MCAT: Foundation 1
1/829
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
830 Terms
Enzyme
acts as a catalyst in biochemical reactions
Substrate
the molecules that serve as starting material for the reactions enzyme speed up
Hormones
long distance chemical signals released by endocrine cells
Phospholipids:
amphipathic molecules that are insoluble in water and soluble in non polar organic solvents
Glycerophospholipids:
lipids that contain a glycerol backbone
Sphingolipids:
lipids that contain a sphingosine backbone
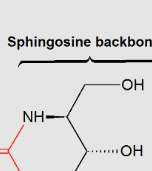
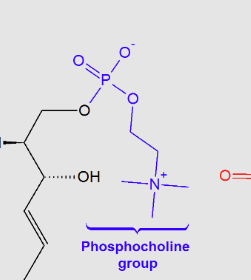
Sphingomyelins:
the major class of sphingophospholipids that are a major component of the myelin sheath, , with a “choline group”
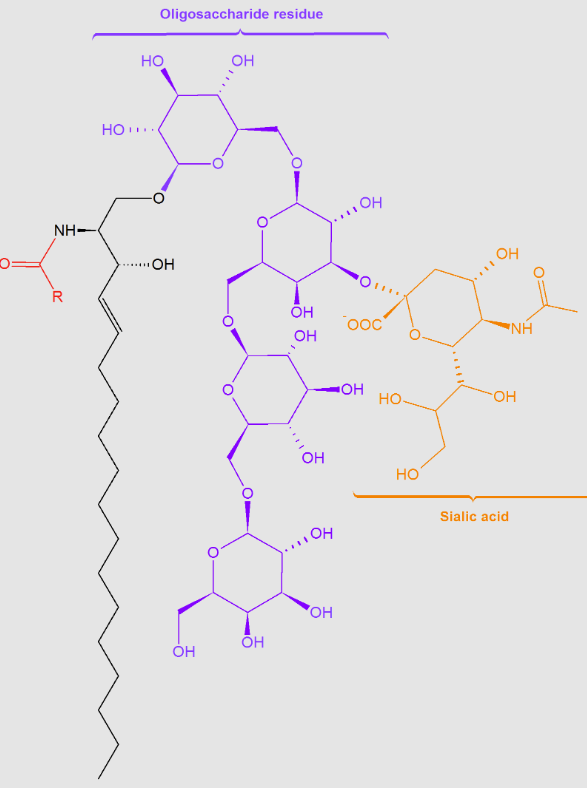
Glycosphingolipids:
attached sugar moieties
Gangliosides:
oligosaccharides with at least one terminal
Proteins
diverse and abundant molecules in living systems
Amylase
digestive enzyme, break down nutrients for absorption (carbohydrates)
Lipase
digestive enzyme, break down nutrients for absorption (fats, lipids)
Pepsin
digestive enzyme, break down nutrients for absorption (proteins to polypeptides)
Hemoglobulin
transport protein, carry substances through the blood or lymph
Actin
structure protein, build different structures, makes thin filaments that help cells move and change shape (like in muscles)
Tubulin
structure protein, build different structures, forms microtubules, which act like tracks that move things inside the cel
Keratin
structure protein, build different structures, makes strong fibers that give structure and protection (like in hair, skin, nails)
Insulin
hormone signaling protein, coordinate the different body systems
Glucagon
hormone signaling protein, coordinate the different body systems
Antibodies
defense protein, defends body from foreign pathogens
Myosin
contraction protein, carry out muscle contraction
Albumin
Legume storage protein, provide the nutrients for early embryo development
Amino Acids
monomers that make up proteins (polypeptides)
amino acids structure
alpha carbon bonded to COOH group (carboxyl), NH2 (amino), and H (hydrogen) at physiological pH, the amino group is protonated and bears a positive charge (NH3+) while the carboxyl group is deprotonated and bears a negative charge (COO-)
amino acid if the pKa>pH
protonated form
amino acid if the Ka<pH
deprotonated form
Protein Synthesis
DNA –transcription→ mRNA –translation→ protein
Polypeptides:
chain of amino acids held together by covalent bonds, known as peptide bonds
Peptide bond mechanism
formed in a dehydration synthesis reaction, the COOH reacts with the NH2 of another amino acid, releasing water and forming a bond, connect amino acids, rigid and planar bond that is stabilized by delocalization from the carbonyl oxygen and the nitrogen
the free amino group is on the left always and the free carboxyl group is on the right
what is the amino acid orientation?
n-terminus
free amino group
c-terminus
free carboxyl group
Primary structure
order of the amino acids
Secondary structure
interactions of the peptide backbone
Alpha-helix
right hand coil of a single polypeptide chain, stabilized by hydrogen bonds every four carbons (3.6 amino acids per curl)
Parallel Beta-Pleated sheet
a protein structure where the strands run in the same direction and are angled with less stable hydrogen bonds
Anti-Parallel Beta-Pleated sheet
a protein structure where strands run in opposite directions, straight, and form stable hydrogen bonds between them
Tertiary structure:
interactions of side chains
Hydrophobic effect:
The entropy driven clustering of non polar amino acid side chains in the protein due to the expelling of water from the structure to increase protein stability
Hydrogen Bond:
Polar interaction between side chains or separate polypeptides that can increase protein stability
Ionic Bonds
Salt bridges, strong interactions between negative and positive side chains
Vander Waals Forces
Weak interactions between all molecules including amino acid
Disulfide Bonds
covalent linkages between the Sulphur containing side chains of cysteine that keep the polypeptides linked firmly together (favored in extracellular environments)
Quaternary structure
arrangement multiple polypeptide chain interactions
Conformational Entropy:
The protein folds and comes into its structure and decreases the entropy to offset other effects
Solvent Entropy
The hydrophobic effect, involving the water molecules being released from clustering structures creates a blockade from the solvent and the release increases the entropy of the water molecules
Molecular Chaperones:
Bind to fresh or partial polypeptides to prevent improper interactions
Chaperonins
large, cylindrical complexes that provide a proper environment for protein folding, after folding the protein is released
Denaturation
the alteration of protein structure, except the primary structure due to extreme conditions
Temperature Denaturation
higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy interfering with the non-covalent interactions that hold the protein together and expose interior hydrophobic regions
pH denaturation
increased pH can change the charge states of amino acids with acidic or basic side chains and interfere or break ionic and hydrogen bonds that hold the protein together
Chemical Agents denaturation
disrupt hydrogen bonds and unfold the proteins (urea)
Reversible Denaturation
A protein can refold into its functioning shape with the removal of the denaturing agent
Irreversible Denaturation
Permanent damage to protein structure due to covalent bond interruption
Proper Conformation
correct primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure, if not misfolding can occur (active or folded form of a protein)
Conformation Stability
the various forces that act to keep a protein properly folded
Essential Amino Acids
Histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine cannot be synthesized from the body
Non-Essential Amino Acid
Alanine, asparagine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, serine, arginine, cysteine, glutamine, glycine, proline, tyrosine can be synthesized from the body
Phosphorylation
addition of a phosphate group, typically to serine, tyrosine, threonine, affects signaling pathways
Glycosylation
attachment of carbohydrate groups affecting protein folding, stability, and cell recognition
Carbohydrate groups
monsaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
Acetylation and Methylation
epigenetic modifications that occur often on lysine, that influence gene expression and protein function
Epigenetic
heritable changes in gene expression that occur without alterations to the underlying DNA sequence
Histone Acetylation
acetyl groups are added to lysine residues on histone tails (protein part of chromatin), done by neutralization of the positive charge on the histones and weakening the interactions there is a relaxation of the chromatin allowing for the increased transcription factors
DNA Methylation
methyl groups are added to DNA, cytosine, then alter a transcription factor which activates or represses gene expression
Histone Methylation
methyl groups are added to histone tails, lysine, and can alter gene expression
Ubiquitination
tagging lysine for protein degradation with a small high conserved protein
Peptide Bond formation
nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction, lone pair on nitrogen in the amino group attacks the carbonyl hydrogen and attaches itself forming an amide bond, water leaves
Acid Hydrolysis
non-specific way of breaking a peptide bond, addition of heat allows the bond to break leaving multiple fragments of amino acids
Proteolysis
regulatory mechanism of gene expression, the specific breaking of a peptide bond , use of enzymes called proteases
Trypsin fragmentation
only fragments at the C terminus of Arginine and Lysine
prefers to fragment at the C terminus of phenylalanine, leucine, tyrosine, tryptophan
Pepsin fragmentation
Elastase
what enzyme fragments at the C terminus of smaller amino acids?
Thermolysin
what enzyme fragments at the N-terminus of hydrophobic residues?
Isoelectric Point:
a point on the pH scale in which an amino acid exists as neutral, no charge
pI: average of the pKas of all the functional groups in an amino acid
pKa1 + pKa2 / 2
PI equation
isoelectric focusing
a gel cascade path with and anode and cathode probing the proteins to move along the gradient as they need fit to neutralize the charges
more basic amino acids, needs a higher pH to balance the charges
higher pI means…
more acidic amino acids, needs lower pH to balance the charges
lower pI means…
Zwitterion:
a neutral molecule that contains both a positive charge and negative charge
Protein Electrophoresis
separates protein based on their size and charge in a gel mixture that allows proteins to migrate toward the probe of the opposite charge
Native PAGE
proteins are separated by their native size and charge
SDS PAGE
proteins are denatured and coated in a negative charge to be separated by their molecular weight
sodium dodecyl sulfate(reducing agent)
SDS
poly acrylamide gel electrophoresis
PAGE
SDS function
masks the proteins original charge and creates a linear chain to make an equal mass to charge ratio and separate them solely based on size
BME and DTT
reducing agents, break disulfide bonds
SDS-PAGE gel
stacking and resolving gels
(low and high concentration)
Buffer
maintain pH and conductivity
Tracking dye
visualize the separation (blue or silver stain)
Western Blotting:
gel electrophoresis that combines antibody interactions to identify a target protein with sensitivity and specificity
SDS page gel
protein separation
WB Primary Antibody
Targets the protein
Conjugates the enzyme that binds to the protein
Western Blot Secondary Antibody
SDS page gel
Transfer Membrane
Primary Antibody
Secondary Antibody
Buffer
WB Materials
Quantifying protein expression, analyzing post-translational modifications, and protein identification
Applications of WB
identify proteins, analyze their purity, and determine the molecular weight
Applications of SDSPAGE
Electroblotting
transfers protein samples from electrophoresis gel to a membrane using an electric field
Enzyme-linked Immunoassay (ELIZA):
uses antibodies to detect and quantify directly in a liquid sample, a protein binds to a solid surface and a signal if produced often color change
Southern Blotting
Used to detect specific DNA sequences from a complex sample