Emotion
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Made by @agreyr
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Emotion
A subjective experience accompanied by distinctive cognition, behavior, and physiological changes
Must be experienced in the body; involves characteristics of valence and arousal
Examples of high arousal, positive valence emotions
Excited, astonished, aroused, delighted, glad, happy
Examples of low arousal, positive valence emotions
Pleased, satisfied, content, serene, calm, at ease, relaxed, sleepy
Examples of high arousal, negative valence emotions
Alarmed, afraid, angry, tense, distressed, annoyed, frustrated
Examples of low arousal, negative valence emotions
Miserable, depressed, sad, bored, gloomy, droopy, tired
Emotion theories
All theories of emotion involve a stimulus, a physiological state, and an emotional experience; the difference lies in which comes first (informs cause and effect)
James-Lange theory, Cannon-Bard theory, Schacter & Singer two factor theory
James-Lange theory of emotion
The stimulus first triggers a physiological response in the body which in turn triggers the emotional experience in the brain; the rapid heartbeat produces the fear

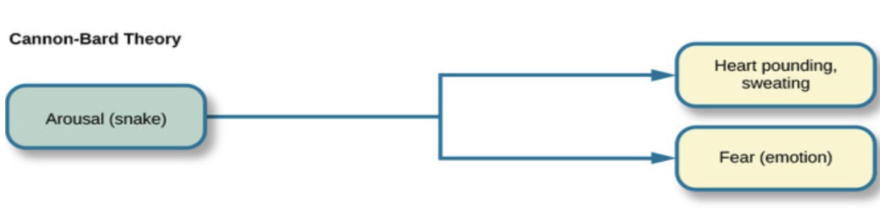
Cannon-Bard theory of emotion
The stimulus simultaneously triggers the physiological response in the body and triggers the emotional experience in the brain; they are parallel processes
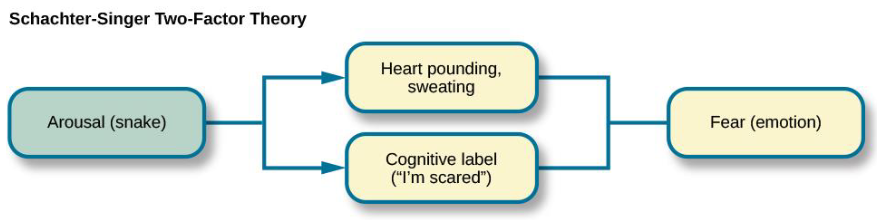
Schacter & Singer two factor theory of emotion
Emotions are based on inferences about the causes of general physiological reactions; it has to involve a cognitive appraisal of the current context