Physics 2 Ch12-13
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
compression
a region of high molecular density and high pressure
rarefaction
a region of lower density and air pressure
pitch
measure of how high or low a sound is perceived to be depending on the frequency of the sound wave
doppler effect
an observed change in frequency when there is relative motion between the source of waves and an observers
sine waves
represent the changes in air pressure due to the transmission of sound waves
frequency
number of cycles per unit of time (helps determine pitch)
audible sound waves
sound waves that an average human ear can hear (20 to 20,000 Hz)
(the frequency of audible sound waves determines how high or low we perceive sound)
infrasonic waves
sound waves with frequencies below 20 Hz
ultrasonic waves
sound waves with frequencies above 20,000
spherical waves
sound waves produced by very small sources diverge in the shape of a ‘V’
(represented graphically in 2 dimensions with series of circles surrounding the source)
wave fronts
they are circles that represent the centers of compression that surrounds the source
(each circle represents a spherical area)
rays
the radial lines perpendicular to the wave fronts
(distance between adjacent wave fronts = 1 wavelength)
(it indicates the direction of the wave motion)
plane waves
moving waves that have compressions in parallel straight lines
intensity
the rate at which energy flows throughout a unit area perpendicular to the direction of a wave motion
decibel (dB)
a dimensionless unit that describes the ratio of 2 intensities of sound; the threshold of hearing is commonly used as the reference intensity
resonance
a phenomenon that occurs when two objects naturally vibrate at the same frequency
relative intensity
the ratio of the intensity of a given sound wave to the intensity of the threshold of hearing
decibel level
used to measure loudness (dimensionless)
forced vibrations
the setting up of vibrations in an object by vibrating force
sympathetic vibrations
caused when an object vibrates as a reaction to sound waves that match its resonating frequency
natural frequency
the frequency at which an object vibrates when it is disturbed
fundamental frequency
the lowest frequency of vibration of a standing wave
harmonic series
a series of frequencies that includes the fundamental frequency and integral multiples of the fundamental frequency
timbre
the musical quality of a tone resulting from the combination of harmonics present at different intensities
beat
the periodic variation in the amplitude of a wave that is the superposition of 2 waves of slightly different frequencies.
(it’s the variation from soft to loud and back to soft)
electromagnetic wave
a wave that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, which radiate outward from the source at the speed of light
wavelet
a small wave created as a result of a Huygens’s principle
Huygens’s Principle
every point on wavefront acts as a source of a secondary wavelets, and the new wavefront is the surface that touches all these wavelets
ray approximation
treating the propagation of light waves as though they move in straight lines perpendicular to the wave front
luminous flux
the rate at which light is emitted from a source (measured in lumens lm)
illuminance
the amount of light energy produced from the source that’s inversely proportional to the distance (measured in Joules)
reflection
the change in direction of an electromagnetic wave at a surface that causes it to move away from the surface
angle of incidence
the angle between a ray that strikes a surface and the line perpendicular to the surface at the point of contact
angle of reflection
the angle formed by the line perpendicular to the a surface and the direction in which a reflected ray moves
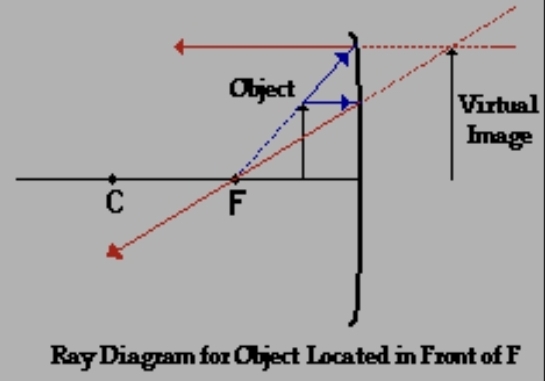
virtual image
an image from which light rays appear to diverge, even though they are not actually focused there; a virtual image can’t be projected on a screen
diffuse reflection
the reflection of waves in many directions from a rough surface
ex: paper, cloth, unpolished wood
specular reflection
reflection of light off a smooth surface in only 1 direction
ex: mirror or water
flat / plane mirror
simplest mirror
concave spherical mirror
a mirror whose reflecting surface is a segment of the inside of a sphere
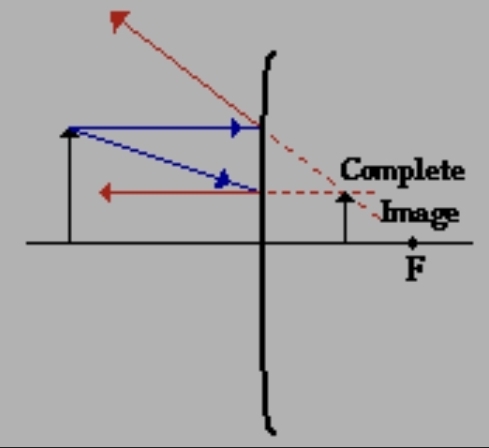
real image
an image that is formed by the intersection of light rays; a real image can be projected on a screen
convex spherical mirror
a mirror whose reflecting reflecting surface is an outward, curves segment of a sphere
radius of curvature
the distance between the center of curvature and the mirror’s surface
spherical aberration
inability of spherical mirrors to focus all parallel rays to a single point
paraxial rays
light rays that are very near the principal axis of the mirror
focal point
the point where parallel light rays converge after passing through a lens or reflecting off a mirror
focal length
the distance from the center of a lens to the focal point
magnification of the image
measure how large or small the image is with respect to the object’s original size
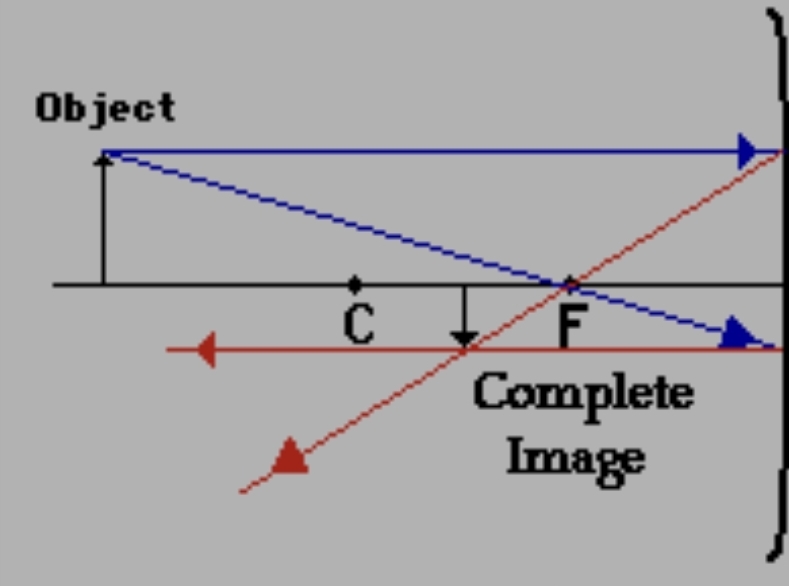
concave mirror with the object before c and f
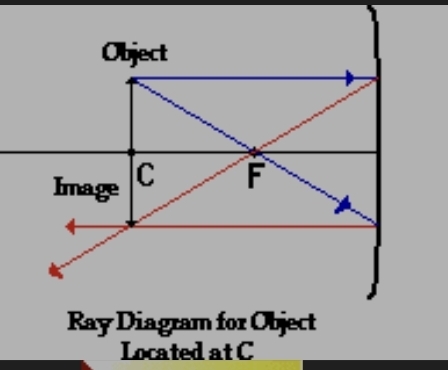
concave with object on c
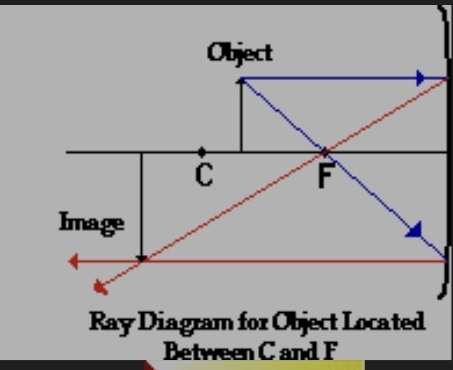
concave with object between c and f
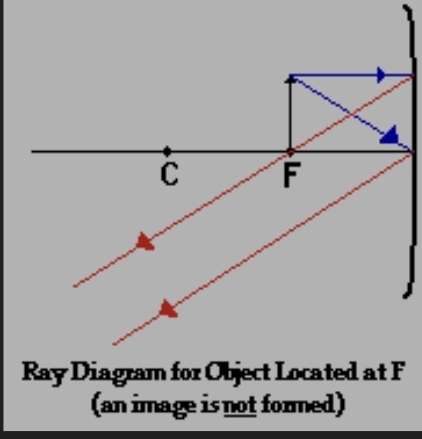
concave with object at f
(no image formed)
concave with object after f (in front of it)
convex mirror
wave speed formula
f = c / wavelength
fundamental frequency
(open ended pipe & vibrating string)
f_n = (n)v/2L
fundamental frequency
(pipe closed at one end)
f_n = (n)v/4L
intensity formula
i = P/(4)(pi)(r²)
mirror equation
1/p + 1/q = 1/f
magnification formula
-q/p or h’/h