Cell Organelles & Transport
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
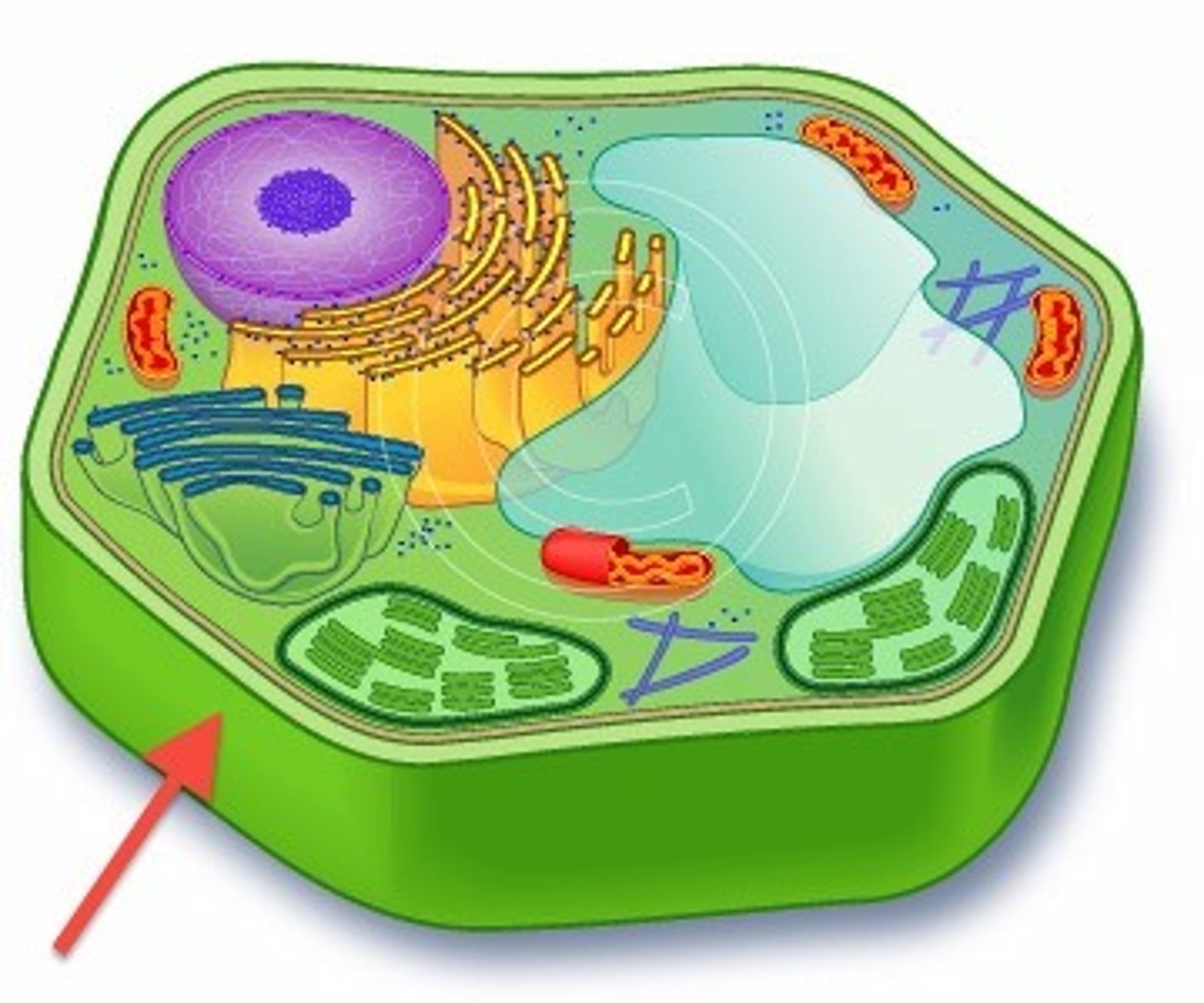
cell wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
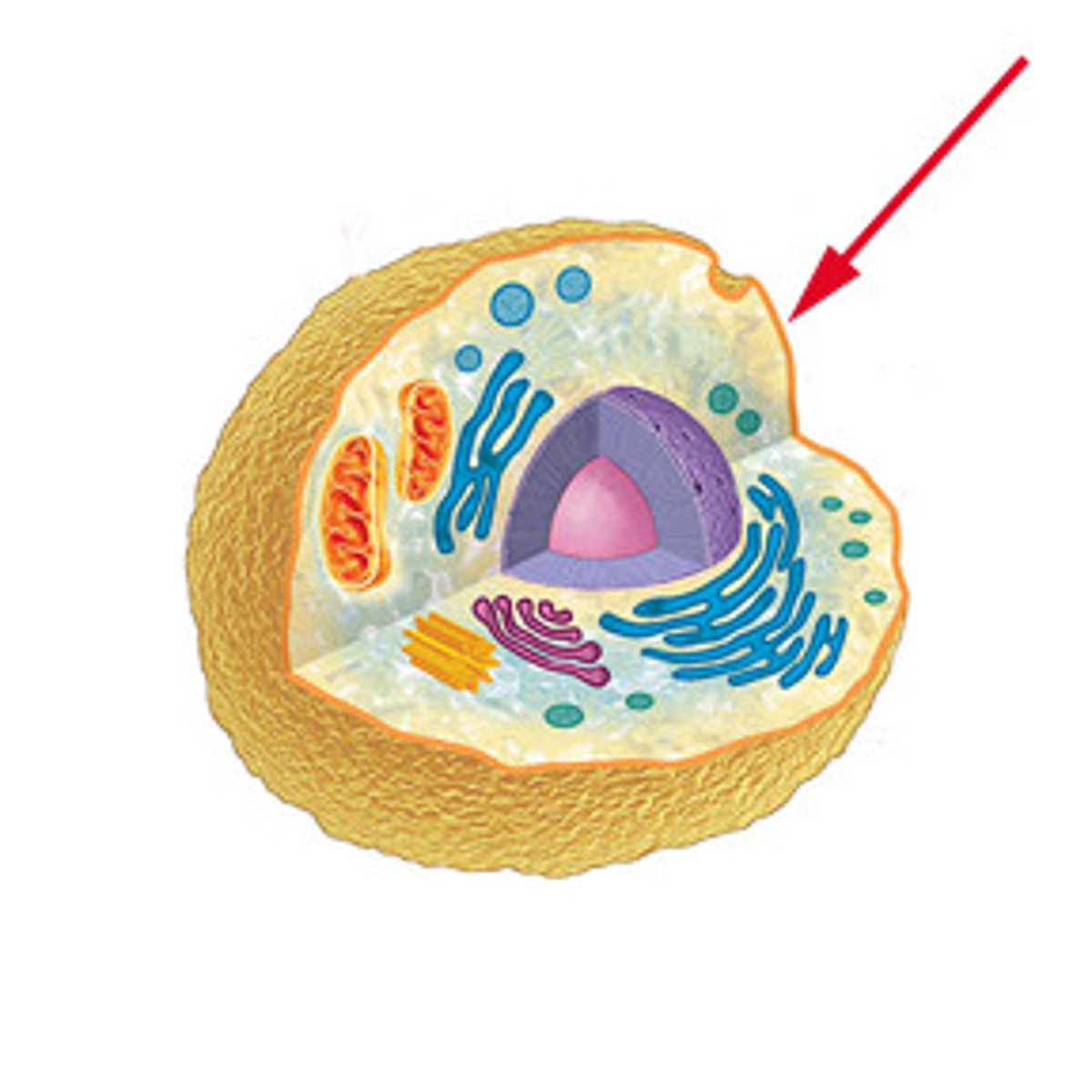
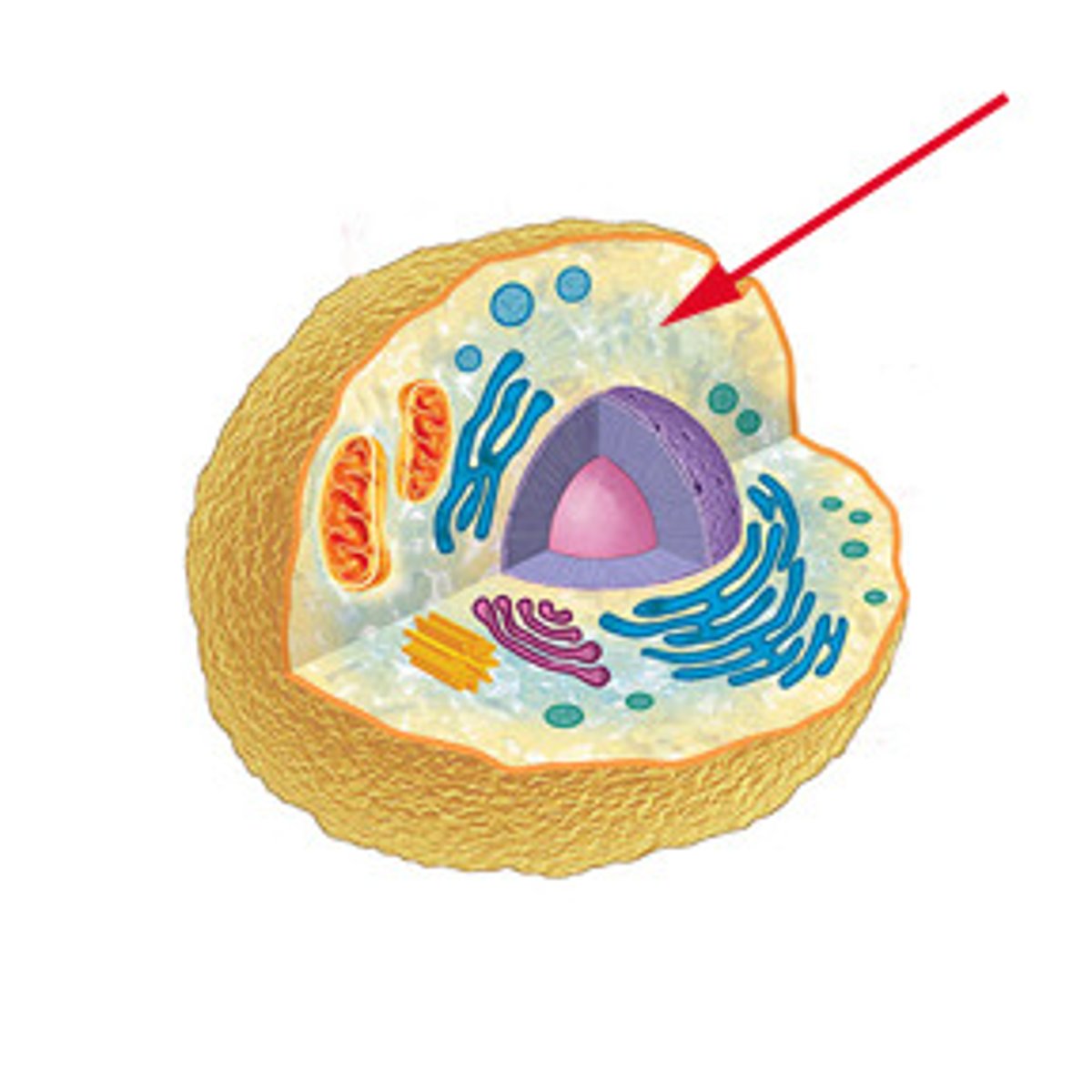
cell membrane
thin, flexible barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
Cytoplasm
the material or protoplasm within a living cell, excluding the nucleus. (jelly like fluid)
Flagella
a slender threadlike structure, especially a microscopic whiplike appendage that enables many protozoa, bacteria, spermatozoa, etc., to swim. (like in sperm)
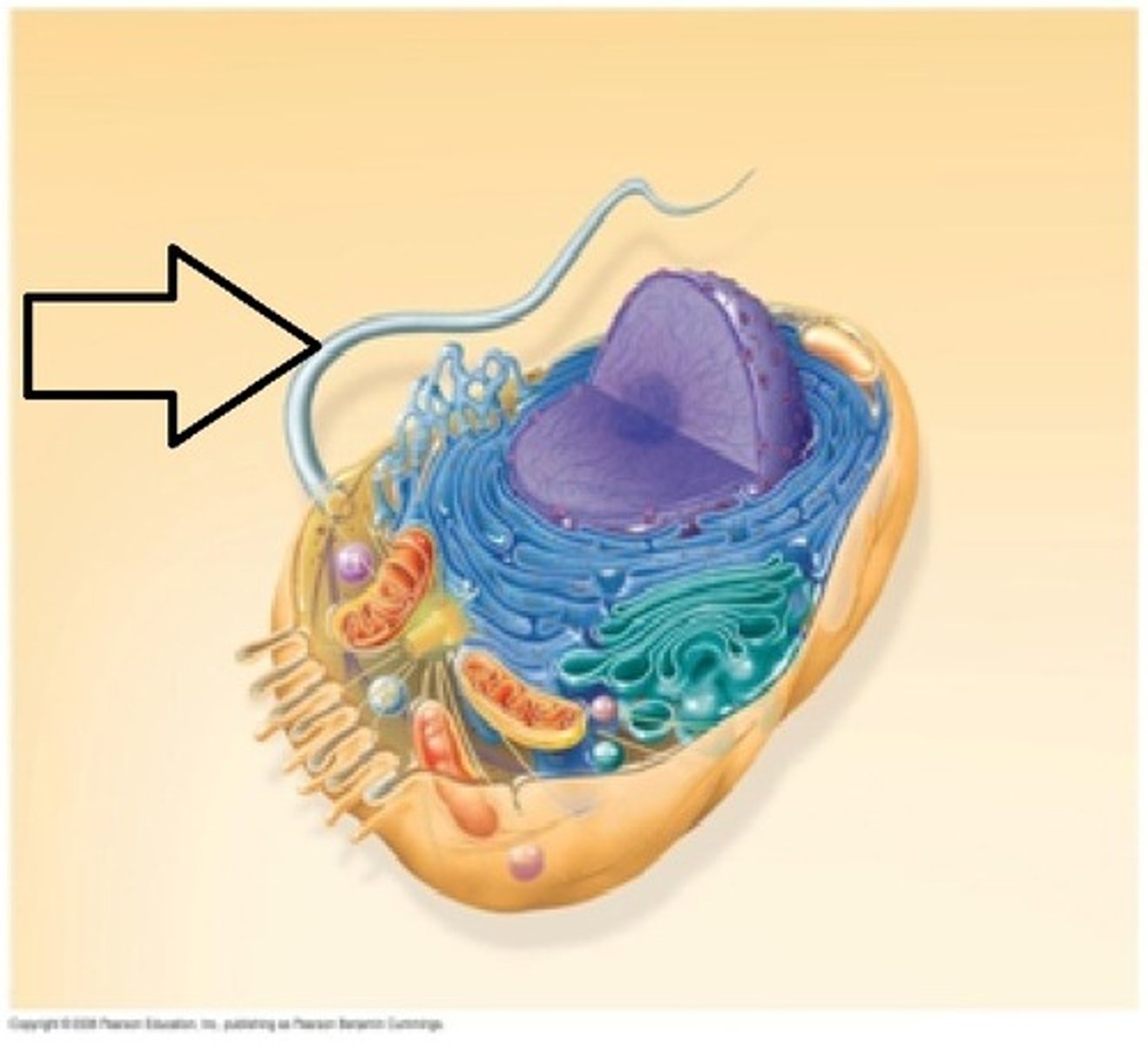
ribosome
a cell organelle composed of RNA and protein; the site of protein sythesis.
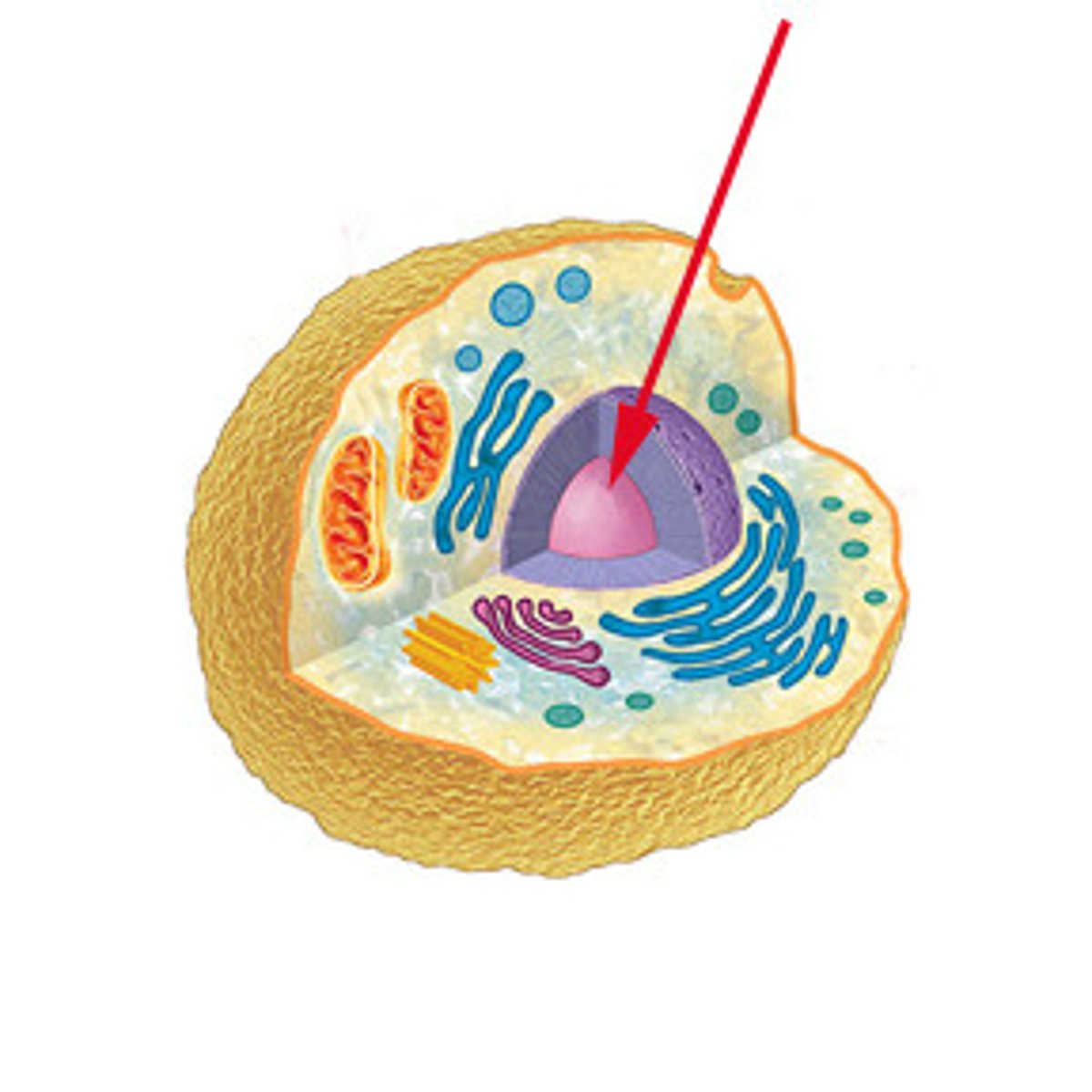
nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction; control center of the cell
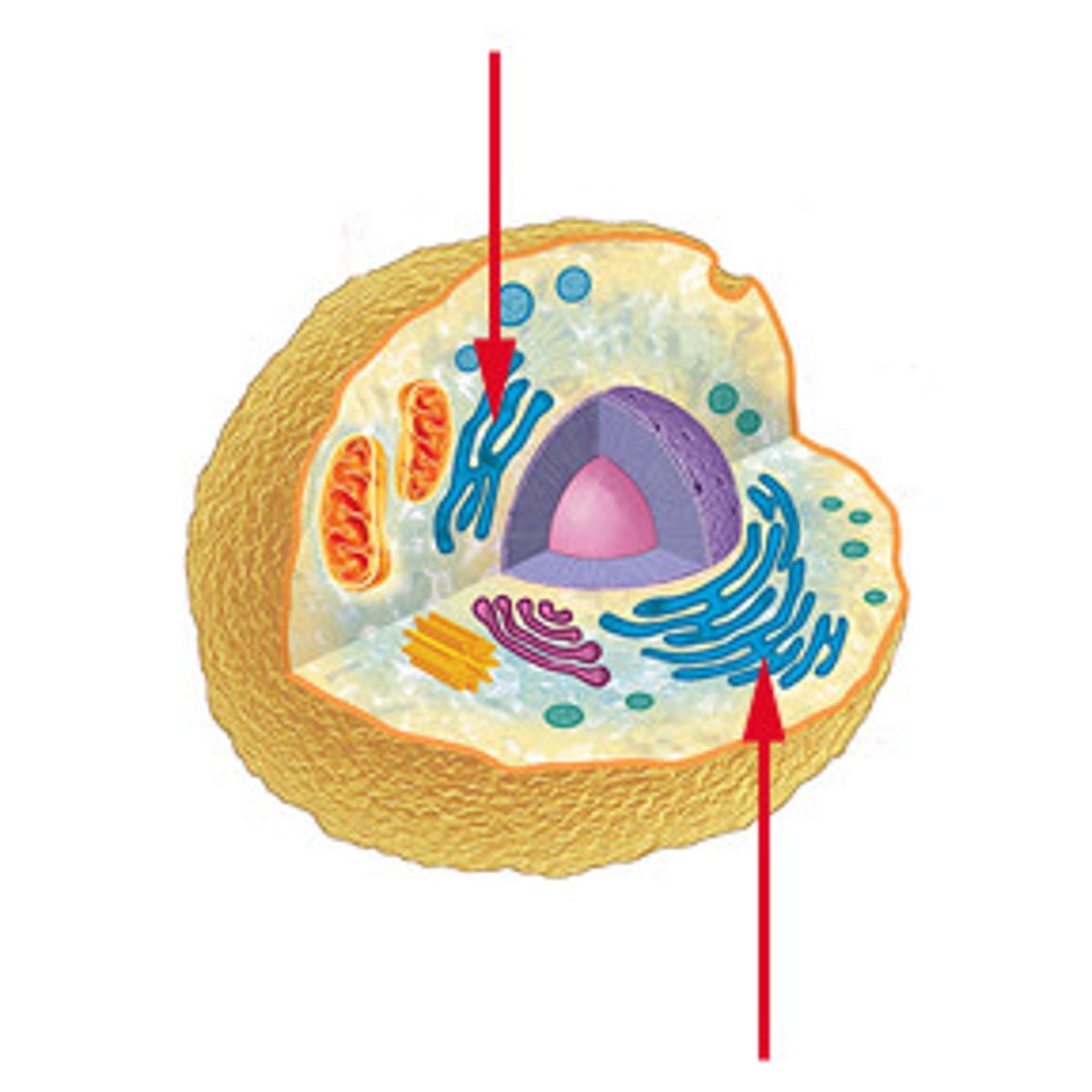
endoplasmic reticulum
An organelle that forms a maze of passege ways for protiens and other materials through the cell
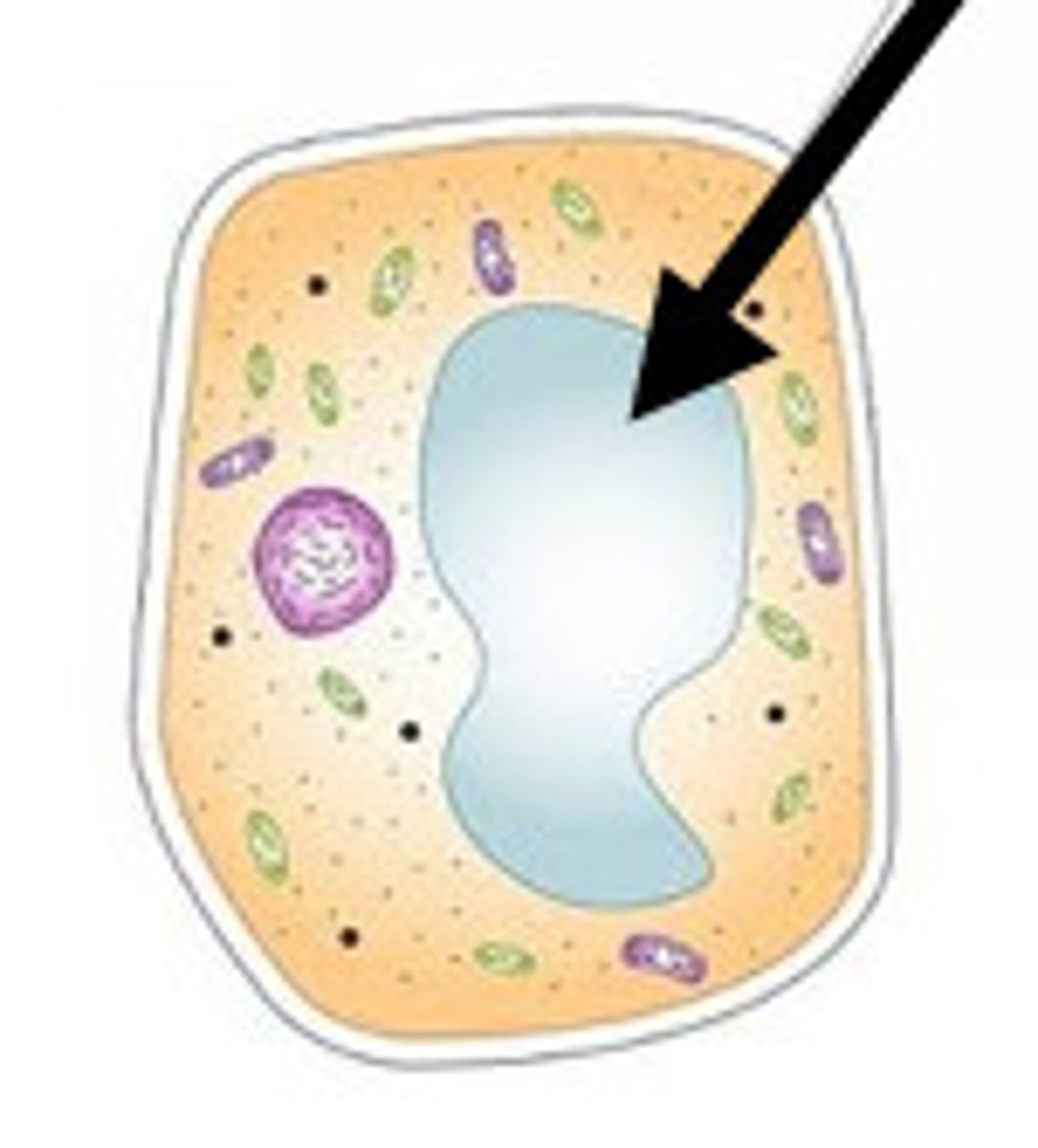
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
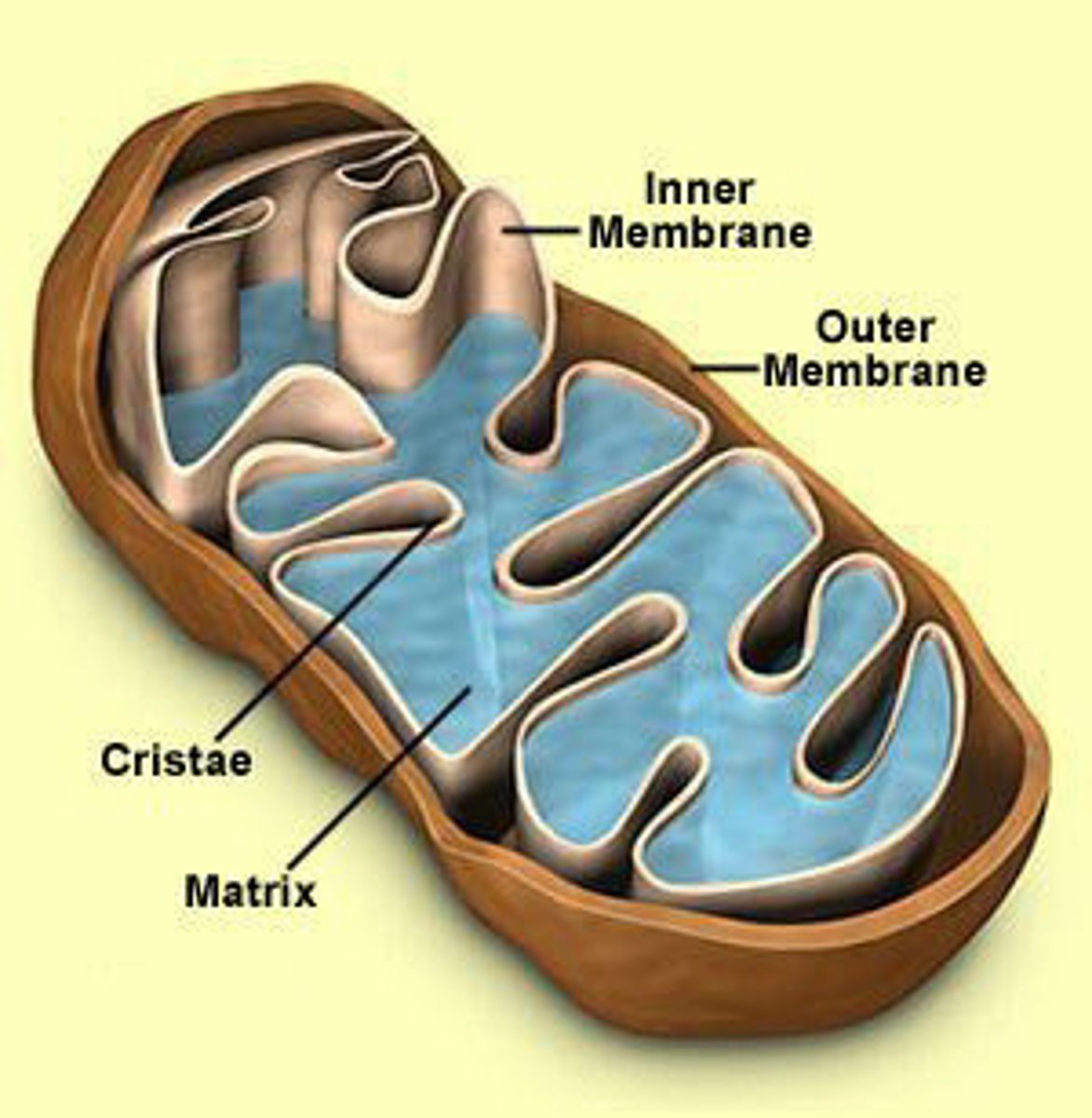
Mitcochondria
POWER HOUSE OF THE CELL, breaks down intermediate products of fuels to carbon dioxide and water (cellular respiration).
Turns glucose into ATP.
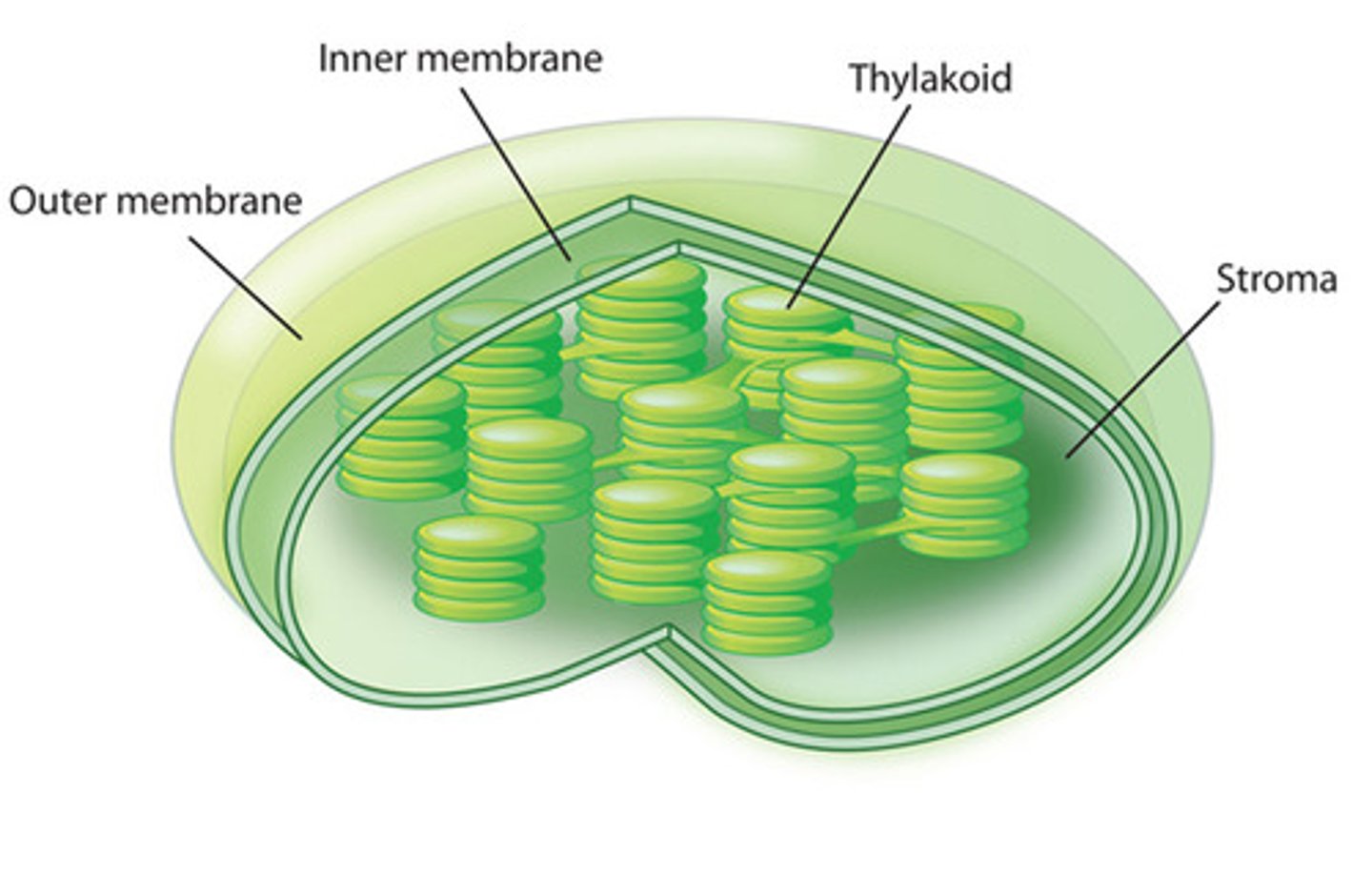
Chloroplast
organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy
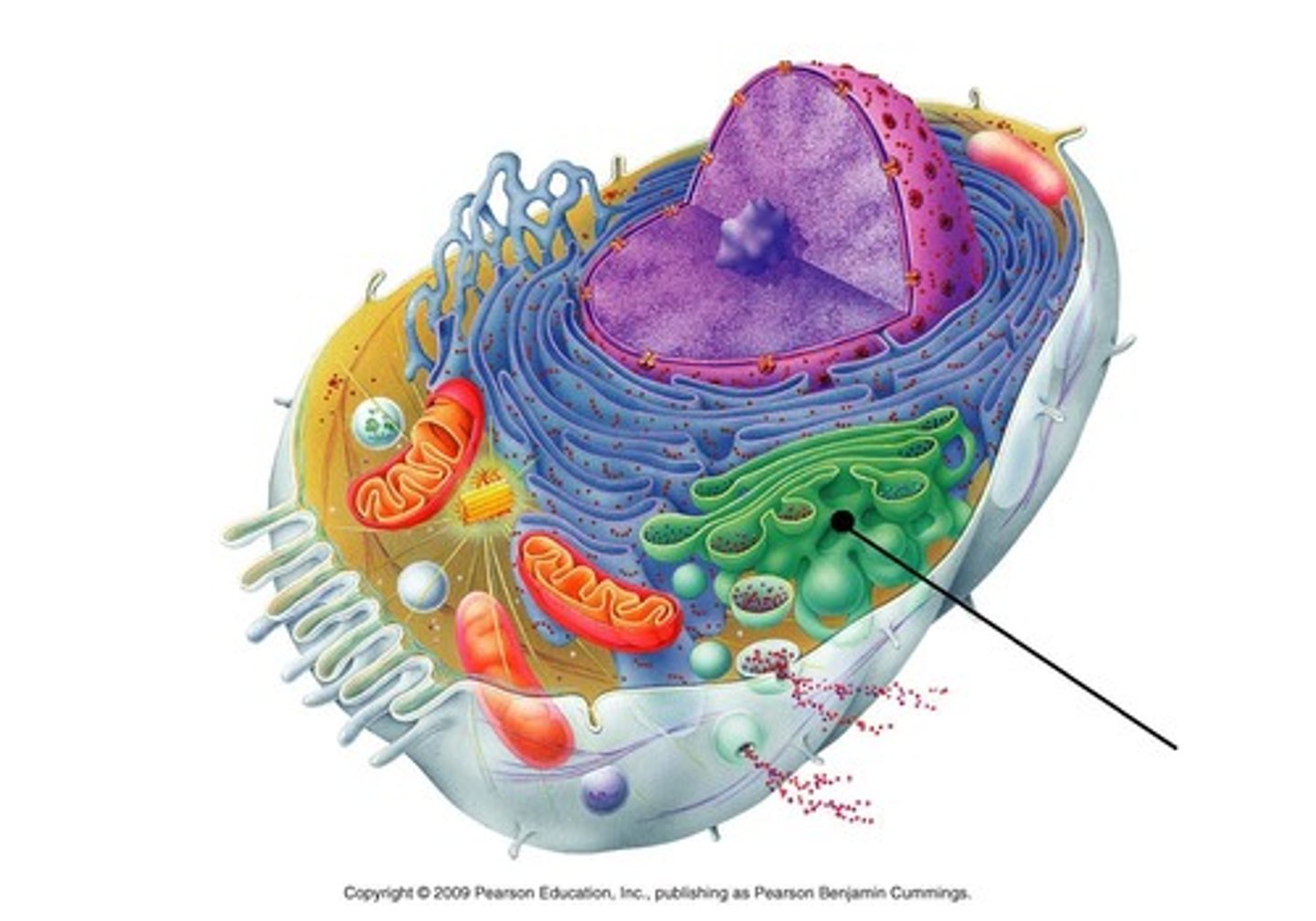
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
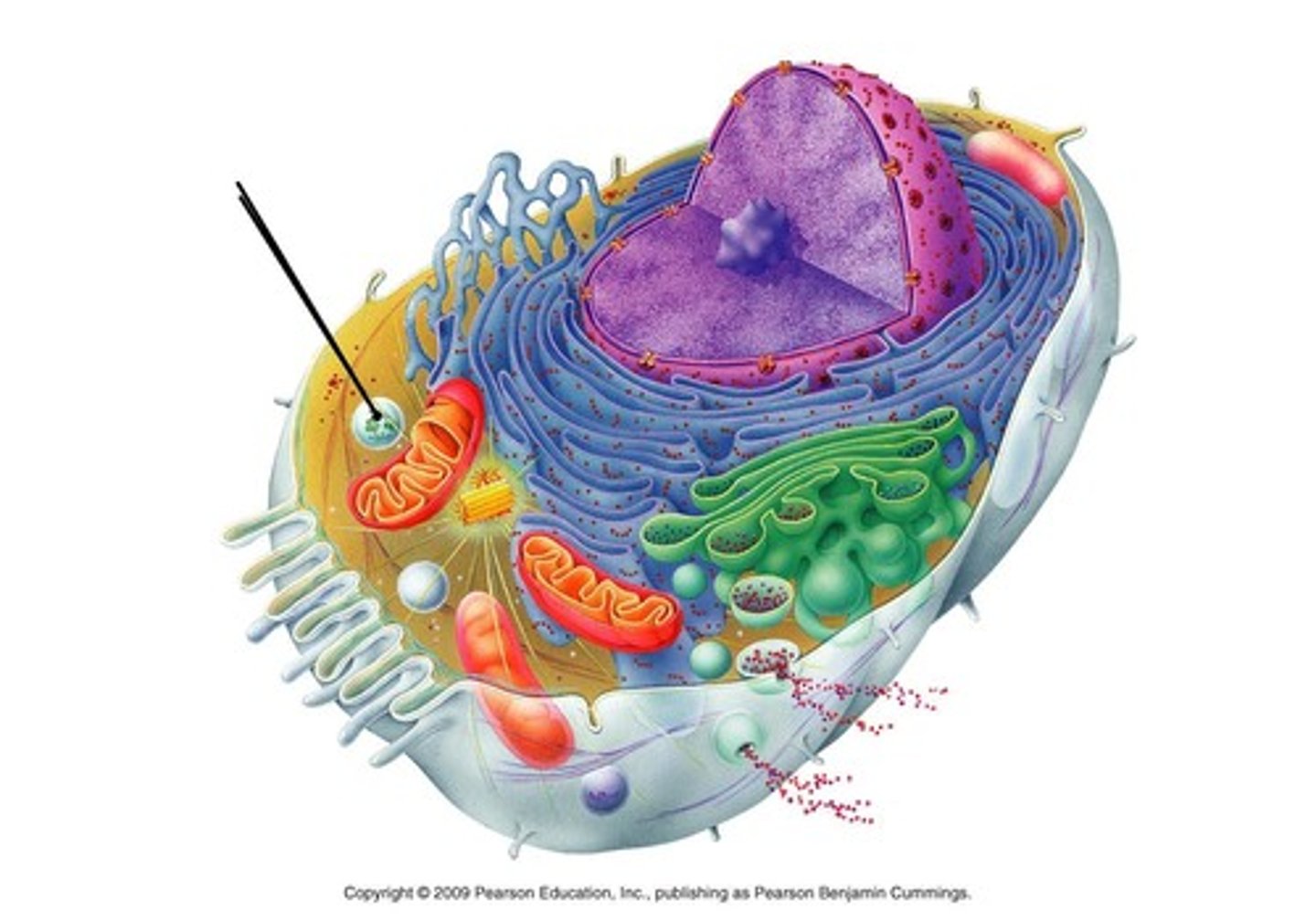
lysosome
cell organelle that breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into small molecules that can be used by the rest of the cell
cell theory
everything is composed of cells cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced from existing cells
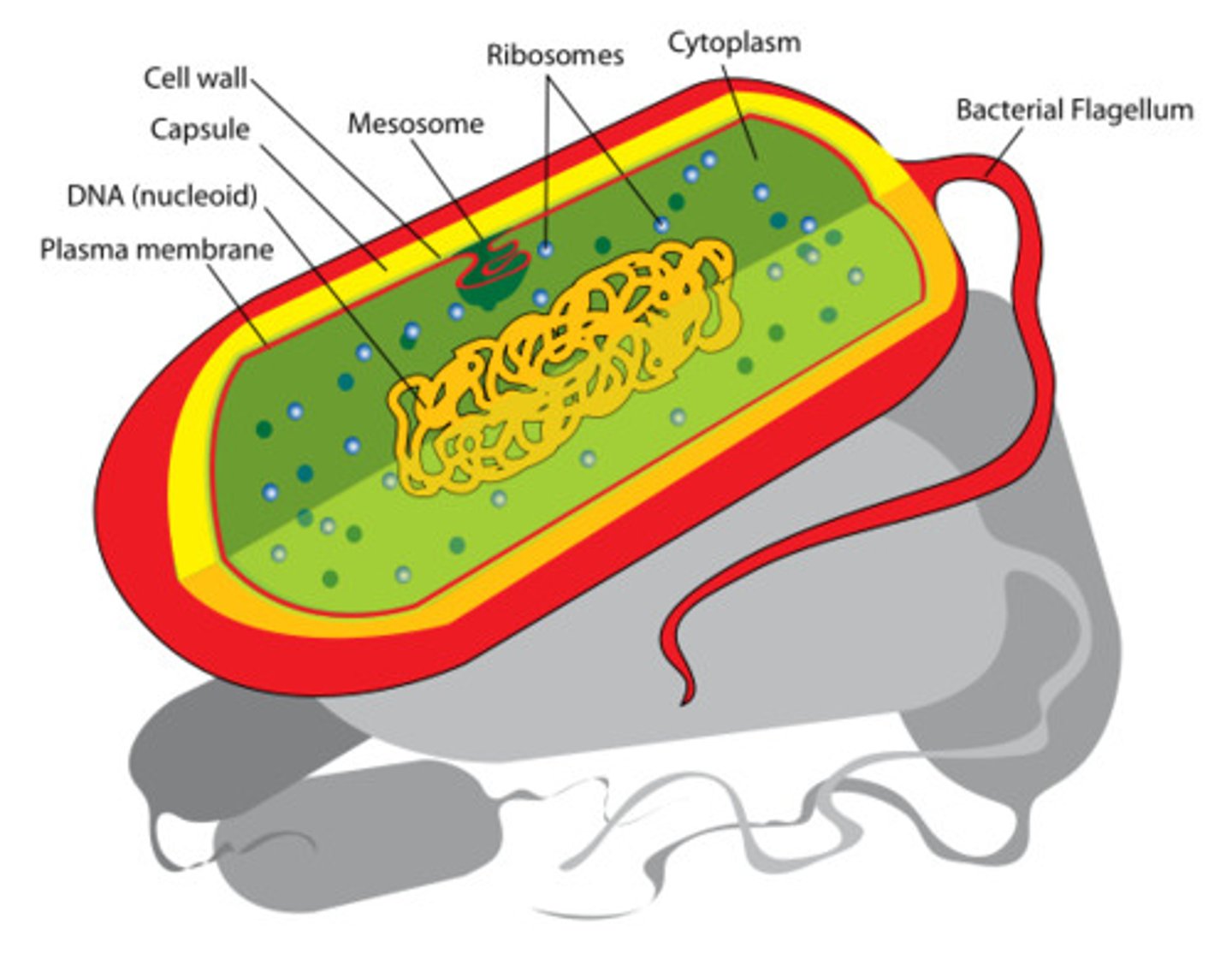
prokaryotes
Cells that lack nuclei and membrane-bound organelles, usually smaller and unicellular, (ex. bacteria)
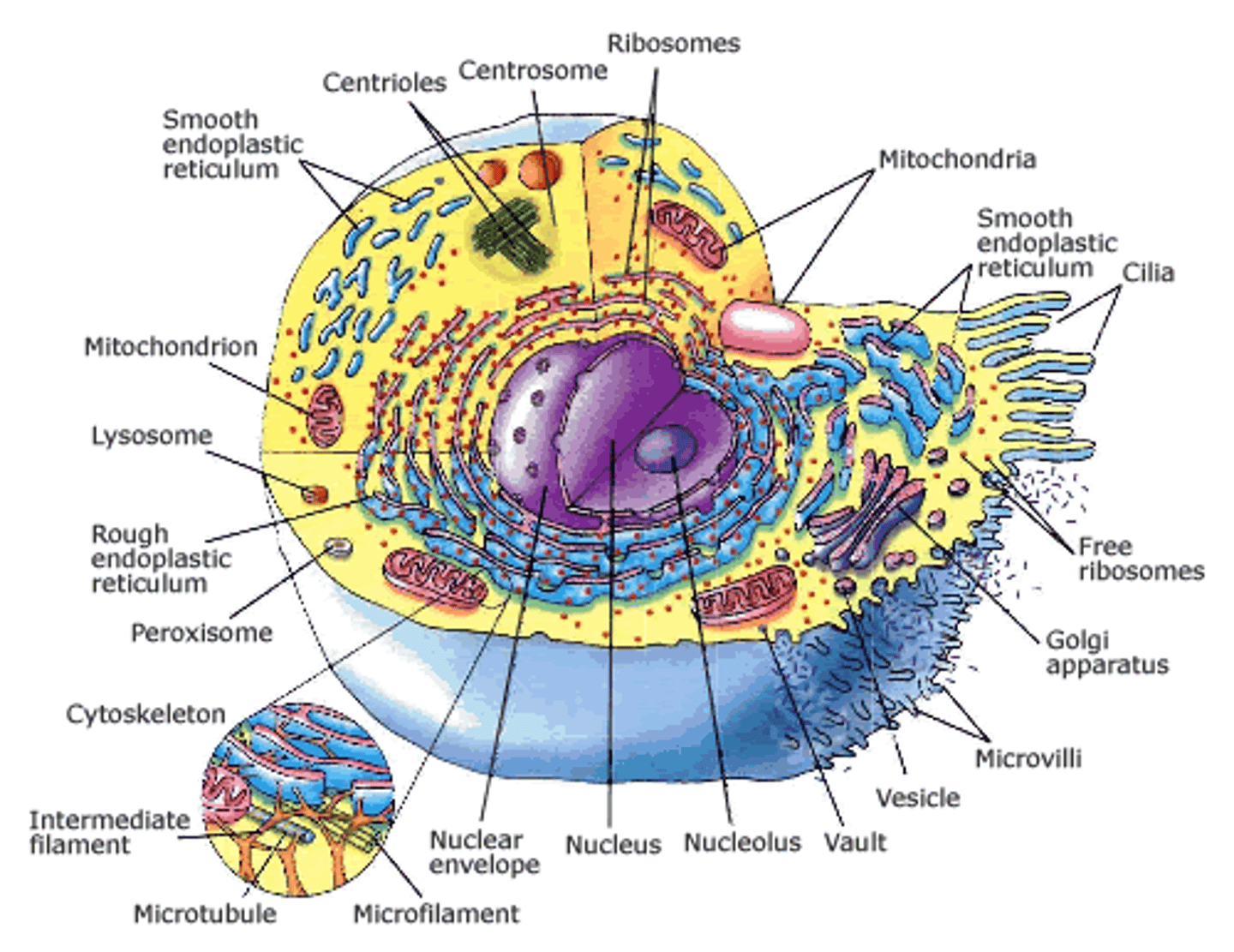
eukaryotes
organisms made up of one or more cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, usally multicellular, (ex. plants, animals, & protista)
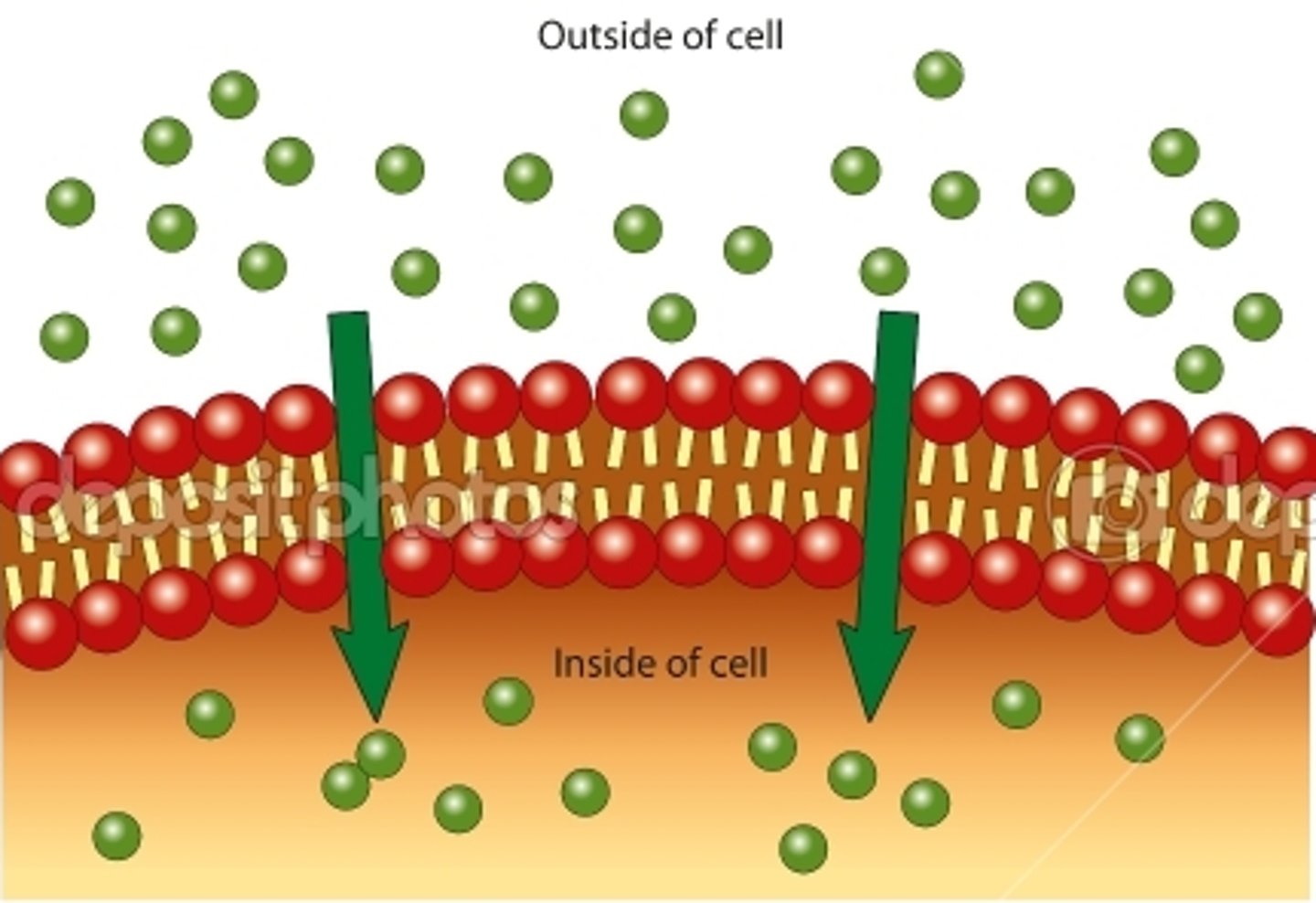
Passive Transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell, from high concentration to low concentration
simple diffusion
movement of a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
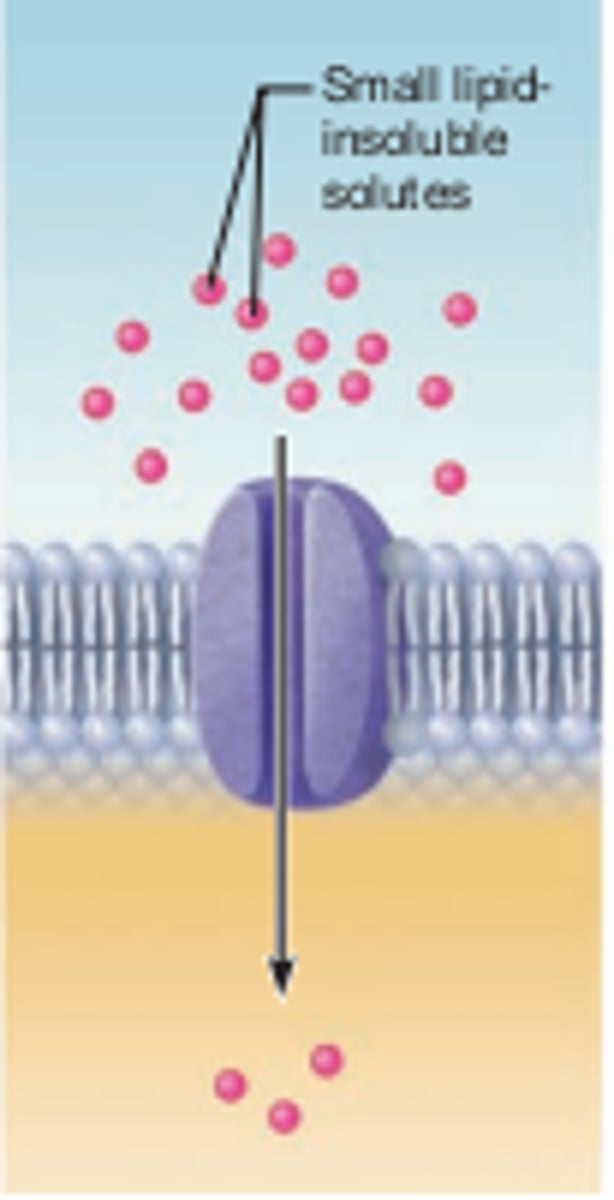
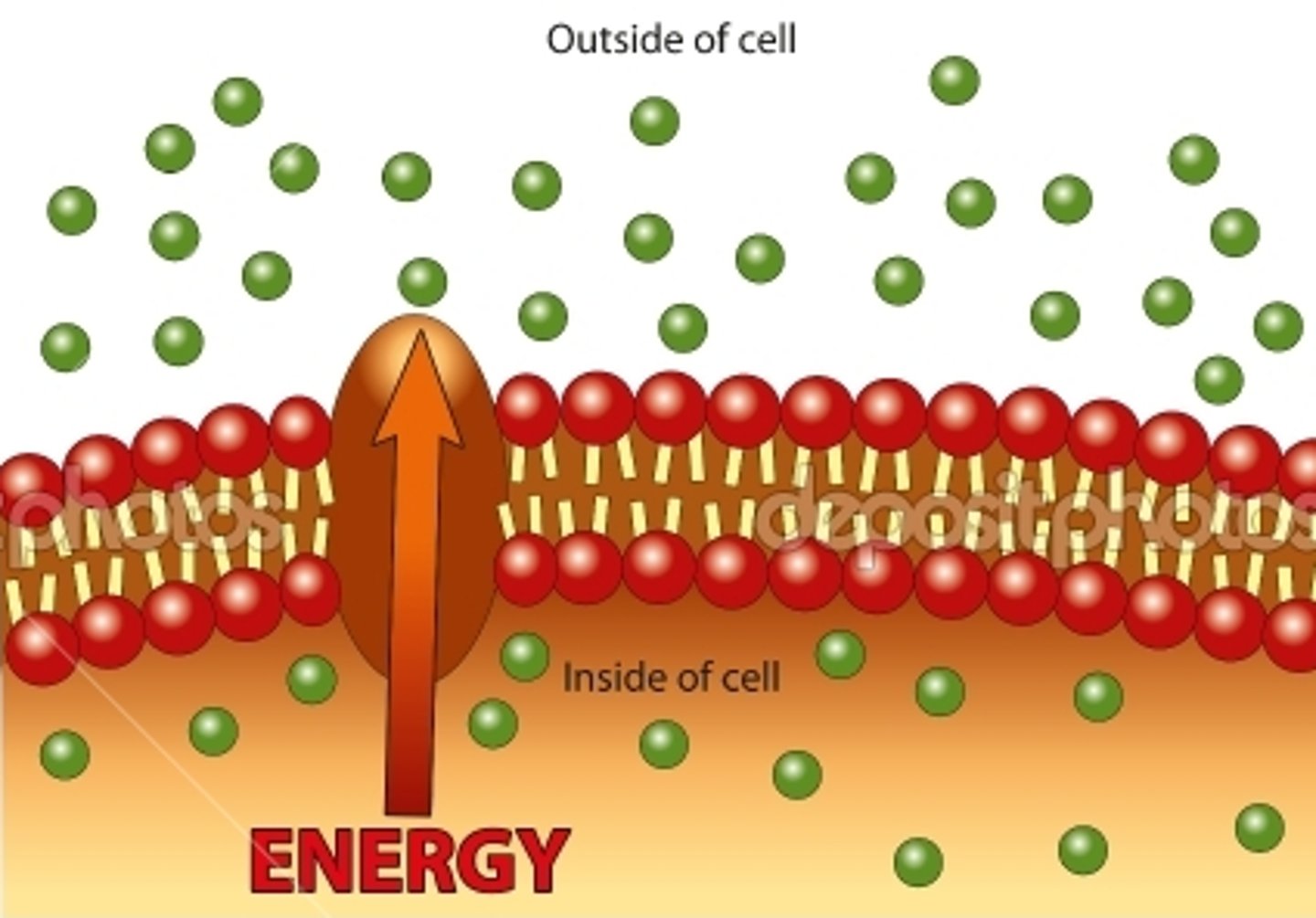
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
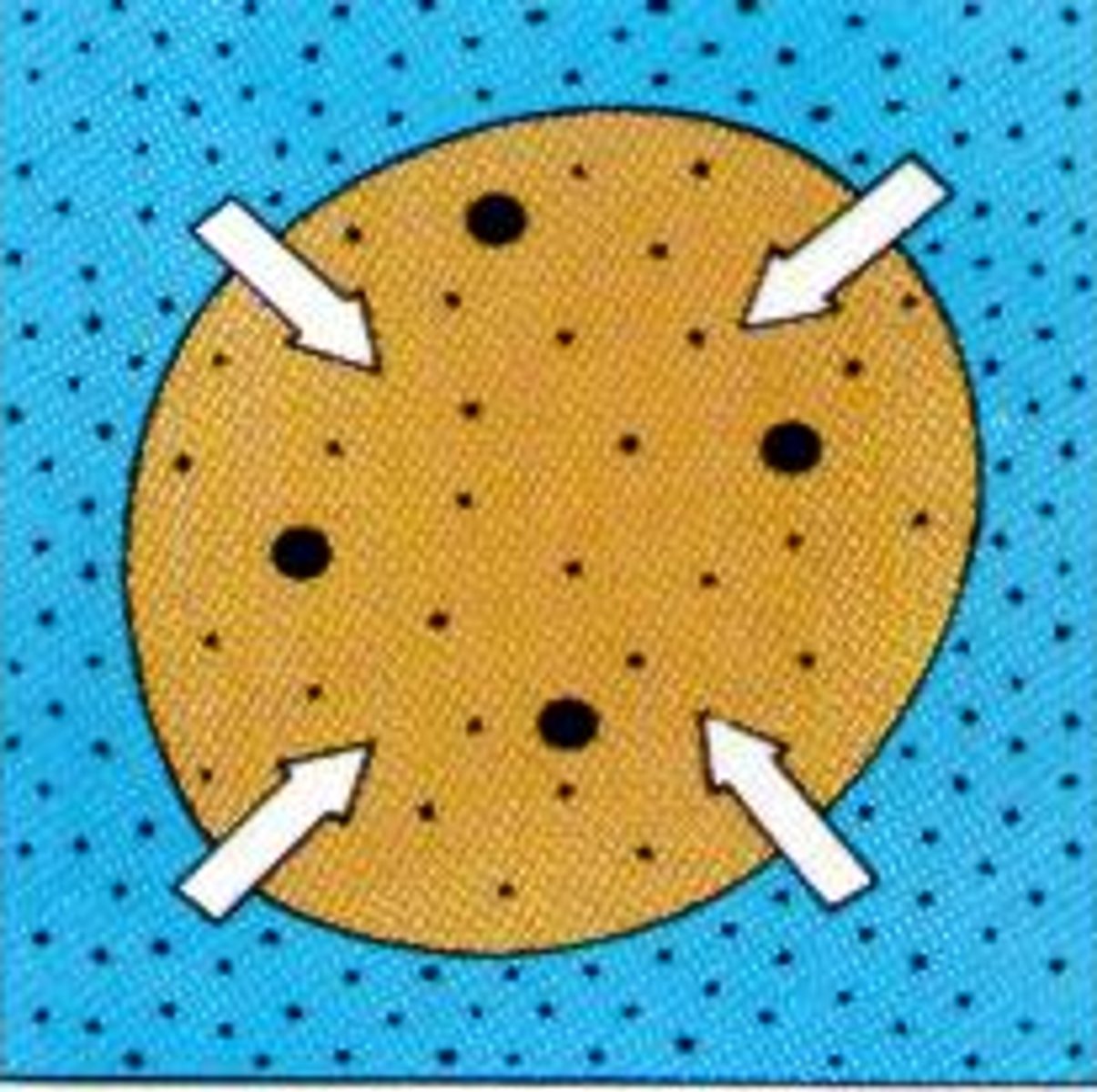
Hypertonic
when comparing two solutions, the solution with the greater concentration of solutes
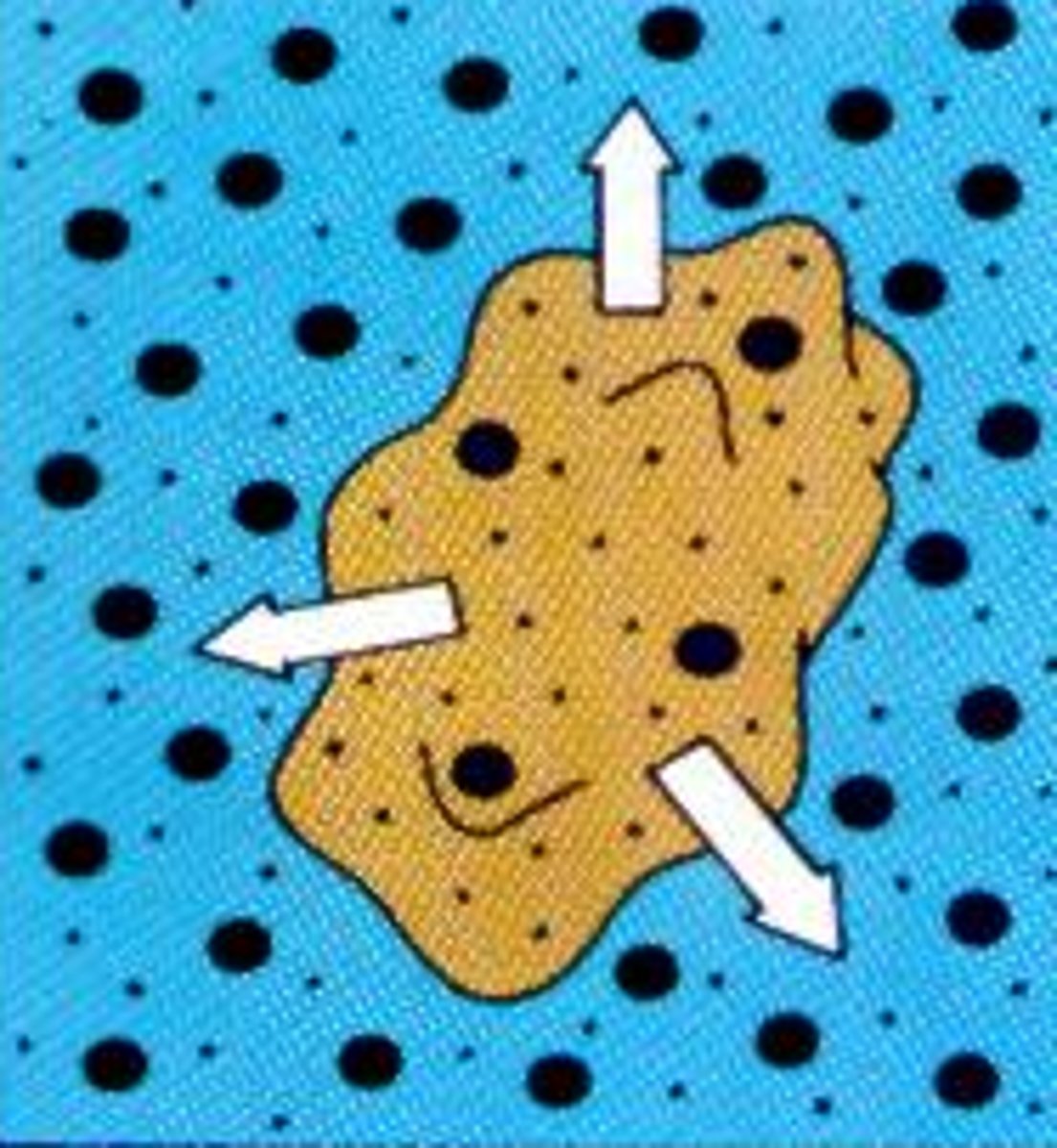

Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
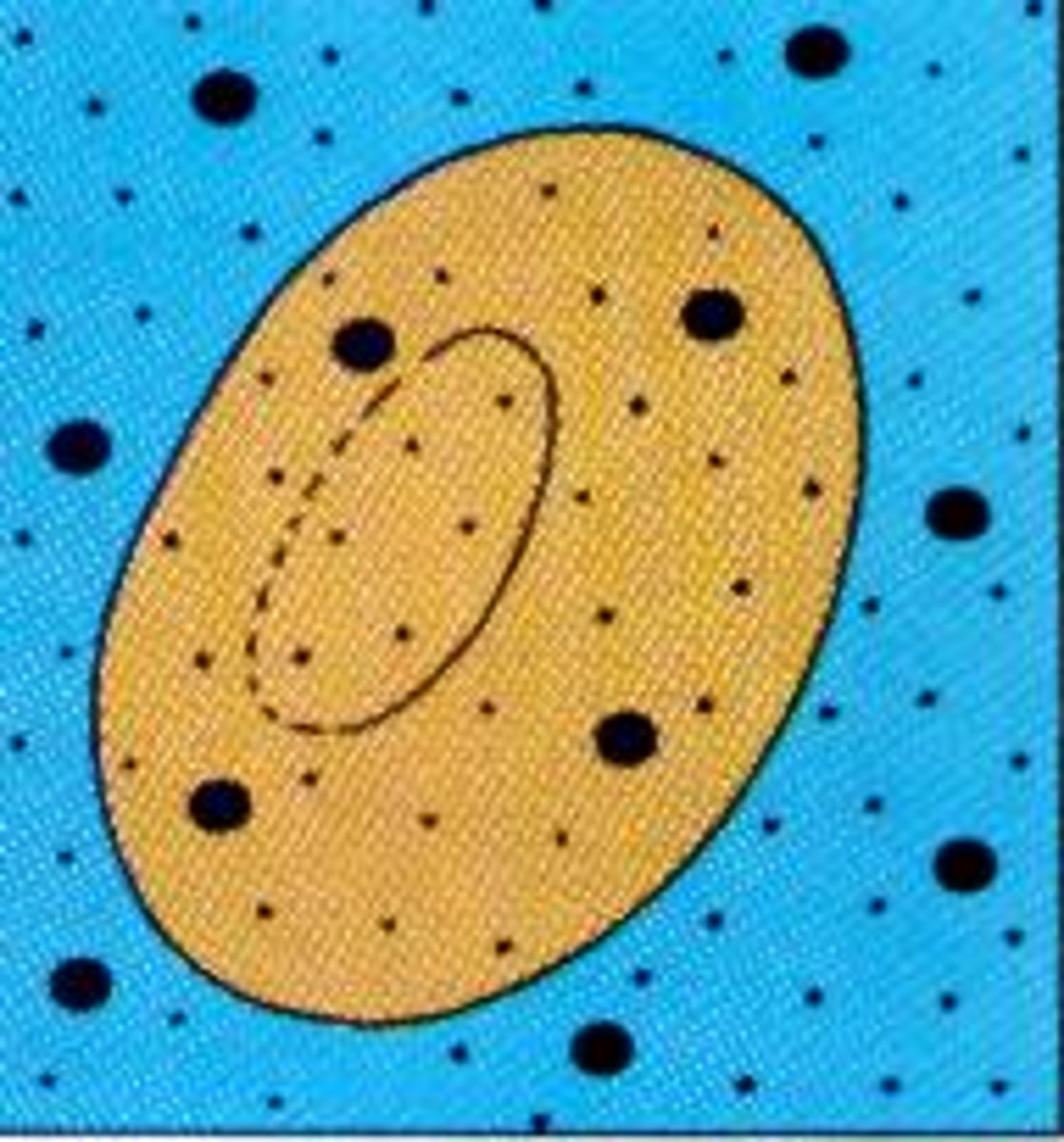
Isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same
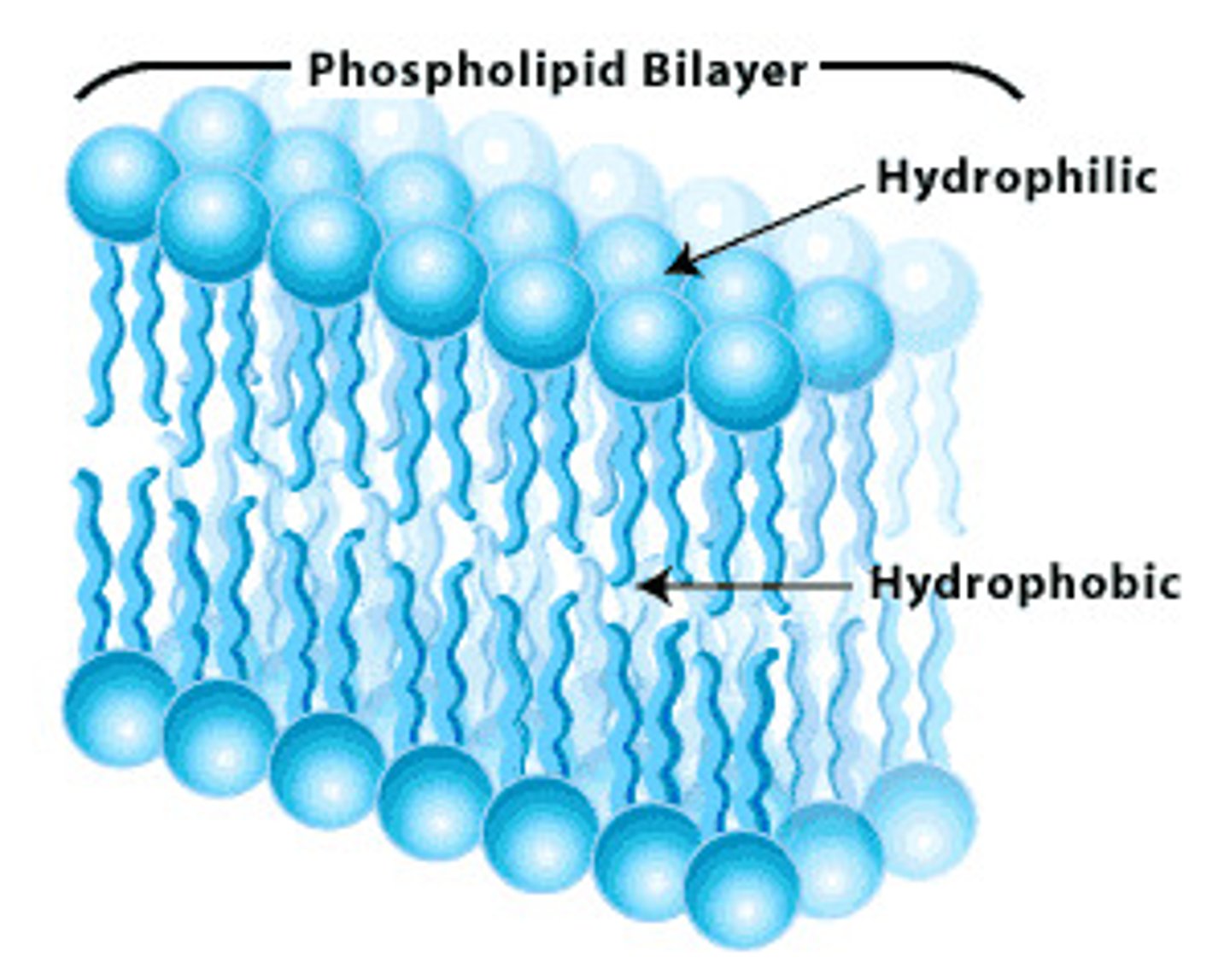
Phospholipids
A molecule that is a constituent of the inner bilayer of biological membranes, having a polar, hydrophilic head and a nonpolar, hydrophobic tail.
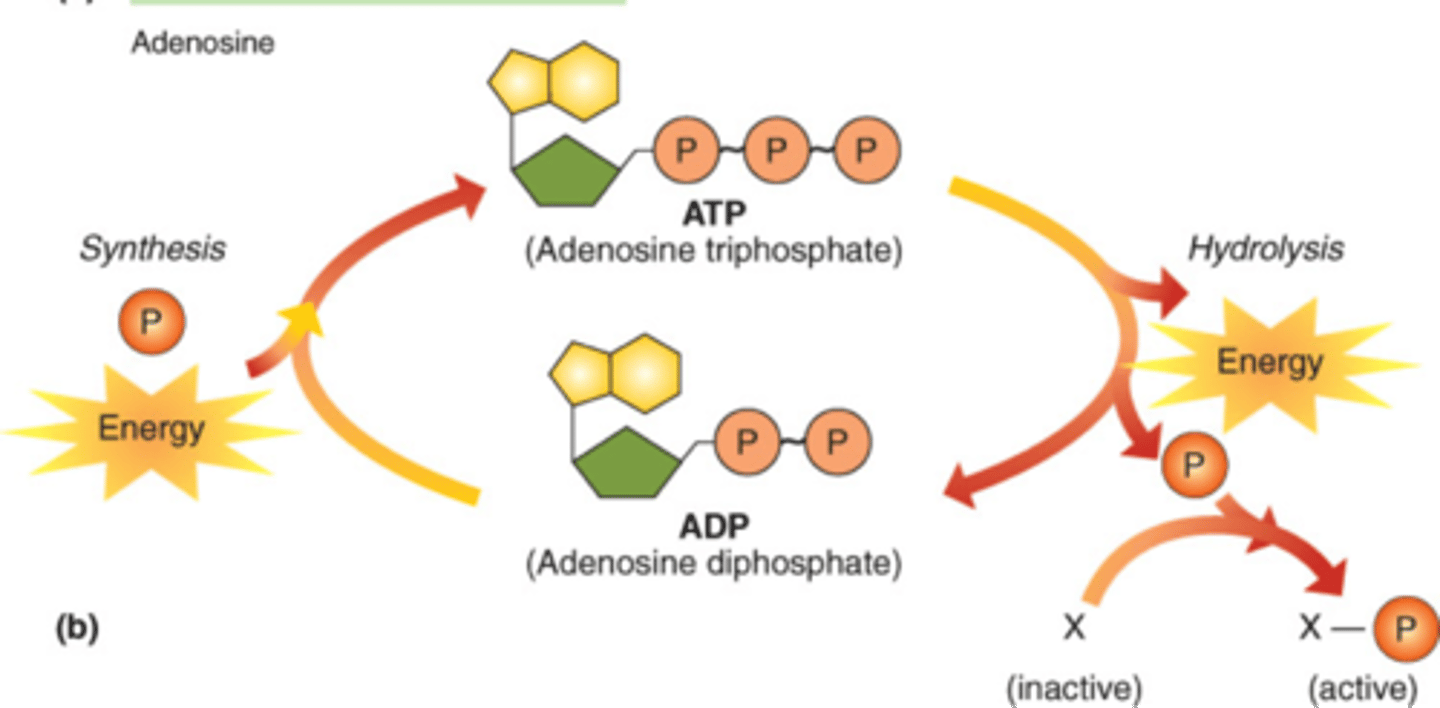
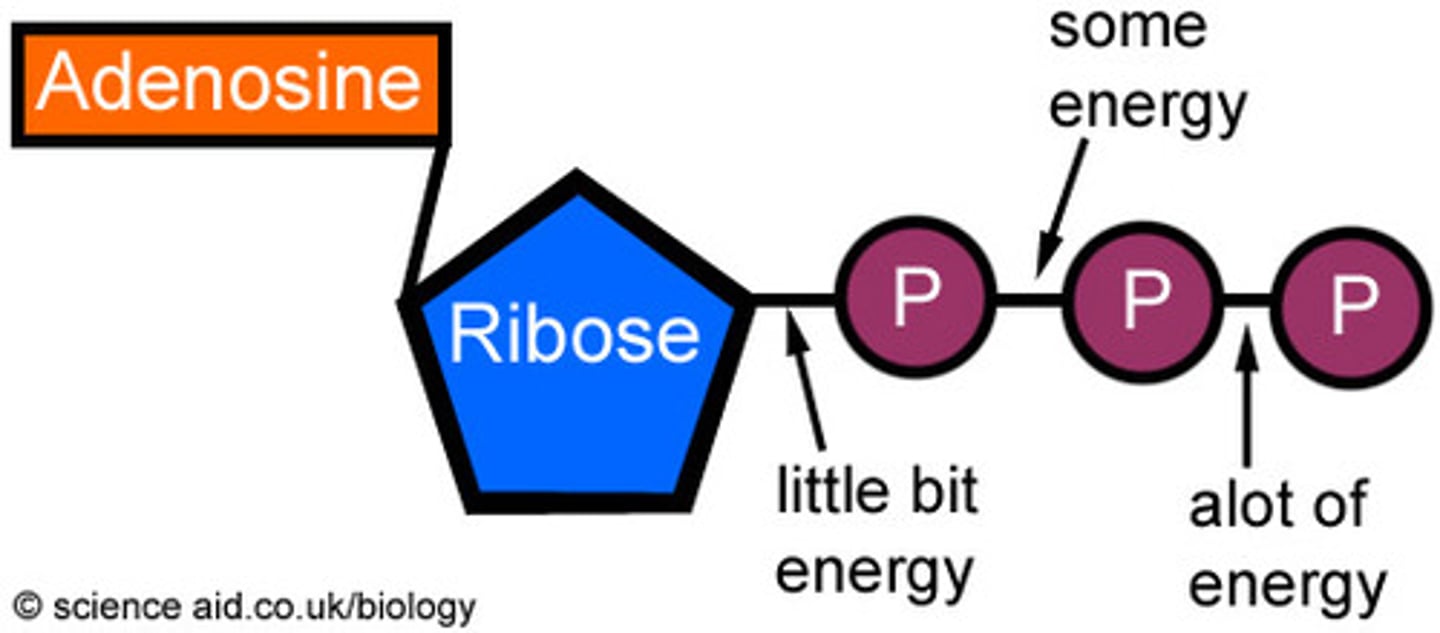
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
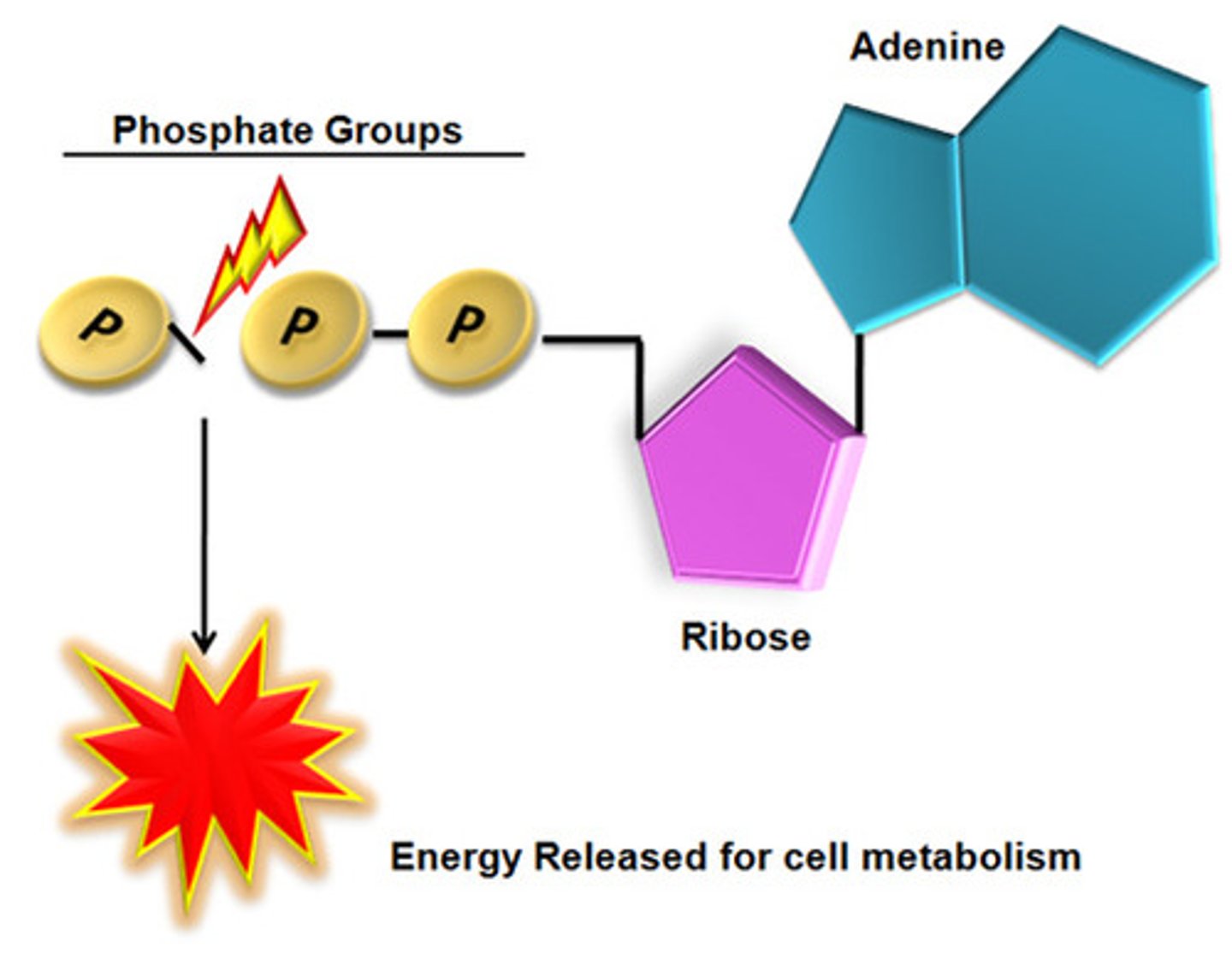
ADP
(Adenosine Diphosphate) The compound that remains when a phosphate group is removed from ATP, releasing energy
cellular respiration
Process that creates ATP in the mitochondria