articulations a&p
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
main function of joints
joints connect two bones
how do joints help with movement
surrounding muscles and tendons exert the necessary amount of force across the joint allowing movement.
how do joints help with stability
joints that allow limited to no movement are very stable. critical for joints that protect underlying structures.
how do joints help bones lenghten
the epiphyseal plate is the location in long bones that grow during skeletal development
synarthrosis
no movement between two bones; provides most stability
ampiarthrosis
small amount of movement; provides significant amount of stability
diarthrosis
freely moveable joint with a wide variety of movements. least amount of stability.
fibrous joints
united by dense regular collagenous connective tissue, no joint space. synarthroses or ampiarthroses.
cartilagenous joints
cartilage between articulating bone, no joint space. synarthroses or ampiarthroses.
synovial joint
joint cavity, filled with fluid between articulating bone. diarthroses.
sutures
joint between bones of the skull. held together by short collagen fibers. stable synarthroses.
gomphoses
joint between a tooth and corresponding alveolus in the mandible or maxilla. attached to bone fibers called peridontal ligament.
syndesmosomes
articulating bones are joined by an interosseous membrane or ligament. composed of dense regular collagenous connective tissue.
synchondroses
bones united by hyaline cartilage
symphyses
bones united by a fibrocartilage pad
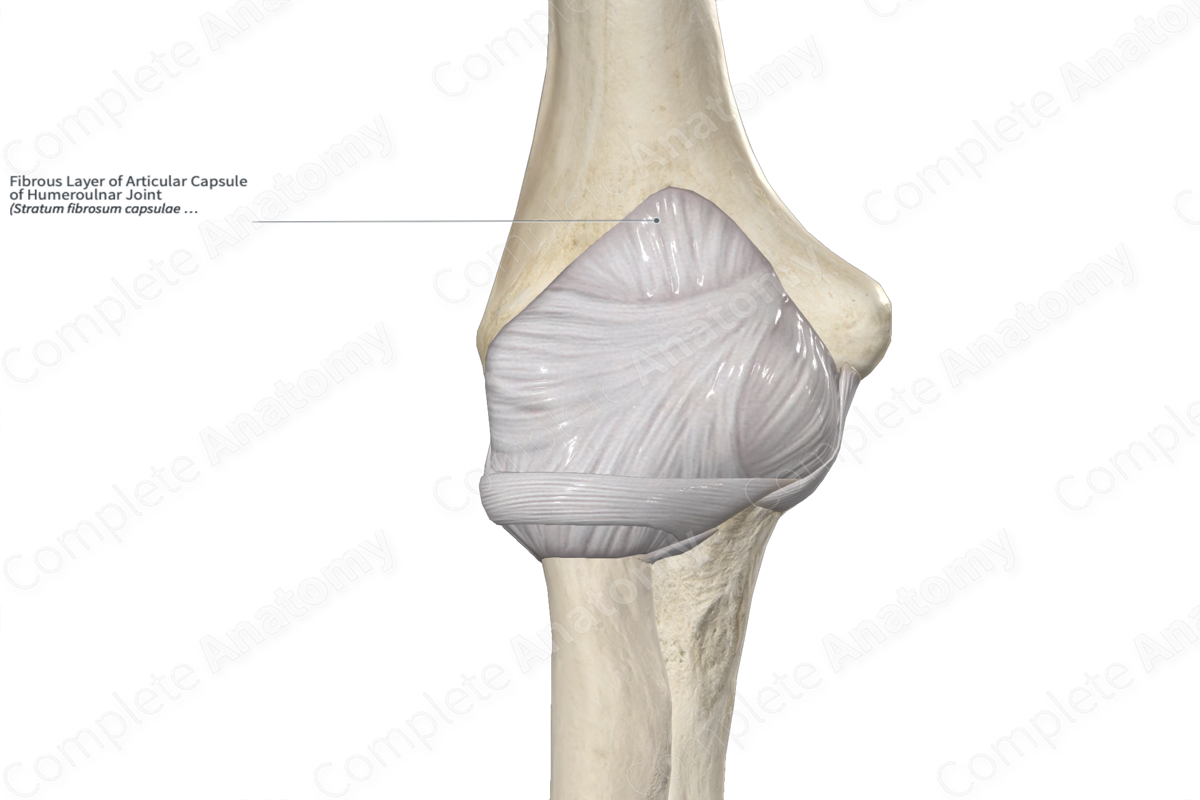
articular capsule
double layered structure. outer fibrous layer made of dense irregular ct. inner synovial membrane is made of loose ct.
lubrication
reduces friction
metabolic function
supplies nutrients like glucose. removes metabolic waste
shock absorption
evenly distributes force and stress on articular surfaces of bones during movement
ligament
made of dense regular collagenous ct that connects one bone to another bone
intrinsic ligament
thickened region of the articular capsule
extrinsic ligament
not part of articular capsule that may be inside or outside of the joint cavity
tendons
made of dense regular collagenous ct that connects a muscle to a bone or another structure
bursae
synovial fluid-filled structure with a synovial membrane. found in regions of high stress where bones, tendons, and muscles interact in a small space to minimize friction
tendon sheaths
long bursae that surround some tendons in high stress regions of the body. protects long tendons as they course over and around synovial joints
bursaitis
inflammation of a bursa, most commonly in the shoulder, elbow, hip, and knee
arthritis
inflammation of one or more joints, resulting in pain, joint stiffness, and decreased range of motion
osteoarthritis
most common form of arthritis, occurs from wear and tear
rheumatoid arthritis
autoimmune disease that results in joint destruction mediated by individuals own immune system
gouty arthritis
joint damage due to inflammatory reaction to excess uric acid crystal deposits
nonaxial joints
motion occurs in one or more planes, but don’t move around an axis.
uniaxial joints
motion around one axis
biaxial joints
motion around two axes
multiaxial joints
motion around three axes.
gliding movements
sliding motion between the articulating surfaces of bones in a joint
angular movements
increase or decrease the angle between articulating bone
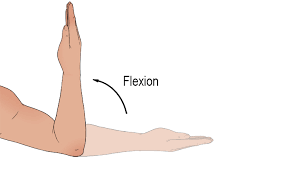
flexion
decreases angle between articulating bones by bringing them together.
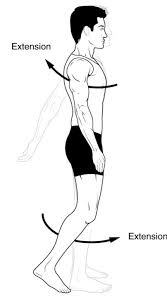
extension
increases angle between articulating bones
hyperextension
extension beyond the anatomical position of a joint
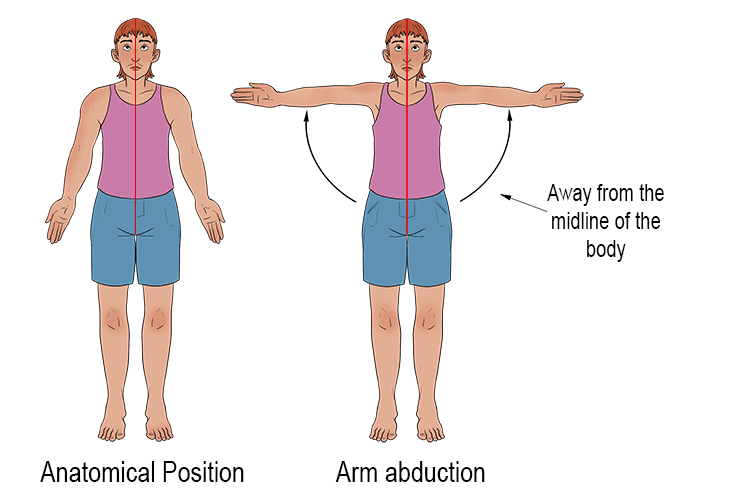
abduction
motion of body away from midline or another reference point
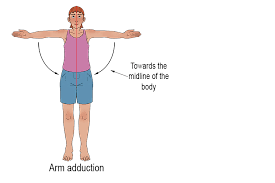
adduction
towards the midline of the body or another reference point
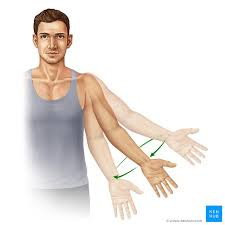
circumduction
a freely moveable distal bone moves around a stationary proximal bone in a cone-shaped motion
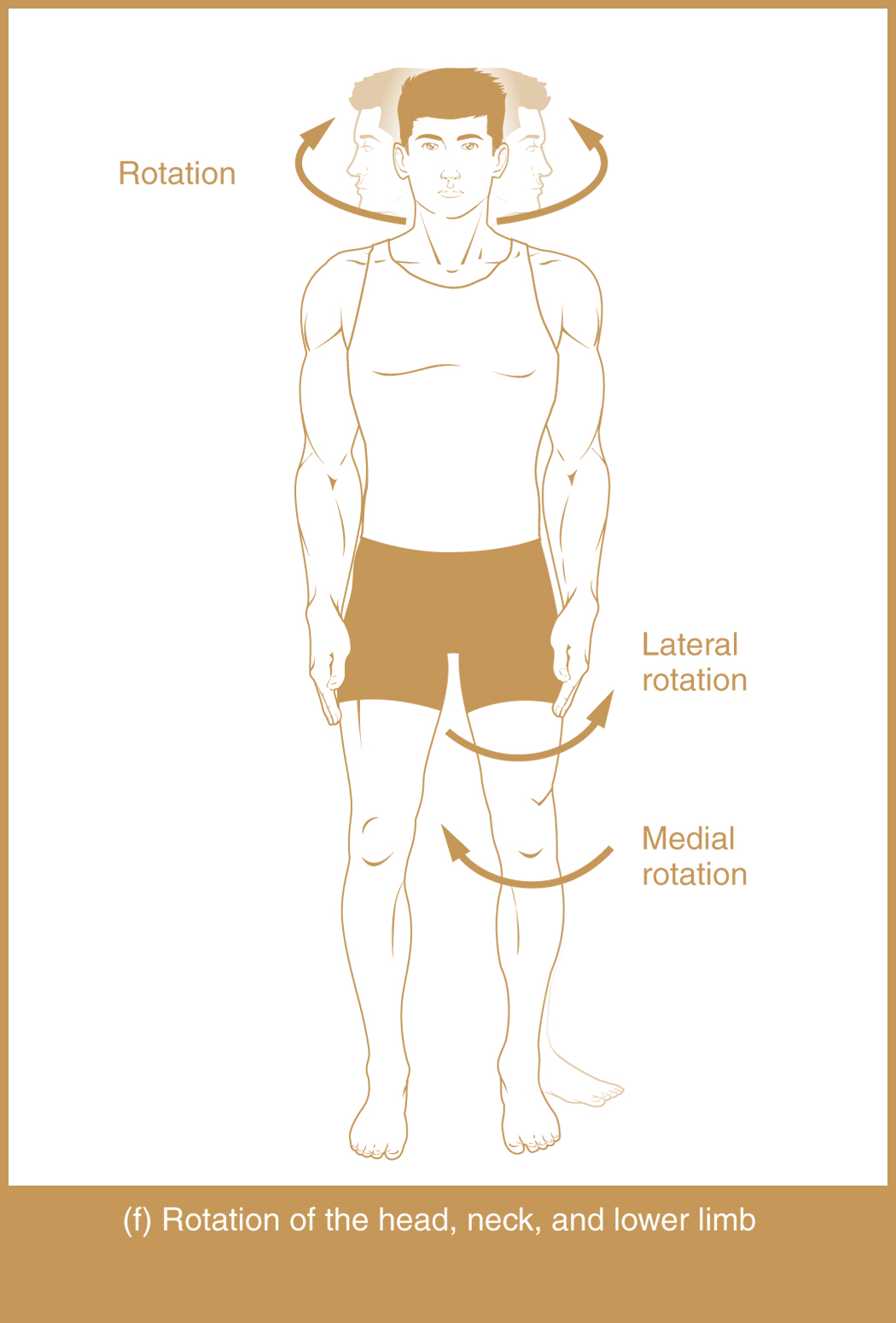
rotation
nonangular pivoting movement one bone twists or rotates on a longitudinal axis (internal is rotation towards midline while external is rotation away from midline)
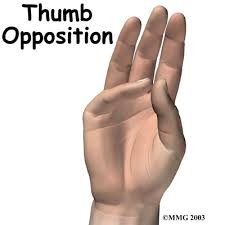
opposition
occurs with thumb. movement of thumb across palmar surface of hand
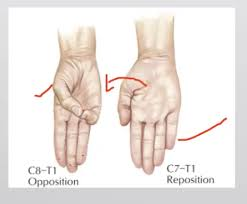
reposition
return of thumb to anatomical position
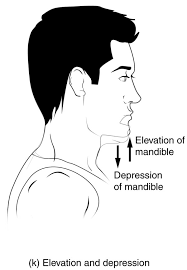
depression
movement of body part in an inferior direction
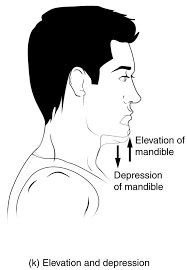
elevation
movement of body part in a superior direction
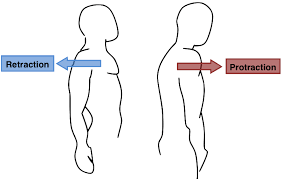
protraction
moves body part in an anterior direction
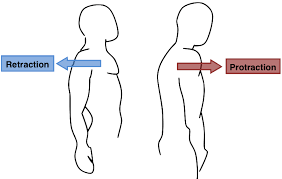
retraction
moves a body part posteriorly
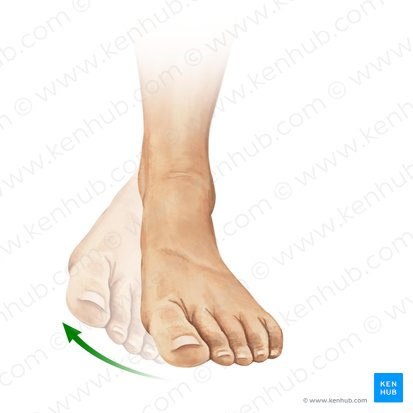
inversion
rotational movement of foot, plantar surface rotates medially towards midline
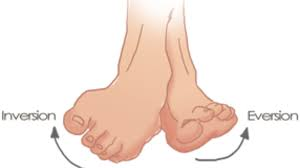
eversion
movement of plantar surface of foot laterally away from the midline
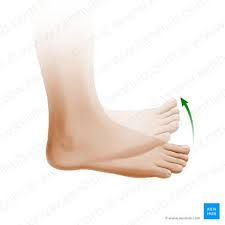
dorsiflexion
angle between foot and tibia decreases. toes are pulled towards head
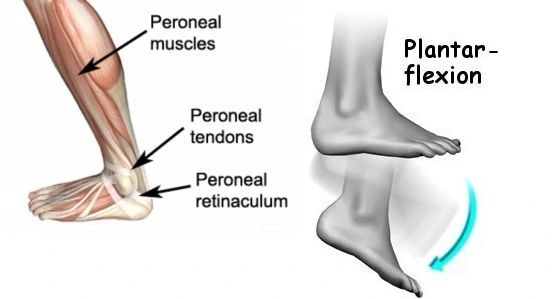
plantarflexion
angle between foot and tibia increases toes point towards ground
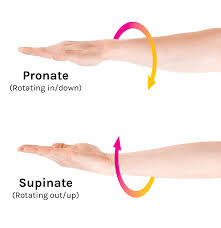
supination
forearm is supinated when palm faces anteriorly with thumb pointing laterally
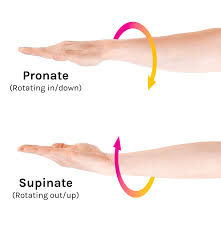
pronation
palmar surface of hand faces medially until it faces posteriorly with thumb pointing medially
range of motion
amount of movement a joint is capable of under normal circumstances
nonaxial joints
smallest range of motion. ex = intercarpal joints
multiaxial joints
greatest range of motion. ex = shoulder
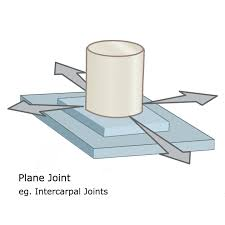
plane joint
nonaxial joint, two bones whose flat surfaces sit next to each other
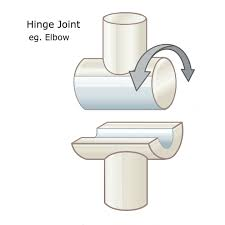
hinge joint
uniaxial joint, convex surface of one bone fits into a concave depression of another bone
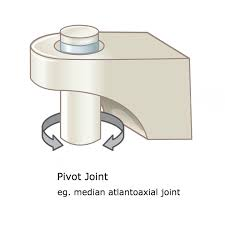
pivot joint
uniaxial joint, rounded surface of one bone fits into a groove on the surface of another bone.
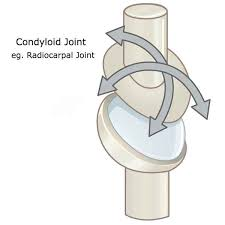
condylar joint
biaxial joint, oval, convex joint surface of one bone fits into a shallow concave surface of another bone
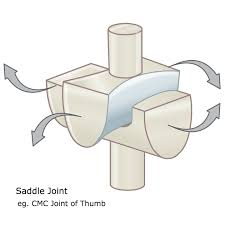
saddle joint
biaxial joint, surface of each articulating bone has both convex and concave regions that complement each other.
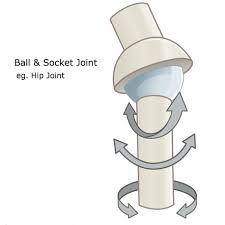
ball-and-socket joint
multiaxial joint. articulating surface of one bone is ball shaped and fits into a cup or socket formed by the articulating surface of the other bone
elbow
hinge joint composed of two articulations
humeroulnar joint
between trochlea of humerus and trochlear notch of the ulna
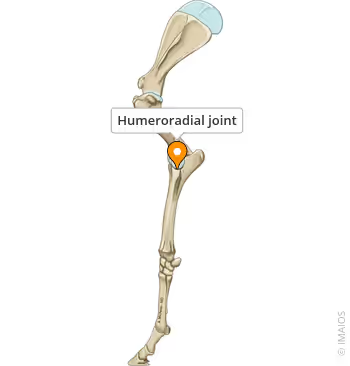
humeroradial joint
between capitulum of humerus and the head of the radius
radial collateral ligament
supports lateral side of joint
ulnar collateral ligament
supports medial side of joint
anular ligament
stabilizes the radial head
knee
largest diarthrosis of the body. hinge joint that allows for some degree of rotation and lateral gliding
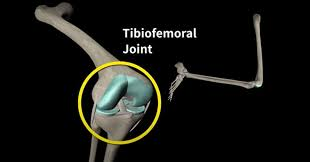
tibiofemoral joint
between femoral and tibial condyles.
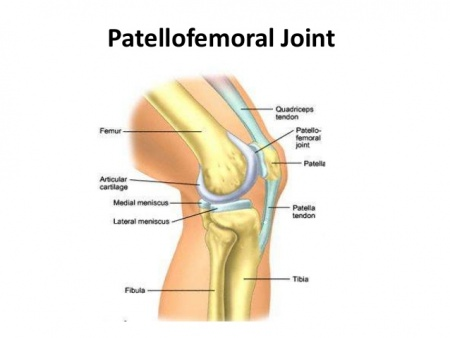
patellofemoral joint
between patella and patellar surface of the femur.
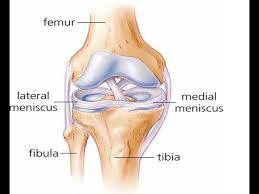
medial and lateral menisci
pair of c-shaped fibrocartilage pads on the tibial condyles
tibial collateral ligament
links femur with the tibia and attaches to medial meniscus
fibular collateral ligament
links femur with fibula but does not attach to the lateral meniscus
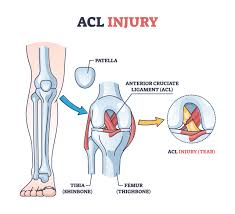
anterior cruciate ligament
runs from anterior insertion site on tibia to the posterior aspect of the femur
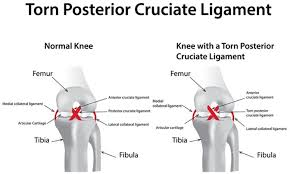
posterior cruciate ligament
runs from posterior side of tibia to anterior femur
shoulder (glenohumeral joint)
made up of ball-shaped humeral head and the glenoid cavity on the lateral scapula
glenoid labrum
fiqrocartilogenous ring that sits on the rim of the glenoid cavity
dislocated shoulder
glenohumeral joint with traumatic displacement of the head of the humerus from the glenoid cavity
separated shoulder
acromioclavicular joint (not a component of the shoulder)
hip (coxal joint)
Articulation between the acetabulum and the ball-shaped head of the femur; Multiaxial ball-and-socket joint; More stable than the shoulder joint
Acetabular Labrum
Fibrocartilage ring strengthens the fit between the bones
Iliofemoral Ligament
Reinforces anterior side of the hip joint
Ischiofemoral Ligament
Supports posterior side of the hip joint
Pubofemoral Ligament
Triangular thickening of the inferior portion of the articular capsule
Ligament of the Head of the Femur
Links the center of the head of the femur with the acetabulum