Characteristics and classification of living organisms.
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
respond to changes in the internal or external environment
plants need CO2, light, water, ions.
animals need organic compounds, ions and usually water
warm blooded
give birth to live young
\
the more similar the base sequence in the DNa of two species, the more closely related those 2 species r
five kingdoms
animals, plants, fungi, prokaryotes, protoctists/protists
characteristic of animals
multicellular ingestive heterotrophs (they get their nutrition by eating other living things)
eukaryotic (their cells contain a nucleus, but no cell wall or chloroplasts)
characteristics of plants
multicellular autotrophs
eukaryotic - their cells contain a nucleus, cell wall and chloroplasts (cell wall made of cellulose)
They make their own organic nutrients/food, using energy from sunlight, through photosynthesis
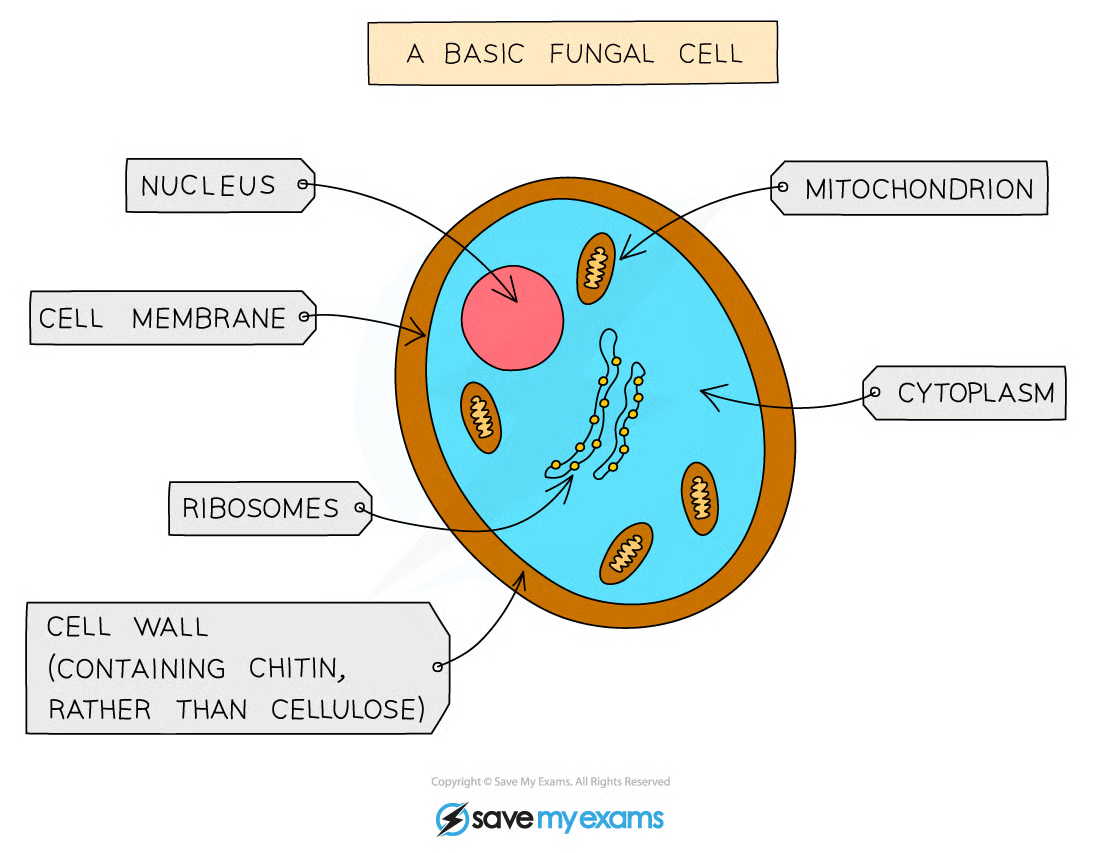
characteristics of fungi
usually multicellular
have nuclei, cell wall not made of cellulose
they feed via
parasitic nutrition
saprophytic nutrition - feeding on dead material
don’t photosynthesise
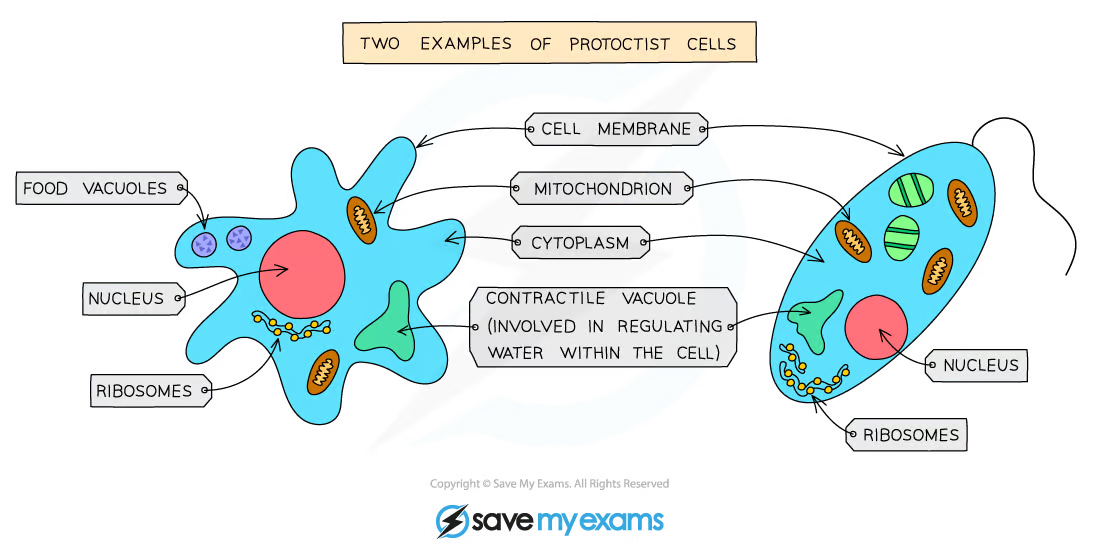
characteristics protoctists
most unicellular, but some r multicellular
all have a nucleus, but some have a cell wall and chloroplasts
some get their nutrition by photosynthesise, and some feed on organic substances made by other living thing
characteristics of prokaryotes
often unicellular
cells have cell walls not made of cellulose, cytoplasm, no nucleus or mitochondria
circular chromosome of DNA that floats in the cytoplasm instead of a nucleus
mammal features
have fur or hair
young feed on milk from mammary glands
external ears/pinna visible
heart has four chambers
bird features
have a beak
lay eggs with hard shells
have wings instead of forelimbs
have feathers
* lay eggs with rubbery shell
* moist skin without scales * lay eggs in water * larvae live in water so have gills * adults usually live on land so have lungs
gas exchange occurs through skin an lungs.
fish features
gills
fins, which are streamlined
loose and wet scales
almost all live in water except one or two
cold-blooded
lay soft eggs without shells in water
external fertilisation
include:
arachnids
myriapods
insects
crustaceans
myriapod features
body has segments
each segment has a pair of jointed legs
exoskeleton
many legs
many segments
elongated bodies
* three pair of jointed legs
* two pair of wings
arachnid features
four pair of jointed legs
breath through structures called book lungs
body divided into two parts: cephalothorax and abdomen
no antennae
crustacean features
four pairs of jointed legs
not millipedes or centipedes
breathe thru gills
chalky exoskeleton made of calcium
do not flower
reproduce via spores
* their seeds are produced in the ovaries, in the flower
monocotyledons
fibrous roots
veins run in parallel to one another
petals/flower parts in multiples of three
narrow and elongated leaves
dicotyledonous plants
contain a tap root system
broad leaves
petals or flower parts in multiples of 4-5
network of veins on leaves
* not part of any classification system
* they can only take over other cells to make more copies of themselves
* they are not made of cells they are just genetic material (either RNA or DNA) surrounded by a protein coat
groups of organisms which share a more recent ancestor (are more closely related) have base sequences in DNA that are more similar than those that share only a distant ancestor
how does DNA help us identify people?
Individuals have different or unique DNA.
DNA has genes or alleles or sequence of bases.