Earth Science Finals 2024
1/543
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is missing a few units so I'll get that sorted out. Happy finals! *sobs* Some other important science finals flashcard sets: Places (plus a few events): https://knowt.com/flashcards/d5dd2e9f-94e6-410a-bc0a-ba6f22d1626f People: https://knowt.com/flashcards/96f33e34-194d-4f81-a49f-578fc4ac4f15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
544 Terms
Tunguska, Chixulub, and Chelyabinsk
three impact events we talked about in class
Oceans, forests, sediment, etc.
What can cover up the craters on Earth?
It has no atmosphere
Why can’t the moon burn through asteroids?
Volcanos
What landforms could have caused the dinosaurs to go extinct?
Mammal competition
How could other lifeforms cause the dinosaurs to go extinct?
Eggs took too long to hatch
How could reproduction impact the dinosaur extinction?
Climate Change
What environmental changes could’ve impacted the dinosaur extinction?
66 mya
When did the KT extinction impact occur?
meteor impact
What is the leading theory as to what caused the KT extinction?
Gas
What are jovian planets (planets located beyond the asteroid belt) made of?
Rock
What are terrestrial planets (planets located closer to the sun) made of?
Distance from Earth to Sun
How large is an AU?
Red
What colour is the light of objects moving away from us?
Blue
What colour is the light of objects moving towards us?
Time and space
Light is stretched over __________
Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin
Who discovered the amount of hydrogen and helium in space?
74.5%
What percentage of hydrogen is there in the universe?
24%
What percentage of helium is there in the universe?
Hydrogen and Helium
Which elements were created moments after the Big Bang (hint: easiest elements to make)
expanding
Everything in the universe is showing up as redshifted, meaning the universe is _________
Doppler effect
What is this phenomenon called: when you hear a car’s horn, it will sound different coming toward you (sound is compressed) and different when moving away from you (sound is stretched).
Edwin Hubble
Who discovered a formula that showed which way galaxies are moving?
Penzias and Wilson
Who discovered Cosmic Background Radiation?
Leftover energy from the Big Bang
What is Cosmic Background Radiation?
13.82 billion years old
How old is the universe?
singularity
An infinitely hot and dense point in space that doesn’t take up any space at all is a ____________
expansion
The universe was not an explosion, but a(n) __________
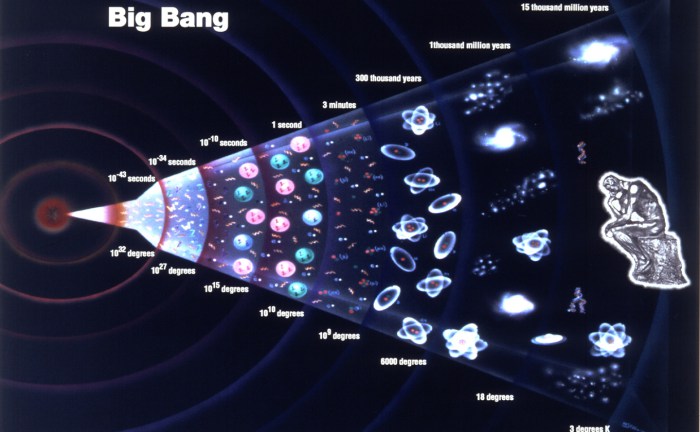
Big Bang
Time, space, energy, and matter were created as soon as the __________ occurred

Matter clumped together
What happened as the universe began cooling and particles started to form atoms?

end of a star’s life
Black Holes, White Dwarf Stars, and Neutron Stars are all things that stars can become at the ____________

Star-forming nebula
What are both sun-like stars and massive stars formed in?

protostar
The name for an early/very young star

Massive star
Larger type of star
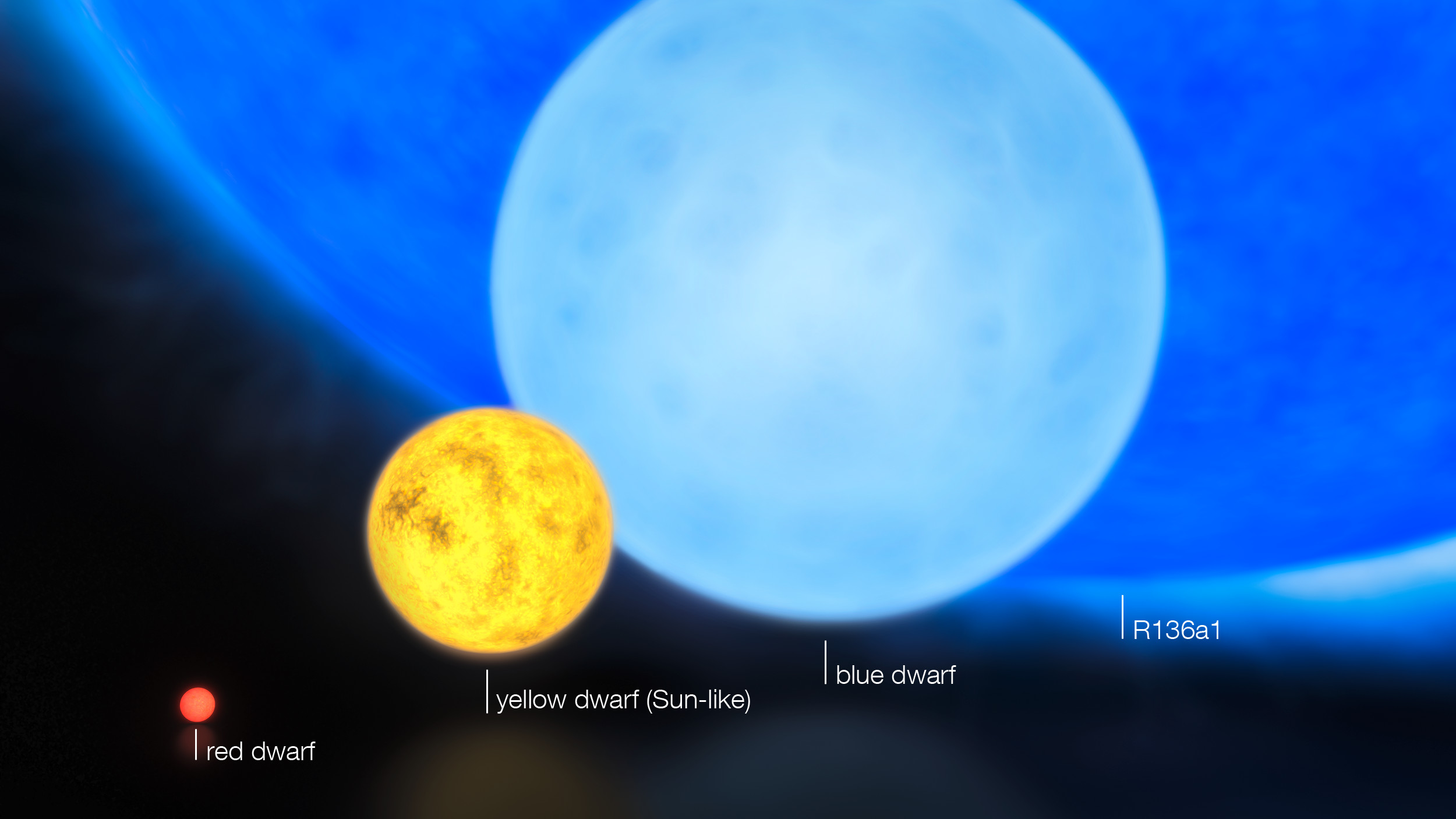

Sun-like star
Smaller type of star
red supergiant
Massive stars turn into _______

red giant
Sun-like stars turn into _______

Mass x width x velocity
Conservation of Angular Momentum formula
Fermi Paradox
Where all signs point to aliens being real but we have no evidence of them ever existing

2.537 million ly
How far away are we from the Andromeda Galaxy?

4.2 ly
How far away are we from Proxima Centauri?

Proxima Centauri
What is the closest star to us?
spiral galaxy
What type of galaxy is the Milky Way?
100,000 ly by 10,000 ly
What are the dimensions of our Milky Way?

1 AU
149,597,871 KM is the same length as __________

Planets
They need to be round.
They have to orbit the sun.
They have to clear their orbit
What are they?

Mercury, Mars, Earth, and Venus
Name the terrestrial planets

Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
Name the jovian planets
Kuiper belt
The two rocky belts in our solar system are the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, and the ___________
Iridium
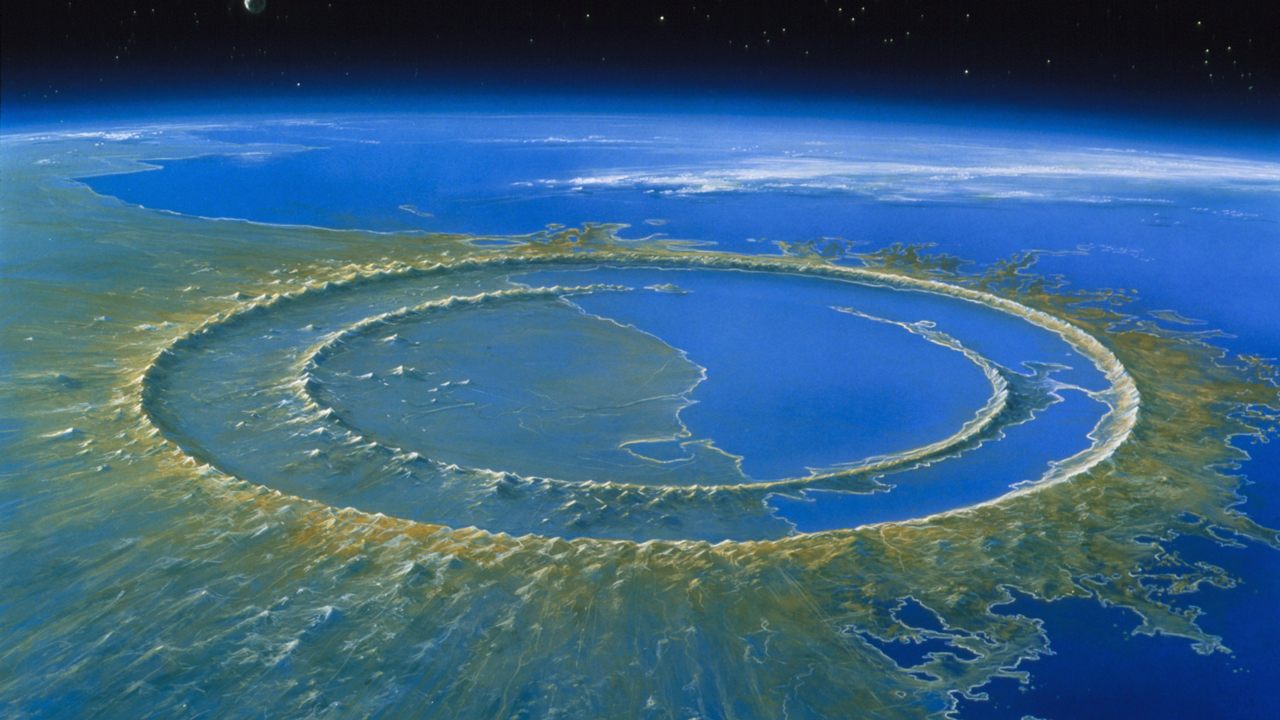
Element that is rare on Earth but common in asteroids (hint: Walter Alverez)

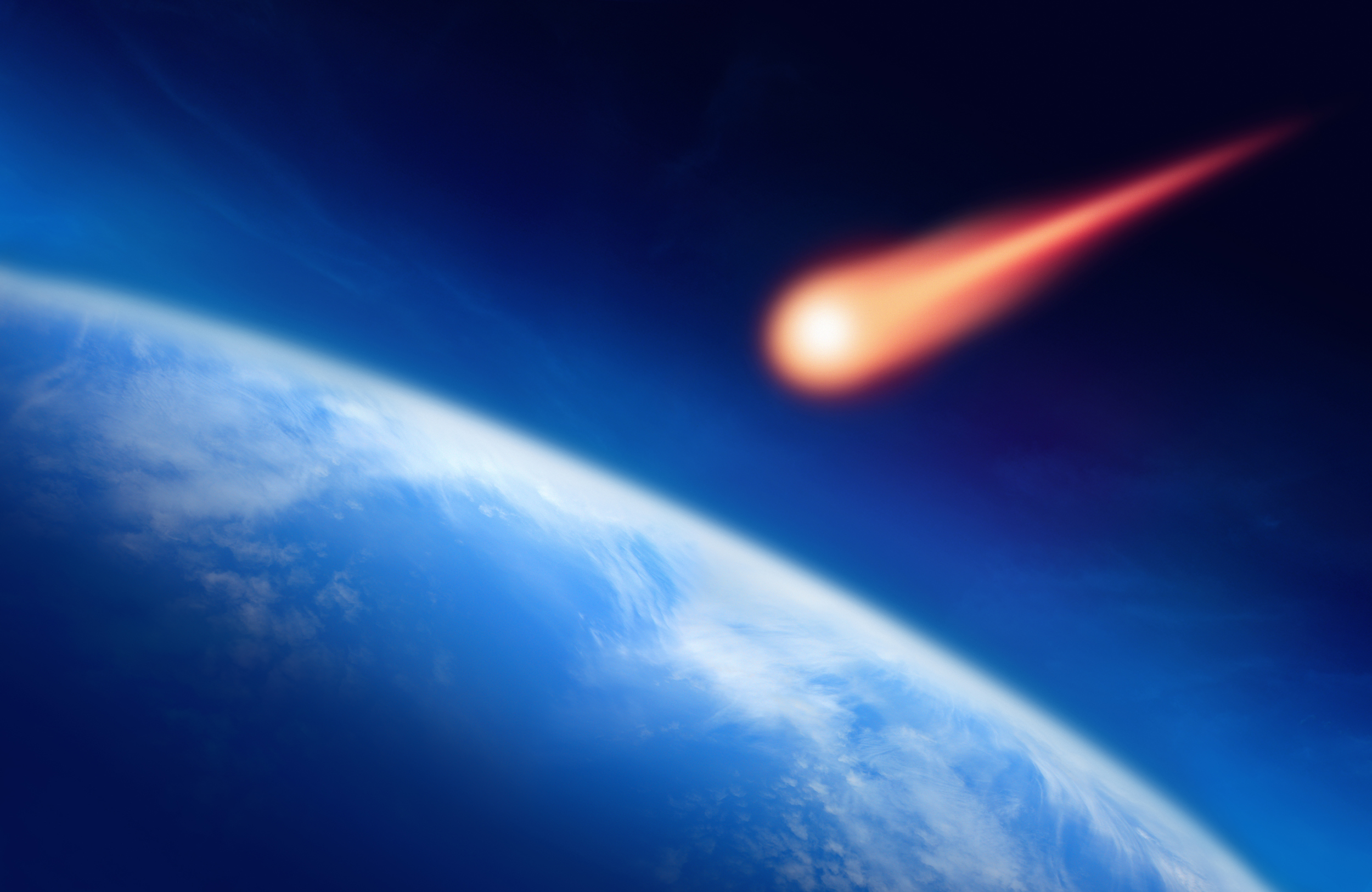
Meteor
Something that’s entered Earth’s atmosphere

Meteoroid
Something traveling through space

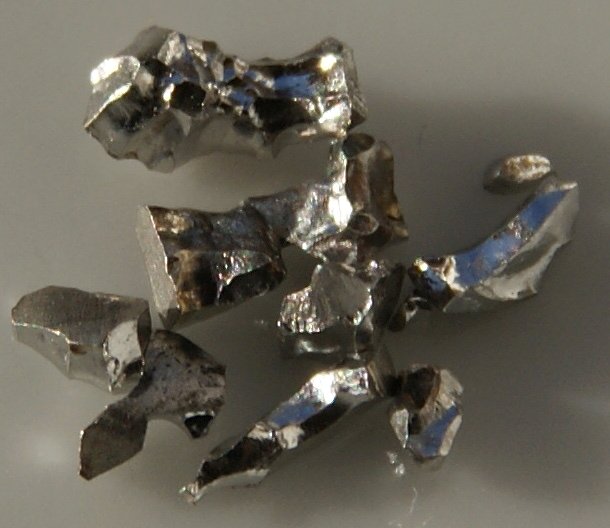
Meteorite
The part of the meteor that survives Earth’s atmosphere and hits the Earth
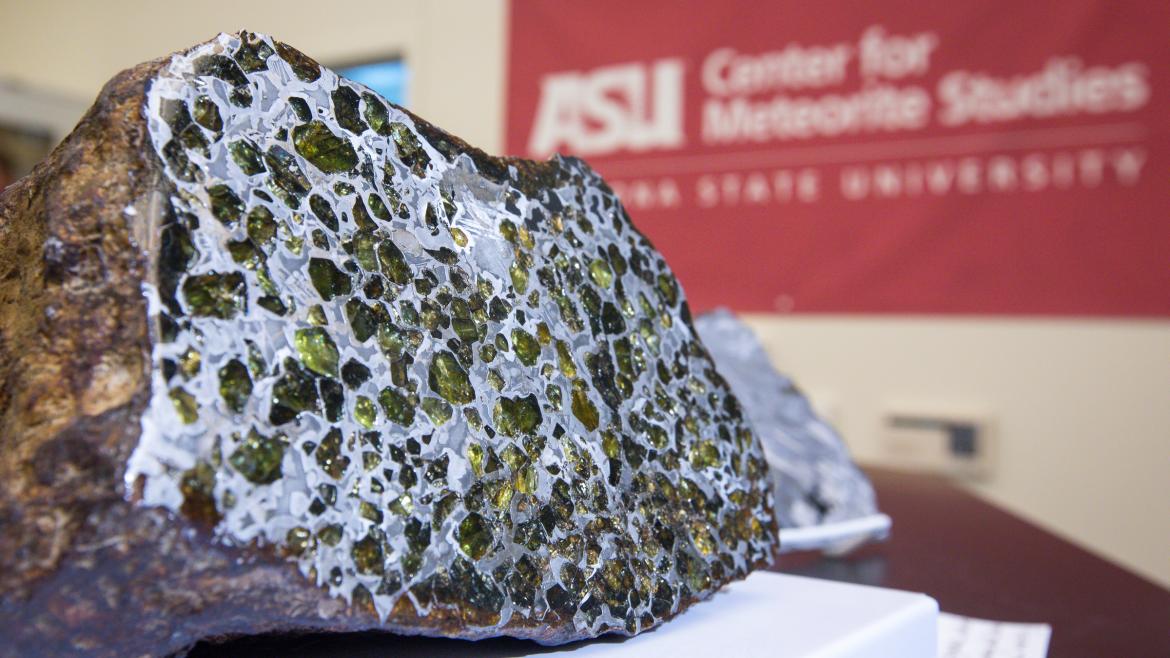

Chixulub
What was the name of the impact that killed the dinosaurs?
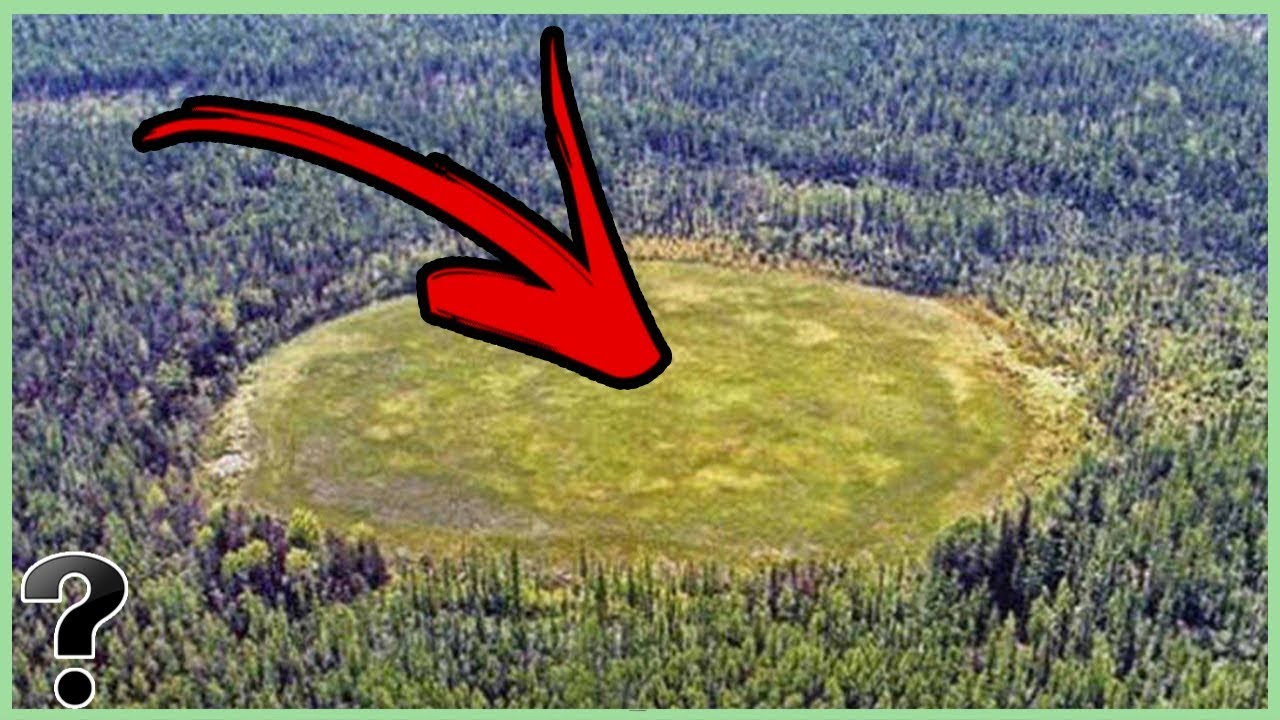
Tunguska
in Siberia, only witnesses were yak herders

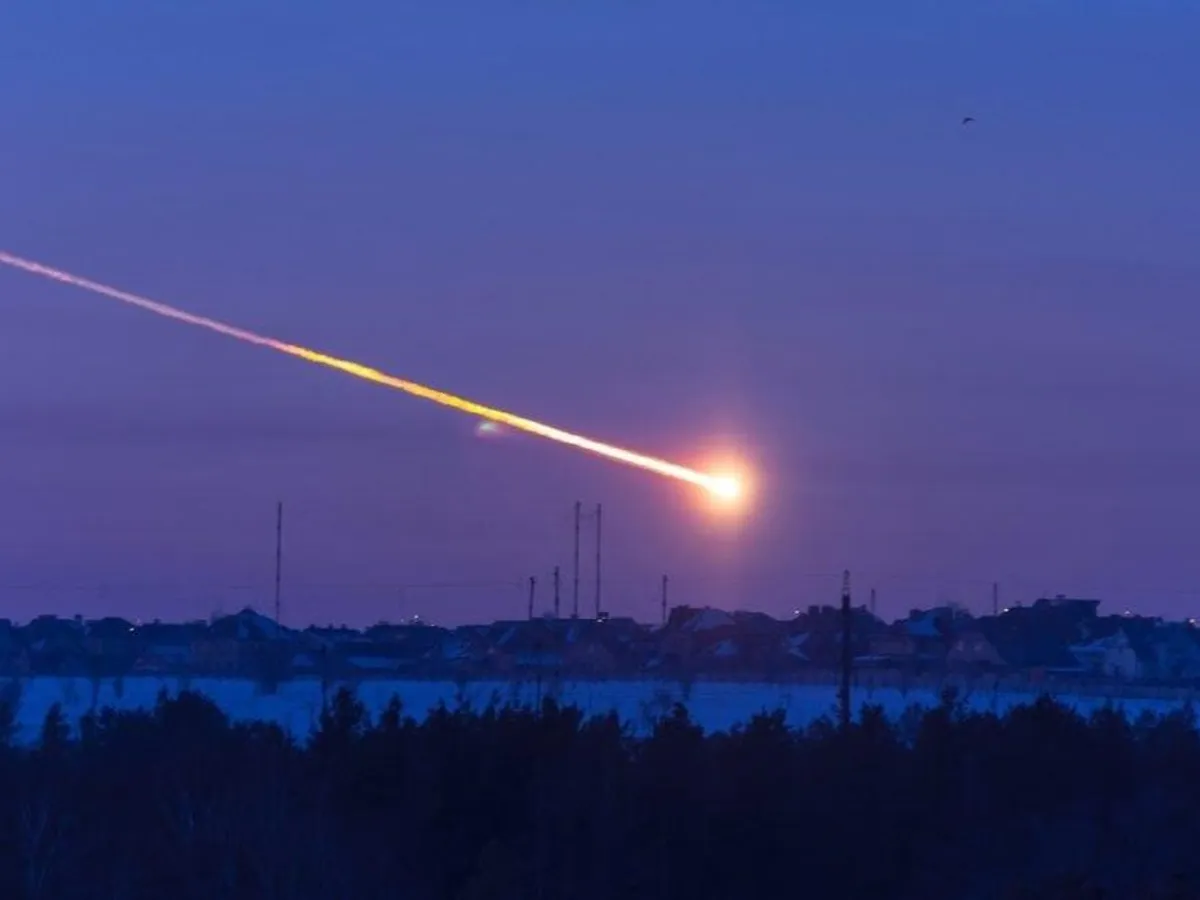
Chelyabinsk
the meteor that exploded in the city in Russia

adiabatic cooling
the cooling effect of reduced pressure on air as it rises higher in the atmosphere and expands
Alto
prefix meaning cloud is found higher in the sky than usual
atmosphere
the envelope of gases surrounding the earth
Capacity
the maximum amount of water that can be present in the air at a certain temperature; increases with increasing temperature.
Cirrus*
high-altitude clouds that are thin*
Climate
A description of aggregate weather conditions; the sum of all statistical weather information that helps describe the weather of a region
Cloud
a collection of small water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air
Condensation Nuclei
microscopic particles on which water vapor condenses to form cloud/fog droplets (ex. dead skin, dust…)
Condensation
the change from water vapor to liquid water
Convergence
as air is drawn together at the surface
Cumulonimbus
a type of cumulus cloud that has vertical development
Cumulus
low altitude thick, puffy, white clouds with flat bases, formed by vertically rising air currents often localized convective lifting or convergence
Dew Point
the temperature at which condensation occurs because the air is saturated
Dew
tiny drops of water that form on cool surfaces when water vapor condenses
Evaporation
the change from liquid water to water vapor
Fog
a cloud in contact with the ground
Frost
feathery crystals of ice formed on surfaces when water vapor in the air deposits at a temperature below freezing
Halo
a circle of light around the sun or moon in a cirrostratus cloud
Latent Heat
heat absorbed or radiated during a change of phase
leeward side
Protected side; the direction opposite from which the wind is blowing.
Mare's Tail
type of cirrus cloud with a hook shape that can indicate rain within 24 hours if caused by a warm front
Mesopause
The boundary between the mesosphere and the thermosphere
Mesosphere
The layer of the Earth's atmosphere that extends from the stratosphere to the thermosphere, temp decreases with height, coldest part of the atmosphere is at the top of this layer, idk kinda boring
Meteorology
The scientific study of the atmosphere and atmospheric phenomena; the study of the weather and climate
Mountain Wave Cloud
stationary lenticular clouds situated over and downwind of a prominent mountain range
Nimbo
prefix-suffix to indicate that a cloud is rain-bearing
Orographic Lifting
mountains acting as barriers to the flow of air
Outgassing
The process of gases contained within the Earth being put into the atmosphere by volcanic eruptions.
Ozone
a form of oxygen that has three oxygen atoms in each molecule instead of two. In the stratosphere it protects us from dangerous ultraviolet radiation. In troposphere it is considered a pollutant as it is a main ingredient in photochemical smog and damaging to plants and people.
precipitation
Any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth's surface.
rain shadow
a region with dry conditions found on the leeward side of a mountain range as a result of humid winds from the ocean causing precipitation on the windward side
Relative Humidity
a comparison of the actual amount of water vapor in the air with the maximum amount of water vapor that can be present in the air. (Specific Humidity/Capacity)
Saturation
the condition in which the air is holding as much water vapor as possible at a given temperature and pressure. Hint: it’s not capacity lmao
Specific Humidity
the amount of water vapor in the air at a given time and place; expressed as the number of grams of water vapor per kilogram of air.
Stratopause
The boundary between the stratosphere and the mesosphere
Stratosphere
The layer of Earth's atmosphere that extends from the troposhere to the mesosphere; concentration of ozone in this layer causes the temperature to rise as you go up.
Stratus
clouds that form in low, horizontal layers, covering all or most of sky
Thermosphere
The layer of Earth's atmosphere above the mesosphere
Transpiration
the emission of water vapor into the atmosphere from the leaves of plants
Tropopause
The boundary between the troposphere and the stratosphere.
Water Vapor
water in its gaseous form
Weather
the state of the atmosphere at any given time
windward side
the side or direction from which the wind is blowing.
Cap Cloud
Person A: “It’s a cloud”
Person B: “No cap”

cirrostratus
