Chapter 11: Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
C
1. Objectives for performing an exchange transfusion include all of the following
except to:
a. decrease the level of maternal antibody
b. reduce the level of indirect bilirubin
c. provide platelets to prevent disseminated intravascular coagulation
d. provide compatible RBCs to correct anemia
B
2. The greatest danger to the fetus (before delivery) affected by HDFN is:
a. kernicterus
c. hyperbilirubinemia
b. anemia
d. hypertension
C
3. A 300-pg dose of RhIG covers a maximum FMH of how many milliliters of whole blood?
a. 10 mL
c. 30 mL
b. 15 mL
d. 50 mL
C
4. RhIG should be administered within how many hours of delivery?
a. 6
c. 72
b. 48
d. 96
C
5. An often fatal condition characterized by general edema that results from anemia is:
a. kernicterus
c. erythroblastosis fetalis
b. DIC
d. hydrops fetalis
C
6. HDFN occurs when:
a. maternal antigens react with fetal antibodies
b. fetal antibodies react with maternal antibodies
c. maternal antibodies react with fetal antigens
d. fetal antigens react with maternal antigens
A
7. The greatest danger to the newborn affected by HDFN is:
a. kernicterus
c. conjugated bilirubin
b. anemia
d. low L/S ratio
A
8. Which of the following women should receive postpartum RhIG?
Mother’s ABO; Mother’s antibody screen; Newborn’s
a. A, D-negative Negative O, D-positive
b. O, D-negative Negative A, D-negative
A
9. Which of the following antibodies carries no risk of HDFN?
a. anti-Lea
c. anti-K
b. anti-C
d. anti-S
C
10. Which of the following is not a characteristic of ABO HDFN? a. may occur in first pregnancy
b. usually treated with phototherapy
c. strongly positive DAT
d. most frequent in babies born to group O mothers
D
11. Which of the following requirements is important when selecting blood for exchange transfusion to avoid high levels of potassium?
a. irradiated blood
c. leukocyte-reduced blood
b. CMV-negative blood
d. blood less than 7 days old
A
2. A mother is group A, D-negative with anti-D in her serum. Which of the following units should be selected for an intrauterine transfusion?
a. group O, D-negative
c. group A, D-negative
b. group O, D-positive
d. group A, D-positive
B
13. The rosette test is:
a. performed on a cord blood sample
b. used to screen for FMH
c. a quantitative test used to calculate the volume of FMH
d. an acid elution used to estimate the volume of FMH
D
14. Which of the following tests is not necessary when testing a cord blood sample?
a. ABO
c. DAT
b. D
d. antibody screen
C
15. The Liley method of predicting the severity of HDFN is based on the:
a. resistance of fetal hemoglobin to acid elution
b. ratio of lecithin to sphingomyelin
c. change of optical density of amniotic fluid measured at 450 nm
d. direct bilirubin evaluation of a cord blood sample
16. A titer was performed on a prenatal sample from a D-negative woman with anti-D. The sample was tested 4 weeks later in parallel with a current sample. The following results were obtained:
How would the titer results be interpreted?
a. an intrauterine transfusion is necessary
b. early induction of labor should be considered
c. color Doppler ultrasonography should be considered
d. RhlG should be administered
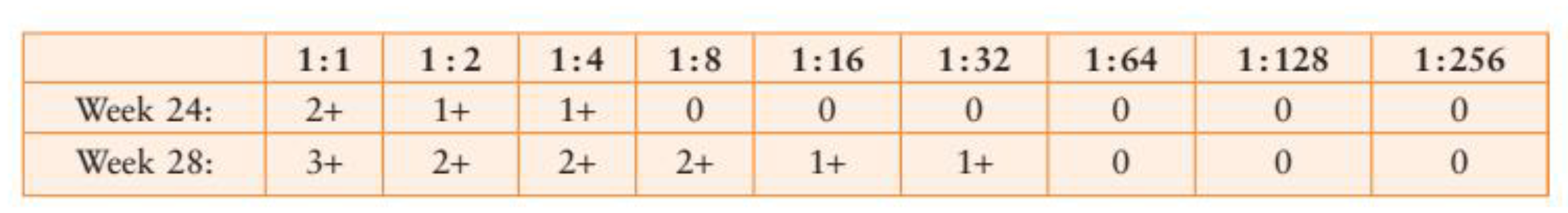
B
17. A group A, D-negative mother demonstrating anti-D antibodies delivered a group O, D-negative baby with a positive DAT (2+), elevated bilirubin (18 mg/dL), and low hemoglobin (8 g/dL). Which is the most probable explanation for these test results?
a. ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn
b. hemolytic disease of the newborn with a false-negative D typing due to blocking antibodies
c. large fetomaternal hemorrhage causing discrepancy in the blood type
d. prenatal RhlG administration
A
18. The appearance of spherocytes in a baby’s blood smear after delivery is usually associated with:
a. ABO HDFN
b. HDFN caused by anti-D
c. HDFN caused by other IgG antibodies
d. normal physiologic anemia detected in newborns
C
19. The purpose of irradiation of blood selected for an exchange transfusion is to prevent:
a. formation of HLA antibodies
c. graft-versus-host disease
b. sepsis from bacterial contamination
d. transmission of viruses
B
20. The rosette test used for screening for a fetomaternal hemorrhage can detect a bleed as small as:
a. 5 mL
c. 20 mL
b. 10 mL
d. 30 mL
A
21. A Kleihauer-Betke stain performed on a postpartum blood sample demonstrated 10 fetal cells in a field of 2000. What is the estimated blood volume of the fetomaternal hemorrhage expressed as whole blood?
a. 25 mL
c. 45 mL
b. 30 mL
d. 100 mL
A
22. A rosette test performed on a D-negative mother who delivered a D-positive baby demonstrated two rosettes per three fields observed. The correct course of action is to:
a. submit the sample for a Kleihauer-Betke test
b. recommend two vials of RhIG
c. suggest that RhIG is not necessary because records indicate that the mother received prenatal RhIG
d. recommend one vial of RhIG because it is below the cutoff for the fetal screen
A
V23. The principle of the Kleihauer-Betke test is that:
a. fetal hemoglobin resists acid elution
b. adult hemoglobin resists acid elution
c. fetal red cells lose hemoglobin under alkaline conditions
d. adult red cells accept dye under alkaline conditions
B
24. Results of a Kleihauer-Betke test determine there was a fetomaternal hemorrhage of 35 mL of whole blood during delivery. What is the correct dosage of RhIG?
a. one vial
c. three vials
b. two vials
d. four vials
C
25. A weakly reactive anti-D test was identified in a postpartum sample from a D-negative woman who gave birth to a D-positive baby. What is the most likely cause?
a. immune anti-D produced from exposure during the first pregnancy
b. immune anti-D produced from exposure during the current pregnancy
c. antenatal RhIG given
d. error in antibody identification or D typing