Rates, equilibrium and pH
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Define the rate of reaction?
the change in the amount of reactants or products per time
State the unit for rate of reaction?
mol dm-3s-1
what does the order of reaction tell you?
it tells you how the reactant’s concentration affects the rate
Define overall order?
the sum of the orders of all the different reactants
Give the rate equation?
k[A]m[B]n
What is k?
the rate constant
What are m and n?
the orders of the reaction with respect to the reactant A and reactant B
What does m tell you?
how the concentration of reactant A affects the rate
What does n tell you?
how the concentration of reactant B affects the rate
Define the half life of a reaction?
the time it takes for half of the reactant to be used up
Define a 0 order reaction?
where the reactants concentration is doubled and the rate stays the same
Define a 1 order reaction?
where the reactants concentration is doubled and rate also doubles
Define a 2 order reaction?
where the reactants concentration doubles and rate quadruples
What does the shape of a rate -concentration graph tell you?
the order of the reaction
What does a horizontal line mean on a rate-concentration graph mean?
changing concentration doesn’t change rate
it’s order is therefore 0
What does a straight line mean on a rate concentration graph?
the rate is proportional to [X]
The order is 1
What does a curve mean on a rate concentration graph?
the rate is proportional to [X]2
it’s order is 2
What do colorimeters measure?
the absorbency of a particular wavelength of light by a solution
State the steps to use a colorimeter?
Set the colorimeter to measure the wavelength of light
place a sample of distilled water into a curette and place into the colorimeter
Set the absorbance to 0
Take samples form the reaction mixture at regular intervals and measure the absorbance of each one using the colorimeter
What can be used to convert from absorbance to concentration?
a calibration curve
If the half life of a reaction is known, state the equation which can work out the rate constant of a first order reaction?
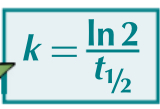
Define the rate determining step?
the step with the slowest rate
What 3 events must happen in order for a relation to occur?
collide with each other
Have sufficient energy to react
Have the correct orientation
What does the Arrhenius equation link together?
the rate constant (k) with activation energy(Ea) and temperature
State the formula and what the key components mean in the Arrhenius equation?
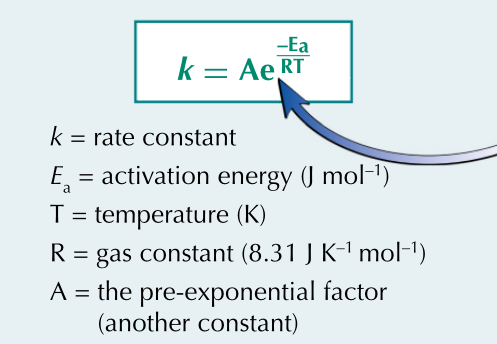
What does a larger activation energy result in?
A slower rate of reaction
Not many of the reactant particles will have enough energy to reacts so only a few of the collisions will result in the reaction actually happening the the rate of reaction will be slow