Bio 006 - 15A: From Genes to Proteins 2
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
RNA Polymerase
Enzyme that makes a copy of a gene from the genome so it can be sent to a ribosome.
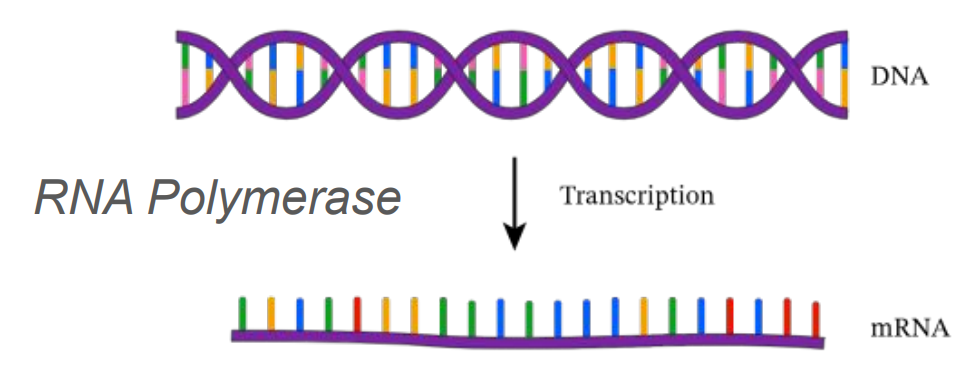
mRNA
Messenger RNA that carries genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosome.
Ribosome
Cellular structure that builds proteins (aka amino acid sequence)
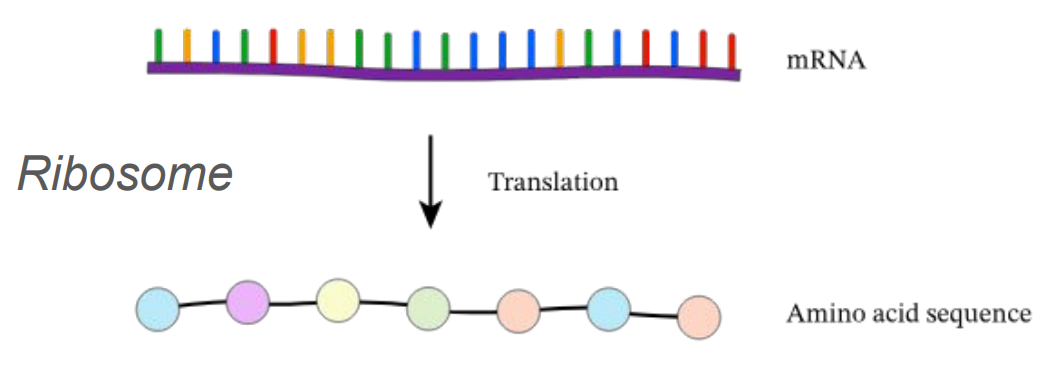
tRNA
Transfer RNA that brings amino acids to ribosomes.
Codon
Set of three mRNA nucleotides coding for an amino acid.
Anticodon
Set of three tRNA nucleotides pairing with mRNA codon.
Exons
Coding sequences that remain in mRNA after processing.
Introns
Non-coding sequences removed from mRNA.
Post-transcriptional modification
Editing of mRNA in between transcription and translation in eukaryotes.
Introns → DON'T code for proteins → CUT OUT
Exons → actually code for proteins → STAY IN
Initiation
First step of translation; mRNA binds to ribosome.
Elongation
Step of translation where amino acids are added.
Termination
Step of translation where protein synthesis ends.
Promoter
DNA sequence where transcription begins.
Ori
Origin of replication in DNA replication.
Leading strand
DNA strand synthesized continuously during replication.
Lagging strand
DNA strand synthesized in short segments.
Genome
Complete set of genetic material in an organism.
AUG
Start codon for protein synthesis.
Stop codons
UUA, UAG, UGA; signal termination of translation.
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA that makes up ribosomes.
P site
Ribosome site holding the growing polypeptide.
A site
Ribosome site where new tRNA enters.
E site
Ribosome site where tRNA exits.
Genetic Code
Set of rules defining how mRNA codons translate to amino acids.
5' to 3' direction
Direction in which RNA and DNA strands are synthesized.
antiparallel
2 stands running in opposite directions (5’ to 3’)
uracil
In RNA, thymine is switched with _________
RNA
Single stranded and has a ribose sugar (missing an oxygen)
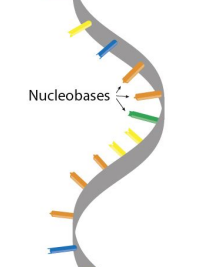
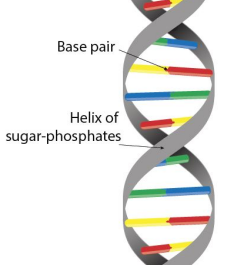
DNA
Double stranded with deoxyribose sugar.