TOPIC 10- Plant Reproduction and Development
1/49
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
homospory
haptophytes and bryophytes- sex chromosomes
monilophytes- hermaphroditic gametophytes
antheridgen
pheromone released by the first hermaphroditic monilophyte present, that causes neighbouring spores to develop into males
the presence of other sperm in the environment helps prevent self-fertilization
heterospory
coniferophyta and anthophyta
top bottom
females near the ____ of the tree, and males at the ____ of the tree to prevent self-pollination in coniferophytes
caused by a hormone gradient in the tree
abc hypothesis

phyla anthophyta
phylum in which both sperm are involved in fertilization

terminal basal
the anthophytes’ zygote first divides into ____ and ____ cell
terminal cell
develops into proembryo and then into an embryo
basal cell
develops into the suspensor (umbilical cord) that connects the embryo to the parent sporophyte
does
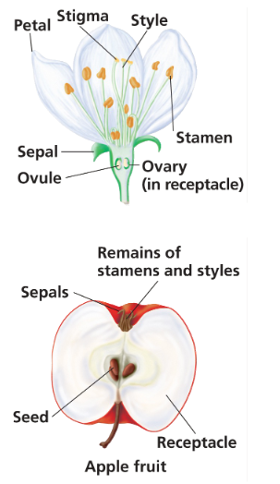
ovary forms ____ form into the fruit
-simple fruit, aggregate fruit, and multiple fruit
does not
ovary ___ form into the fruit
accessory fruit
simple fruit

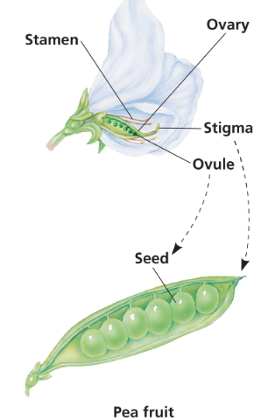
aggregate fruit

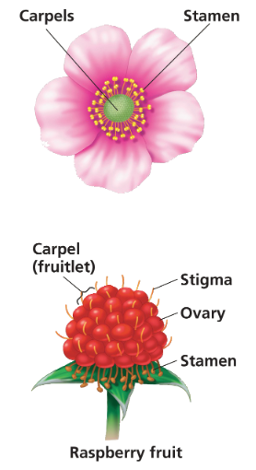
multiple fruit
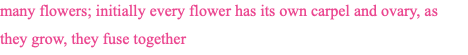

accessory fruit

dermal tissue
tissue type made from epidermal cell that protects cells from injury
waxy cuticle stops them from drying out
stoma
opening (pore) on the plants that allows for gas exchange
surrounded by guard cells
trichome

periderm
the name of secondary tissue for old-growth plants
increases the plant's width
forms the outer bark
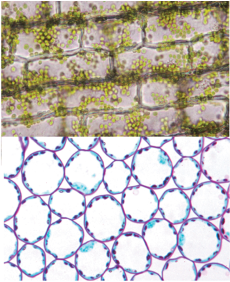
parenchyma

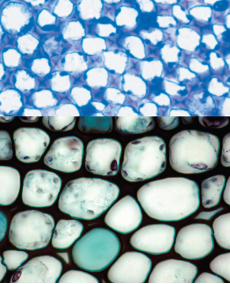
collenchyma

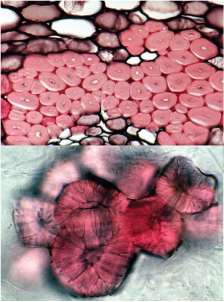
sclerenchyma

xylem
vascular tissue used for water and mineral transport
transports from root to shoot
dead at maturation
phloem
vascular tissue that transports sugars
transports in either direction depending on the time of year
alive at maturity
vascular cambium call
meristem that produces xylem (inside) and phloem (outside)
cork cambium
meristem that produces cork cells (periderm)
always adds onto the outside of the bark
forms the outer bark
function of roots

primary root
first root that emerges from the seed
continued growth from the embryonic radicle
lateral root
root that grows from another root
adventitious root
roots that grows from something other than a root
monocot root
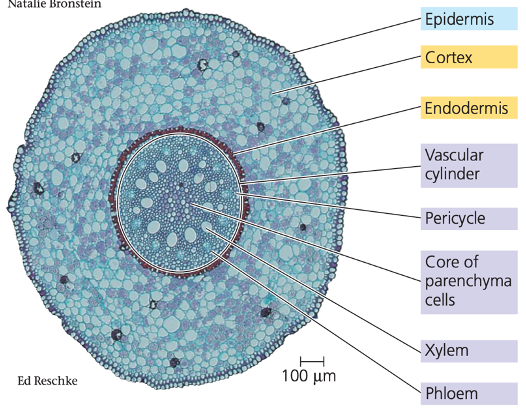
eudicot root
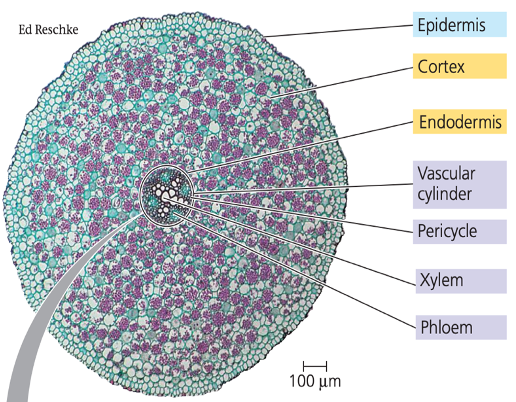
root cap
protects the RAM and produces the root
endodermis

cortex
type of ground tissue made up of layers of cells
stores nutrients and transports water and salts from the root hairs to the center of the root
pericycle
lateral root growth starts from the ______
terminal bud
houses the SAM at the end of each branch
axillary bud

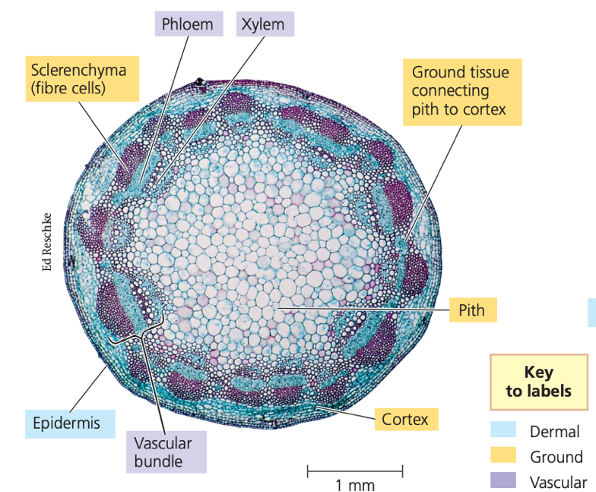
pith
located at the center of stem cross-sections
parenchyma; ground tissue
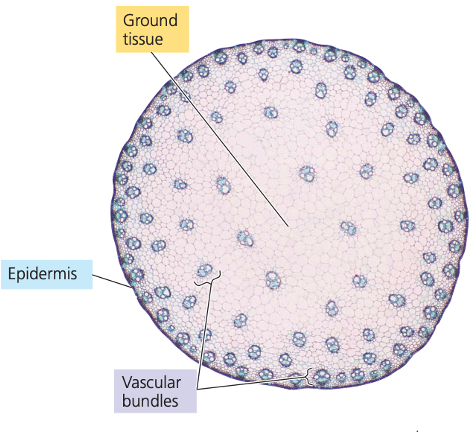
monocot stem
eudicot stem
leaf growth

simple leaf

compound leaf
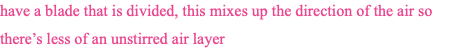
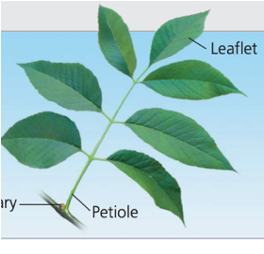
axillary bud
part of the leaf that includes the dormant SAM
palisade mesophyll
ground tissue in leaves

spongy mesophyll
ground tissue in leaves
secondary xylem
product of the vascular cambium
wood
appears once plant isnt green
grows one ring every year
secondary phloem
forms the bark
initials
dividing cells of the vascular cambium