AP Exam Terms
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bio, Lang, APUSH, & Calc AB terms to study for 2025 AP exams
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
exigence
the moment or event that motivates someone to write or to speak about a specific issue, problem, or situation
Virginia Plan
bicameral, 3-branch plan for a strong central government with representation based off population; benefitted large states
New Jersey Plan
unicameral, 3-branch plan for a stronger federal government with equal representation in one legislative house regardless of population; benefitted small states
The Great Compromise/Connecticut Plan
compromise of the VA and CT plans that called for a bicameral legislative body: the Senate would have equal representation regardless of population while the House would depend on population; also established 3 branches of government (executive, legislative, judicial)
f(x) = logax
f’(x) = 1/(a lnx); a = base of the logarithm
Marbury v. Madison
John Marshall established judicial review in this landmark court case which challenged John Adams’ “midnight appointments” in the court.
Mcculloch v. Maryland
established that federal law trumps state law
French & Indian War
French & native Americans fighting British for rights to the Ohio River Valley
War of 1812
US fought against Britain & France over maritime issues & trade restrictions (impressment); Jefferson’s Embargo Act enacted in 1807 due to rising tensions before war broke out
14th Amendment
granted citizenship and equal protection under the law to all persons born or naturalized in the United States; protected citizens from state governments as opposed to the federal government; Confederate states had to ratify this to be readmitted to the Union after the Civil War
Compromise of 1850
a package of five laws designed to address the issue of slavery in newly acquired territories after the Mexican-American War, including California's admission as a free state, the Fugitive Slave Act, and the abolition of the slave trade in Washington, D.C.
1492
Columbus encounters the Americas, facilitating the Columbian Exchange
1607
Founding of Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in America
1763
End of French & Indian War (Treaty of Paris signed)
1776
Declaration of Independence adopted
1787
American Constitution drafted at the Continental Congress, Northwest Ordinance of 1787 passed
1848
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo signed, ending the Mexican-American War; Mexican cession ceded a vast amount of territory to the United States
1860
Abraham Lincoln elected as President, signaling tensions leading to secession & Civil War
1865
The end of the Civil War; the 13th Amendment abolished slavery in the United States
1877
The end of Reconstruction, leading to the withdrawal of federal troops from the South (Compromise of 1877) and the beginning of Jim Crow laws
1898
The Spanish-American War began, resulting in the U.S. gaining territories like Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines
1901
The assassination of President William McKinley, leading to Theodore Roosevelt's presidency and progressive reforms
1929
The stock market crash marking the beginning of the Great Depression
1941
The attack on Pearl Harbor leading the United States to break isolationist policy and enter World War II
1945
The end of World War II following the surrender of Germany in May and Japan in September
1989/1991
The collapse of the Soviet Union and the end of the Cold War, symbolized by the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 and the dissolution of the USSR in 1991
Civil Rights Act of 1866
grants citizenship and the same rights enjoyed by white citizens to all male persons in the United States "without distinction of race or color, or previous condition of slavery or involuntary servitude” and passed over Johnson’s presidential veto
Vietnam War
lasted from 1955 to 1975
Civil War
1861-1865
Revolutionary War
1775-1783
steps to determine continuity algebraically
find the output at the specific x-value & then determine if the one-sided limits are equal
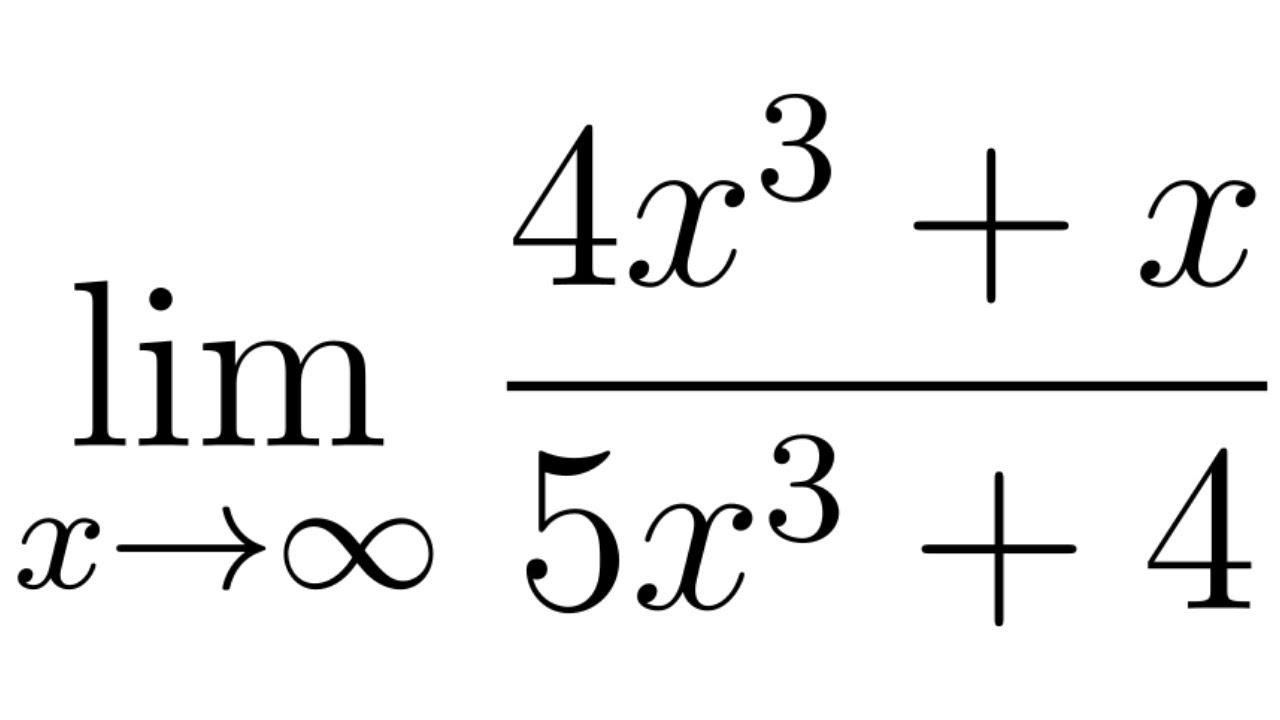
limit of f(x) as x → infinity
example of a function with a horizontal asymptote
when the output of a function approaches infinity as it approaches a specific x-value
vertical asymptote (unbounded)
glasnost
policy of increased openness and transparency in the Soviet Union introduced by Mikhail Gorbachev during the late 1980s, contributing to the end of the Cold War
perestroika
policy of economic and political restructuring in the Soviet Union initiated by Mikhail Gorbachev during the late 1980s, contributing to the end of the Cold War
Keynesian economics
economic theory that promoted federal deficit spending to pull an economy out of recession and advocated for government intervention in the economy; prevalent particularly during the years of the Great Depression
Bacon’s Rebellion (1676)
pre-American Revolution rebellion that increased fear of riots and uprisings of laborers (indentured & enslaved) leading to a shift away from indentured labor & the beginnings of white supremacy rhetoric
Populist/People’s Party
grassroots movement of poor, aggrieved farmers in the 1890s who wanted radical reform from the government; platform included nationalization of railroads, coinage of silver (for inflation), and a graduated income tax
Progressivism
prevalent in the early 20th century & made up of urban middle-class activists with savior complexes who held enough economic and political clout to influence change on a federal level; wanted increased government regulation & reform while maintaining the capitalist system
platform included women’s rights, labor rights, civil rights; pioneered by Robert La Follette and Teddy Roosevelt
Shay’s Rebellion (1786)
a strong example of the weakness of the federal government under the Articles of Confederation; in part led to the Constitutional Convention and the strengthening of federal power through the new Constitution