Clinical Immunology - Leukocytes
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Granulocytes and mononuclear
What are the two major types of leukocytes?
Segmented nuclei and cytoplasmic granules
What are the two main characteristics of granulocytes?
Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
What are the subtypes of granulocytes?
Lymphocytes and monocytes
What are the subtypes of mononuclears?
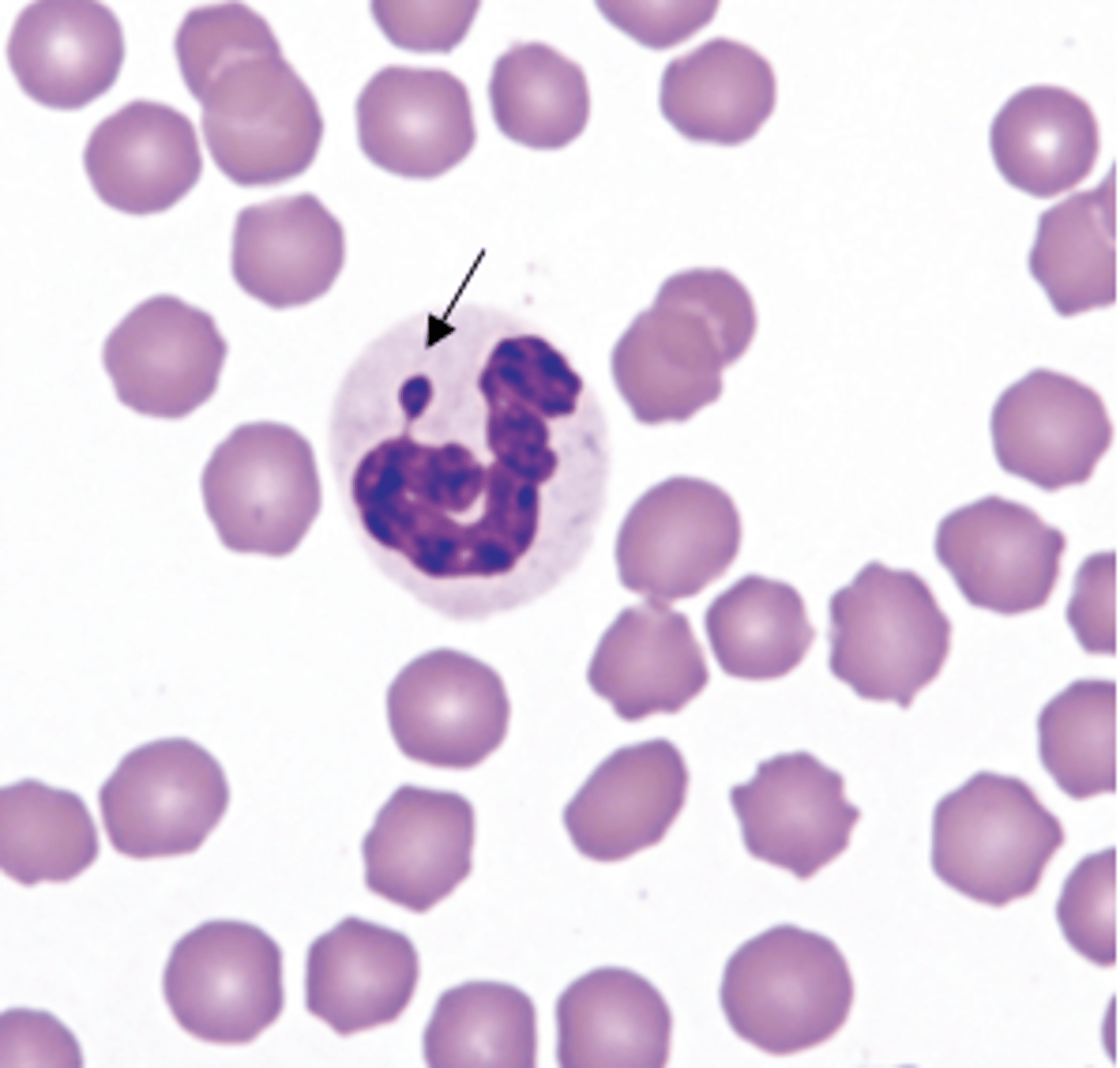
A Barr body or inactive X chromosome; implies that this sample is from a female patient
The arrow in the image is pointing to what structure? What does this imply?
3-5 lobes and condensed chromatin
The nucleus of a neutrophil has what characteristics?
Colorless, or neutral
The specific granules of neutrophils appear how in a stain?
Heterophils
Which cells in exotics are analogous to neutrophils?
Defend host against invading microbes, recognize and migrate to inflammatory signals, phagocytosis, and bacterial killing
What are the main functions of neutrophils in the immune system?
Endothelium
Neutrophils bind to what structure for transmitigation to tissues?
Actin and myosin filaments in the cytoplasm
Neutrophils are motile die to the presence of?
Acidic
The pH of an activated neutrophil is (basic/acidic) in order to inhibit bacterial activity
Defensin and lysozyme
Which enzymes in neutrophils are bactericidal?
Binds to iron to inhibit microbial replication
Lactoferrin is a substance found in the granules of neutrophils. What is its purpose and method of action?
Decrease; bacterial infection and sepsis
Neutropenia, which is a ___ in the number of neutrophils, enhances the risk of what?
Neutrophils cannot enter or exit blood or tissue due to endothelial adhesion defect
BLAD or CLAD are dysfunctions of neutrophils in what capacity?
Blood
Neutrophils migrate from ___ to tissues
False (There are two; circulating and marginated)
True or False: There is only one main pool of neutrophils in the body
Inflammation
An increased number of 'bands' seen in blood is indicative of what process in the body?
Segmented neutrophil
The most mature type of neutrophil is a?
Segmented neutrophils only
The neutrophilic storage pool is made up of what types of neutrophils?
Cattle; with acute inflammation, they will lose neutrophils and quickly become neutropenic
Which type of animal has a poor neutrophilic storage pool? What issue does this cause?
2-3 days
The neutrophilic pool in species like dogs has a supply for how long?
1:1; exception in cats, 3:1
The ratio of marginated to circulating neutrophils is what in most species? What is the main exception?
Circulating pool
The type of neutrophilic pool detected in a CBC is the?
6-10 hours in blood; 1-2 days in tissue after
How long do neutrophils stay in the blood? In tissue?
Left shift
An elevation in bands and metmyelocytes is known as?
Colony stimulating factor
What factor mediates stimulation of neutrophil production?
Major basic protein, peroxidase, etc
The cytoplasm of eosinophils have granules which contain what?
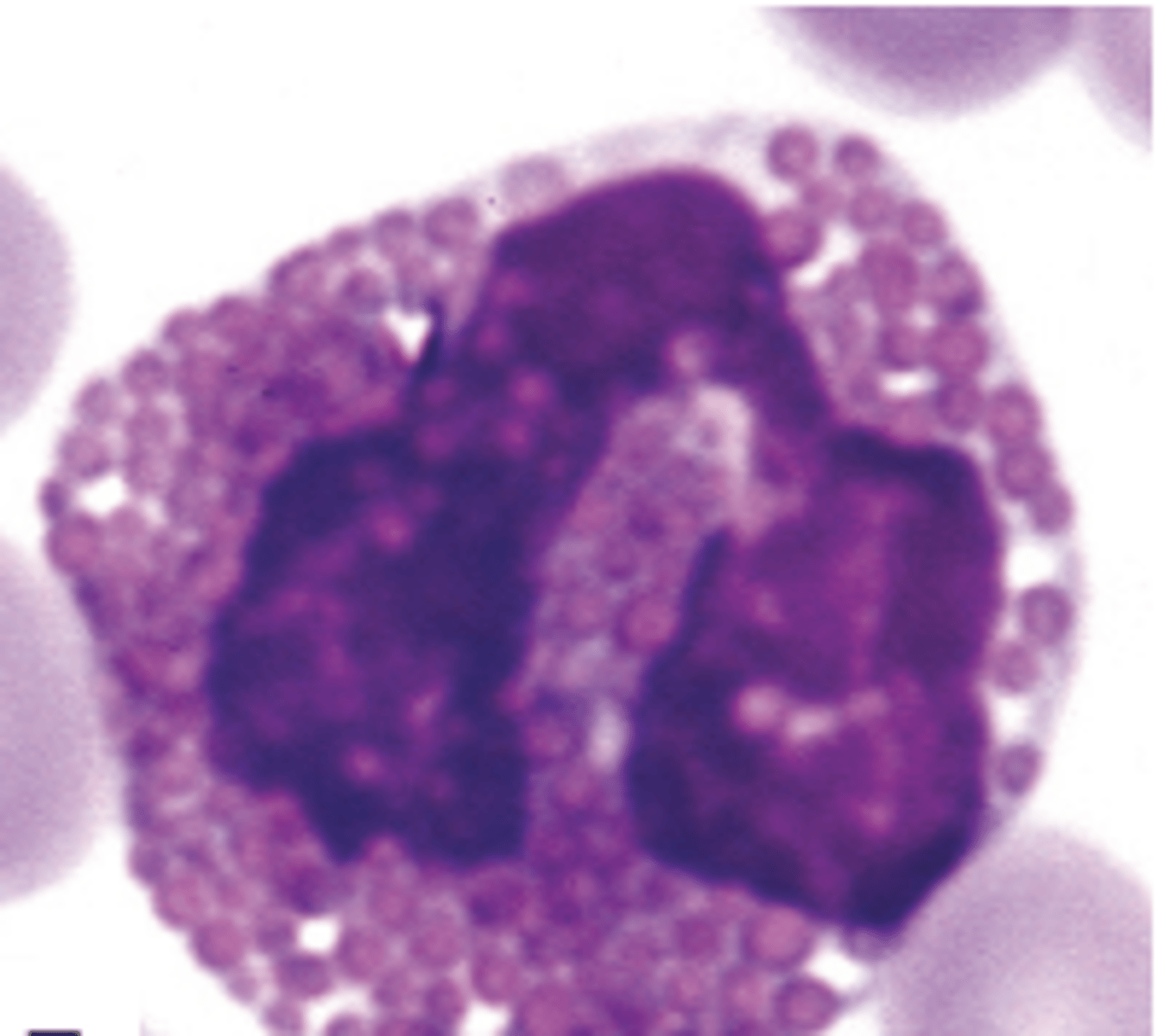
A ruminant
What type of animal is this eosinophil from?
Cats
Which animals have eosinophils with more rod-shaped granules?
Basophil
The largest granulocyte is the?
Vasoactive substances amd bronchoconstrictive mediators
Which substances do basophils release?
True
True or False: Though they are agranulocytes, monocytes may have vacuoles or azurophilic granules
Hematopoietic recovery; share a stimulator with neutrophils and an increase in monocytes indicates a future increase in neutrophils
Monocytes may serve as a marker for what clinical process? Explain.
Antimicrobial, tumorcidal, removal of cell debris, source of specialized phagocytic cells
List some of the functions of monocytes in the immune system
Small
Most lymphocytes should be (small/large) in size with the exception of in ruminants
T lymphocytes
60% of blood lymphocytes are what type?
30; produce antibodies by plasma cells
B-lymphocytes compose ___% of blood lymphocytes and do what?
Blood and lymphoid tissues
Lymphocytes re-circulating between what two pools?
Lymphopenia
Disruption of lymphatic flow can cause what clinical sign?
Automated cell counting, hemocytometer, and blood smear estimates
What are the main methods for obtaining total leukocyte concentrations?
Automated cell counting
What is typically the most accurate method of total leukocyte counting?
Because they have nucleated erythrocytes, an analyzer will not count correctly; a hemocytometer or blood smear estimate must be used
What is the main issue with counts and non-mammalian blood?
Manual differential counting
The gold standard leukocyte differential method is?
100
How many white blood cells are counted during a manual differential?
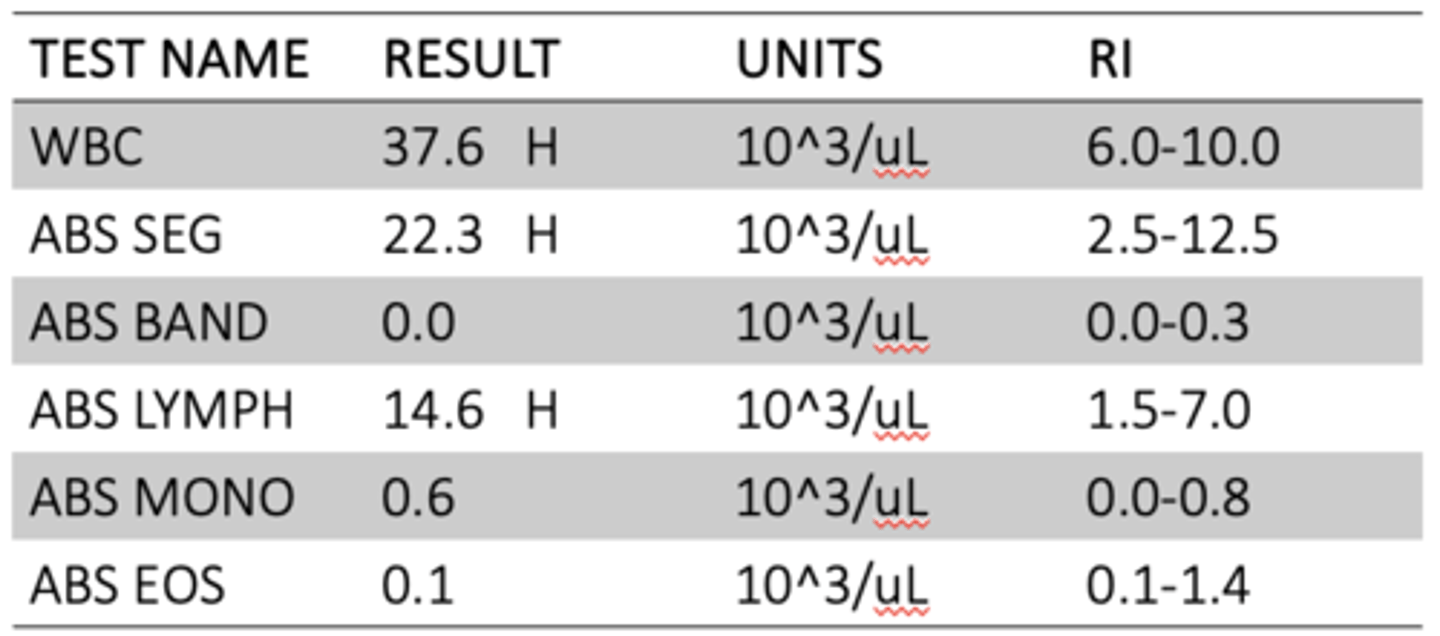
Neutrophilia and lymphocytosis
Name the two issues seen on this diagnostic
Neutrophilia with left shift and monocytosis
What leukocyte issues are noted?