Lec 2, Cell Theory and Eukaryotic Cells
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
EARLY CELL THEORY, ________ (1839)
The cell is the basic _____ and _____ unit of life
All living organisms are composed of ___ or ____ cells
All cells arise only from division of ______ cells
MODERN CELL THEORY (3 tenets above + these)
An organism’s activity depends on the activity of its _____ cells
All or most energy flow occurs _____
The activities of cells are governed by ______ consisting of ______
All cells are of similar _____ and _____ composition
All living cells are descended from a ______ cell
Schwann, Schleiden, structural, functional, one, more, pre-existing, independent, within cells, genetic material, DNA, chemical, structural, common ancestor
What are the two types of cells?
Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes both have:
______ as a cell barrier
_______ aqueous fluid composition
______ for protein synthesis
______ that contains their genes
cell membranes, cytosol, ribosomes, DNA
What’s the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes are more ______. The organelles are_______.
Eukaryotes have a ______. Prokaryotes have a _______.
Prokaryotes have _____ DNA
Prokaryotes are ______. Eukaryotes are ______.
complex, membrane-bound, nucleus, nucleal region, circular, tiny, large
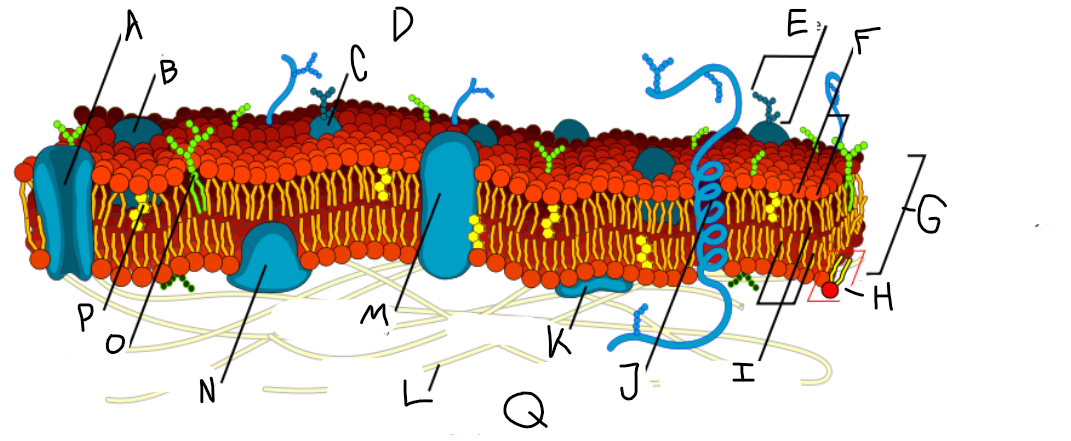
A
Protein channel (transport protein)
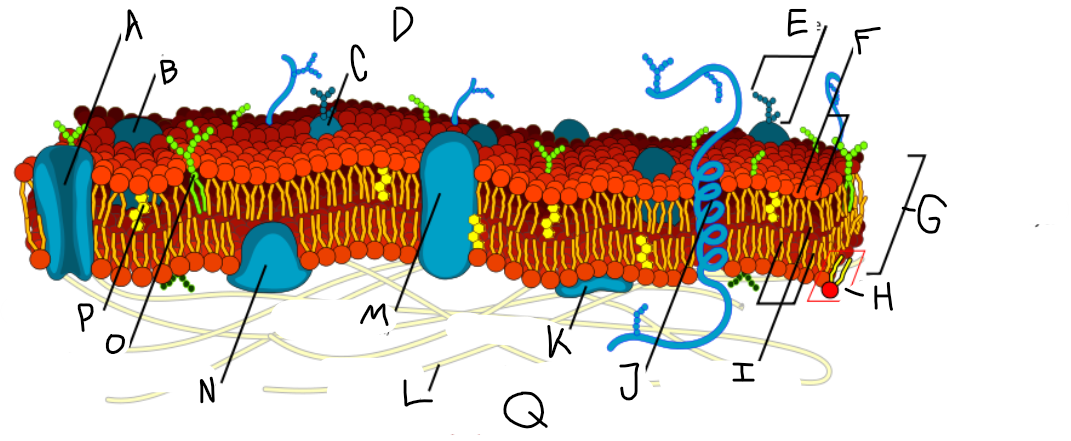
B
Globular protein
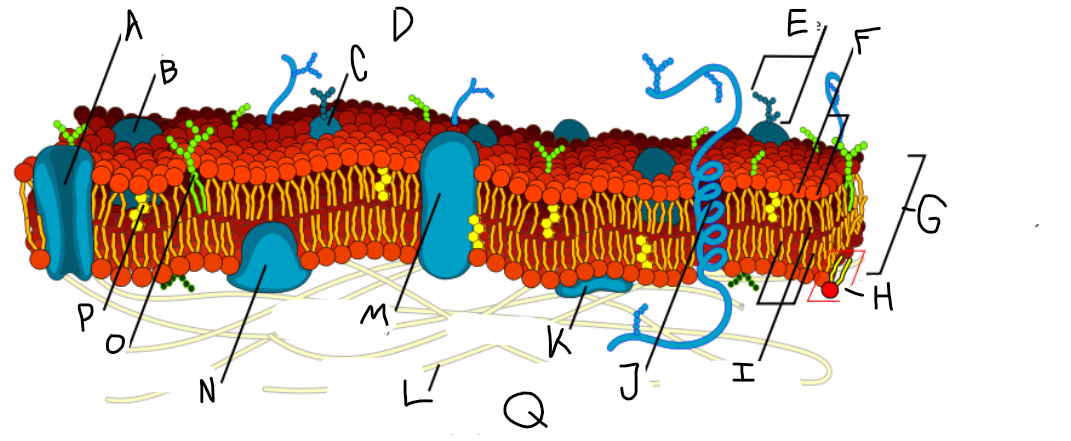
C
Glycoprotein
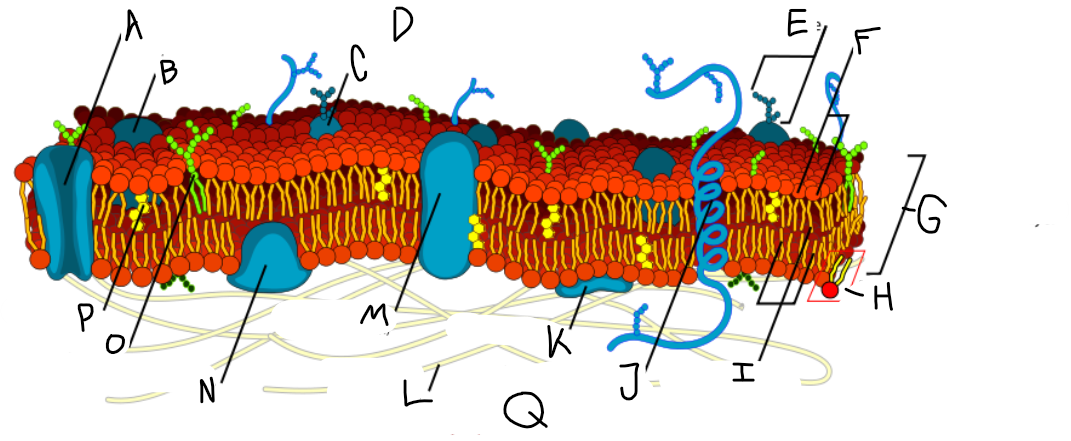
D
Extracellular fluid
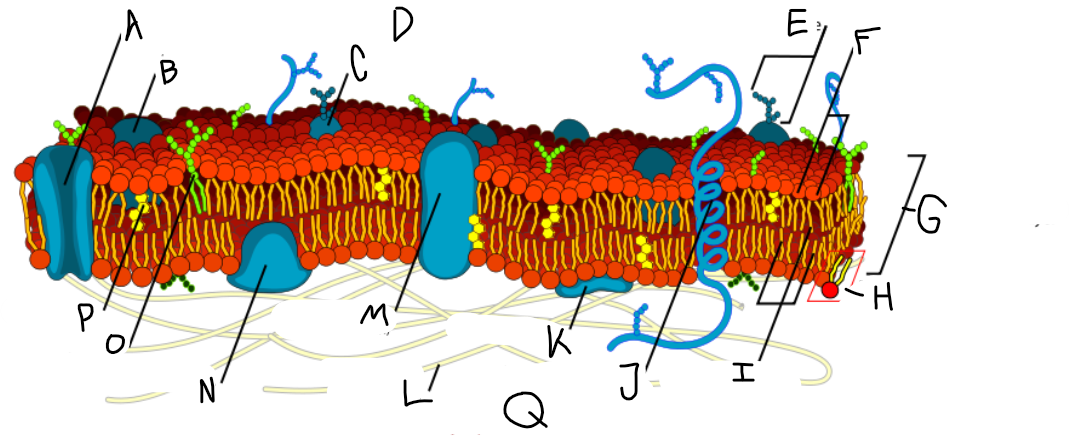
E
Carbohydrate
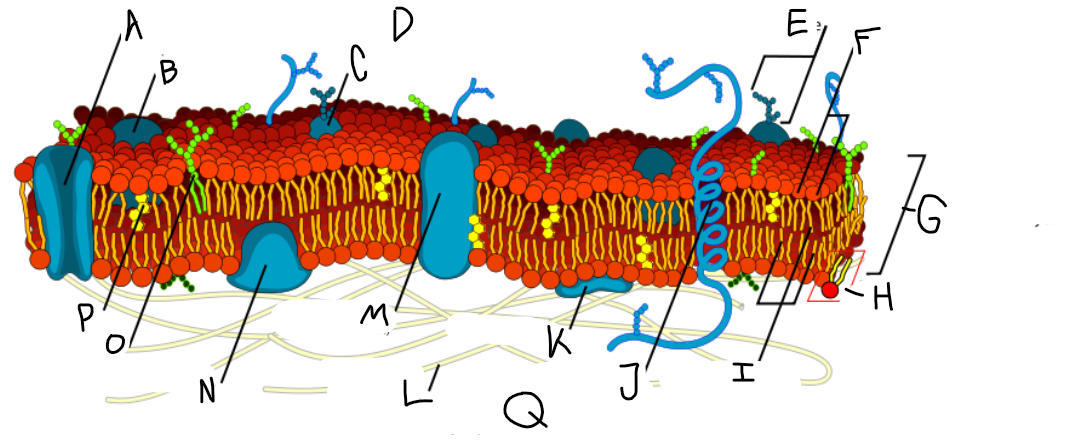
F
Hydrophillic heads
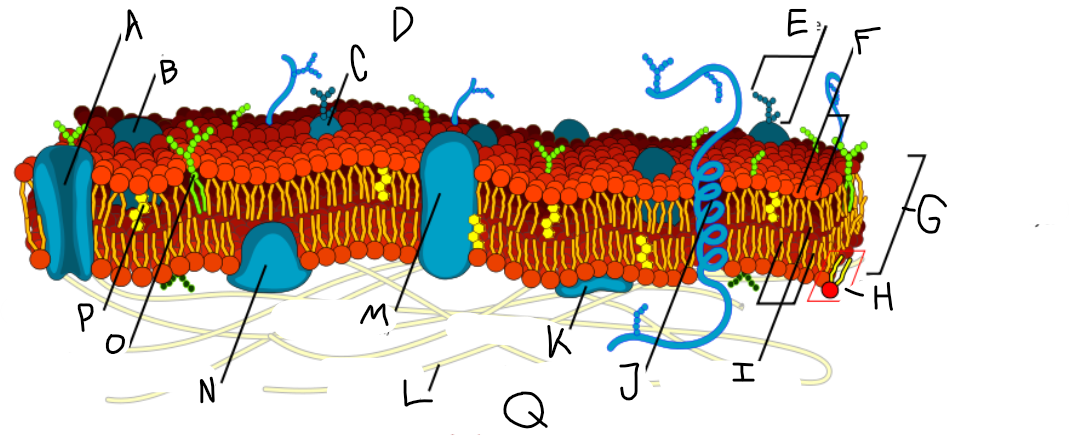
G
Phospholipid bilayer
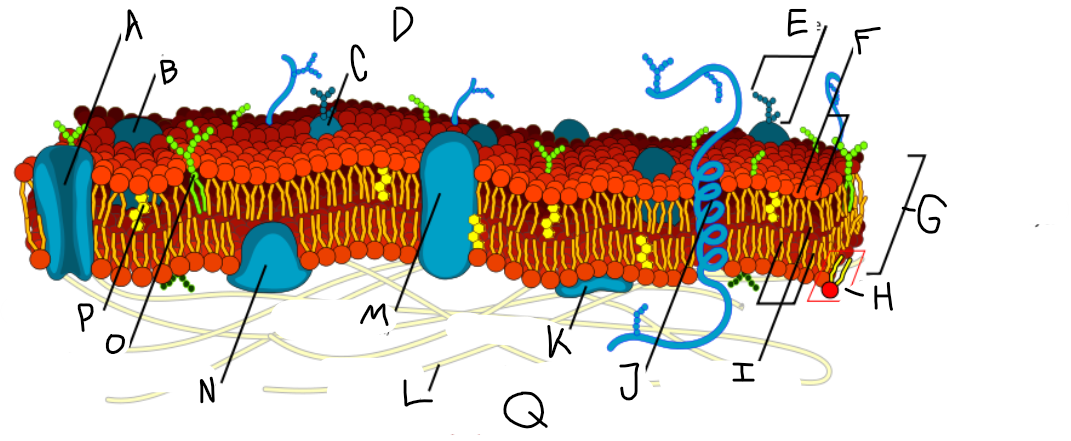
H
Phospholipid molecule
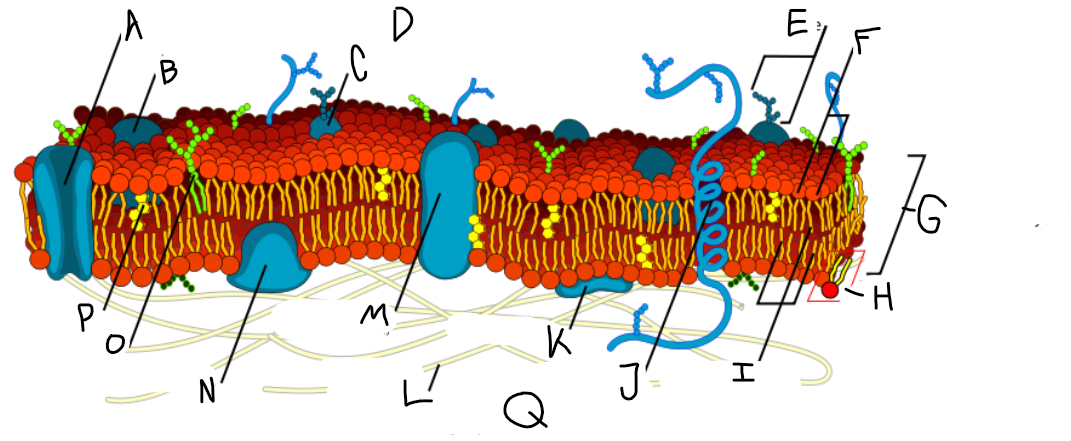
I
Hydrophobic tails
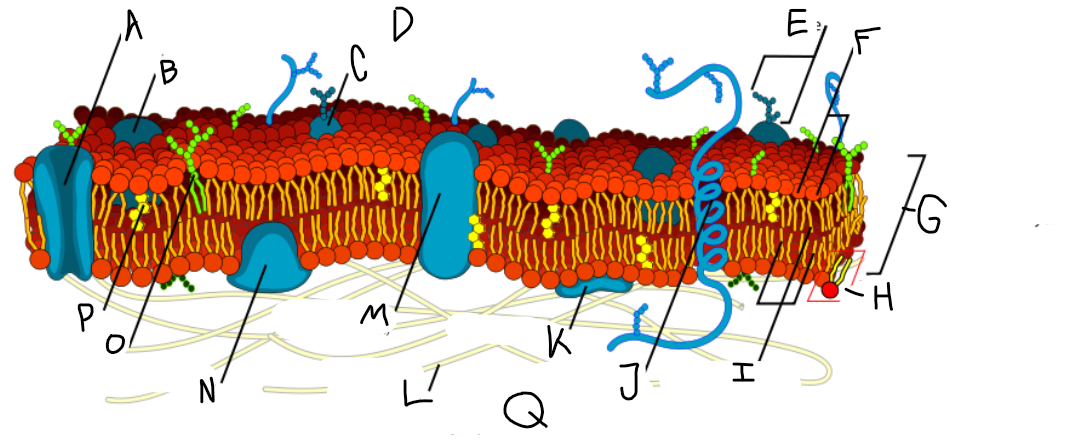
J
Alpha-helix protein (integral protein)
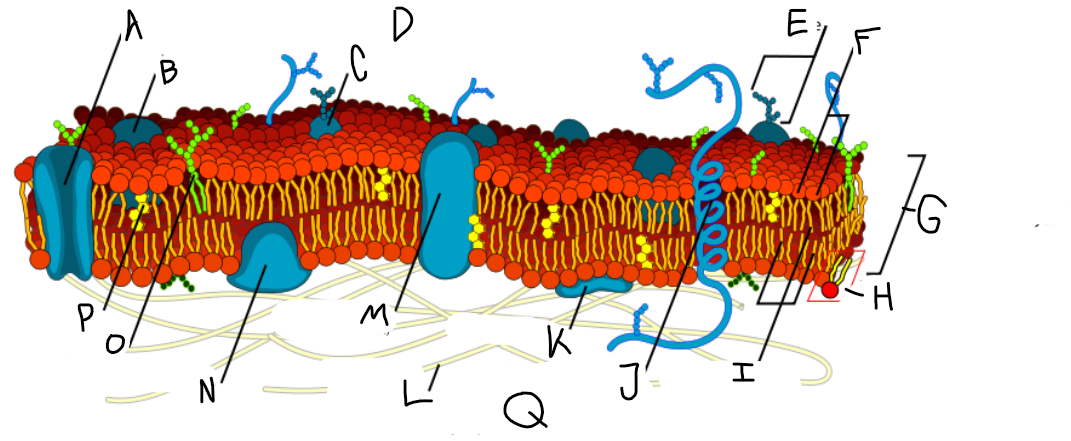
K
Surface protein
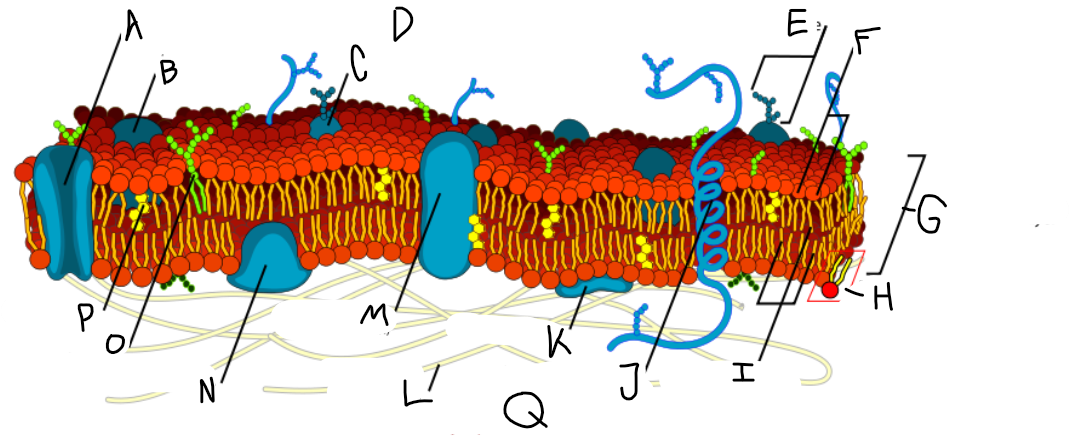
L
Filaments of cytoskeleton
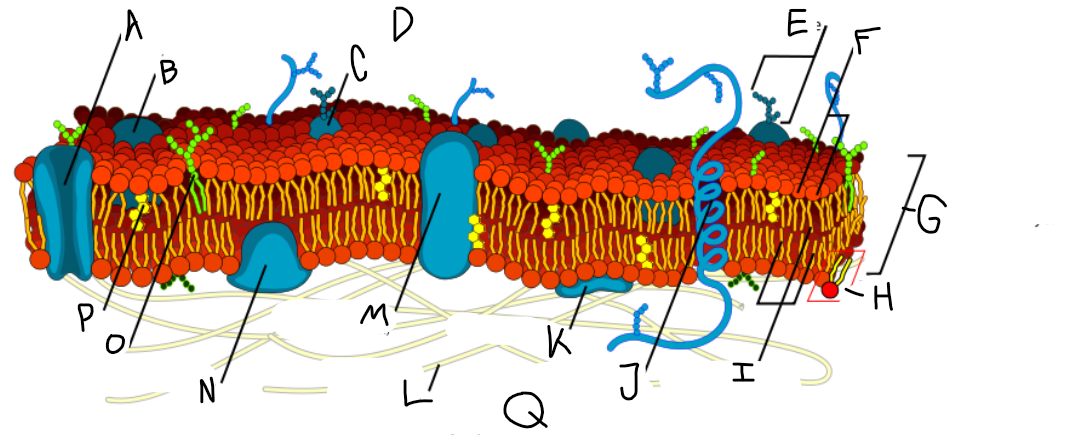
M
Globular protein (integral protein)
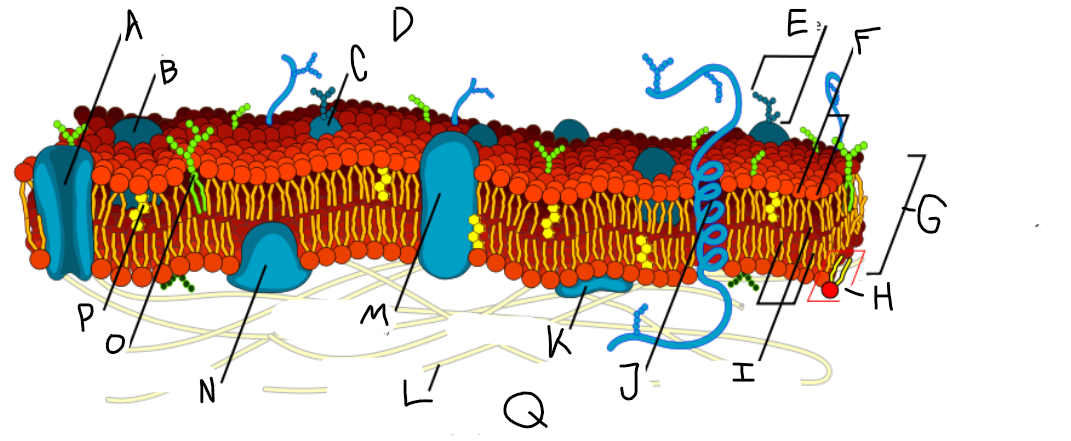
N
Peripheral protein
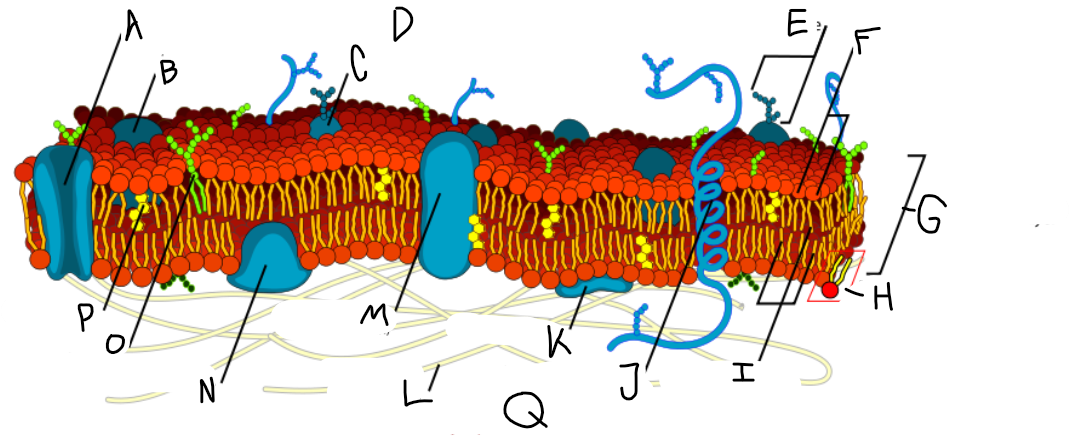
O
Glycolipid
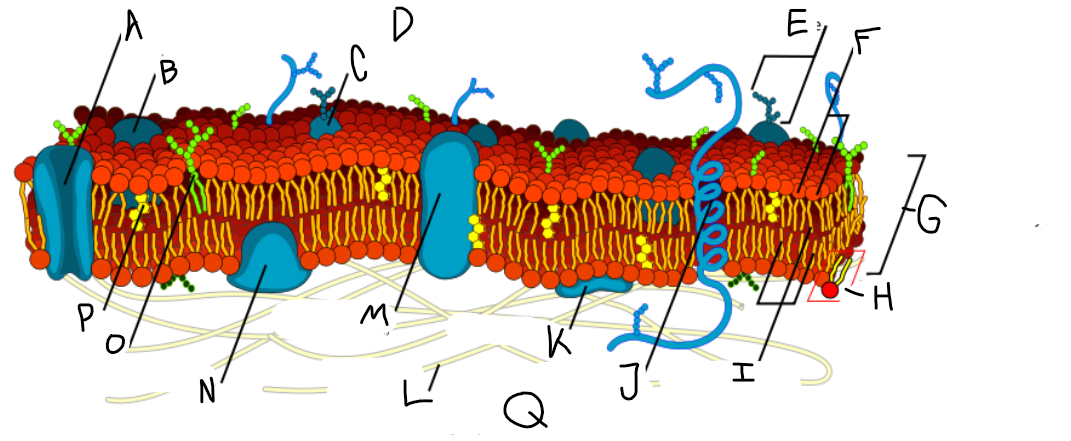
P
Cholesterol
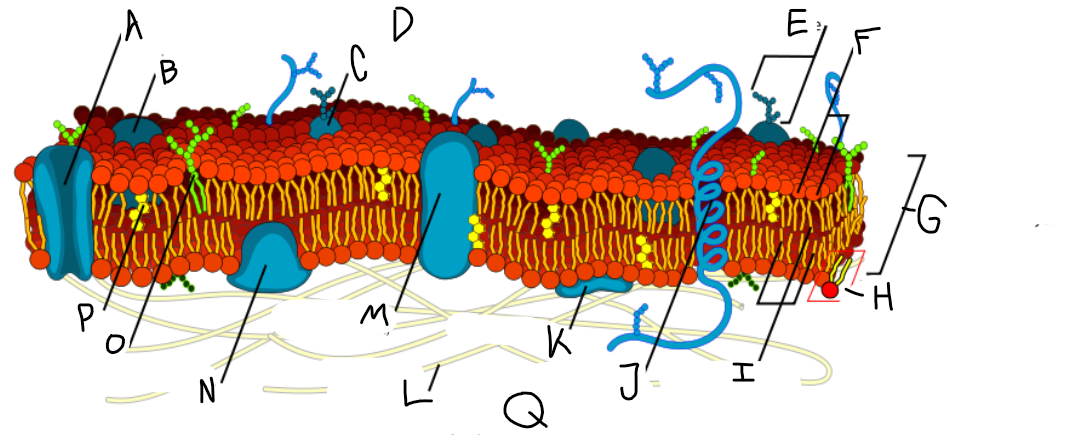
Q
Cytoplasm