PCR and gel electrophoresis
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what does PCR stand for and what is it used for
polymerase chain reaction is used to copy DNA to produce millions of identical DNA molecules so that a usable sample is produced
What are primers
short single stranded sequence of ~20 bases long
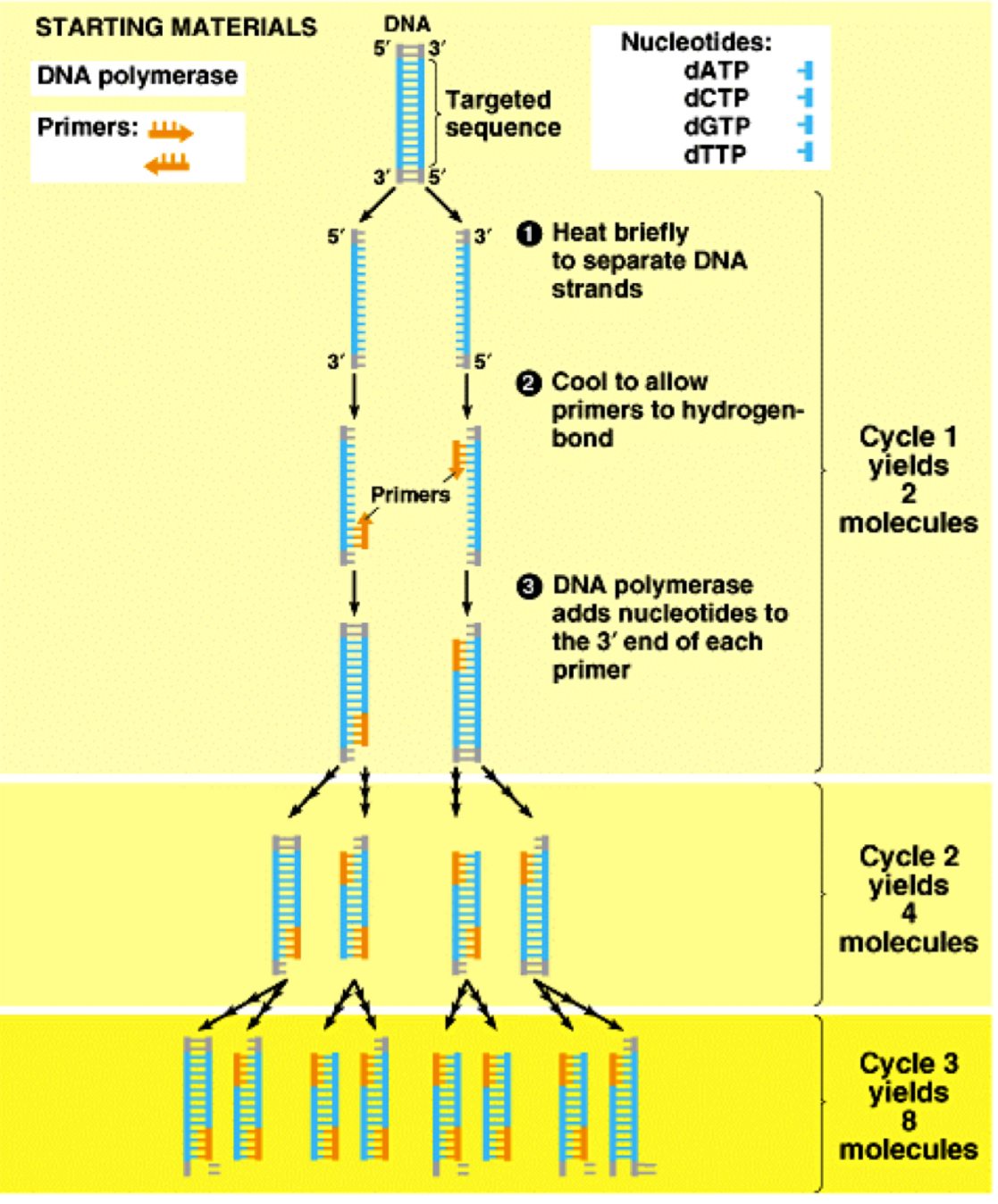
outline the steps of PCR (6)
DNA is denatured by heating to 95˚C to break H bonds between the strands exposing the bases
Primers are added. Can be made into complementary base sequences found either side of the desired DNA sequence so that only that section is copied
Primers anneal when the temperature is cooled (~65˚C), as they base pair with the complementary sequence on the template strand
Taq polymerase and free activated DNA nucleotides are added. Taq polymerase can bind to the double stranded section provided by the primer.
Elongation - taq polymerase moves along the strand adding the nucleotides to create a double stranded DNA molecule (occurs at 72˚C)
Once copied, the mixture is heated to 95˚C again to denature DNA strands
Cycle is repeated to produce many of desired DNA
what temperature is required to denature DNA
95˚C
What does Taq polymerase do
binds to double stranded section provided primer
What temperature does elongation happen during the PCR
72˚C
What type of DNA polymerase is used for the PCR and why
Taq polymerase as it is thermostable at high temperatures, isolated from bacterium Thermus aquaticus
How are DNA strands from PCR cut up
Using restriction endonucleases giving different sized fragments of DNA
What is gel electrophoresis and why does it work
process used to separate DNA fragments based on their size and charge
Phosphate groups in DNA are negatively charged
how does gel electrophoresis work
dna fragments are placed in wells at the end of a plate of agarose gel
Plate of agar gel is placed into a buffer solution
A potential difference is passed through the gel, and the dna fragments will be repelled away from the negative electrode towards the positive electrode.
Shorter fragments will move faster through the gel than longer fragments
Fragments of different sizes separated
How is dna visualised
dna is heated to separate the strands and single stranded DNA probes are added which bind to DNA
DNA probes contain radioactive phosphorous isotope, so when placed on an X-ray film, the radiation caises a patternn of bands to be formed
What is a DNA probe
Single stranded specific DNA sequence used to find DNA
What are some examples of other things that can be separated using gel electrophoresis
proteins - polypeptides have net negative charge (with buffer of constant pH)
Alloenzymes (formed from different alleles of same gene)
Variants of haemoglobin (eg sickle cell) as mutation causes an amino acid with non-polar r group to replace one that is charged therefore sickled is less negatively charged.