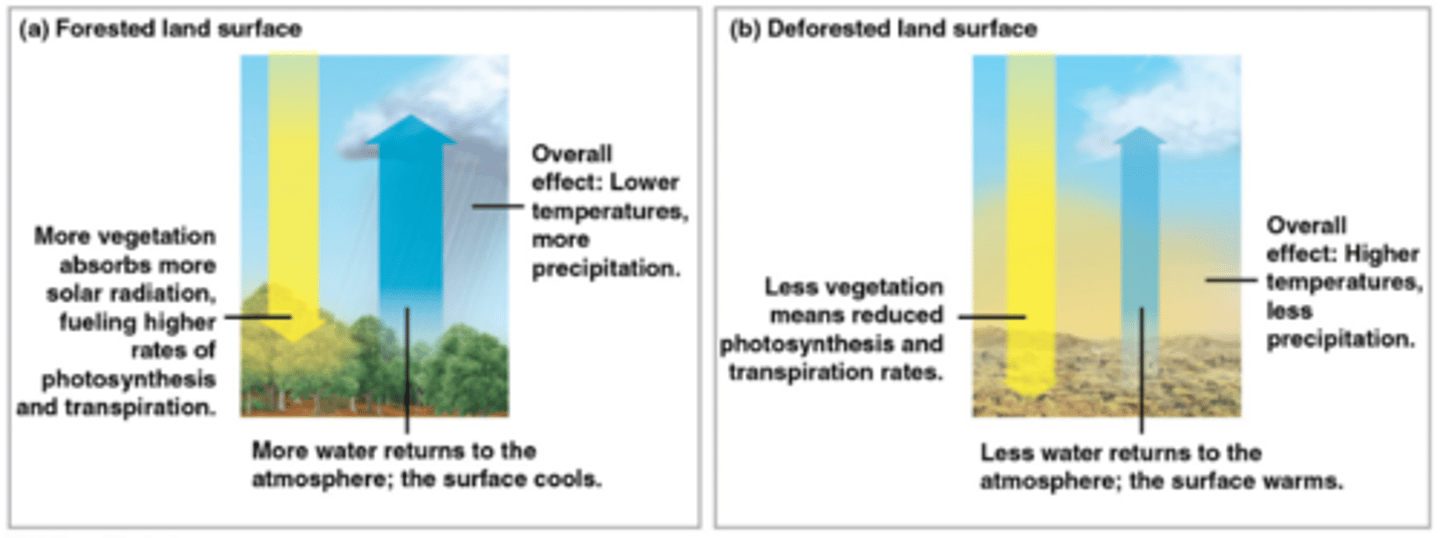
How vegetation influences coastal climates
Forests absorb solar energy
Offset by transpiration
Lots of veg: low temp, high precipitation
Little veg: high temp, low precipitation
Tropical forest
High precipitation
High temp
Along equator
Drip tips on leaves allows water run off without damaging trees
Nutrient poor soil
Desert
Dry
High temp fluctuation
Low precipitation
Fat sacks i.e. humps on camels
Cacti survive on low water
Savanna
Warm year round
Low precipitation
Few trees, small and thorny leaves - minimize water loss, adapted to forest fires
Chaparral
Hot and dry summer
Cold and wet winter
Shrubs and small trees
Reptiles
Temperate grassland
Wet summer
Dry winter
Fertile soil
Field of grass
Northern coniferous forest
Stable temperatures
Dominant cone trees
Needles on trees prevent water loss
Lower temperatures than tropic forest
Broadleaf forest
Large trees
Low light penetration
Humid summers
Vertical layering
Tundra
Cold all the time
Layer of permafrost
Permafrost prevents roots of plants from reaching down or up
Small, low growing, clustered shrubs
Short roots, small leaves
Seasonal turnover
Plankton carried downward, nutrients carried upward
Phytoplankton have access to both nutrients and light
Eutrophication
Nutrient enrichment
Oligotrophic lakes
Low nutrient levels
Low algal growth
Good light penetration
High dissolved oxygen
Deep waters
Eutrophic lakes
High nutrient levels
High algal growth
Poor light penetration
Low dissolved oxygen
Shallow waters
Lake threats
Eutrophication --> algal bloom --> algae dies in lifecycle --> aerobic decomposers consume all oxygen
Excess fertilization runoff
Streams and rivers
Go downstream --> warmer, more sunlight, more turbid, suspended sediments, slower moving, more salt and nutrient dense, finer particles
Wetlands
Earth's kidneys
Take up pollution - N and P
Same threats
Brackish biomes
Estuaries connect rivers and oceans
High salinity
Plants are adapted to high salinity i.e. mangrove
Salt marsh plants
Adapted to high salinity and low oxygen
Intertidal zones
Where tide comes in
Tide comes in --> more nutrients
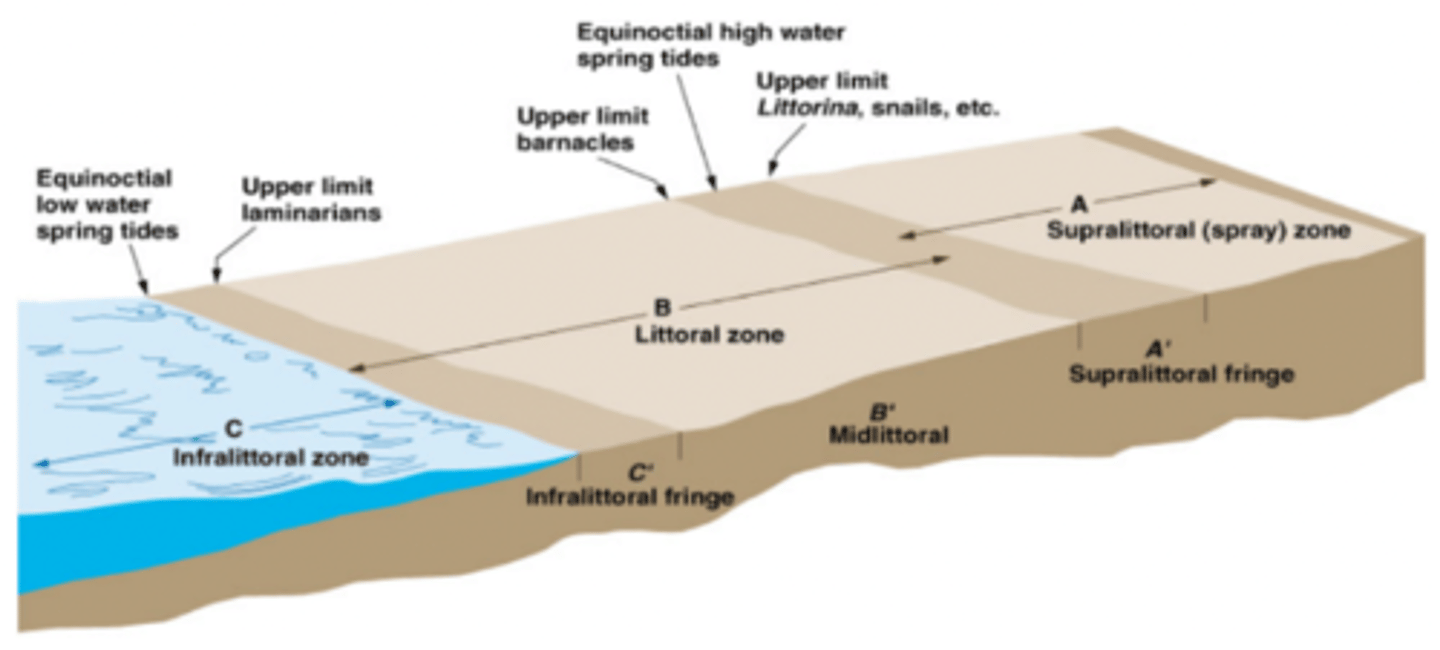
Pelagic zone
No turnover
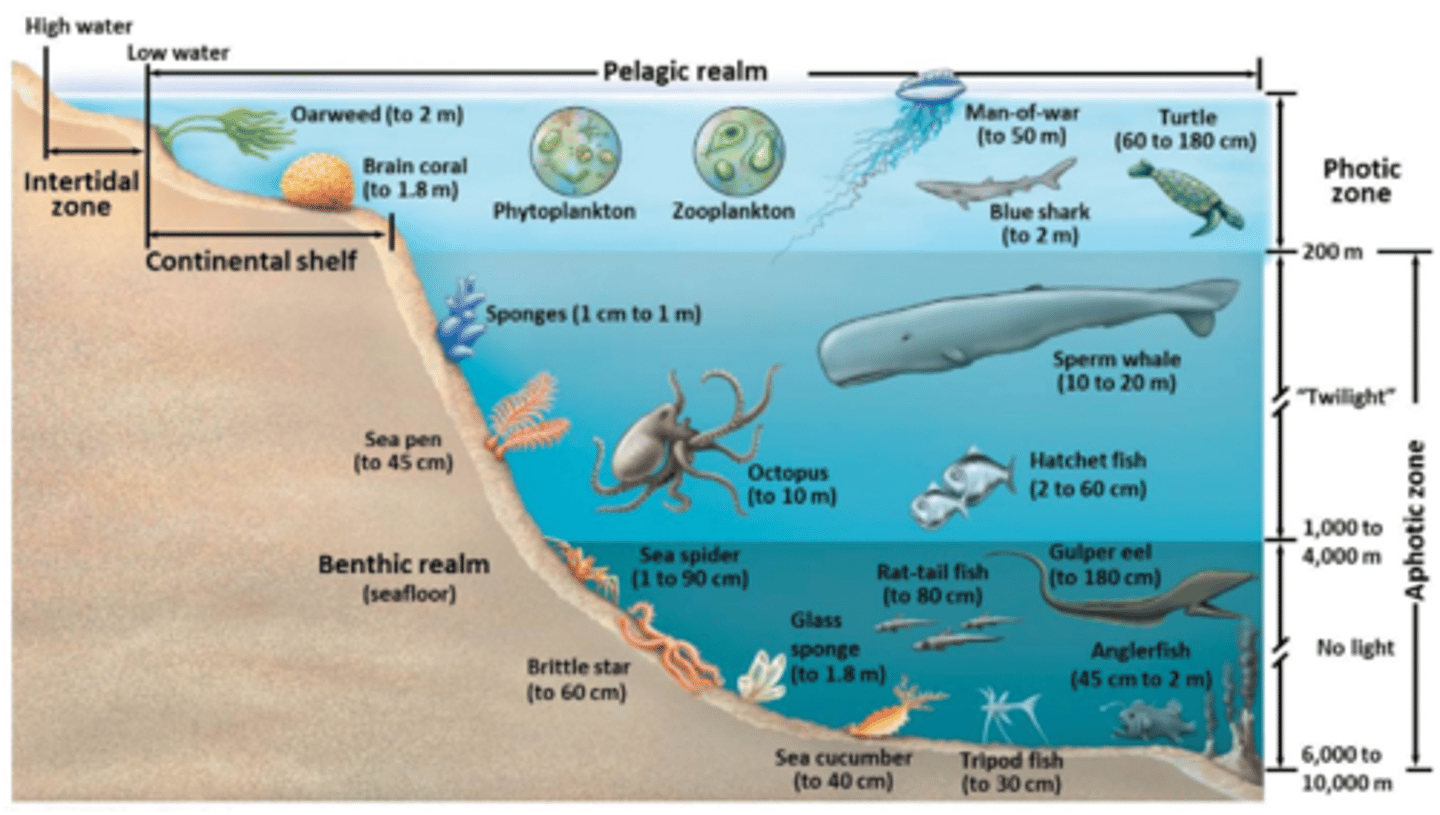
Benthic zone
Hydrothermal vents
Chemoautotrophs
Hydrogen cyanide
High pressure prevents water from boiling
Mark recap equation
N = sn/x
s = number of individuals in first sample/marked
n = number of individuals in second sample
x = marked individuals recaptured
Mark recap assumptions
Marked and unmarked individuals have same probability of being captured or sampled
Marked organisms mix completely into population
No individuals are born, die, immigrate, or emigrate during resampling interval
Clumped
Most common
Presence of one individual increases probability of others being there too
Results from:
Clumped resource or favorable condition distribution
Mating or social behavior
Uniform
Presence of one individual decreases probability of other individuals being there
Results from:
Interactions between individuals of a population
E.g., plants release chemicals that inhibit nearby growth, animals have territorial behavior
Random
Rare
Equal probability of individual occupying any point
Type 1 survivorship curve
Mortality at end of max life span
Ex. humans
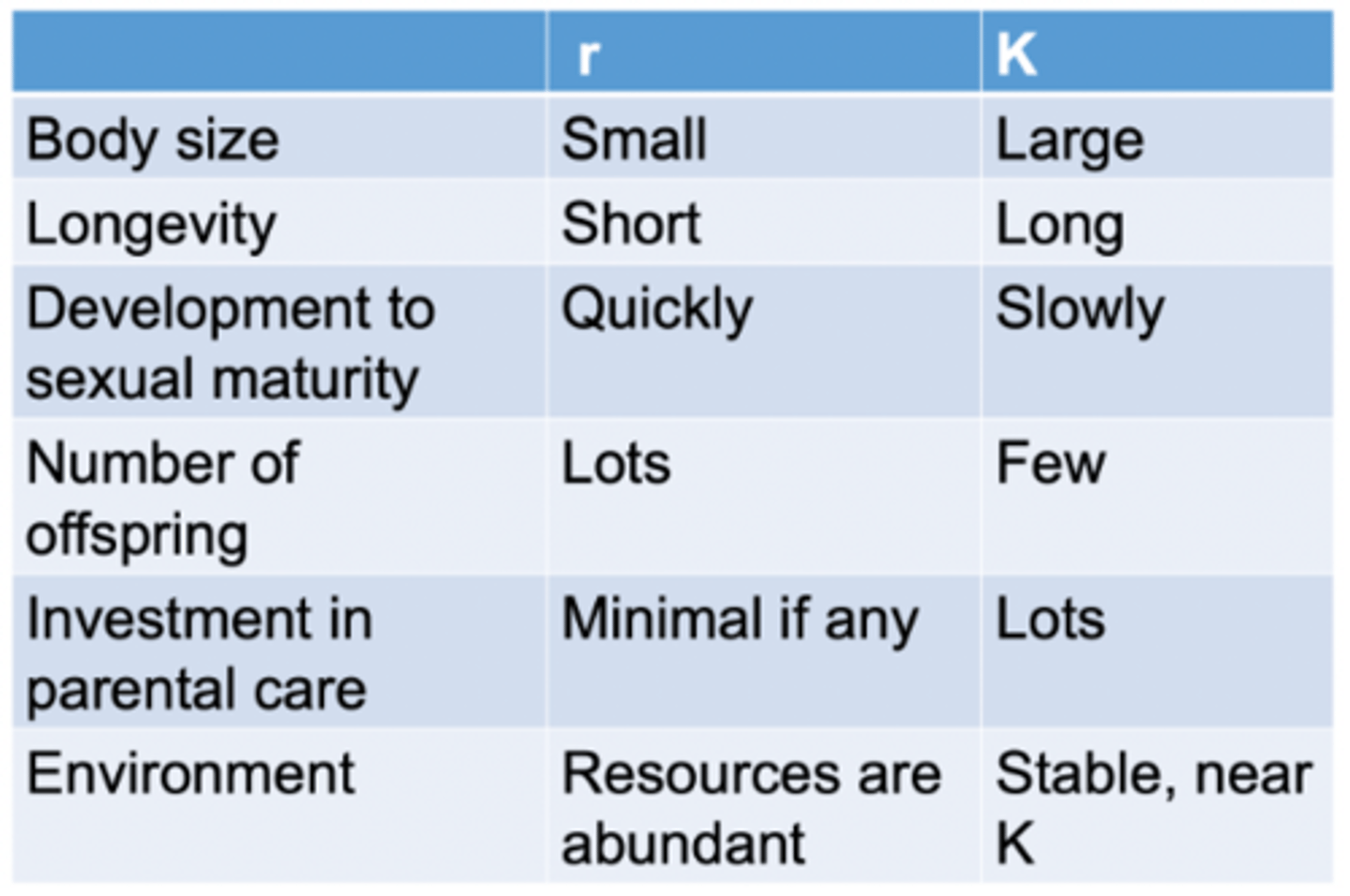
K-selected
Type 2
Constant mortality rate from birth to death
Ex. rodents
Mix of r and K selected
Type 3
Extensive mortality rate after birth; high rate of survival if live
Ex. marine invertebrates, insects
r selected
Exponential growth
dN/dt = rN
r = intrinsic/instantaneous rate of change
Logistic growth
dN/dt = rN*((K-N)/N))
((K-N)/N)) --> places a constraint
N = 0.5K --> population grows the fastest
K = carrying capacity
Life history traits
Affects organism's schedule of reproduction and survival
Factors:
Age of first reproduction, frequency of reproduction, number of offspring, amount of parental care
Semelparity
Die after first reproduction
More offspring in a single brood
Iteroparity
Breed repeatedly
Devote resources to survival to breed more
Produce fewer offspring in single reproductive event
K-selection
Life history strategy
Selection for traits that are sensitive to population density; favored at high density
Ex. large mammals, long-lived mature trees, old growth forests
r-selection
Life history strategy
Selection for traits that maximize reproductive success in uncrowded environments
Ex. rabbits, weedy species in abandoned fields
r vs K traits graph
Population regulation factors
Density-independent: birth/death rate don't change with population density
Density-dependent: birth/death rate change with population density
Density-dependent regulation mechanisms
Competition resources, territoriality, disease, intrinsic factors, toxic wastes
Population cycles
Plant-herbivore cycle that influences predator-prey interaction
Metapopulations
Groups of local populations linked by immigration and emigration
Habitat fragmentation
Habitat is destroyed --> leaves behind smaller unconnected areas
Corridors
Man-made plant bridges
Promotes dispersal, migration, gene flow
Reduces inbreeding
Can be harmful
Island biogeography theory
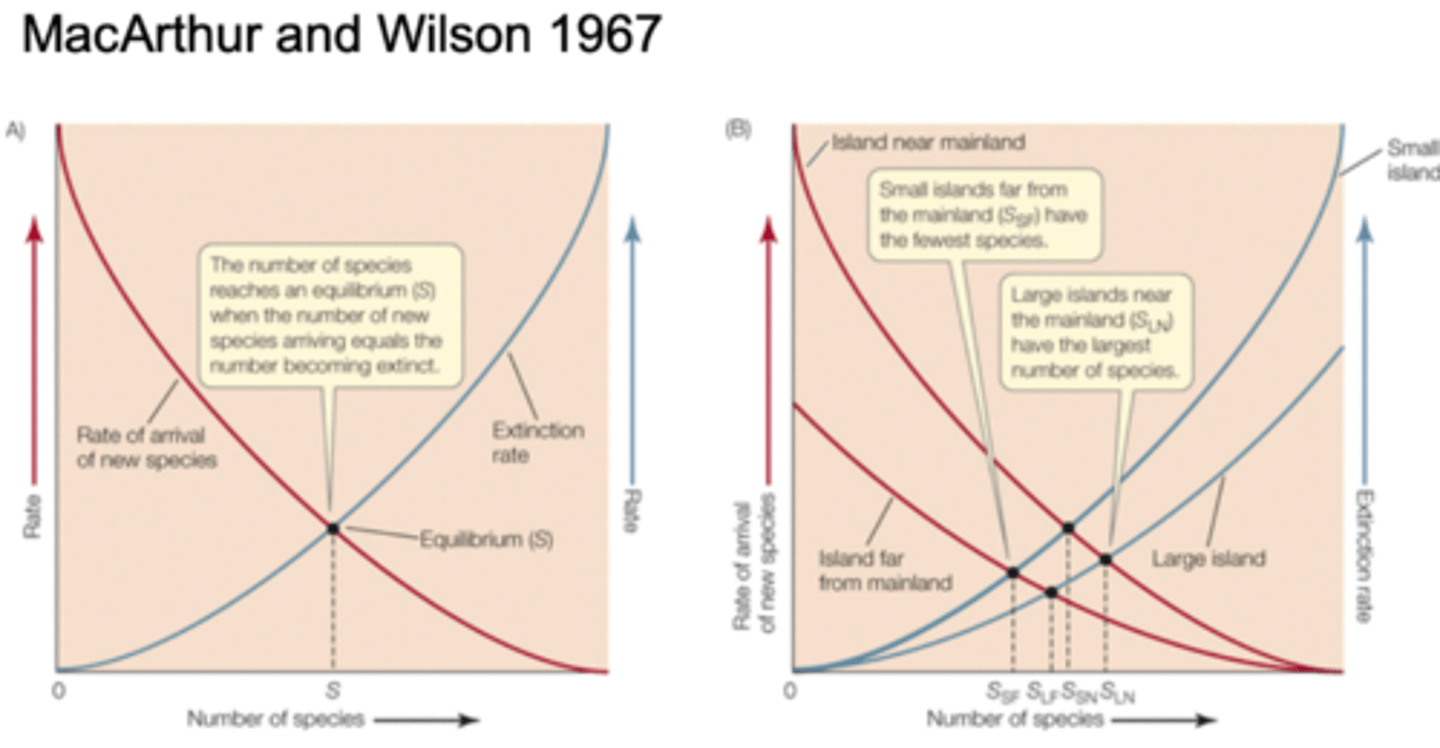
Latitude
Species richness and diversity generally declines along an equatorial-polar gradient
Shannon diversity index
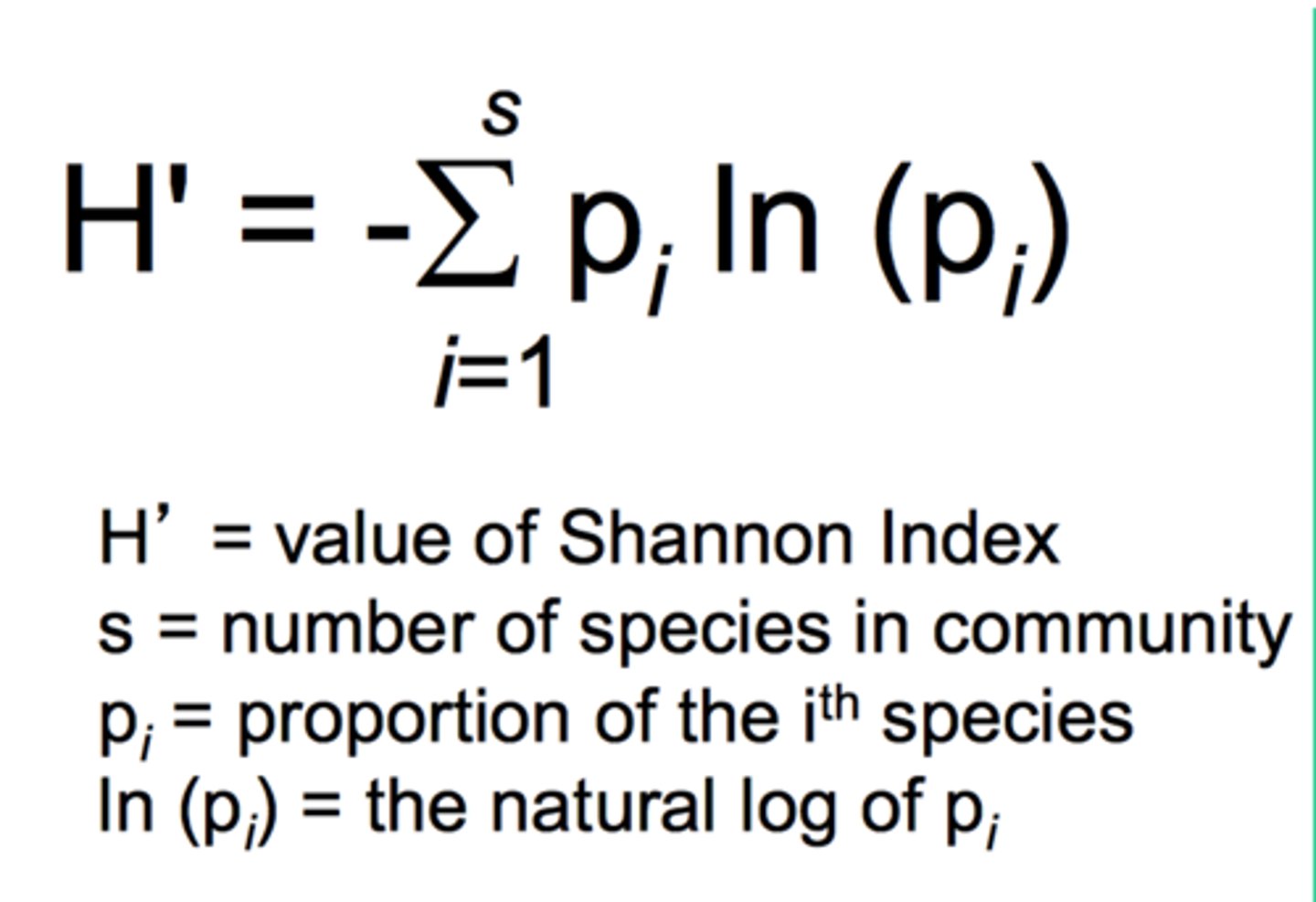
Foundation species
Dominant in terms of abundance or size
Tend to be strongest competitors --> exert control over occurrence and distribution of other species
Usually occupy low trophic levels
Provide habitat or food
Keystone species
Not usually abundant or big in size
Occupy niche that hold rest of community in place
Ecosystem engineers
Create or alter environment
Ex. beaver
Intermediate disturbance hypothesis
Moderate levels of disturbances foster greater species diversity than extremes
High disturbance --> too much stress, species can't tolerate
Low disturbance --> allow competitively dominant species to exclude less competitive species
Primary succession
Occurs after disturbance has left land devoid of nearly all life
Ex. volcanic eruption, moraine left by retreating glacier
Secondary succession
Primary succession but there was more life left
Facilitation
Early successional species modify environment to be more suitable for successive species to invade and grow
Inhibition
Early colonists make the site less suitable for both early and late successional species
Tolerance
Species neither inhibited nor facilitated by species of earlier stages